ex1 lab values
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
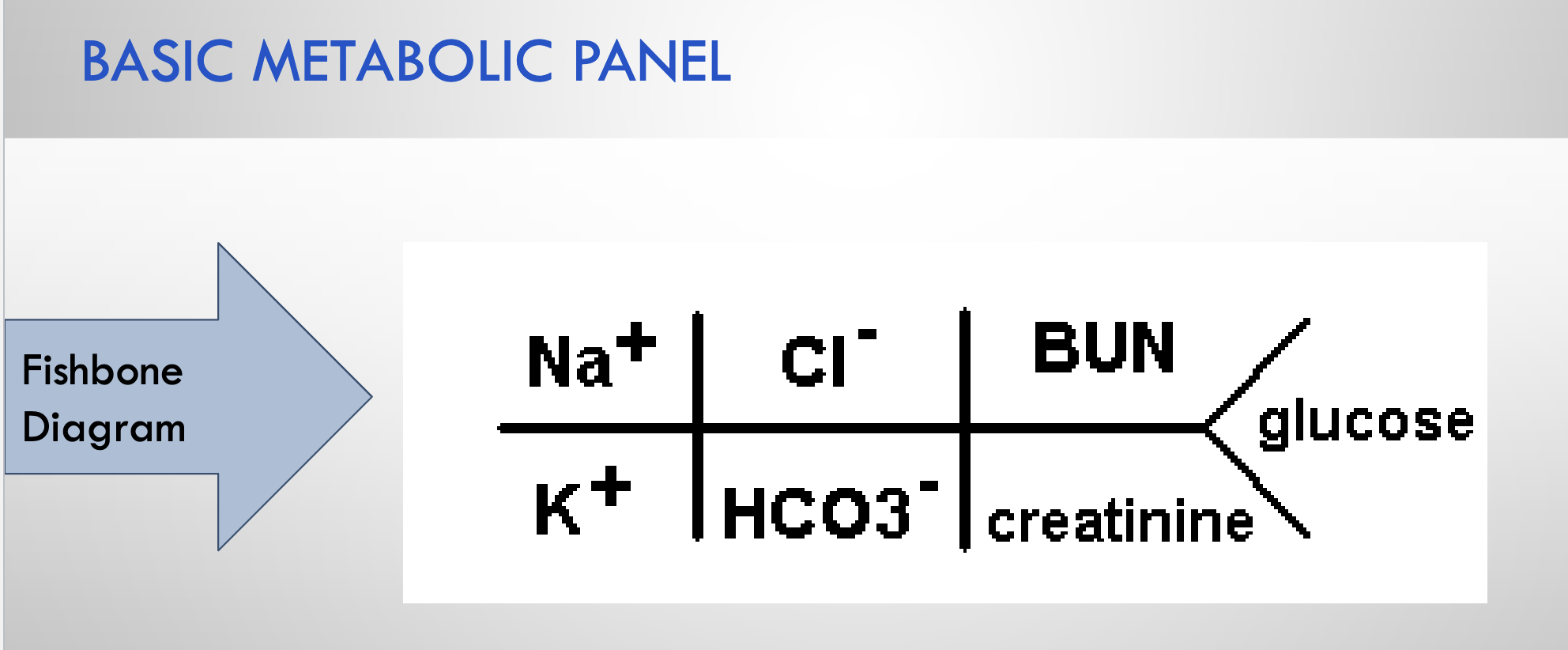
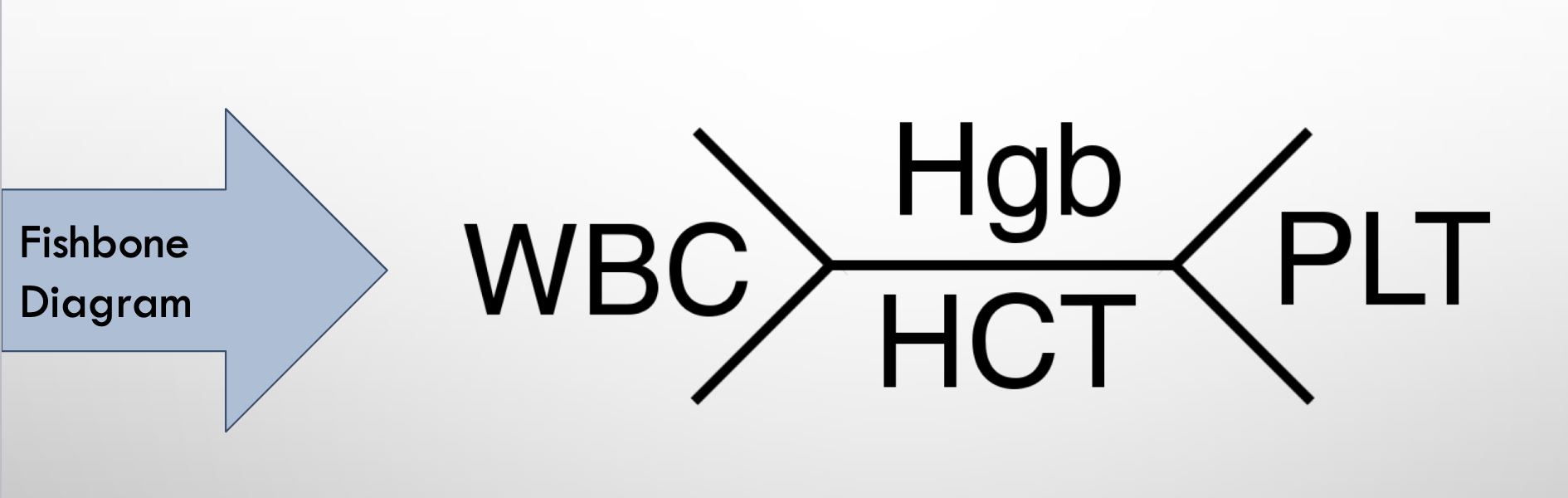
Note the location of each component on a Fishbone diagram (BMP)
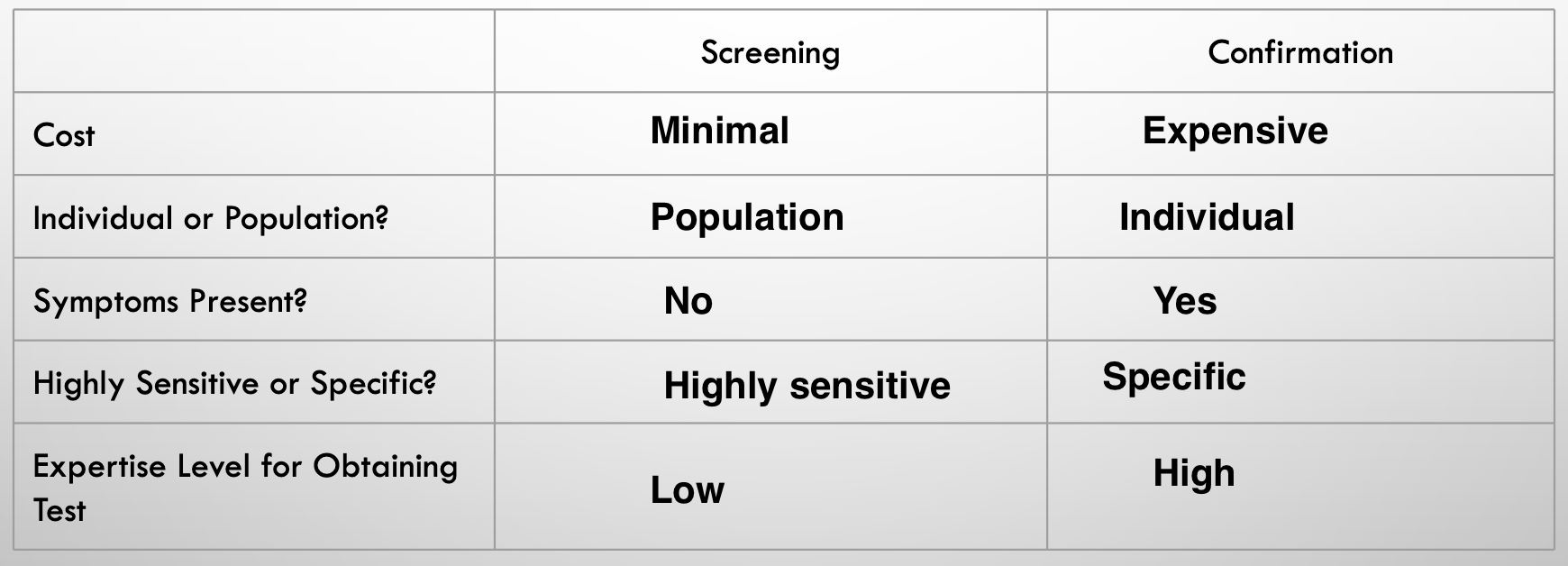
Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative, screening and confirmation laboratory tests
Qualitative vs. quantitative test
- Yes/No answer or numerical value?
- Quantitative: frequently provided with reference range
Understand influences that may impact interpretation of values
- Free vs. protein bound assays - albumin
- Drug-assay interactions
- Timing of day
- Fasting status
- Source
- Gender
- Age
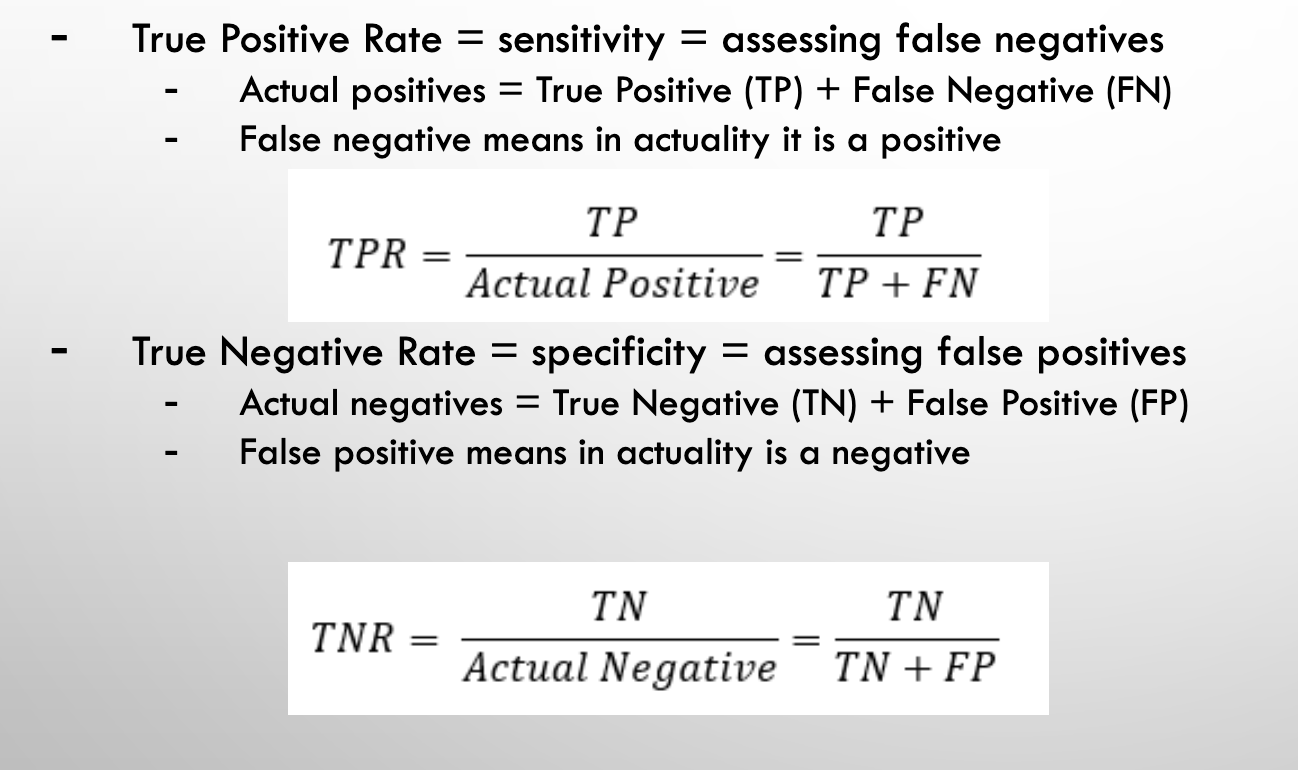
TRUE POSITIVE RATE VS. TRUE NEGATIVE RATE
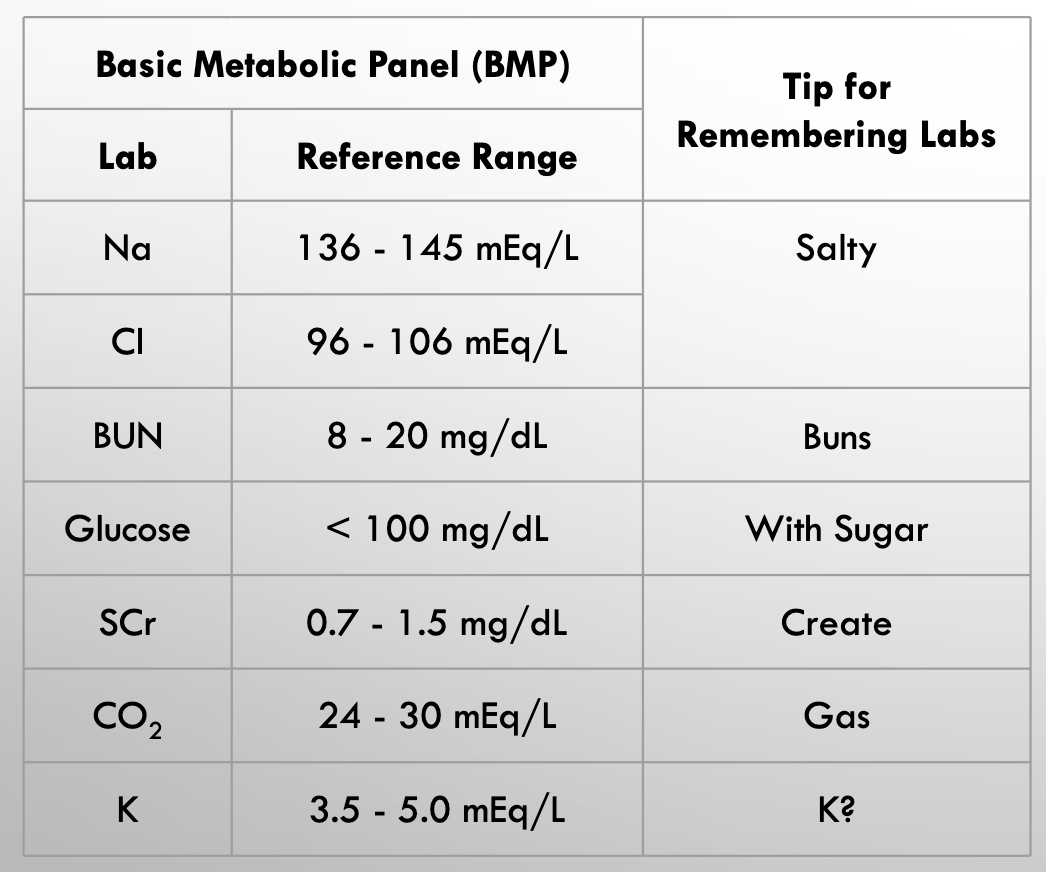
BMP labs
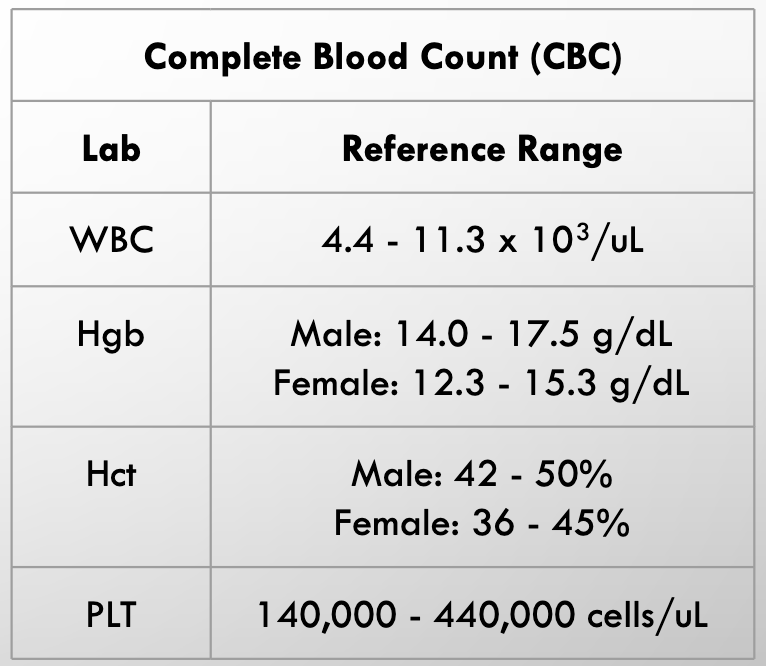
CBC labs
Hyperglycemia/sodium relationship
Hyperglycemia causes pseudohyponatremia
Hemoglobin A1C (reference range: ?)
(reference range: 4 - 5.6%)
- 3 month average
- Glucose irreversibly binds to hemoglobin proportionally to average serum glucose
- Useful for assessing diabetes therapy, adherence
- Fasting state not important in assessing A1C
Serum creatinine
Kidney damage likely - renal function
Creatine is decomposed to creatinine
Sodium
body water homeostasis by kidneys
influences serum osmolarity
Chloride
High Na typically = High Cl, visa versa
Bicarbonate
Used to assess acid-base disorders
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
BUN - renal
Waste product from protein decomposition
- Formed in liver
- Marker for hydration status, renal function, protein tolerance
Phopshorus
Several roles
- Metabolism of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates
- Co-factors
- Cellular energy
Corrected calcium equation
[(4 - albumin) * 0.8] + Total Serum Calcium
Looking at albumin levels
Hypomagnesemia - what syndrome is associated with it?
Low magnesium levels
Refeeding syndrome
Liver function tests
Acute vs Chronic
abnormal labs do not indicate symptoms present
Hepatocellular injury (LFT)
ACUTE
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Indirect and direct bilirubin
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT)
- Amylase
- Lipase
Synthetic tests (LFT)
CHRONIC - LIVER ISNT WORKING
- Albumin
- Coagulation studies
AST AND ALT
Hepatocyte injury
>2:1 AST:ALT ratio, marker for potential alcoholic liver disease
BILIRUBIN
Hepatocyte injury
-Indirect (aka unconjugated)
- NOT water soluble
- Elevated with hepatic impairment, certain medications
- Direct (aka conjugated)
- Water soluble
- Excreted through bile, feces, urine
- Elevated possibly due to biliary obstruction
ALBUMIN
Synthetic tests
anything bound to albumin is physiologically inactive
COAGULATION STUDIES
Synthetic test for liver function
Monitor anticoagulants (warfarin)
Assess syntheitc hepatic impairment
ACTIVATED PARTIAL THROMBOPLASTIN TIME (APTT)
another marker of synthetic liver impairment
FASTING LIPID PANEL (FLP)
Total cholesterol (impacted by both HDL - good and LDL - bad)
Triglycerides (TG, <150 mg/dL)
- Potential for false elevation if not fasting
- Elevated with:
- Diabetes
- Alcohol ingestion
- Liver disease
- High carbohydrate diet
THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING (TDM)
- Therapeutic confirmation
- Avoidance of inefficacy
- Dosage optimization
- Suspected toxicity
- Avoidance of toxicity
- Assess adherence
- Concern for drug interactions impacting level
IDEAL AGENT FOCUS - PHENYTOIN
- Seizures
- Toxicity
- Numerous drug interactions
- Narrow therapeutic window
- Assess adherence
- Unpredictable dose/response (aka level) relationship
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC) fishbone diagram
CBC’s
Measure different values involving blood
White blood cells
Common marker of infection
Red blood cells
carry O2 to tissues
URINE ANALYSIS (UA)
illicit drug use/infection
Urine drug screen
Qualitative tests (different illicit drugs)
Urine analysis
Seeing different cells/proteins in the urine
NEVER SHOULD BE PROTEIN IN THE URINE (kidney damage)