National parks 2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is the rock cycle starting with magma and ending with it
magma, igneous rock, sediment, sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock, magma
two types of weathering
Mechanical and chemical
mechanical weathering
physical breaking down of rock
chemical weathering
chemical reaction that changes a minerals chemical composition
agents of weathering
wind, water, freezing, heat/cool
types of mechanical weathering
frost wedging, organic activity, exfoliation,

what is this?
exfoliation
example of organic mechanical weathering
roots prying apart rock
physical weathering _____ the rock’s surface area
increases
what type of areas would have more mechanical weathering
arctic and dry areas
types of chemical weathering
leaching, oxidation, dissolution
leaching
the removal of soluble components
dissolution
rock dissolves completely in water
sinkholes are what type of weathering
chemical- dissolution
what controls the rate of weathering
climate, parent material, presence of absence of soil
erosion
the breakdown and Transportation of material
how are materials transported
water, wind, glaciers
what size rock does water transport
large and small sediment
what size rock does wind transport
fine sediment
what size rock does glaciers transport
all sizes
plateau
broad level region with high elevation
types of streams
straight, braided, meandering
straight streams
simple single channels
braided stream
shifting streams with sediment bars
meandering streams
constantly shiftinghighly snarky rivers
what stream has a steep gradient
braided
what stream has a gentle gradient
meandering

what is this
braided stream
what are the three ways streams transport sediment
bead load, suspended load, dissolved load
bead load
particles rolling underwater on ground
suspended load
particles floating throughout water
dissolved load
atoms that are dissolved in the water (salt)
how does salt water occur
chemical weathering of rock and the dissolved ions make it to the ocean and the fresh water evaporating

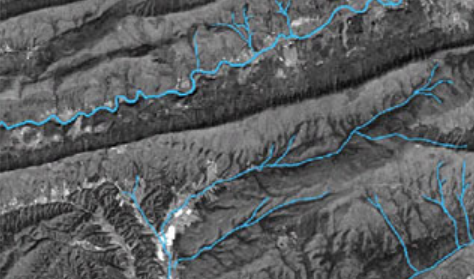
what drainage pattern is this
rectangular
what does a rectangular drainage pattern tell you
fractured bedrock
what drainage pattern is this
trellis
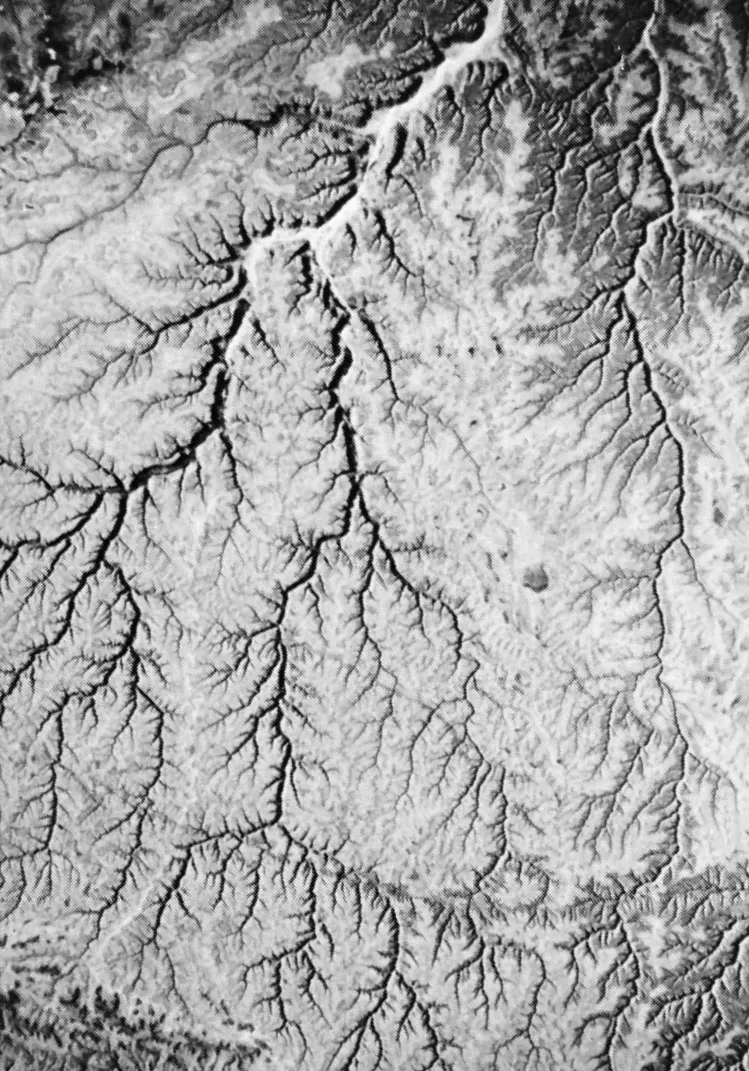

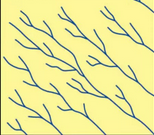
what drainage pattern is this
dendritic
reasons for dendritic drainage
horizontal layered rocks
rocks that have no layering (granite)
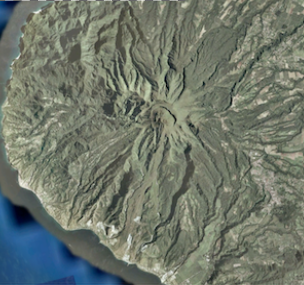
what drainage pattern is this
radial
drainage pattern?
parallel
why does parallel drainage occur
sloped surface
what rock is the majority of the slopes in utah parks
red shale
types of differential weathering
hoodoos, tafoni, arches
hoodoos
balanced rocks
tafoni
honeycomb holes
how do tafoni form
fractures in sandstone, minerals deposit in the fracture, new minerals more resistant to weathering
formation of arches
resistant rock, form joints, weathering form fins, underlying rocks form arch
continential glaciation
ice on land that spreads out
In alpine glaciers ice flows
forward and scratch the earth underneath it
types of glacial sediments
till, erratic, loess
till sediment
course boulders, cobbles, sand and silt
erratic sediment
large boulders dropped by glaciers
loess sediment
finely ground sand
two types of sedimentary deposits
moraine, striations
moraine
limits of ice advancements
striations
scratches on rocks made by ice dragging stones
how to tell how big glaciers are
sea level changes
how does sea level changes tell size of iceages
water level lowers as water is locked on land as ice
term for earths crust bouncing back after heavy sheets melt away
isostatic rebound
how do we know the conditions of the ice ages
shell composition of marine organisms, ice cores
how does the composition of microscopic marine organisms tell conditions of ice age
O16/O18 isotopic ratio
which oxygen isotope is rich in summer ice
O18
why do ice ages happen
earths orbit, axis and precession of equinoxes
High eccentricity
difference in heating throughout the year (ellipsical)
Low eccentricity
even heating throughout the year (circular)
greater tilt in earth’s axis
greater difference in summer and winter, more shadowing effect
precession of equinoxes
the position of the earth relative to the sun
summer when the earth is close to the sun
warmer summers, cooler winters
boundary between the rock filled with air and rock filled with water
watertable
porosity
amount of holes in the rock
zone of saturation
groundwater filled porosity
CaCO3 + 2H+ = H2O+CO2 + Ca2+
dissolution
speleothems
cave structures
stactities
ceiling ones
stalagmites
on the ground
speleothems examples
stalactites, stalagmites, columns, flowstone
mesa verde cave formation
sandstone is permeable, shale is not