L21: The kidneys
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
When estimating the size of the kidneys in dogs or cats on radiographs, what lumbar vertebrae is used as the reference?
L2
what is the location of the right kidney in dogs?
ventral to the last thoracic and first two/three lumbar vertebrae
what is the location of the left kidney in dogs?
below the first/second to fourth lumbar vertebrae
what kidney is more restricted in canines?
right kidney
why is the right kidney more restricted in canines?
deeply recessed within the caudate lobe of the liver
what structures is the right kidney related to medially?
right adrenal gland and caudal vena cava
which kidney in the dog is located more cranially?
right kidney
what is the clinical consideration of the right kidney in canines?
more difficult to visualize and more difficult to access in surgery
where is the cranial end of the right kidney located in canines?
within the rib cage usually bisected by the 13th rib
in canines, what structures is closely related to the cranial end of the right kidney?
right adrenal gland
what is the cranial end of the right kidney in dogs closely related to medially?
vena cava
what is the cranial end of the right kidney in contact with ventrally in dogs?
right lobe of pancreas
descending duodenum
ascending colon
what is the cranial end of the left kidney in dogs in contact with?
spleen
greater curvature of the stomach
left adrenal gland
what is the left kidney in contact with caudally in dogs?
descending colon
what is the left kidney in contact with mediallly in dogs?
descending colon
ascending duodenum
what is the left kidney in contact with ventrally?
descending colon
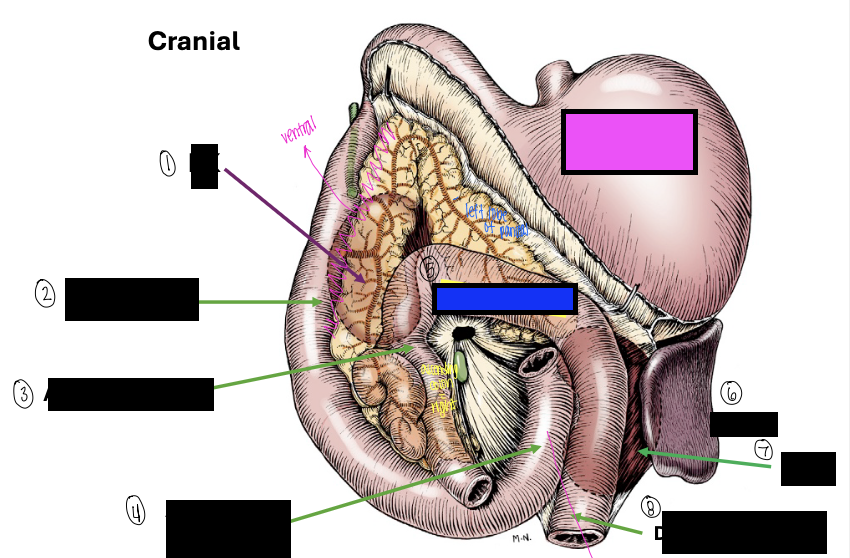
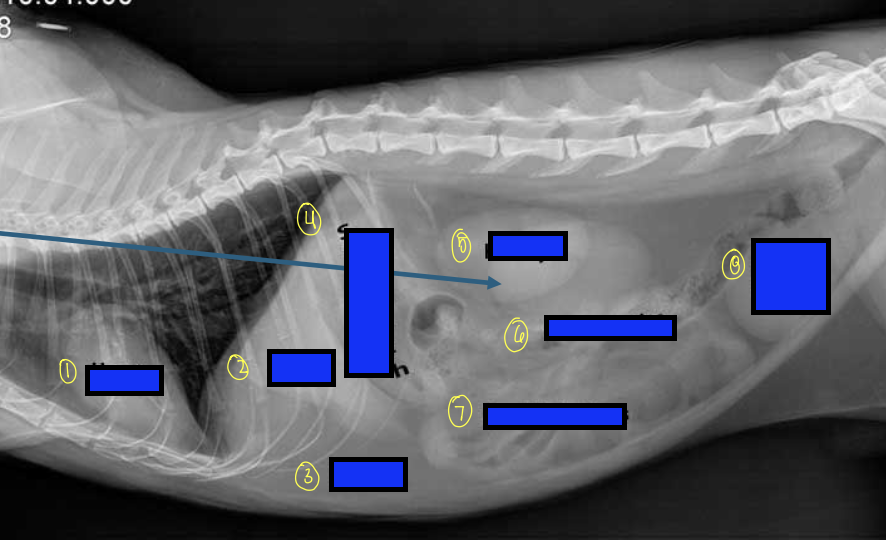
what is 1?
right kidney
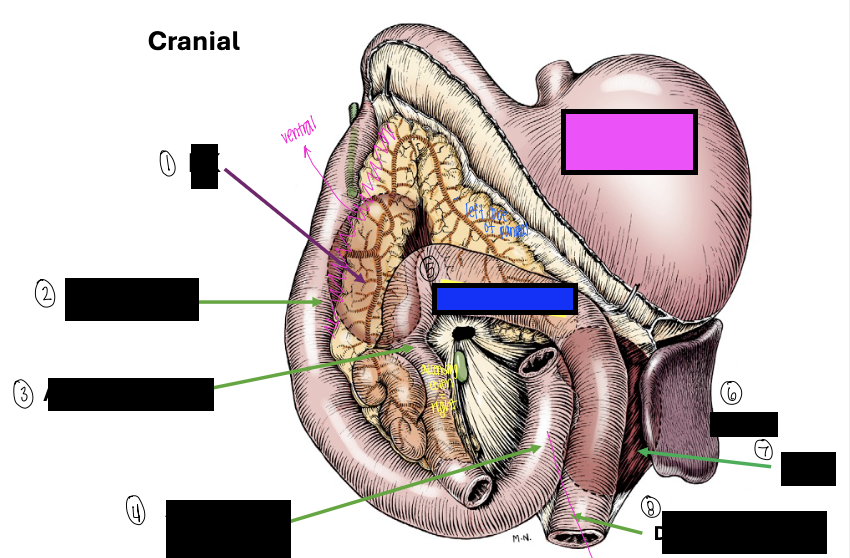
what is 2?
descending duodenum
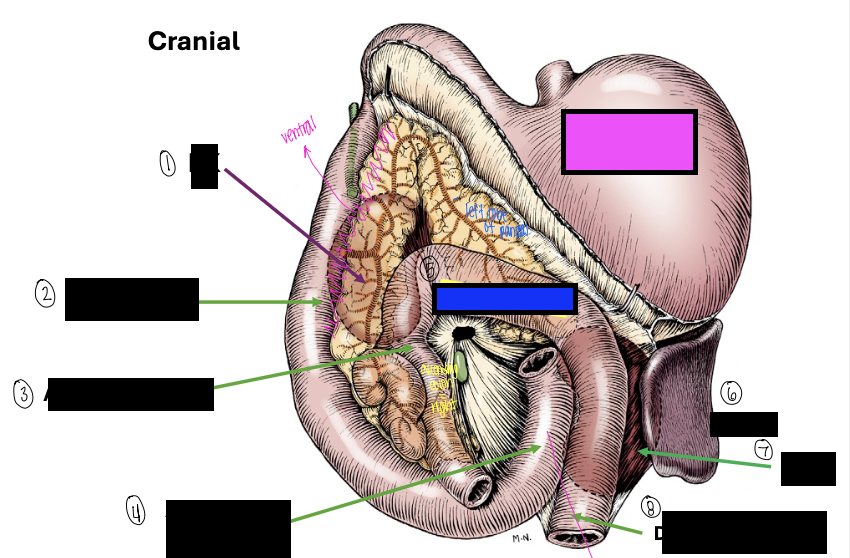
what is 3?
ascending colon
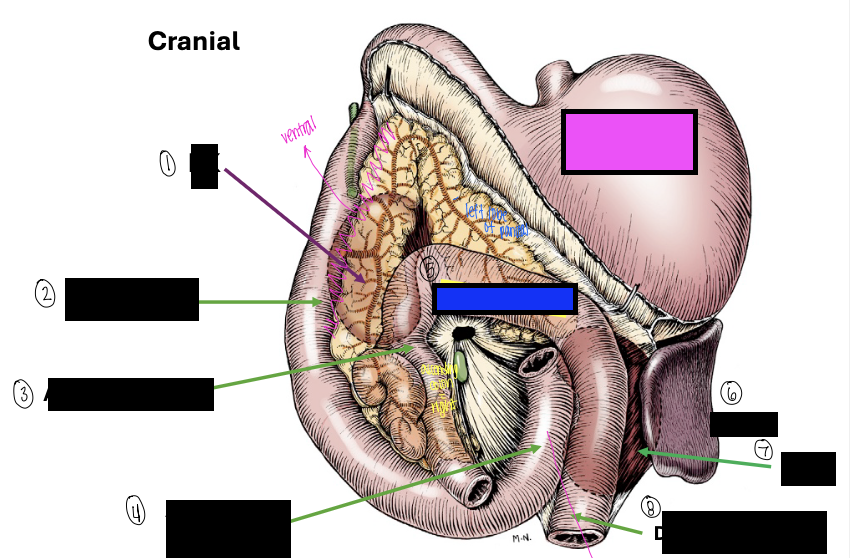
what is 4?
ascending duodenum
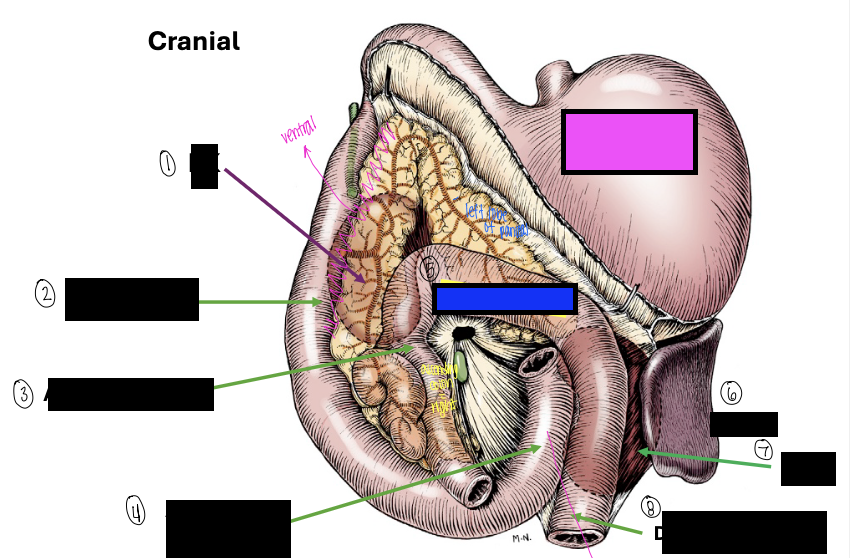
what is the blue box?
transverse colon
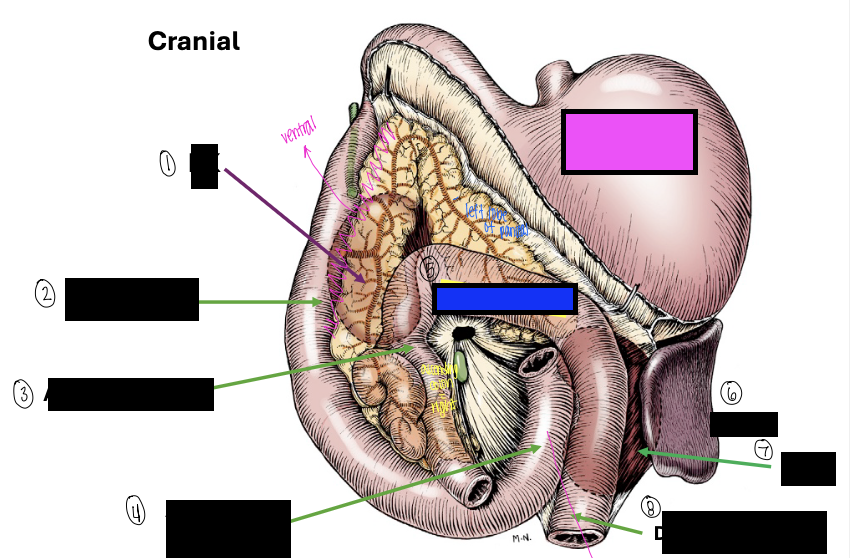
what is the pink box?
stomach
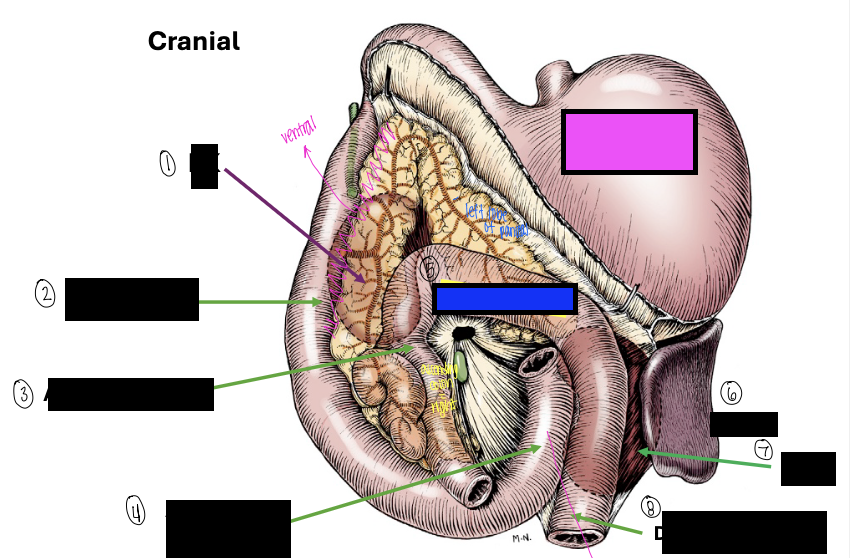
what is 6?
spleen
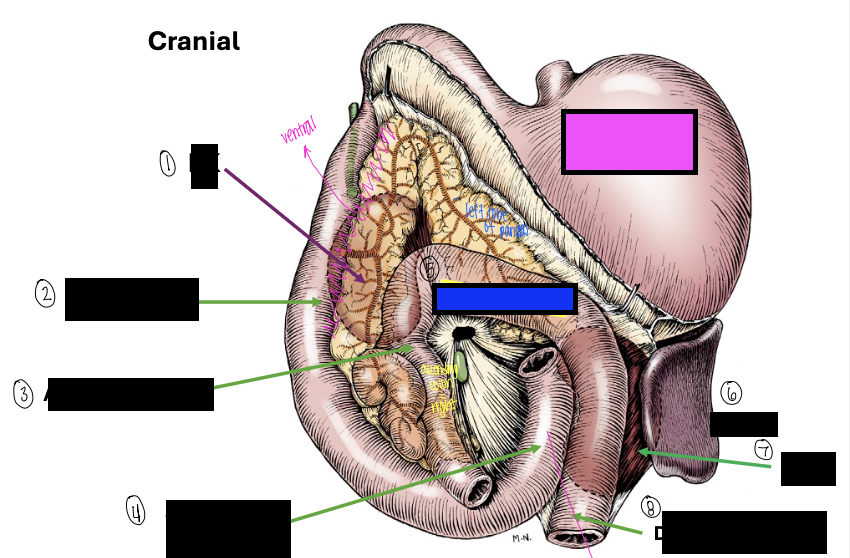
what is 7?
left kidney
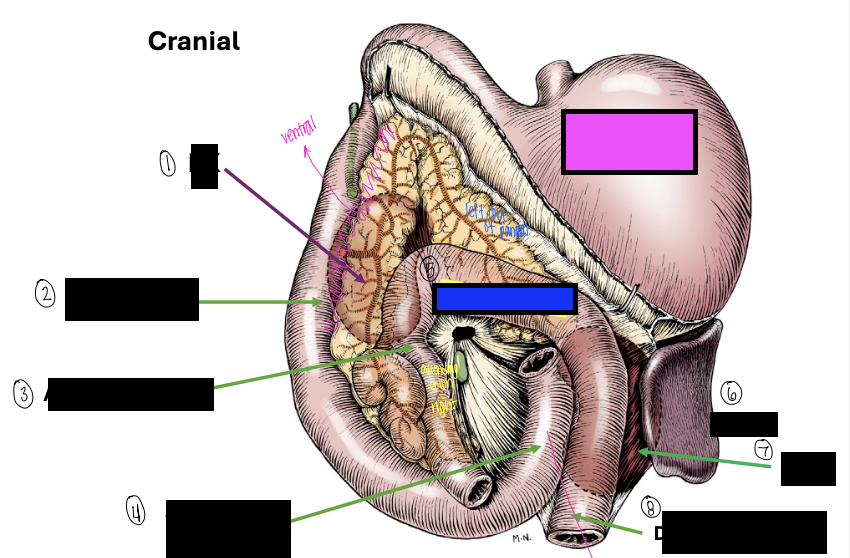
what is 8?
descending duodenum
where do the paired kidneys lie?
retroperioneally pressed against the dorsal abdominal wall on either side of the vertebral column
where do the paired kidneys lie cranially?
extend under the last ribs
what shape kidneys do dogs and cats have?
bean shaped
what species have capsular veins present on the surface of the kidneys?
cats
what surrounds the kidneys?
renal capsule
renal capsule
thin sheath of connective tissue that surrounds the kidneys
what can the renal capsule tell you about the state of the animal?
if peeling away can mean inflammation, injury, or necropsy
lateral border of the kidneys is…
convex
medial border of the kidneys is…
concave and indented at the hilas
what enters the kidneys at the hilus?
renal artery and vein
ureters
what are the two internal regions of the kidney?
cortex and medulla
what is the appearance of the cortex?
granular
what is the appearance of the medulla?
striated
describe the cortex in cows.
remains unfused to form lobes
describe the medulla in cows
medulla is unfused and for renal/medullary pyraminds
what does the cortex contain?
renal corpuscles and convoluted parts of the tubules
what does the medulla contain?
collecting ducts
renal crest
inner margin of the medulla where the ducts empty into the renal pelvis
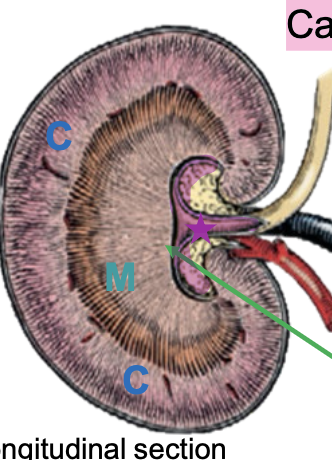
what is the purple highlight indicating?
renal crest
which species have medullary pyramids?
cows and pigs
which species have false pyramids?
dogs and cats
medullary pyramids
Medullary zones divided by inter-lobar vessels
false pyramids
Pyramids will be seen in the paramedian sagittal section only and there are no true renal/medullary papillae present
renal pelvis
wide funnel-shaped structure that collects the urine
which structure is the terminal dilated part of the ureter within the kidney?
renal pelvis
renal/pelvic recesses
Depressions caused by extensions of the renal pelvis into the medulla on both sides of the crest
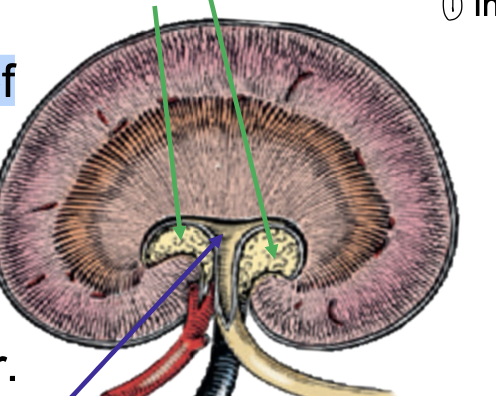
what is the green arrow pointing to?
renal sinus
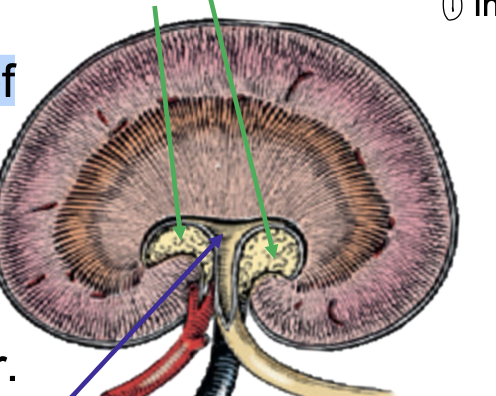
what is the blue arrow pointing to?
renal pevis
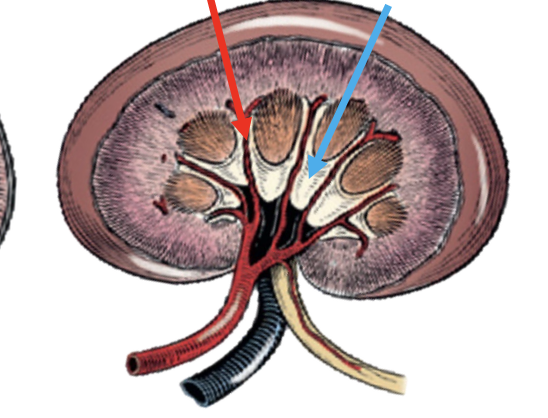
what is the red arrow pointing to?
interlobar vessels
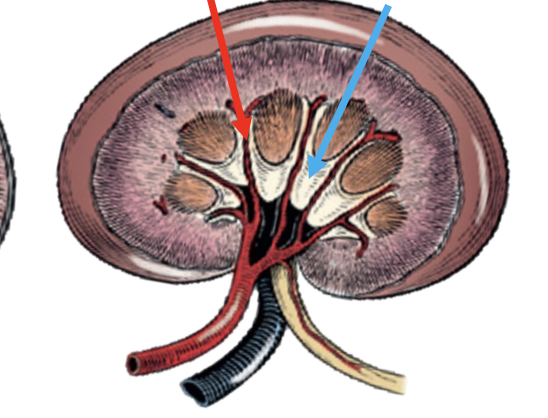
what is the blue arrow pointing to?
pelvic recess
renal sinus
the fat-filled space surrounding the renal vessels and the ureter
which species are the kidneys more identifiable on a radiograph?
cats
what radiography do we use to get a more detailed study of the kidneys?
contrast radiography
what radiography do we use for the kidneys?
intravascular perfusion with a contrast agent
what is the contrast agent used for kidney radiographs?
intravenous urogram
what type of view will we typically use when doing a radiograph of the kidneys?
lateral and ventral
which is used more to visualize the kidneys: right or left lateral view?
right lateral views
why is the right lateral view used more often to visualize the kidneys?
right kidney will be pushed into right caudate lobe of the liver to be more easily seen
which kidney is more cranial: left or right?
right
describe how kidneys appear on a radiograph
bean shaped with a smooth, homogenous, soft tissue opacity
describe how the kidneys are superimposed on each other on a radiograph
the cranial pole of the left kidney overlapping the caudal pole of the right
what is the normal canine kidney size on the ventrodorsal view?
2.5 to 3.5 times the length of L2
what is the normal feline kidney size on the ventrodorsal view?
2.4 – 3 times L2
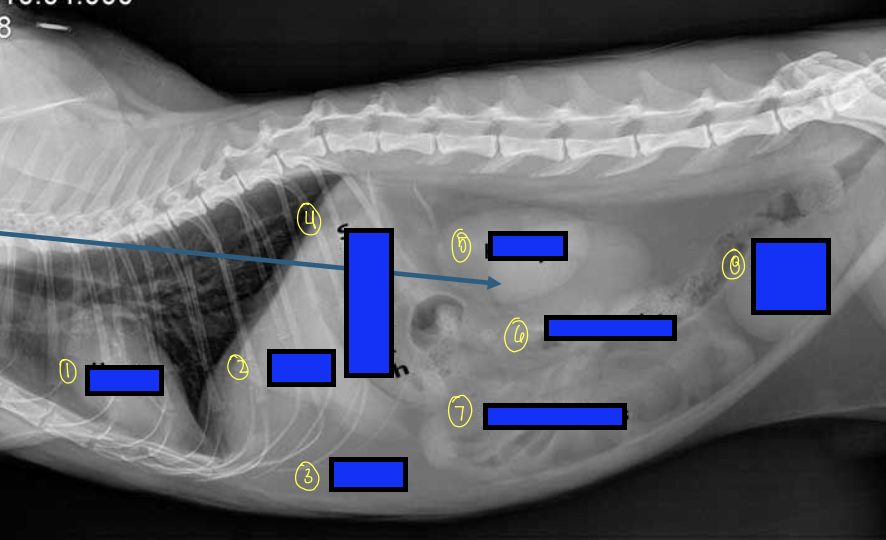
what is 1?
heart
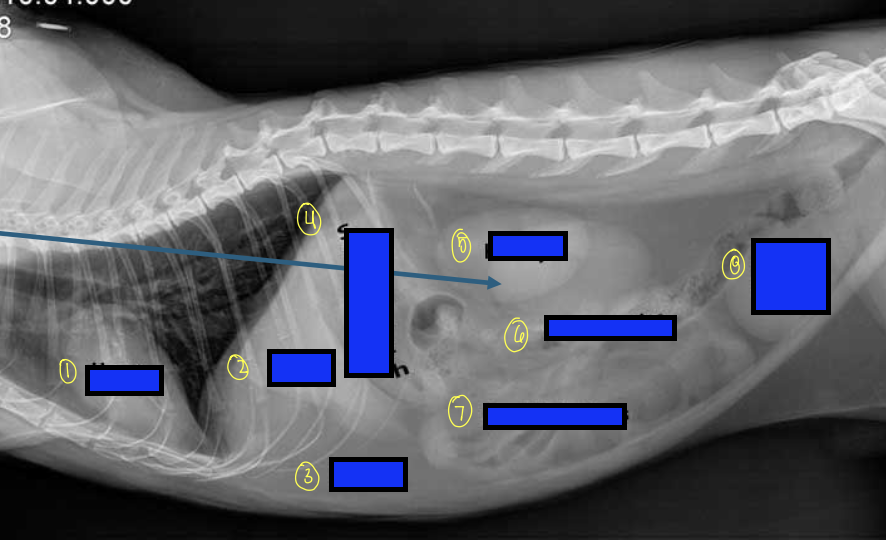
what is 2?
liver
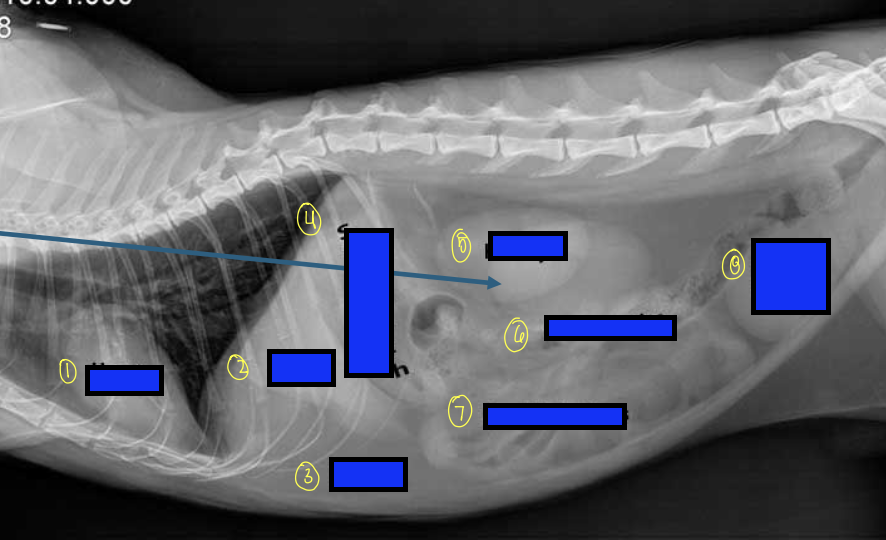
what is 3?
fat
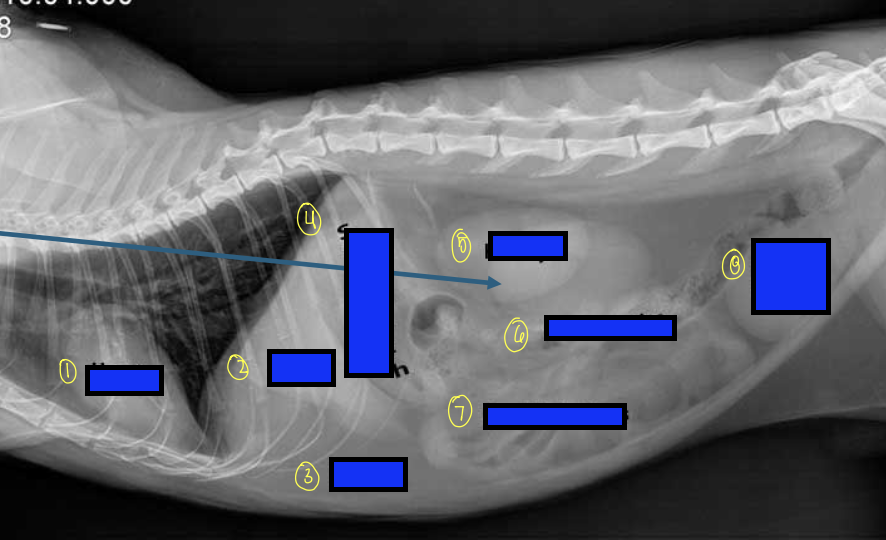
what is 4?
stomach
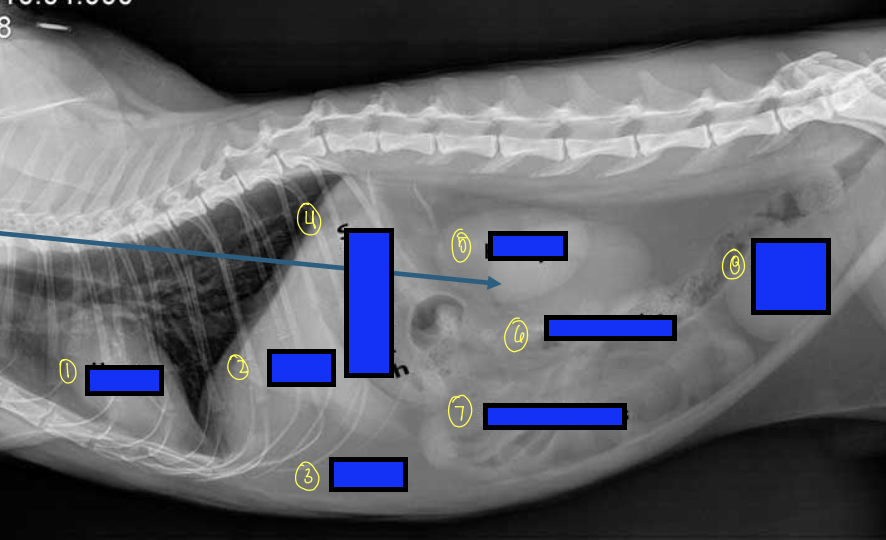
what is 5?
kidneys
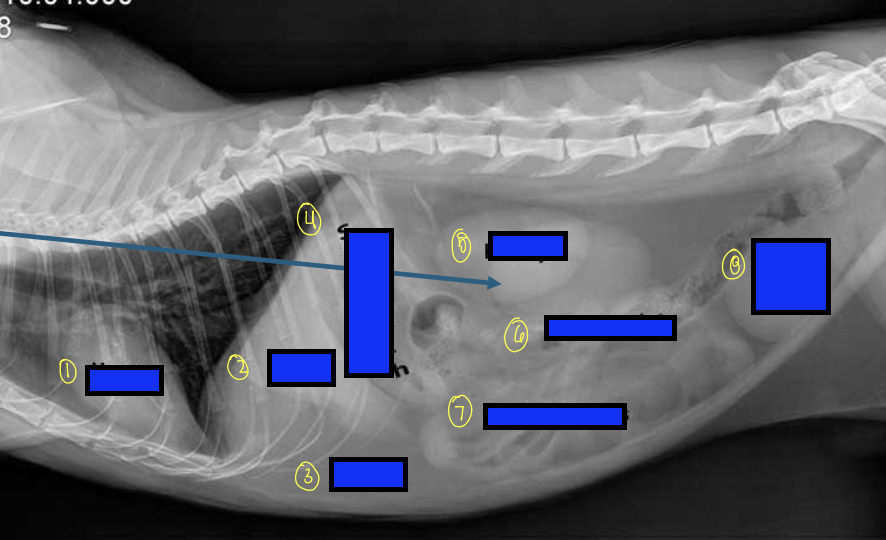
what is 6?
large intestines
what is 7?
small intestines
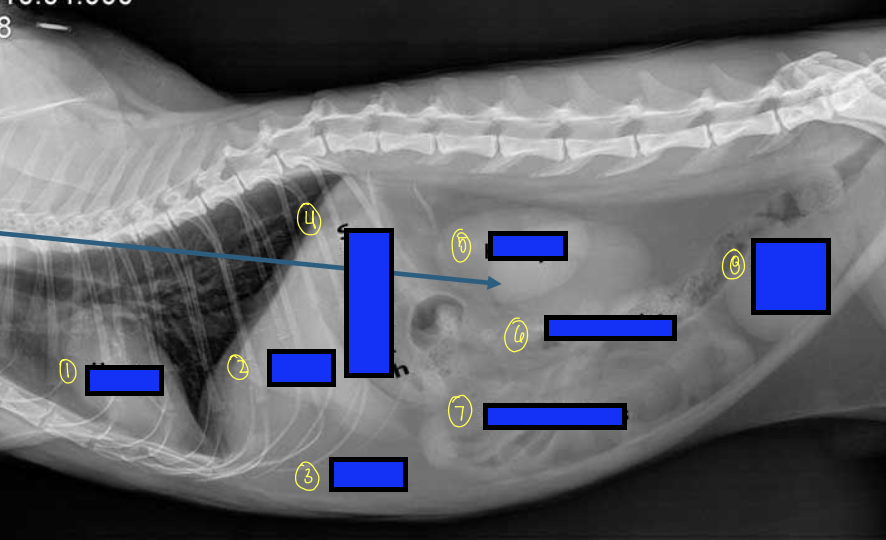
what is 8?
urinary bladder
what is the topographic location of the right kidneys in dogs?
T13-L2
what is the topographic locations of the left kidney in dogs?
L1-L3
what is the topographic location of the right kidney in cats?
L2-L4
what is the topographic location of the left kidney in cats?
L3
how should both kidneys appear on a contrast study?
renal cortices opaque
smooth in outline
pelvic recesses together with the pelvis
pelvic recesses
the collecting channels that extend into the medulla from the pelvis of the kidney

what is the yellow?
renal pelvis

what is the purple?
medullary region

what is the blue?
medullary cortex
what is hyperechoic on ultrasound?
bone/gas
connective tissue
what is anaechoic on ultrasound?
blood/fluid
what structure is hypoechoic or isoechoic as compared with the liver on ultrasound?
renal cortex
what structure is hypoechoic or anechoic in relation to the renal cortex?
renal medulla
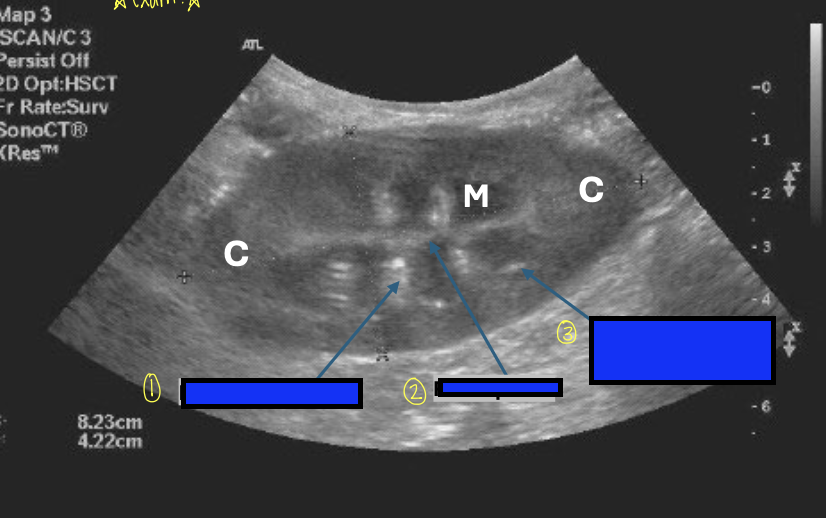
what is 1?
interlobar vessels
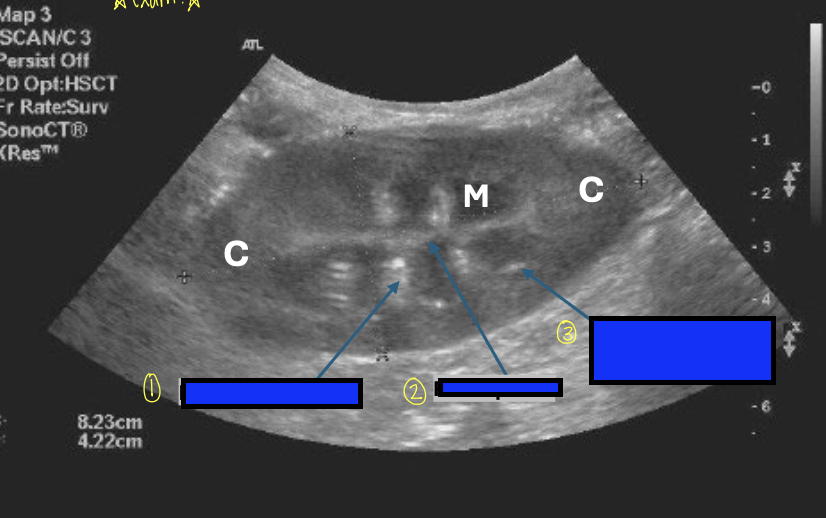
what is 2?
renal pelvis
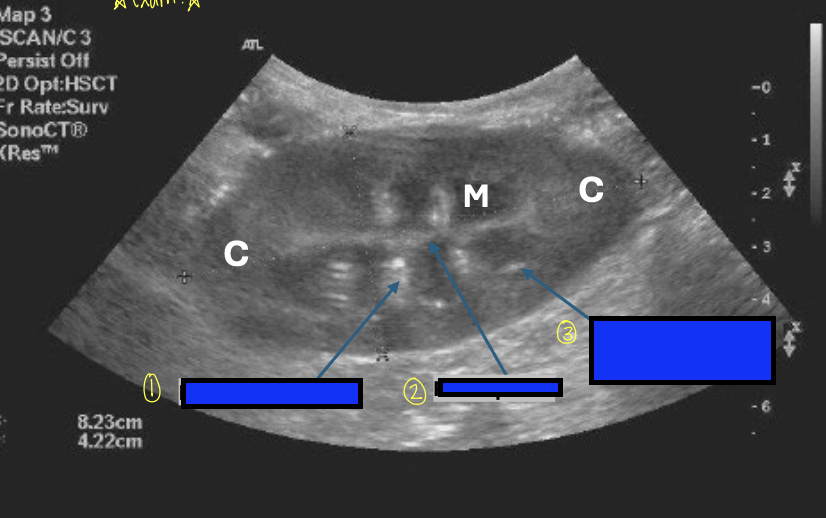
what is 3?
corticomedullary junction
corticomedullary junction
defined by the presence of bright hyperechoic specks that represent the arcuate vessels
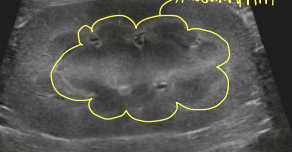
what is the yellow indicating?
medullary rim
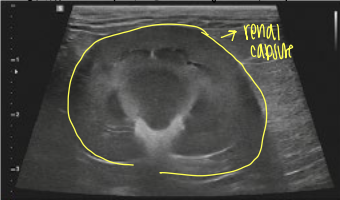
what view is this ultrasound of the kidneys?
dorsal
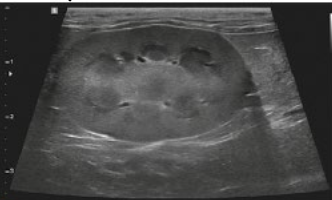
what view is this ultrasound of the kidneys?
saggital
what view is this ultrasound of the kidneys?
transverse
describe cortex and medulla of pig kidneys.
cortex fused
medulla not fused, pyramids
describe cortex and medulla of dog kidneys.
cortex fused
medulla fused