P 102, Exam 2
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Sensation
Detection of physical energy by sensory organs
The brain’s interpretation of raw sensory data
Perception
External stimulus turned into neural activity
Transduction
The lowest level of a stimulus we can detect 50% of the time
Absolute Threshhold
The stronger the stimulus, the greater the change needed to detect
Weber’s Law
Hearing sounds when one sees/ tastes colours
Synesthesia
What’s in our sensory field
What was there a moment ago
What we remember from our past
What our brain maps
Lets us choose which sensory outputs to focus on and turn off
Selective attention
Not detecting certain stimulus because we do not look for it
Inattention
Brightness
Hue
Saturation
Three aspects colour depends on
The white portion of the eye
Sclera
Coloured portion of the eye, controls how much light is let in
Iris
The hole in the eye where light enters
Pupil
The transparent cells that focuses light on the back of the eye
Cornea
Curves to retract light onto back of the eye
Lens
The thin membrane at the back of the eye
Retina
Center, responsible for acuity
Fovea
Rods
Cones
Two types of retina receptors
Made of axons and is the nerve at the back of the eye
Axons
Allows us to detect lines and edges
Feature detector cells
Theory: colour vision is based on our sensitivity to three primary colours
Blue
Green
Red
Trichromatic theory
Theory: colour vision is a function of complementary, opposing colours
Opponent process theory
Inability to perceive motion
Motion blindness
Object recognition deficit
Visual agnosia
pitch
Loudness
Timbre
Three aspects sound relies on
The outer ear where we see skin cartilage and flap.
Pinna
Middle ear where the hammer, anvil, and stirrup vibrate and transmits sound to the inner ear
Ossicles
The inner ear that converts vibrations to neural activity. Has the Corti and basilar mambrane
Cochlea
Theory: specific location along the basilar membrane is also the specific tone and pitch
Place theory
Theory: the speed neurons fire action potentials reproduces the pitch.
Frequency theory
Failure of eardrum or ossicles of inner ear
Conductive deafness
Damage to audition nerve
Nerve deafness
Damage to hair cells in cochlea due to repeated loud noises
Nerve-induced hearing loss
Smell senses
Olfaction
Taste senses
Gustation
Sweet
Salty
Sour
Bitter
Umami
The five basic tastes
somatosensory (touch and pain)
Proprioception (kinaesthetic sense)
vestibular sense (equilibrium and balance)
The three tandem body systems
Responds to stimuli applied to the skin, temperature, and injury, through free nerve endings
Somatosensory
Helps us keep track of where we are and move effectively
Proprioception
Allows us to maintain equilibrium and maintain balance
Vestibular sense
bottom up processing
Top-down processing
To types in parallel processing
When our expectations influence our perceptions
Perceptual sets
Perceiving stimuli consistently accords conditions
Perceptual constancy
relative size
Texture gradient
Interposition
Linear perspective
Height in plane
Light and shadow
Monocular depth (one eye)
Binocular disparity (depth)
Binocular convergence (distance)
Binocular depth cues (both eyes)
Muller-Lyre illusion
Ponzu Illusion
Horizontal-vertical illusions
Ebbinghaus-Titchner illusions
Deceptions of perception
Processing many sensory inputs unconsciously
Subliminal information processing
A state of being unable to move just after falling asleep or right before waking up
Sleep paralysis
Our subjective experience of the world, our bodies, and our mental perspectives
Consciousness
learning
Long term memory
Emotional memory recap
Immune system health
Insight/ problem solving
Neural development and neural connectivity
Energy conservation
Why we need sleep
What triggers people to fall asleep?
Increase in melatonin
weight gain
Depression
Risk of cardiovascular problem
Decreased immune system
Consequences with lack of sleep
1 - 4 (non-REM sleep)
5 (REM sleep)
Five stages of sleep
shorter
More thought-like
Repetitive
Daily task concerned
NREM dreams
Difficulty going to sleep/staying asleep/early waking
Insomnia
The rapid unexpected onset of sleep
Narcolepsy
Blockage of the airway during sleep
Sleep Apnea
Sudden waking episodes characterized by screaming, sweating, and confusion. Then followed by a deep sleep.
Night terrors
Where you move in the middle of the night but still unconscious.
Sleepwalking
processing emotional memories
Integrating new experiences with established memories
Learning new strategies
Simulating threatening events to cope
Reorganizing/ consolidating memories
reasons why we dream
Theory: Dreams transform our sexual and aggressive instincts into symbols that represent wish fulfillment.
Freud’s Dream Protection Theory
Theory: dreams are a meaningful product of our cognitive capacities, which shape what we dream about.
Neurocognitive theory
Realistic perceptual experiences the absence of external stimuli
Hallucinations
Sense that our consciousness has left our body
Out of body experience (OBE)
The feeling of reliving a certain experiences
Deja Vu
A sense of unity or oneness with the world
Mystical experiences
A set of techniques that provides people with suggestions for alterations in behaviour
Hypnosis
Hypnosis theory: a persona approach to hypnosis is based on their attitudes, beliefs, and experiences
Sociocognitive theory
Hypnosis theory: hypnosis is based on a separating between personality functions that are normally well intergrated.
Dissociation theory
Contains chemicals similar to those found naturally in our brains
Psychoactive drugs
Decreases activity in the central nervous system
Depressants
Increases activity in the central nervous system
Stimulants
Sense of euphoria and decreased pain
Opiates
Dramatically altered perception, mood, and thoughts
Psychedelics
Barbiturates
Nonbabriturates
Benzodiazepines
Three classes of selective hypnotics
Discovered classical conditioning through his dogs
Ivan Pavlov
Neutral stimulus (NS)
Unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
Unconditioned response (UCR)
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
Conditioned response (CR)
Five primary components Oc classical conditioning
The CR returns after time has passed
Spontaneous recovery
The CR returns in a novel setting different from the one in which the response was acquired
Renewal
When a conditioned stimulus creates a conditioned response
Stimulus generalization
When a conditioned response is exhibited only to certain stimuli
Stimulus discrimination
When learning is controlled by the consequences of the organism’s behaviour
Operant conditioning
If we’re rewarded for a response to a stimulus, we’re more like the to repeat that response in the future
The Law of Effect
Giving a stimulus
Positive reinforcement
Taking away a stimulus
Negative reinforcement
Any outcome that weakens the probability of a response
Punishment
continuous reinforcement
Partial reinforcement
Types of reinforcement in conditioning
The way organisms respond to a stimulus depending on what the stimulus means to it
Stimulus-organism-response (SOR)
Learning that is not directly observable
Latent learning
Learning by watching others. Not engaging with the trial and error to learn how to do the task
Observational learning
Learning by thinking about the problem and coming with an immediate answer
Insight learning
Activated when an organism observes or performs an action. Plays a role in having empathy
Mirror neurons
The tendency for animals to return to innate behaviours following repeated reinforcement
Instinctive drift
Techniques that say they will help you learn faster but have no scientific evidence to support it.
Learning fads
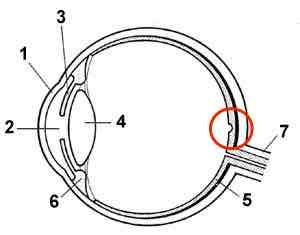
The lens
What is 4?
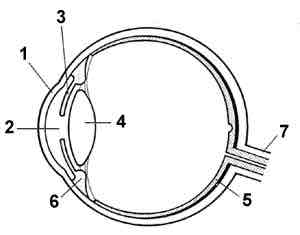
The Iris
What is 3?
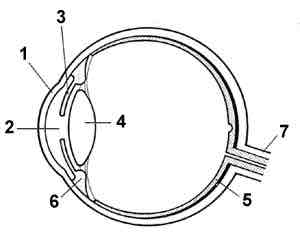
The pupil
What is 2?
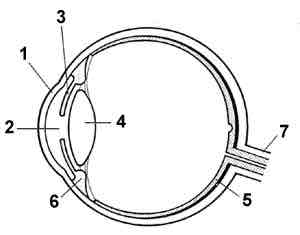
The optic nerve
What is 7?
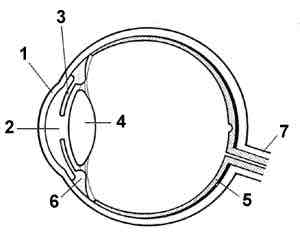
The retina
What is 5?
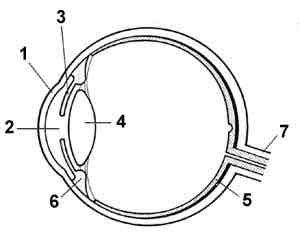
The Fovea
What is in the red circle?