Keating Mistakes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:27 PM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
Draw DME
Dimethoxyethane
\-o/\\/o-
\-o/\\/o-
2
New cards
Draw Bz
Bz
Z is a rare letter
It’s a thing you never see! BENZOYL= ketone bit branched out of benzene
Z is a rare letter
It’s a thing you never see! BENZOYL= ketone bit branched out of benzene
3
New cards
Draw Bn
Benzyl
Benzene w/ methyl
Benzene w/ methyl
4
New cards
Why does EtOH have a larger b.p. than Et2O
Ethanol can self associate with h-bonds
5
New cards
Why can’t you get 100% pure ethanol via distillation?
Vapour reaches 96% purity- same as liquid- no more purification
6
New cards
Draw propylene glycol
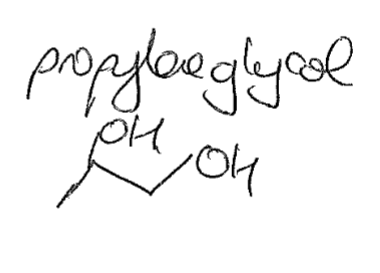
7
New cards
List three solvents for oral medicines-
* glycerol
* ethanol
* propylene glycol ( 2 hydroxyls, 3 carbon chain)
* ethanol
* propylene glycol ( 2 hydroxyls, 3 carbon chain)
8
New cards
Name a cationic surfactant
benzylalkonium chloride
9
New cards
draw beznyl alkonium chloride
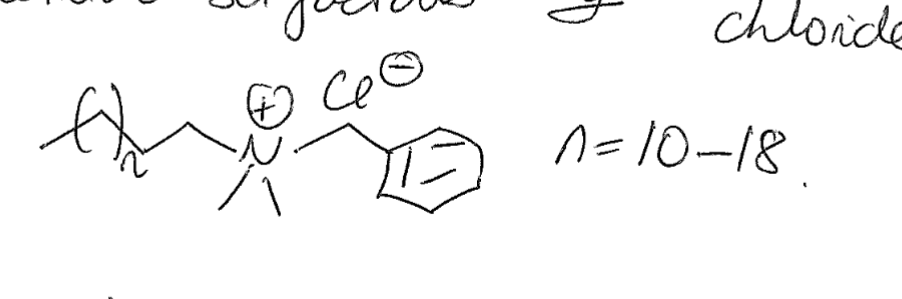
10
New cards
draw sodium lauryl sulfate
Na+ is the floaty bit
Sulphate is attached to the carboxylic bit, replacing H
Sulphate is attached to the carboxylic bit, replacing H
11
New cards
give other names for surfactants
detergent
emulsifying agents
emulsifying agents
12
New cards
explain amphillic
Compounds which simultaneously have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties in the one molecule
13
New cards
draw
**sodium stearate**
**sodium stearate**
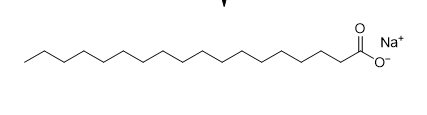
14
New cards
Give the systematic name for S
stearic acid C=18
remember the n-
n-octadecanoic acid (an= no alkyne/alkene bonds)
remember the n-
n-octadecanoic acid (an= no alkyne/alkene bonds)
15
New cards
Whats SDS
sodium dodelyl sulphate
16
New cards
describe the lenght of Benzalkonium chloride
8-18 carbon chain
17
New cards
draw **cetyl pyridinium chloride**
pyridine = 6 membered aromatic ring
16 carbon chain atatched to the N
hence quartenary amine= + charge
16 carbon chain atatched to the N
hence quartenary amine= + charge
18
New cards
how many c in myristic acid
14
19
New cards
how many c in palmic acid
16
20
New cards
how many c in stearic acid
18
21
New cards
how many c in lauric acid
12
22
New cards
how many c in capryl acid?
8
23
New cards
How many c in caprylyl acid
10
24
New cards
draw sorbitan monostearate
the fatty acid added at the primary alcohol of sorbitan
25
New cards
what’s the structure of oleic acid
\
\
Oleic acid
9*Z*-hexadecenoic acid
16 carbion chaiin
cis alkene bond at C9
\
9*Z*-hexadecenoic acid
16 carbion chaiin
cis alkene bond at C9
\
26
New cards
which have PEG units
tweens/ spans
tweens/ spans
Tweens HAVE FATTY ACID + PEGS
spans have ONLY the monopalmitate bit (fatty acid bit!)
spans have ONLY the monopalmitate bit (fatty acid bit!)
27
New cards
draw a polysorbate monoester (tween)
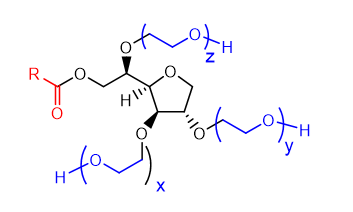
28
New cards
describe how to increase / decrease aq solubity of a polysorbate monoester
for an x amount of ethoxy groups within the molecule→ more esters= more lipophillic
\
more ethoxy groups (n /o\\/ ) more hydrophillic
\
more ethoxy groups (n /o\\/ ) more hydrophillic
29
New cards
draw azo
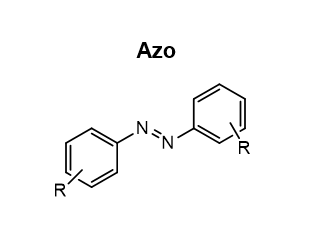
30
New cards
Draw quinine
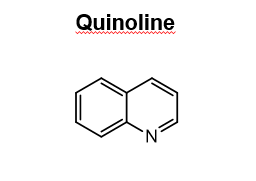
31
New cards
draw an indigoid
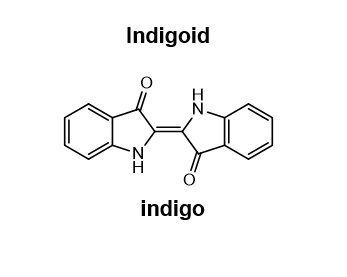
32
New cards
draw triarylmethane
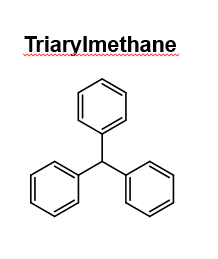
33
New cards
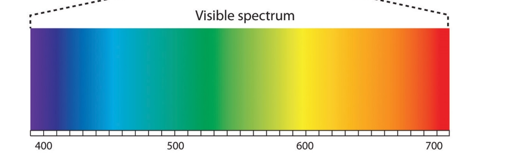
whtas the range of the visible sprectrum?
400-800nm
34
New cards
where is red absorbed
500nm lamba max
35
New cards
what’s used to measure the lamba max?
visible spectrometer
36
New cards
what’s electron delocation
e- movement throught the overlapping pi orbitals
37
New cards
what’s a conjugated system
system of overlapping pi orbitals tahts allows for delocalisation of pi electrons (in double bonds/triple/lone pairs)
38
New cards
what controls the colour
The greater the degree of conjugation, the longer the wavelength required (lower energy) for π-electrons to undergo transition
→ pi electrons bounce more easily if more conjugation so less energy needed= longer wavelenght (red absorbed)
\
→ pi electrons bounce more easily if more conjugation so less energy needed= longer wavelenght (red absorbed)
\
39
New cards
why does pH alter colour
partially protenated= no lone pairs on amine for example
less conjugation → higher energy, shorter wavelenghts absorbed wh
less conjugation → higher energy, shorter wavelenghts absorbed wh
40
New cards
what happens when electrons absorb energy from wavelnghts
promoted to a higher energy level
no longer have opposite spin
→ quantum of specific energy is absorbed by one of the electrons, it may undergo a transition to a higher, excited state (↑↑) – σ to σ\* or π to π\*.
no longer have opposite spin
→ quantum of specific energy is absorbed by one of the electrons, it may undergo a transition to a higher, excited state (↑↑) – σ to σ\* or π to π\*.
41
New cards
what are the rules for a ring flip?
up stays up
down stays down
equitorial becomes axial (and vice versa)
where C2 was, C1 replaces it
the first two / / parrallel lines are drawn in the opposite direction→ \\ \\
wedge = up
dash=down
down stays down
equitorial becomes axial (and vice versa)
where C2 was, C1 replaces it
the first two / / parrallel lines are drawn in the opposite direction→ \\ \\
wedge = up
dash=down
42
New cards
explain the difference between monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes
monoterpene→ one set of C-10
sesqui (1.5) terpene→ one and a half sets of C10→ C15 in total
\
sesqui (1.5) terpene→ one and a half sets of C10→ C15 in total
\
43
New cards
what measures the composition of oils?
gas chromotography
44
New cards
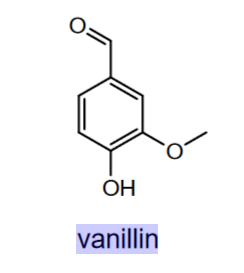
draw vanillin
benzyladehyde base
hydroxy group at C4
methoxy group at C3
when naming the hydroxy group goes firts despite being @ C4 due to alphabetical order
hydroxy group at C4
methoxy group at C3
when naming the hydroxy group goes firts despite being @ C4 due to alphabetical order
45
New cards
what’s the difference between vanillina nd vanillic acid?
vanillic acid has the benzylALDEHYDE oxidised to the acid form
46
New cards
what’s the difference between thymol and methanol
thymol is an aromatic ring
planarhow
planarhow
47
New cards
how do amine taste
bitter
48
New cards
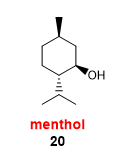
draw methanol
one methyl
one isopropyl group
one hydroxyl
one isopropyl group
one hydroxyl
49
New cards
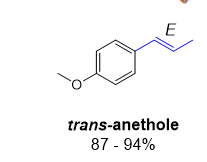
draw the major componnemt of aniseed oil
trans!
methoxy para to the propene substituent
called trans anethole
methoxy para to the propene substituent
called trans anethole
50
New cards
what can bond to H by h bonding?
lone pairs of e- of O / N
51
New cards
whats a furanose
5 memberred ring with o
52
New cards
what molecules are chiral
ones with 4 dif substituents
SOS TAG isnt chiral, O bit has 2 S subsituents
SOS TAG isnt chiral, O bit has 2 S subsituents
53
New cards
where can you start the mesomeric move of e- when doing resonance structures
not only at the lone pair
go ahead and start at the middle of the ring!
go ahead and start at the middle of the ring!
54
New cards
what’s the hawroth projection
the ring onede
55
New cards
describe the stereohemistry of fisher prohection
vertical bonds→ dashed
horizontal bonds→ wedged
horizontal bonds→ wedged
56
New cards
whats \[a\]d
specific optical rotation
independent of conc and sample tube lenght
independent of conc and sample tube lenght
57
New cards
whats the anomeric carbon
carbon derived from the carbonyl
new chiral centre
new chiral centre
58
New cards
how does a mutorotation work
all three (alpha, beta, aliphatic) in equilibrium in aq sol
beta→ aliphatic→ alpha and so on by doing a twistyy
beta→ aliphatic→ alpha and so on by doing a twistyy
59
New cards
what wavelenght is sodium d light?
589nm
60
New cards
whats th flash point?
min temp needed to vapourise
61
New cards
why does the sulfone group increase solubility
allows partial ionisation at a pH of 7
62
New cards
what’s e delocalisation
the movement of e- through overlapping pi orbotals due to conjugation
63
New cards
if pka>ph protenated / deprotenated?
protenated
remmeber
amines @peptide pka= 9 , at phys pH they are protenated
remmeber
amines @peptide pka= 9 , at phys pH they are protenated
64
New cards
draw vinylchrolide
vinyl→ c=c bond
chloride replaces a H
chloride replaces a H
65
New cards
Draw PVC and assign polymer type
homopolymer linear
66
New cards
draw acrylnitrile
C=C
one H replaced with cyano group
one H replaced with cyano group
67
New cards
whats methin
R3-C-H
the carbon attached to three Rs
the carbon attached to three Rs
68
New cards
how are graft polymers made?
x/ gamma radiationde
69
New cards
describe graft polymer structure
made with homopolymers
a-a-a-a branched off of b-b-b-b
a-a-a-a branched off of b-b-b-b
70
New cards
describe the properties of graft polymers
retain some of the homopolymers
71
New cards
how are random polymers made
radical mechanism
72
New cards
how are block copolymers made
ionic polymerisation
73
New cards
describe propertie of block copolymers
retain some from homopolymers
74
New cards
draw ethylene oxide
epoxide
2c one Od
2c one Od
75
New cards
draw propylene oxide
3carbon - epoxide and a methyl CHIRAL!!!
\
\
76
New cards
describe the sterreochem of polyoxalane
if the propylene oxide racemic then polyoxalene is also racemic
77
New cards
draw vinylbenzene
benzene-C=C
78
New cards
what kimd of polymer does vinylbenzene and acrylnitrile make?
regualr polymer
a-b-a-b
a-b-a-b
79
New cards
what are crosslined polymers
their branches are also linked to each other
80
New cards
describe the phys properties of crosslinked polymers
swell when a=water added
decreased solubility
decreased solubility
81
New cards
whats the name of acrrylic acid with a methyl replacing H on the hydroxy group
methyl acrylate w
82
New cards
whats the name of acrrylic acid with a methyl replacing H on the ethene
methyl acrylic acid d
83
New cards
draw acrylic acid
ethene with COOH on it
84
New cards