BCHM Practice Questions 2023
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:24 PM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
Erythrocytes possess which one of the following enzymes:
A. pyruvate kinase
B. pyruvate dehydrogenase
C. isocitrate dehydrogenase
D. b-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
E. malate dehydrogenase
A. pyruvate kinase
B. pyruvate dehydrogenase
C. isocitrate dehydrogenase
D. b-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
E. malate dehydrogenase
A. pyruvate kinase
2
New cards
Glucagon upregulates or leads to activation of which of the following enzymatic steps OR proteins:
A. GLUT-4 glucose transporters
B. glucokinase/hexokinase IV
C. phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1)
D. fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2)
E. glycogen synthase
A. GLUT-4 glucose transporters
B. glucokinase/hexokinase IV
C. phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1)
D. fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2)
E. glycogen synthase
D. fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2)
3
New cards
In the sequence of steps in the mid to latter stages of glycolysis, which of the following steps involves substrate-level phosphorylation?
A. Fructose-6-phosphate -> Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate
B. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate -> 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
C. 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate -> 3-Phosphoglycerate
D. 3-Phosphoglycerate -> 2-Phosphoglycerate
E. 2-Phosphoglycerate -> Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
A. Fructose-6-phosphate -> Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate
B. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate -> 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
C. 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate -> 3-Phosphoglycerate
D. 3-Phosphoglycerate -> 2-Phosphoglycerate
E. 2-Phosphoglycerate -> Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
C. 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate -> 3-Phosphoglycerate
4
New cards
Which of the following statements about glycogen synthase is INCORRECT:
A. it is directly phosphorylated by protein kinase A
B. it is activated by insulin in the hepatocyte
C. it involves inactivation of GSK-3 (glycogen synthase kinase-3)
D. it requires glucose-1-P to be energized by UTP
E. it adds glucose molecules to non-reducing ends of the growing chains by forming (a1->4) linkages
A. it is directly phosphorylated by protein kinase A
B. it is activated by insulin in the hepatocyte
C. it involves inactivation of GSK-3 (glycogen synthase kinase-3)
D. it requires glucose-1-P to be energized by UTP
E. it adds glucose molecules to non-reducing ends of the growing chains by forming (a1->4) linkages
A. it is directly phosphorylated by protein kinase A
5
New cards
Which of the following statements about the citric acid cycle is INCORRECT:
A. it directly generates 1 GTP (or ATP), 3 NADH and 1 FADH 2 per cycle
B. it stops in the liver during starvation for the organ to carry out gluconeogenesis
C. it involves four dehydrogenase enzymes
D. it is dependent on a constant supply of oxaloacetate provided by anaplerotic pathways
E. it directly generates 2 water molecules per acetyl CoA
A. it directly generates 1 GTP (or ATP), 3 NADH and 1 FADH 2 per cycle
B. it stops in the liver during starvation for the organ to carry out gluconeogenesis
C. it involves four dehydrogenase enzymes
D. it is dependent on a constant supply of oxaloacetate provided by anaplerotic pathways
E. it directly generates 2 water molecules per acetyl CoA
E. it directly generates 2 water molecules per acetyl CoA
6
New cards
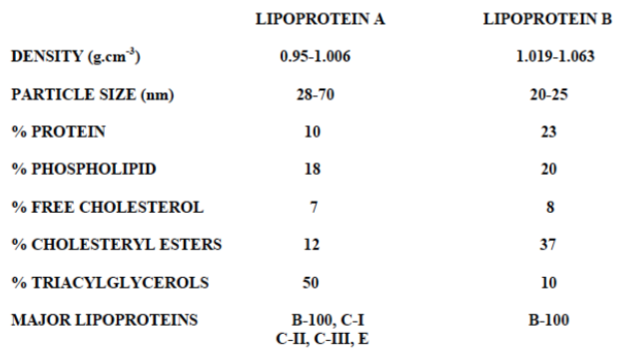
Using the compositional data in the table below select the combination which best fit \n lipoprotein particle descriptors for Lipoprotein A & B respectively:
VLDL and LDL
7
New cards
Which of the following is a (are) high energy phosphate bond(s)
A. adenosine - a PO4 bond only
B. a PO4 - b PO4 bond only
C. b PO4 - g PO4 bond only
D. both adenosine - a PO4 bond and a PO4 - b PO4 bond
E. both a PO4 - b PO4 bond and b PO4 - g PO4 bond
A. adenosine - a PO4 bond only
B. a PO4 - b PO4 bond only
C. b PO4 - g PO4 bond only
D. both adenosine - a PO4 bond and a PO4 - b PO4 bond
E. both a PO4 - b PO4 bond and b PO4 - g PO4 bond
E. both a PO4 - b PO4 bond and b PO4 - g PO4 bond
8
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding ketogenesis/ketone body utilization is CORRECT:
A. ketone bodies are made exclusively in the liver and kidney
B. ketogenesis involves the mitochondrial enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
C. ketogenesis is absent in individuals with myopathic carnitine deficiency
D. ketone body use by the liver depends upon oxaloacetate supply by pyruvate carboxylase
E. ketone body utilization is absent from the brain due to the blood-brain barrier
A. ketone bodies are made exclusively in the liver and kidney
B. ketogenesis involves the mitochondrial enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
C. ketogenesis is absent in individuals with myopathic carnitine deficiency
D. ketone body use by the liver depends upon oxaloacetate supply by pyruvate carboxylase
E. ketone body utilization is absent from the brain due to the blood-brain barrier
B. ketogenesis involves the mitochondrial enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
9
New cards
Muscle contains which of the following combinations of transporters, enzymes and receptors:
A. GLUT2, hexokinase I and ONLY the glucagon receptor
B. GLUT4, hexokinase IV and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
C. GLUT2, hexokinase IV and ONLY the glucagon receptor
D. GLUT4, hexokinase I and ONLY the epinephrine receptor
E. GLUT2, hexokinase IV, and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
A. GLUT2, hexokinase I and ONLY the glucagon receptor
B. GLUT4, hexokinase IV and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
C. GLUT2, hexokinase IV and ONLY the glucagon receptor
D. GLUT4, hexokinase I and ONLY the epinephrine receptor
E. GLUT2, hexokinase IV, and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
D. GLUT4, hexokinase I and ONLY the epinephrine receptor
10
New cards
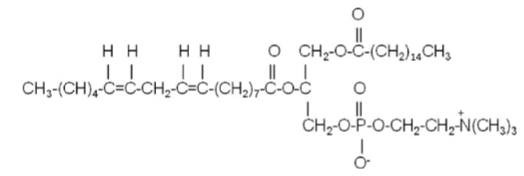
The lipid structure below is best classified as
1-palmitoyl, 2-linoleoyl phosphatidyl choline
11
New cards
The carnitine transport system for fatty acids:
1. requires two pools of CoA in the cytoplasm and the mitochondrial matrix
2. exists to help fatty acids to traverse the impermeable outer mitochondrial membrane
3. is down regulated by malonyl CoA levels
4. transports fatty acids with a range of chain lengths from C 12 to C 22
\*type II
1. requires two pools of CoA in the cytoplasm and the mitochondrial matrix
2. exists to help fatty acids to traverse the impermeable outer mitochondrial membrane
3. is down regulated by malonyl CoA levels
4. transports fatty acids with a range of chain lengths from C 12 to C 22
\*type II
1 and 3 are correct
12
New cards
Peroxisomal β-oxidation of fatty acids involves:
1. oxidation of medium chain (>C10 -C14 ) fatty acids
2. export of NADH + H+ to mitochondria for reoxidation to NAD
3. regeneration of FAD using the enzyme catalase to reoxidise the FADH 2
4. export of acetyl CoA to mitochondria to enter the citric acid cycle
\*type II
1. oxidation of medium chain (>C10 -C14 ) fatty acids
2. export of NADH + H+ to mitochondria for reoxidation to NAD
3. regeneration of FAD using the enzyme catalase to reoxidise the FADH 2
4. export of acetyl CoA to mitochondria to enter the citric acid cycle
\*type II
2 and 4 are correct
13
New cards
The steps of mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids to acetyl CoA:
1. directly releases about 75% of the available energy as ATP
2. involves two dehydrogenation (oxidation) steps each generating NADH
3. directly releases 1 water molecule per β-oxidation cycle
4. occurs while the fatty acid is attached to coenzyme A
\*type II
1. directly releases about 75% of the available energy as ATP
2. involves two dehydrogenation (oxidation) steps each generating NADH
3. directly releases 1 water molecule per β-oxidation cycle
4. occurs while the fatty acid is attached to coenzyme A
\*type II
only 4 is correct
14
New cards
The action of adipocyte lipases involves:
1. lipolysis of the triglyceride to three “free” fatty acids and glycerol
2. recycling of the glycerol backbone by glycerol kinase in the adipocyte
3. direct phosphorylation of perilipin and activation of a lipase by protein kinase A
4. transport of the fatty acids on LDL back to the liver
\*type II
1. lipolysis of the triglyceride to three “free” fatty acids and glycerol
2. recycling of the glycerol backbone by glycerol kinase in the adipocyte
3. direct phosphorylation of perilipin and activation of a lipase by protein kinase A
4. transport of the fatty acids on LDL back to the liver
\*type II
1 and 3 are correct
15
New cards
Muscle carries out glycogenolysis and glycolysis during fasting because:
1. muscle lacks glucagon receptors so cannot inhibit glycolysis
2. muscle lacks glucose-6-phosphatase
3. muscle needs glycolysis to generate energy from the G-6-P formed during glycogenolysis
4. muscle exports pyruvate to the liver as part of the Cori cycle
\*type II
1. muscle lacks glucagon receptors so cannot inhibit glycolysis
2. muscle lacks glucose-6-phosphatase
3. muscle needs glycolysis to generate energy from the G-6-P formed during glycogenolysis
4. muscle exports pyruvate to the liver as part of the Cori cycle
\*type II
1, 2 and 3 are correct
16
New cards
Which of the following enzymes/pathways is (are) CORRECTLY listed with one of its (their)
regulators:
1. pyruvate carboxylase- acetyl CoA
2. glycogen phosphorylase a- glucose
3. pentose phosphate pathway- NADPH
4. pyruvate dehydrogenase- \[NADH/NAD\] ratio
\*type II
regulators:
1. pyruvate carboxylase- acetyl CoA
2. glycogen phosphorylase a- glucose
3. pentose phosphate pathway- NADPH
4. pyruvate dehydrogenase- \[NADH/NAD\] ratio
\*type II
all are correct
17
New cards
Which of the following enzymes depends upon pyrophosphatase for energy needed to drive it:
1. glucose-6-phosphatase
2. fatty acyl CoA synthetase
3. fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
4. UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
\*type II
1. glucose-6-phosphatase
2. fatty acyl CoA synthetase
3. fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
4. UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
\*type II
2 and 4
18
New cards
Which coenzymes of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase bind the substrate or release the product:
1. NAD
2. thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP)
3. FAD
4. lipoic acid
\*type II
1. NAD
2. thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP)
3. FAD
4. lipoic acid
\*type II
2 and 4
19
New cards
\
Human Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficiency results in:
1. compromised NADPH production for antioxidant defenses
2. reduced biosynthesis of ribose-5-phosphate needed for nucleic acid biosynthesis
3. increased sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs
4. decreased protection from malaria in mosquito-affected areas
\*type II
Human Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficiency results in:
1. compromised NADPH production for antioxidant defenses
2. reduced biosynthesis of ribose-5-phosphate needed for nucleic acid biosynthesis
3. increased sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs
4. decreased protection from malaria in mosquito-affected areas
\*type II
1, 2 and 3 are correct
20
New cards
Which of the following statements about the synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
from an essential fatty acid in mammals is (are) CORRECT:
1. the initial steps alternate between firstly a) desaturation and then b) elongation steps
2. desaturation steps involve sequentially: Δ 6 -desaturase, Δ 5 -desaturase & Δ 6 -desaturase again
3. it starts with 18:3Δ 9,12,15 and involves the intermediate 24:6Δ 6,9,12,15,18,21
4. the final step involves removal of a C-2 unit by mitochondrial β-oxidation
\*type II
from an essential fatty acid in mammals is (are) CORRECT:
1. the initial steps alternate between firstly a) desaturation and then b) elongation steps
2. desaturation steps involve sequentially: Δ 6 -desaturase, Δ 5 -desaturase & Δ 6 -desaturase again
3. it starts with 18:3Δ 9,12,15 and involves the intermediate 24:6Δ 6,9,12,15,18,21
4. the final step involves removal of a C-2 unit by mitochondrial β-oxidation
\*type II
1, 2 and 3
21
New cards
The regulation of glycolysis/gluconeogenesis is mainly through the action of insulin:
1. activating phosphofructokinase-2 activity in a bifunctional (PFK-2/FBPase-2) enzyme
2. by causing a dephosphorylation event which inactivates FBPase-2
3. thereby generating increased concentrations of the activator, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
4. which up-regulates glycolysis and down-regulates gluconeogenesis
\*type II
1. activating phosphofructokinase-2 activity in a bifunctional (PFK-2/FBPase-2) enzyme
2. by causing a dephosphorylation event which inactivates FBPase-2
3. thereby generating increased concentrations of the activator, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
4. which up-regulates glycolysis and down-regulates gluconeogenesis
\*type II
all are correct
22
New cards
During the later stages of fasting the brain becomes dependent upon which of the following enzymes to efficiently generate energy:
1. thiolase
2. PEP carboxykinase
3. 3β-ketoacyl CoA transferase
4. isocitrate dehydrogenase
\*type II
1. thiolase
2. PEP carboxykinase
3. 3β-ketoacyl CoA transferase
4. isocitrate dehydrogenase
\*type II
all are correct
23
New cards
Which of the following enzyme/pathways is INCORRECTLY listed with its **subcellular** location?
a) glucose-6-phosphate; lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum
b) pyruvate dehydrogenase; cytoplasm
c) malate dehydrogenase; mitochondrion
d) inactive hexokinase IV (glucokinase); nucleus
e) phospholipid biosynthesis; endoplasmic reticulum
a) glucose-6-phosphate; lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum
b) pyruvate dehydrogenase; cytoplasm
c) malate dehydrogenase; mitochondrion
d) inactive hexokinase IV (glucokinase); nucleus
e) phospholipid biosynthesis; endoplasmic reticulum
* b
* in mitochondria
* in mitochondria
24
New cards
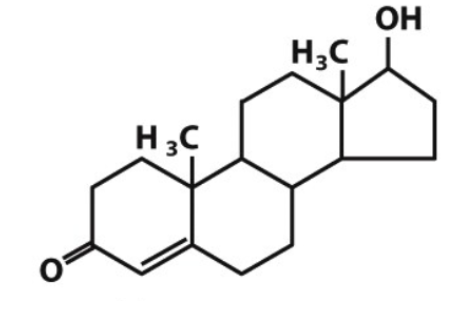
identify the following steroidal molecule:
a) testosterone
b) estradiol
c) 25-hydroxyvitamin D3
d) cortisol
e) progesterone
a) testosterone
b) estradiol
c) 25-hydroxyvitamin D3
d) cortisol
e) progesterone
a) testosterone
25
New cards
The **CORRECT** sequence of intermediates (not all shown in each answer) in the **Urea Cycle** is:
a. citrulline, ornithine, aspartate, arginine
b. argininosuccinate, aspartate, fumarate, urea
c. ornithine, aspartate, citrullyl-AMP, arginine, urea
d. citrulline, argininosuccinate, urea, arginine
e. carbamoyl phosphate, argininosuccinate, arginine, ornithine
a. citrulline, ornithine, aspartate, arginine
b. argininosuccinate, aspartate, fumarate, urea
c. ornithine, aspartate, citrullyl-AMP, arginine, urea
d. citrulline, argininosuccinate, urea, arginine
e. carbamoyl phosphate, argininosuccinate, arginine, ornithine
e. carbamoyl phosphate, argininosuccinate, arginine, ornithine
26
New cards
Which of the following amino acids is **BOTH glucogenic and ketogenic**?
a. alanine
b. aspartate
c. glutamate
d. tryptophan
e. serine
a. alanine
b. aspartate
c. glutamate
d. tryptophan
e. serine
d. tryptophan
27
New cards
Which of the following statements about ω-oxidation of fatty acids is CORRECT:
a. it involves sequentially acid, aldehyde and alcohol intermediates
b. it involves a cytochrome P450, molecular oxygen & NADPH to oxidize the ω-carbon
c. it uses catalase to regenerate FAD
d. it shortens the fatty acid by cleaving off a C-2 unit
e. it prepares the very long-chain chain fatty acid for mitochondrial β-oxidation
a. it involves sequentially acid, aldehyde and alcohol intermediates
b. it involves a cytochrome P450, molecular oxygen & NADPH to oxidize the ω-carbon
c. it uses catalase to regenerate FAD
d. it shortens the fatty acid by cleaving off a C-2 unit
e. it prepares the very long-chain chain fatty acid for mitochondrial β-oxidation
b. it involves a cytochrome P450, molecular oxygen & NADPH to oxidize the ω-carbon
28
New cards
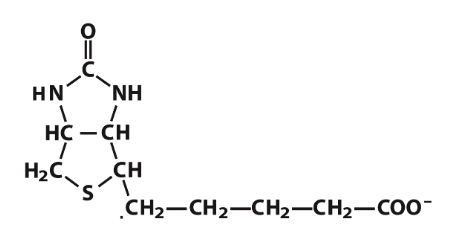
The following coenzyme is involved in:
a. methylation
b. single carbon transfer
c. carboxylation
d. hydroxylation
e. transamination
a. methylation
b. single carbon transfer
c. carboxylation
d. hydroxylation
e. transamination
c
29
New cards
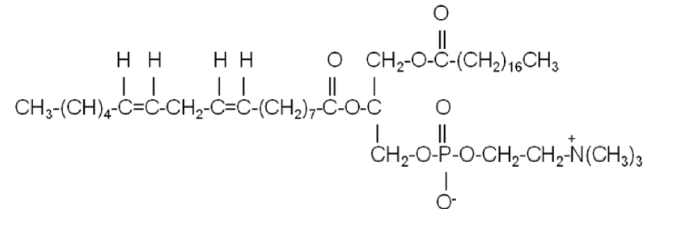
The lipid structure below is best classified as:
a. 1-steroyl, 2-linolenoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine
b. 1-oleoyl, 2-linoleoyl phosphatidyl inositol
c. 1-palmitoyl, 2-linolenoyl phosphatidyl glycerol
d. 1-palmitoyl, 2-linolenoyl phosphatidyl serine
e. 1-steroyl, 2-linoleoyl phosphatidyl choline
a. 1-steroyl, 2-linolenoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine
b. 1-oleoyl, 2-linoleoyl phosphatidyl inositol
c. 1-palmitoyl, 2-linolenoyl phosphatidyl glycerol
d. 1-palmitoyl, 2-linolenoyl phosphatidyl serine
e. 1-steroyl, 2-linoleoyl phosphatidyl choline
e. 1-steroyl, 2-linoleoyl phosphatidyl choline
30
New cards
Which of the following statements about isoprenoid biosynthesis is INCORRECT:
a. isoprene units are branched 5-carbon modules made by decarboxylation of mevalonate
b. isoprenoid synthesis involves the mitochondrial enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
c. the rate limiting step of isoprenoid biosynthesis is HMG-CoA reductase
d. intermediates in the pathway such as C5 , C10 & C15 are made as pyrophosphate derivatives
e. squalene, a C30 linear isoprenoid, is cyclized into a C30 steroidal structure, lanosterol
a. isoprene units are branched 5-carbon modules made by decarboxylation of mevalonate
b. isoprenoid synthesis involves the mitochondrial enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
c. the rate limiting step of isoprenoid biosynthesis is HMG-CoA reductase
d. intermediates in the pathway such as C5 , C10 & C15 are made as pyrophosphate derivatives
e. squalene, a C30 linear isoprenoid, is cyclized into a C30 steroidal structure, lanosterol
b. isoprenoid synthesis involves the mitochondrial enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
31
New cards
Which of the following statements about the regulation of Acetyl CoA carboxylase is CORRECT:
a. It is inactivated by insulin
b. it is dephosphorylated by leptin and adiponectin
c. it is phosphorylated by a kinase stimulated by glucagon
d. it is partially activated by citrate
e. it is allosterically inhibited by malonyl CoA
a. It is inactivated by insulin
b. it is dephosphorylated by leptin and adiponectin
c. it is phosphorylated by a kinase stimulated by glucagon
d. it is partially activated by citrate
e. it is allosterically inhibited by malonyl CoA
d
32
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a component part of a ganglioside:
a. N-acetylgalactosamine
b. arachidonate
c. N-acetylneuraminic acid
d. palmitate
e. sphingosine
a. N-acetylgalactosamine
b. arachidonate
c. N-acetylneuraminic acid
d. palmitate
e. sphingosine
b. arachidonate
33
New cards
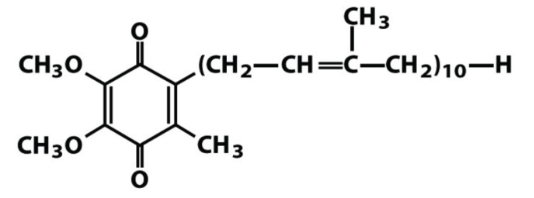
Identify the following isoprenoid:
a. mevalonate
b. dihydrofolate
c. ubiquinone
d. dihydrobiopterin
e. squalene
a. mevalonate
b. dihydrofolate
c. ubiquinone
d. dihydrobiopterin
e. squalene
c. ubiquinone
34
New cards
12\. Which enzyme is the main determinant of the rate of the glyoxylate cycle:
a. citrate synthase
b. aconitase
c. isocitrate lyase
d. isocitrate dehydrogenase
e. malate synthase
a. citrate synthase
b. aconitase
c. isocitrate lyase
d. isocitrate dehydrogenase
e. malate synthase
d. isocitrate dehydrogenase
35
New cards
Which is the principal anapleurotic pathway to maintain the citric acid cycle in heart muscle:
a. pyruvate carboxylase
b. malic enzyme
c. PEP carboxykinase
d. PEP carboxylase
e. pyruvate dehydrogenase
a. pyruvate carboxylase
b. malic enzyme
c. PEP carboxykinase
d. PEP carboxylase
e. pyruvate dehydrogenase
c. PEP carboxykinase
36
New cards
Useable water production from complete b-oxidation of palmitate from a tri-palmitoyl glyceride molecule metabolized to CO2 and ATP arises from:
a. hydrolysis of the triglyceride
b. 4 steps of b-oxidation of the palmitate residues
c. the steps of the citric acid cycle
d. oxidative phosphorylation of NADH and FADH2
e. electron transport chain processing of NADH and FADH2
a. hydrolysis of the triglyceride
b. 4 steps of b-oxidation of the palmitate residues
c. the steps of the citric acid cycle
d. oxidative phosphorylation of NADH and FADH2
e. electron transport chain processing of NADH and FADH2
e. electron transport chain processing of NADH and FADH2
\
\-NOT d) because useable water ALWAYS and ONLY comes from the ETC
\
\-NOT d) because useable water ALWAYS and ONLY comes from the ETC
37
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding important metabolic pathways is INCORRECT:
a. pyruvate kinase is inactive in the fasting liver
b. pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxykinase are absent from adipocytes
c. glucose-6-phosphatase is absent from muscle
d. glycerol kinase is absent from adipocytes
e. 3b-ketoacyl-CoA-transferase is absent from the liver
a. pyruvate kinase is inactive in the fasting liver
b. pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxykinase are absent from adipocytes
c. glucose-6-phosphatase is absent from muscle
d. glycerol kinase is absent from adipocytes
e. 3b-ketoacyl-CoA-transferase is absent from the liver
b. pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxykinase are absent from adipocytes
38
New cards
When ATP, ADP & Pi concentrations are at normal cellular concentrations, the pH is 7.0, the temperature is 25°C and the pressure is 101.3 kPa, the actual free energy of hydrolysis of ATP, ΔGp, in erythrocytes is:
a. -30.5 kJ/mol
b. -43 kJ/mol
c. -52 kJ/mol
d. -63 kJ/mol
e. -75 kJ/mol
a. -30.5 kJ/mol
b. -43 kJ/mol
c. -52 kJ/mol
d. -63 kJ/mol
e. -75 kJ/mol
c. -52 kJ/mol
39
New cards
Which of the following statements about the citric acid cycle is INCORRECT:
a. it involves succinyl CoA synthetase which can use GDP or ADP
b. it directly generates the reducing equivalents 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 per cycle
c. it generates succinyl CoA which can be syphoned off to make heme
d. it involves the generation of two molecules of H20 per cycle
e. it involves oxidative decarboxylation steps using thiamine pyrophosphate as a coenzyme
a. it involves succinyl CoA synthetase which can use GDP or ADP
b. it directly generates the reducing equivalents 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 per cycle
c. it generates succinyl CoA which can be syphoned off to make heme
d. it involves the generation of two molecules of H20 per cycle
e. it involves oxidative decarboxylation steps using thiamine pyrophosphate as a coenzyme
d. it involves the generation of two molecules of H20 per cycle
40
New cards
Which of the following would be INCORRECT for the composition of VLDL?
a. apolipoprotein CII
b. 50% triglycerides
c. 7% cholesterol
d. 18% phospholipids
e. 25% cholesteryl esters
a. apolipoprotein CII
b. 50% triglycerides
c. 7% cholesterol
d. 18% phospholipids
e. 25% cholesteryl esters
e. 25% cholesteryl esters
* should be 12%
* should be 12%
41
New cards
Liver contains which of the following combinations of transporters, enzymes and receptors:
a. GLUT2, hexokinase I and ONLY glucagon receptor
b. GLUT4, hexokinase IV and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptor
c. GLUT2, hexokinase IV and ONLY glucagon receptor
d. GLUT4, hexokinase I and ONLY epinephrine receptor
e. GLUT2, hexokinase IV, and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
a. GLUT2, hexokinase I and ONLY glucagon receptor
b. GLUT4, hexokinase IV and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptor
c. GLUT2, hexokinase IV and ONLY glucagon receptor
d. GLUT4, hexokinase I and ONLY epinephrine receptor
e. GLUT2, hexokinase IV, and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
e. GLUT2, hexokinase IV, and BOTH glucagon and epinephrine receptors
42
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding bioenergetics & the electron transport chain is CORRECT:
a. the standard reduction potential, E°’ of any half-reaction with 1M oxidised and reduced species in the test cell at pH 7.0, measured using a hydrogen electrode in which H2 gas at 101.3 kPa is in contact with 1 M H+ , also at pH = 7.0, and arbitrarily assigned an emf value of 0.00 volts
b. by convention, the standard reduction potential, E°’ of any half reaction is depicted with the oxidised species on the left and the reduced species on the right
c. E°’ for half reaction involving O2 + 2H+ + 2 electrons → H2O has a strongly positive value.
d. for the electron transport chain to work properly electron donors must pass on electrons to acceptors with half reactions with a more negative E°’
e. when two half reactions are combined, then by convention: ΔE°’= E°’ of the electron donor minus E°’ of the electron acceptor
a. the standard reduction potential, E°’ of any half-reaction with 1M oxidised and reduced species in the test cell at pH 7.0, measured using a hydrogen electrode in which H2 gas at 101.3 kPa is in contact with 1 M H+ , also at pH = 7.0, and arbitrarily assigned an emf value of 0.00 volts
b. by convention, the standard reduction potential, E°’ of any half reaction is depicted with the oxidised species on the left and the reduced species on the right
c. E°’ for half reaction involving O2 + 2H+ + 2 electrons → H2O has a strongly positive value.
d. for the electron transport chain to work properly electron donors must pass on electrons to acceptors with half reactions with a more negative E°’
e. when two half reactions are combined, then by convention: ΔE°’= E°’ of the electron donor minus E°’ of the electron acceptor
b or c
43
New cards
When acting upon PIP2 (Phosphatidyl 4,5-bisphosphate) phospholipase C cleaves
a. the C-O bond between the glycerol and the 1-phosphate
b. the O-P bond between the glycerol and the 1-phosphate
c. the P-O bond between the 1-phosphate and the inositol ring
d. the O-C bond between the 1-phosphate and the inositol ring
e. the C-O bond between the inositol ring and the 4-phosphate
a. the C-O bond between the glycerol and the 1-phosphate
b. the O-P bond between the glycerol and the 1-phosphate
c. the P-O bond between the 1-phosphate and the inositol ring
d. the O-C bond between the 1-phosphate and the inositol ring
e. the C-O bond between the inositol ring and the 4-phosphate
b. the O-P bond between the glycerol and the 1-phosphate
* makes IP3 and DAG
* makes IP3 and DAG
44
New cards
Which of the following statements about carbohydrate biochemistry is INCORRECT:
a. mannose is an epimer of glucose differing in stereochemistry ONLY at C-4
b. in determination of D- & L-configuration, the reference carbon for glucose is C-5
c. the anomeric carbon of glucose is C-1
d. fructose is a 6-carbon ketose
e. glucose exists in solution as two 6-membered ring structures a- and b-glucopyranose
a. mannose is an epimer of glucose differing in stereochemistry ONLY at C-4
b. in determination of D- & L-configuration, the reference carbon for glucose is C-5
c. the anomeric carbon of glucose is C-1
d. fructose is a 6-carbon ketose
e. glucose exists in solution as two 6-membered ring structures a- and b-glucopyranose
a. mannose is an epimer of glucose differing in stereochemistry ONLY at C-4
* galactose not mannose
* galactose not mannose
45
New cards
Pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme for which of the following reactions:
a. transamination
b. dehydrogenation
c. carboxylation
d. decarboxylation
e. hydroxylation
a. transamination
b. dehydrogenation
c. carboxylation
d. decarboxylation
e. hydroxylation
a. transamination
46
New cards
Statins block which of the following enzymes
a. 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)
b. phospholipase A2
c. cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2)
d. HMG-CoA reductase
e. cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase
a. 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)
b. phospholipase A2
c. cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2)
d. HMG-CoA reductase
e. cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase
d. HMG-CoA reductase
47
New cards
Glycolysis:
a. forms NADH during anaerobic periods which can be recycled to NAD via lactate dehydrogenase
b. consumes 2 ATPs during the initial preparatory phase
c. operates in cancer cells under anaerobic conditions & at 10x the rate of normal tissues
d. involves a NET production of 5-7 ATPs/glucose molecule en route to pyruvate
\*type II
a. forms NADH during anaerobic periods which can be recycled to NAD via lactate dehydrogenase
b. consumes 2 ATPs during the initial preparatory phase
c. operates in cancer cells under anaerobic conditions & at 10x the rate of normal tissues
d. involves a NET production of 5-7 ATPs/glucose molecule en route to pyruvate
\*type II
all are correct
48
New cards
Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme for one or more steps within which of the following pathways:
a. pentose phosphate pathway
b. ketogenesis
c. citric acid cycle
d. glycolysis
\*type II
a. pentose phosphate pathway
b. ketogenesis
c. citric acid cycle
d. glycolysis
\*type II
a and c
49
New cards
Pancreatic Lipase action involves which of the following:
a. partial lipolysis of the triglyceride core to 2-monoglyceride and two “free” fatty acids
b. the assistance of a bile acid such as taurocholic acid to emulsify the dietary fat
c. a co-lipase for the enzyme to gain access to the interior of the lipid vesicle
d. the acid pH environment of the intestine to provide optimal rates of catalysis
\*type II\*
a. partial lipolysis of the triglyceride core to 2-monoglyceride and two “free” fatty acids
b. the assistance of a bile acid such as taurocholic acid to emulsify the dietary fat
c. a co-lipase for the enzyme to gain access to the interior of the lipid vesicle
d. the acid pH environment of the intestine to provide optimal rates of catalysis
\*type II\*
a, b and c are correct
50
New cards
NADPH is generated by which of the following enzymes: metabolic steps:
a. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: glucose 6-phosphate -> 6-phosphoglucono-lactone
b. malic enzyme: malate -> oxaloacetate
c. 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase: 6-phosphogluconate -> ribulose 5-phosphate
d. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: α-ketoglutarate -> succinyl CoA
\*type II
a. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: glucose 6-phosphate -> 6-phosphoglucono-lactone
b. malic enzyme: malate -> oxaloacetate
c. 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase: 6-phosphogluconate -> ribulose 5-phosphate
d. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: α-ketoglutarate -> succinyl CoA
\*type II
a) and c)
* also malate → pyruvate + Co2
* also malate → pyruvate + Co2
51
New cards
Fatty acid movement and metabolism inside the cell involves which of the following:
a. lipoprotein lipase to free the fatty acid from triglyceride inside the cell
b. non-covalent binding of the free fatty acid to cellular fatty acid binding protein
c. thiolase to complex the fatty acyl group to CoA
d. transport of the fatty acyl group bound to carnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane
\**type II question*\*
a. lipoprotein lipase to free the fatty acid from triglyceride inside the cell
b. non-covalent binding of the free fatty acid to cellular fatty acid binding protein
c. thiolase to complex the fatty acyl group to CoA
d. transport of the fatty acyl group bound to carnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane
\**type II question*\*
b) and d)
52
New cards
Which of the following molecules is paired CORRECTLY with its direct precursor from the citric acid cycle or glycolysis:
a. **glutamate**; ∝-ketoglutarate
b. **heme**; succinyl CoA
c. **aspartate**; oxaloacetate
d. **serine**; 3-phosphoglycerate
\*type II
a. **glutamate**; ∝-ketoglutarate
b. **heme**; succinyl CoA
c. **aspartate**; oxaloacetate
d. **serine**; 3-phosphoglycerate
\*type II
all of the above
53
New cards
Which of the following enzymes couples with inorganic pyrophosphatase to provide the energy released from iPP to drive its/their respective reactions
a. UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
b. fatty acyl CoA synthetase
c. methionine adenosyl transferase
d. glycogen phosphorylase
\*type II
a. UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
b. fatty acyl CoA synthetase
c. methionine adenosyl transferase
d. glycogen phosphorylase
\*type II
a, b and c
54
New cards
Which of the following enzymes is (are) involved in substrate-level phosphorylation?
a. phosphoglycerate kinase
b. succinyl-CoA synthetase
c. pyruvate kinase
d. pyruvate carboxylase
\*type II
a. phosphoglycerate kinase
b. succinyl-CoA synthetase
c. pyruvate kinase
d. pyruvate carboxylase
\*type II
a, b and c
\
NOT involved:
* pyruvate carboxylase
* pyruvate dehydrogenase
* glycogen phosphorylase a
\
NOT involved:
* pyruvate carboxylase
* pyruvate dehydrogenase
* glycogen phosphorylase a
55
New cards
Peroxisomal b-oxidation of fatty acids:
a. exists to metabolize medium chain fatty acids
b. involves regeneration of FAD from FADH2 without formation of ATP
c. utilizes NADH generated to directly drive a peroxisomal electron transport chain for energy
d. allows for acetyl CoA generated to leave the organelle & enter mitochondrion
\*type II
a. exists to metabolize medium chain fatty acids
b. involves regeneration of FAD from FADH2 without formation of ATP
c. utilizes NADH generated to directly drive a peroxisomal electron transport chain for energy
d. allows for acetyl CoA generated to leave the organelle & enter mitochondrion
\*type II
b) and d)
\
ALSO INVOLVES:
* export of NADH + H+ to mitochondria for re-oxidation to NAD
* export of acetyl CoA to mitochondria to enter the CAC
* oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
\
ALSO INVOLVES:
* export of NADH + H+ to mitochondria for re-oxidation to NAD
* export of acetyl CoA to mitochondria to enter the CAC
* oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
56
New cards
During the later stages of fasting the brain becomes dependent upon which of the following enzymes to efficiently generate energy:
a. thiolase
b. PEP carboxykinase
c. 3-ketoacyl CoA transferase
d. malate dehydrogenase
\*type II
a. thiolase
b. PEP carboxykinase
c. 3-ketoacyl CoA transferase
d. malate dehydrogenase
\*type II
all of the above
\
ALSO:
* isocitrate dehydrogenase
* citrate synthase
\
ALSO:
* isocitrate dehydrogenase
* citrate synthase
57
New cards
Lipid rafts are rich in which of the following:
a. cholesterol
b. cholesterol ester
c. sphingomyelin
d. prenylated proteins
\*type II
a. cholesterol
b. cholesterol ester
c. sphingomyelin
d. prenylated proteins
\*type II
a) and c)
\
ALSO rich in:
* caveolin
* acylated proteins
* GPI-linked proteins
\
ALSO rich in:
* caveolin
* acylated proteins
* GPI-linked proteins
58
New cards
PI-specific Phospholipase C-b subtypes possess which of the following regulatory domains:
a. Src homology domain 3 (SH3)
b. pleckstrin homology domain (PH)
c. Src homology domain 2 (SH2)
d. G-protein binding domain (G)
\*type II
a. Src homology domain 3 (SH3)
b. pleckstrin homology domain (PH)
c. Src homology domain 2 (SH2)
d. G-protein binding domain (G)
\*type II
b) and d)
\
ALSO has:
* x and y catalytic domains
* EF-hand
* C2 domains
\
ALSO has:
* x and y catalytic domains
* EF-hand
* C2 domains
59
New cards
The FoF1 ATP Synthase has:
a. a rotating cylindrical proton channel made up of between 8-15 c-subunits
b. a rotating spindle consisting of γ(gamma) and e(epsilon) subunits
c. a static “stanchion” comprising b- and d- subunits to connect F 1 to membrane
d. a static F1 domain consisting of 3b-subunits which have ADP+ Pi, ATP +H2 O or are empty
\*type II
a. a rotating cylindrical proton channel made up of between 8-15 c-subunits
b. a rotating spindle consisting of γ(gamma) and e(epsilon) subunits
c. a static “stanchion” comprising b- and d- subunits to connect F 1 to membrane
d. a static F1 domain consisting of 3b-subunits which have ADP+ Pi, ATP +H2 O or are empty
\*type II
all are true
60
New cards
Erythrocytes possess which of the following metabolic enzymes:
a. isocitrate dehydrogenase
b. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
c. pyruvate dehydrogenase
d. pyruvate kinase
\*type II
a. isocitrate dehydrogenase
b. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
c. pyruvate dehydrogenase
d. pyruvate kinase
\*type II
b and d
DONT HAVE:
* pyruvate dehydrogenase
* a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
* citrate synthase
* carnitine acyl transferase I
DONT HAVE:
* pyruvate dehydrogenase
* a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
* citrate synthase
* carnitine acyl transferase I
61
New cards
Tetrahydrobiopterin is a coenzyme involved in following reaction(s):
a. phenylanlanine -> tyrosine
b. tryptophan -> 5-hydroxy-tryptophan
c. tyrosine -> L-Dopa (L-3,4-dhydroxyphenylalanine)
d. 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 -> 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
\*type II
a. phenylanlanine -> tyrosine
b. tryptophan -> 5-hydroxy-tryptophan
c. tyrosine -> L-Dopa (L-3,4-dhydroxyphenylalanine)
d. 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 -> 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
\*type II
a, b and c
62
New cards
Flippases and floppases:
a. create phospholipid asymmetry between the two leaflets of a natural membrane
b. both move phospholipids across a plasma membrane from the inner to the outer leaflet
c. both contain an ATPase activity
d. are transporters which allow phospholipid transport by facilitated diffusion
\*type II
a. create phospholipid asymmetry between the two leaflets of a natural membrane
b. both move phospholipids across a plasma membrane from the inner to the outer leaflet
c. both contain an ATPase activity
d. are transporters which allow phospholipid transport by facilitated diffusion
\*type II
a and c
63
New cards
Which phospho-/sphingo-lipids are found mainly in the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane:
a. phosphatidyl ethanolamine
b. phosphatidyl serine
c. phosphatidyl inositol
d. phosphatidyl choline
\*type II
a. phosphatidyl ethanolamine
b. phosphatidyl serine
c. phosphatidyl inositol
d. phosphatidyl choline
\*type II
only d
ALSO:
* sphingomyelin
* neutral PL’s
ALSO:
* sphingomyelin
* neutral PL’s
64
New cards
Which of the following phospholipids are found __**PREDOMINANTLY**__ in the **INNER** LEAFLET of the membrane:
1. Phosphatidyl choline
2. Phosphatidyl serine
3. Sphingomyelin
4. Phosphatidyl ethanolamine
\*type II
1. Phosphatidyl choline
2. Phosphatidyl serine
3. Sphingomyelin
4. Phosphatidyl ethanolamine
\*type II
2 and 4
ALSO:
* phosphatidyl inositol-bisphosphate
* phosphatidic acid
* acidic PL’s
ALSO:
* phosphatidyl inositol-bisphosphate
* phosphatidic acid
* acidic PL’s
65
New cards
What is significant about carnitine-mediated entry of fatty acids into hepatocyte mitochondrial matrix?
a. it controls the substrate concentration thereby limiting the rate of β-oxidation
b. it is specific for fatty acids ranging in length from C16 to C22
c. the fatty acid is now committed to β-oxidation and cannot leave without being metabolized
d. the resultant acetyl CoA formed can be further broken down to CO2 by the citric acid cycle
\*type II
a. it controls the substrate concentration thereby limiting the rate of β-oxidation
b. it is specific for fatty acids ranging in length from C16 to C22
c. the fatty acid is now committed to β-oxidation and cannot leave without being metabolized
d. the resultant acetyl CoA formed can be further broken down to CO2 by the citric acid cycle
\*type II
all are correct
66
New cards
Heme biosynthesis involves:
a. δ-levulinate as an initial intermediate
b. an amino acid precursor, glycine or glutamate
c. assembly of 4 porphyrin rings to form protoporphyrin
d. insertion of a metal ion, Fe3+ by the enzyme ferrochelatase
\*type II
a. δ-levulinate as an initial intermediate
b. an amino acid precursor, glycine or glutamate
c. assembly of 4 porphyrin rings to form protoporphyrin
d. insertion of a metal ion, Fe3+ by the enzyme ferrochelatase
\*type II
a, b and c
* not d) because iron is Fe2+
* not d) because iron is Fe2+
67
New cards
The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle or bypass:
a. transports FADH2 instead of NADH across the IMM into the mitochondrial matrix
b. uses mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase to feed electrons from FADH2 to ubiquinone
c. it is more energy efficient than the alternative malate-aspartate shuttle
d. it is faster and therefore used by insect flight muscle
\*type II
a. transports FADH2 instead of NADH across the IMM into the mitochondrial matrix
b. uses mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase to feed electrons from FADH2 to ubiquinone
c. it is more energy efficient than the alternative malate-aspartate shuttle
d. it is faster and therefore used by insect flight muscle
\*type II
b and d
68
New cards
Enzymes involved directly or indirectly in the utilization of ketone bodies for energy in the heart are:
a. β-ketoacyl CoA transferase
b. β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
c. thiolase
d. PEP carboxykinase
\*type II
a. β-ketoacyl CoA transferase
b. β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
c. thiolase
d. PEP carboxykinase
\*type II
all
69
New cards
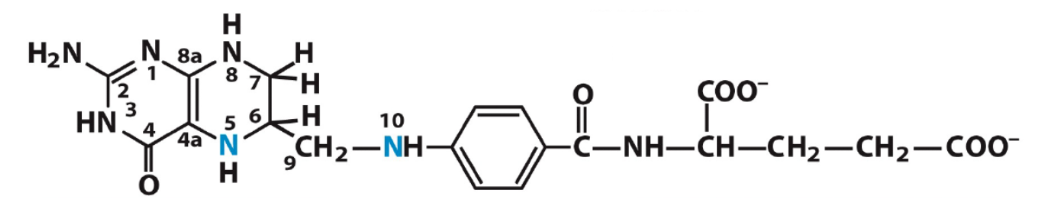
The following molecule or its derivatives are involved in which of the following reactions:
a. transfer of -CH3 groups
b. transfer of -H–C=O groups
c. transfer of -CH2 OH groups
d. transfer of -CH2 C=O groups
\*type II
a. transfer of -CH3 groups
b. transfer of -H–C=O groups
c. transfer of -CH2 OH groups
d. transfer of -CH2 C=O groups
\*type II
tetrahydrofolate
a, b and c
a, b and c
70
New cards
Fatty acid Synthase:
a. generates a palmitate molecule in which each C2-unit is derived from malonyl CoA
b. uses a telescopic pantetheine arm of ACP to reach the malonyl group on the condensing enzyme
c. employs the reducing power of NADH in two reduction steps
d. transcription is increased by a low-fat diet
\*type II
a. generates a palmitate molecule in which each C2-unit is derived from malonyl CoA
b. uses a telescopic pantetheine arm of ACP to reach the malonyl group on the condensing enzyme
c. employs the reducing power of NADH in two reduction steps
d. transcription is increased by a low-fat diet
\*type II
d)
71
New cards
Which of the following enzymes is involved in substrate-level phosphorylation:
1. phosphoglycerate kinase
2. pyruvate kinase
3. succinyl CoA synthetase
4. glycogen phosphorylase a
\*type II
1. phosphoglycerate kinase
2. pyruvate kinase
3. succinyl CoA synthetase
4. glycogen phosphorylase a
\*type II
1, 2 and 3
72
New cards
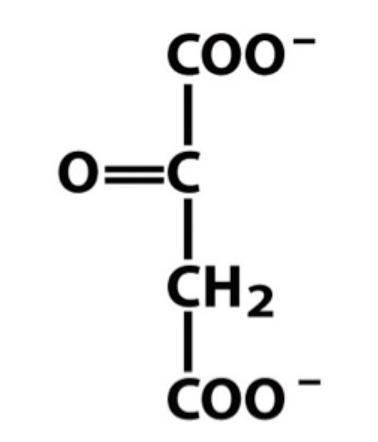
The following structure is:
\
a)pyruvate
b) oxaloacetate
c) succinate
d) malate
e) citrate
\
a)pyruvate
b) oxaloacetate
c) succinate
d) malate
e) citrate
b
73
New cards
During long-term starvation, the energy source for the brain is:
1. glucose only
2. fatty acids only
3. ketone bodies only
4. both glucose and fatty acids
5. both glucose and ketone bodies
1. glucose only
2. fatty acids only
3. ketone bodies only
4. both glucose and fatty acids
5. both glucose and ketone bodies
5
74
New cards
Which of the following di- or poly-saccharides is INCORRECTLY matched with its description:
1. amylopectin is a glucose polymer with both α(1->4) and α(1->6) links
2. cellulose is a glucose polymer with β(1->4) links
3. sucrose is Glc(α1
1. amylopectin is a glucose polymer with both α(1->4) and α(1->6) links
2. cellulose is a glucose polymer with β(1->4) links
3. sucrose is Glc(α1
5. amylose is Glc(β1->4)Glc
* it is (a1→4)Glc
75
New cards
Which of the following enzymes is UNIQUE to the glyoxylate cycle:
1. fumarase
2. aconitase
3. citrate synthase
4. malate dehydrogenase
5. isocitrate lyase
1. fumarase
2. aconitase
3. citrate synthase
4. malate dehydrogenase
5. isocitrate lyase
5
76
New cards
NADPH generation involves:
1. pyruvate dehydrogenase
2. isocitrate dehydrogenase
3. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
4. malate dehydrogenase
5. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
1. pyruvate dehydrogenase
2. isocitrate dehydrogenase
3. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
4. malate dehydrogenase
5. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
3. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
77
New cards
In mammals, which of the following molecules is derived from pyruvate under anerobic conditions:
1. ethanol
2. lactate
3. oxaloacetate
4. alanine
5. acetyl CoA
1. ethanol
2. lactate
3. oxaloacetate
4. alanine
5. acetyl CoA
2. lactate
78
New cards
Insulin upregulates which of the following enzymatic steps OR proteins:
1. glycogen phosphorylase
2. GLUT-4 glucose transporter
3. GLUT-2 glucose transporter
4. glucose 6-phosphatase
5. pyruvate carboxylase
1. glycogen phosphorylase
2. GLUT-4 glucose transporter
3. GLUT-2 glucose transporter
4. glucose 6-phosphatase
5. pyruvate carboxylase
GLUT-4 glucose transporter
79
New cards
Pyruvate dehydrogenase involves which of the following coenzymes as **C2-group carrier**(s):-
1. NAD
2. lipoate
3. FAD
4. thiamine pyrophosphate
\*type II
1. NAD
2. lipoate
3. FAD
4. thiamine pyrophosphate
\*type II
lipoate and thiamine pyrophosphate
80
New cards
Which of the following **enzymes** is CORRECTLY listed with one its *regulators*:
1. **pyruvate dehydrogenase** -*acetyl CoA*
2. **phosphofructokinase-1**--*citrate*
3. **pyruvate carboxylase** -*acetyl CoA*
4. **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase** –*NADPH*
\*type II
1. **pyruvate dehydrogenase** -*acetyl CoA*
2. **phosphofructokinase-1**--*citrate*
3. **pyruvate carboxylase** -*acetyl CoA*
4. **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase** –*NADPH*
\*type II
all
81
New cards
Which of the following statements about triglyceride and glycogen stores is(are) CORRECT:
1. on a wet weight basis, glycogen is lighter to carry around than triglyceride
2. on a dry weight basis, glycogen is about equivalent to triglyceride in energy yield
3. glycogen is more reduced than triglyceride
4. glycogen is more rapidly mobilized than triglyceride
\*type II
1. on a wet weight basis, glycogen is lighter to carry around than triglyceride
2. on a dry weight basis, glycogen is about equivalent to triglyceride in energy yield
3. glycogen is more reduced than triglyceride
4. glycogen is more rapidly mobilized than triglyceride
\*type II
only 4
82
New cards
Pentose phosphate pathway:
1. involves oxidative steps which generate NADH and ribulose-5-phosphate
2. involves non-oxidative steps which convert ribulose-5-phosphate back to glucose-6-phosphate
3. can use non-oxidative steps in reverse to generate ribose-5-phosphate without NADH
4. protects the cell from oxidative damage
\*type II
1. involves oxidative steps which generate NADH and ribulose-5-phosphate
2. involves non-oxidative steps which convert ribulose-5-phosphate back to glucose-6-phosphate
3. can use non-oxidative steps in reverse to generate ribose-5-phosphate without NADH
4. protects the cell from oxidative damage
\*type II
2 and 4
83
New cards
Erythrocytes possess which of the following metabolic pathways/enzymes
1. pyruvate dehydrogenase
2. pentose phosphate pathway
3. citric acid cycle
4. glycolysis
\*type II
1. pyruvate dehydrogenase
2. pentose phosphate pathway
3. citric acid cycle
4. glycolysis
\*type II
2 and 4
84
New cards
Which of the following enzymes are **IRREVERSIBLE** or **operate(s) IRREVERSIBLY** in **muscle** cells:
1. pyruvate kinase
2. PEP-carboxykinase
3. pyruvate dehydrogenase
4. phosphoglycerate kinase
\*type II
1. pyruvate kinase
2. PEP-carboxykinase
3. pyruvate dehydrogenase
4. phosphoglycerate kinase
\*type II
1, 2 and 3
85
New cards
Which of the following statements about g**lycogenolysis** is(are) correct:
1. it is followed by glycolysis in muscle because there is no inhibition of pyruvate kinase by glucagon
2. it is followed by glucose export in liver because of the presence of glucose-6-phosphatase
3. it can be accompanied by gluconeogenesis in liver cells
4. it mainly involves the release of glucose by enzymatic hydrolysis of glycogen during glycogenolysis
\*type II
1. it is followed by glycolysis in muscle because there is no inhibition of pyruvate kinase by glucagon
2. it is followed by glucose export in liver because of the presence of glucose-6-phosphatase
3. it can be accompanied by gluconeogenesis in liver cells
4. it mainly involves the release of glucose by enzymatic hydrolysis of glycogen during glycogenolysis
\*type II
1, 2 and 3
86
New cards
Which of the following statements about the regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase is __**IN**__**CORRECT**
a) palmityl CoA inhibits the enzyme
b) insulin causes dephosphorylation of the enzyme
c) citrate partially activates the enzyme by allosteric binding
d) glucagon blocks phosphorylation of the enzyme
e) adiponectin inactivates the enzyme
a) palmityl CoA inhibits the enzyme
b) insulin causes dephosphorylation of the enzyme
c) citrate partially activates the enzyme by allosteric binding
d) glucagon blocks phosphorylation of the enzyme
e) adiponectin inactivates the enzyme
d) glucagon blocks phosphorylation of the enzyme
87
New cards
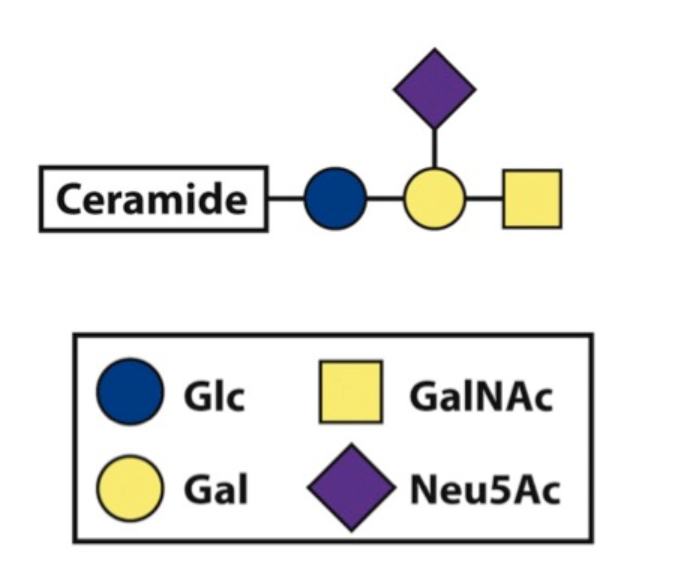
Identify the sphingolipid shown:
\
a) globoside
b) ganglioside
c) lactosylceramide
d) sphingomyelin
e) cerebroside
\
a) globoside
b) ganglioside
c) lactosylceramide
d) sphingomyelin
e) cerebroside
b) ganglioside
88
New cards
If unlabelled acetyl CoA and radioactively-labelled \[2-14C\]malonyl CoA are used as substrates for a PURIFIED fatty acid synthase, which positions of the resulting palmitate molecule will be labelled:
a) only even-numbered carbons.
b) only the carbon at the terminal methyl group
c) only odd-numbered carbons.
d) only the carbon of the carboxyl group.
e) none of the carbons.
a) only even-numbered carbons.
b) only the carbon at the terminal methyl group
c) only odd-numbered carbons.
d) only the carbon of the carboxyl group.
e) none of the carbons.
a) only even-numbered carbons.
89
New cards
The biosynthesis of phosphatidyl ethanolamine involves:
a) phosphatidic acid and CDP-ethanolamine
b) diacylglycerol and CDP-ethanolamine
c) phosphatidyl choline and S-adenosyl methionine
d) CDP-diacylglycerol and ethanolamine
e) CDP-diacylglycerol and phosphoethanolamine
a) phosphatidic acid and CDP-ethanolamine
b) diacylglycerol and CDP-ethanolamine
c) phosphatidyl choline and S-adenosyl methionine
d) CDP-diacylglycerol and ethanolamine
e) CDP-diacylglycerol and phosphoethanolamine
b) diacylglycerol and CDP-ethanolamine
90
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding ketogenesis/ketone body utilization is CORRECT:
\
a) ketogenesis is absent in individuals with myopathic carnitine deficiency
b) ketone body utilization is absent from the brain due to the blood brain barrier
c) ketogenesis involves the cytosolic enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
d) ketone bodies are made exclusively in the liver
e) ketone body use by the liver depends upon oxaloacetate supply by pyruvate carboxylase
\
a) ketogenesis is absent in individuals with myopathic carnitine deficiency
b) ketone body utilization is absent from the brain due to the blood brain barrier
c) ketogenesis involves the cytosolic enzyme HMG-CoA synthase
d) ketone bodies are made exclusively in the liver
e) ketone body use by the liver depends upon oxaloacetate supply by pyruvate carboxylase
d) ketone bodies are made exclusively in the liver
91
New cards
Which of the following metabolic pathways and its subcellular localization are **INCORRECTLY** matched:
a) phospholipid biosynthesis; mitochondrion
b) ketogenesis; mitochondrion
c) fatty acid β-oxidation; peroxisome
d) fatty acid biosynthesis; cytoplasm
e) citric acid cycle; mitochondrion
a) phospholipid biosynthesis; mitochondrion
b) ketogenesis; mitochondrion
c) fatty acid β-oxidation; peroxisome
d) fatty acid biosynthesis; cytoplasm
e) citric acid cycle; mitochondrion
a) phospholipid biosynthesis; mitochondrion
92
New cards
__**Useable**__ metabolic water released during the complete oxidation of a fatty acid to its building blocks is formed during:
1\. the steps of β-oxidation of the fatty acid to acetyl CoA
2\. oxidative phosphorylation
3\. the steps of the citric acid cycle
4\. electron transport chain
\*type II
1\. the steps of β-oxidation of the fatty acid to acetyl CoA
2\. oxidative phosphorylation
3\. the steps of the citric acid cycle
4\. electron transport chain
\*type II
only 4) the ETC
93
New cards
The steps of mitochondria β-oxidation of fatty acids to acetyl CoA:
1\. directly releases about 75% of the available energy as ATP
2\. involves two dehydrogenation (oxidation) steps each generating NADH
3\. directly releases 1 water molecule per β-oxidation cycle
4\. occurs while the fatty acid is always attached to coenzyme A
\*type II
1\. directly releases about 75% of the available energy as ATP
2\. involves two dehydrogenation (oxidation) steps each generating NADH
3\. directly releases 1 water molecule per β-oxidation cycle
4\. occurs while the fatty acid is always attached to coenzyme A
\*type II
only 4
94
New cards
Triglycerides make excellent energy storage forms because they:
1\. are anhydrous and therefore light to transport
2\. require no energy to synthesize from lipoprotein-derived fatty acids
3\. are metabolically-inert and remain resistant to oxidation within the adipocyte
4\. are hydrolyzed initially by hormone sensitive lipase to facilitate rapid energy release
\*type II
1\. are anhydrous and therefore light to transport
2\. require no energy to synthesize from lipoprotein-derived fatty acids
3\. are metabolically-inert and remain resistant to oxidation within the adipocyte
4\. are hydrolyzed initially by hormone sensitive lipase to facilitate rapid energy release
\*type II
only 1 and 3
95
New cards
Triglyceride biosynthesis in the adipocyte:
1\. can involve pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxykinase
2\. is insulin-dependent
3\. involves highly specific acyl transferases which prefer saturated fatty acids
4\. follows a pathway with a FINAL step involving the direct coupling of a fatty acid to phosphatidic acid
\*type II
1\. can involve pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxykinase
2\. is insulin-dependent
3\. involves highly specific acyl transferases which prefer saturated fatty acids
4\. follows a pathway with a FINAL step involving the direct coupling of a fatty acid to phosphatidic acid
\*type II
1, 2 and 3
96
New cards
Carnitine:
1\. synthesis involves the amino acids lysine and methionine
2\. transports medium chain (C6-C14) fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix
3\. commits a fatty acid to be completely oxidized via β-oxidation to produce acetyl CoA
4\. is absent in liver and muscle in individuals with myopathic carnitine deficiency
\*type II
1\. synthesis involves the amino acids lysine and methionine
2\. transports medium chain (C6-C14) fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix
3\. commits a fatty acid to be completely oxidized via β-oxidation to produce acetyl CoA
4\. is absent in liver and muscle in individuals with myopathic carnitine deficiency
\*type II
1 and 3
97
New cards
Cholesterol biosynthesis involves:
1\. HMG-CoA reductase, which is the first committed step of isoprenoid biosynthesis
2\. trimming of a lanosterol intermediate to make a C-27 product
3\. cyclization of the intermediate, squalene
4\. synthesis of a five carbon building block, mevalonate
\*type II
1\. HMG-CoA reductase, which is the first committed step of isoprenoid biosynthesis
2\. trimming of a lanosterol intermediate to make a C-27 product
3\. cyclization of the intermediate, squalene
4\. synthesis of a five carbon building block, mevalonate
\*type II
1, 2 and 3
98
New cards
Peroxisomal β-oxidation of fatty acids involves:
1\. oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
2\. export of NADPH generated to the mitochondrion for oxidation by the electron transport chain
3\. export of acetyl CoA to the mitochondrion for metabolism in the citric acid cycle
4\. export of FADH2 to the mitochondrion for oxidation by the electron transport chain
\*type II
1\. oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
2\. export of NADPH generated to the mitochondrion for oxidation by the electron transport chain
3\. export of acetyl CoA to the mitochondrion for metabolism in the citric acid cycle
4\. export of FADH2 to the mitochondrion for oxidation by the electron transport chain
\*type II
1 and 3
99
New cards
Fluidity of a membrane is INCREASED by:
a) the action of desaturases to increase the degree of unsaturation
b) the removal of hydroxymyristate from membrane phospholipids
c) the introduction of trans-double bonds into saturated OR unsaturated fatty acids
d) the introduction of sphingomyelin into lipid rafts
e) the action of elongases to increase fatty acid length
a) the action of desaturases to increase the degree of unsaturation
b) the removal of hydroxymyristate from membrane phospholipids
c) the introduction of trans-double bonds into saturated OR unsaturated fatty acids
d) the introduction of sphingomyelin into lipid rafts
e) the action of elongases to increase fatty acid length
a) the action of desaturases to increase the degree of unsaturation
100
New cards
Which of the following glucose transporters has a high Kt value of 17 mM and is involved in glucose movement into and out of the hepatocyte:
a) GLUT1
b) GLUT5
c) GLUT2
d) GLUT3
e) GLUT4
a) GLUT1
b) GLUT5
c) GLUT2
d) GLUT3
e) GLUT4
c) GLUT2