Social Class, Status, and Privilege in Society
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Socioeconomic Status (SES)
Measures an individual's or family's social and economic position relative to others.
Wealth
A stock of assets owned at a particular time (minus liabilities), and signifies command over financial resources.
Income
The money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments.
Poverty
A multidimensional concept that presents a series of challenges in conceptualizing and measuring.
Relative Poverty
A condition where household income is a certain percentage below median incomes.
Absolute Poverty
A condition where household income is insufficient to maintain a minimum standard of living.
Low Income Cut-Off (LICO)
An income threshold required to cover basic necessities such as food, shelter, and clothing.
Economic Inequality
A condition and a process in which preferential access to the good things in life is not randomly distributed, but patterned around socially significant human differences.
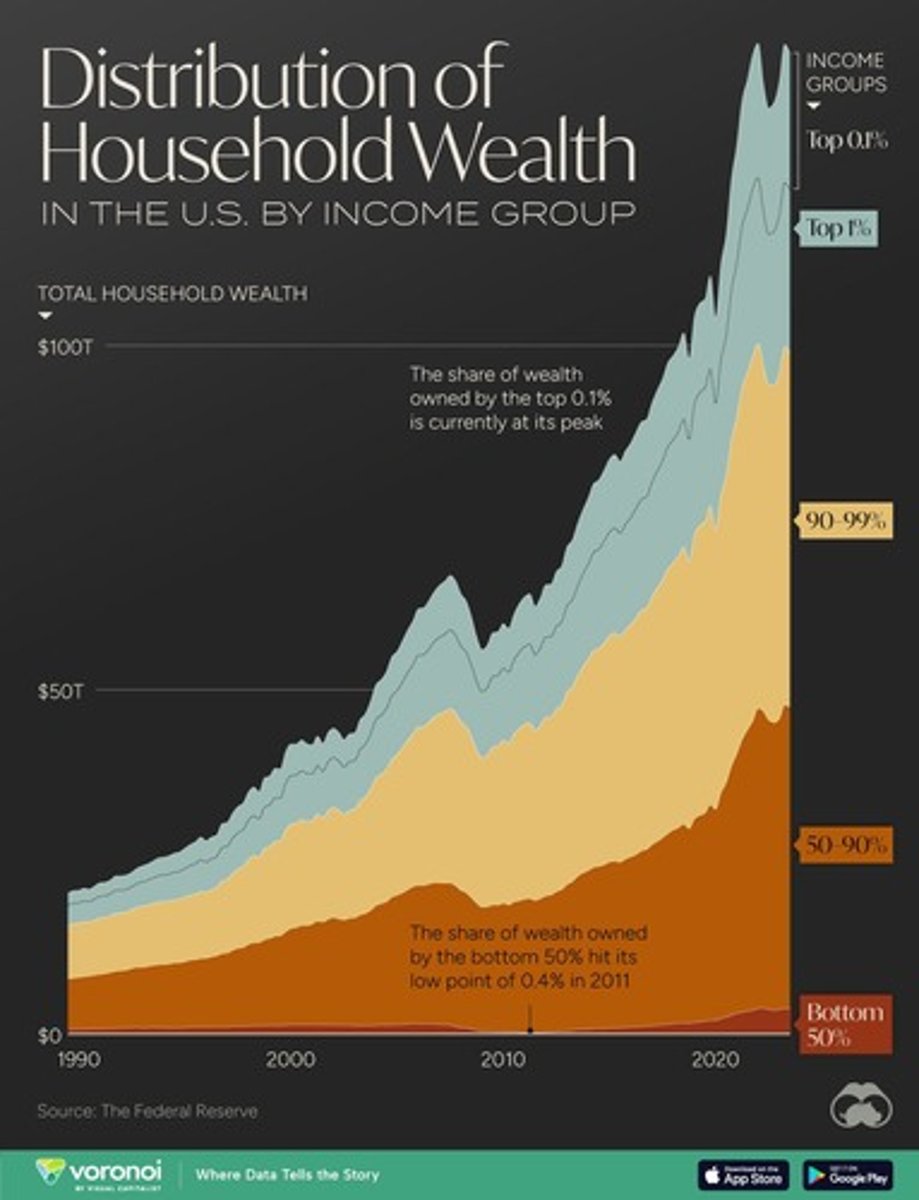
Wealth Inequality
The unequal distribution of assets among residents of the economy.
Educational Attainment
The highest level of education an individual has completed.
Occupational Prestige
The social value associated with a particular job or occupation.
Ideology
A system of conscious and unconscious ideas, beliefs, attitudes, and images that shape a person's or a group's objectives, expectations, and actions.
Patterns of Inequality
The recurring themes and structures that contribute to unequal distribution of resources and opportunities in society.
Cycles of Inequality
The ongoing and reinforcing nature of inequality that perpetuates disadvantage across generations.
Leverage Points for Change
Strategic areas where interventions can be made to alter the dynamics of inequality.
Functionalist Lens
A perspective in sociology that views society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability.
Conflict Lens
A perspective in sociology that focuses on the struggles between different social classes and groups.
Economic Measures of Poverty
Quantitative assessments used to evaluate the financial status of individuals or families, such as $1 or $2 per day headcount.
Access to Basic Needs
The availability of essential resources such as food, water, shelter, and healthcare necessary for survival.
London Township and Sombra Treaties
Historical agreements related to land and resources involving Indigenous peoples.
Dish with One Spoon Covenant Wampum
A treaty that signifies shared stewardship of the land and resources among Indigenous nations.
5% of the Course Grade
The percentage of the total course grade attributed to the Scholarly Skills Upgrade assignment.
Meritocracy
The idea that roles and power are distributed according to 'merits' such as talent, effort, intelligence, creativity, experience, and knowledge.
Inequalities in Meritocracy
Inequalities are 'fair' to the extent that individual traits determine outcome, not random chance or privilege.
Ideology of Meritocracy
Encourages the idea that the rich must deserve the wealth and status they have, and so do the poor.
Self-made Rich
The belief that the rich are 'self-made' individuals who have earned their wealth through their own efforts.
Bootstraps Mentality
The notion that the poor should 'grind' and 'pull themselves up by their bootstraps' to improve their situation.
Social Inequalities
The result of differences in intelligence, work ethic, morality, practicality, or innate talent.
Functionalist Perspective
Focuses on how social forces affect harmony, cohesion, and solidarity within society.
Conflict Perspective
Analyzes society through the lens of conflict and power struggles between different groups.
Analogy of a Cell
People fulfill roles within the system, contributing to the whole, similar to how cells function in a biological system.
Social Institutions
Serve various functions in the regulation of society and promote its healthy functioning.
Emile Durkheim's view of society
Society is the system that bonds us together, regulating our collective activity.
Collective Consciousness
Shared ways of viewing the world among members of a society, influencing perceptions of fairness and truth.
Pathology in Social Systems
Circumstances where the social system experiences dysfunction or problems.
Beneficial Inequality
Gives appropriate rewards for different contributions to society, such as in a meritocracy.
Detrimental Inequality
Arises when people are systematically prevented from contributing to society, leading to social problems.
Warren Buffett on Gender Equality
Expresses optimism about America's potential by utilizing the talents of all individuals, regardless of gender.
Class Wars
Conflict that can arise when people feel that resources and opportunities are unfairly distributed.
Disillusionment with Institutions
Occurs when individuals lose faith in societal institutions due to perceived unfairness.
Altruistic suicide
Excessive bonds lead to self-sacrifice.
Fatalistic suicide
Excessive regulation leaves no other way out.
Egoistic suicide
Weak bonds lead to isolation, nobody to live for.
Anomic suicide
Weak regulation leads to demoralization, nothing to live for.
Functionalist Perspective
The success or failure of a social system rests in how well its subsystems function in maintaining it.
Collective consciousness
Ideas and values like fairness are expressions that hold society together.
Social bonds
Ensure that people feel their lives are worth living.
Conflict perspective
Examines the social processes that maintain hierarchy, domination, and oppression.
Social inequalities
Reflect deeper systems that confer power to one group over another.
Karl Marx
Regarded the values of individuality, freedom, and progress as an unfinished project for humanity.
Class structure of modern capitalism
Focuses on the relation people have to the economic production of society.
Means of economic production
Control over this is embedded within the class structure of society.
Surplus value
Profit obtained through business enterprises, exceeding necessary expenditures.
Labour exploitation
Profit is maximized by paying workers less than the value of the work they contribute.
Bourgeoisie
The ownership class that lives off the surplus value.
Proletariat
The working class that contributes labor power.
Petit bourgeoisie
The small business class.
Lumpenproletariat
The unorganized lower ranks, often in low-paying jobs.
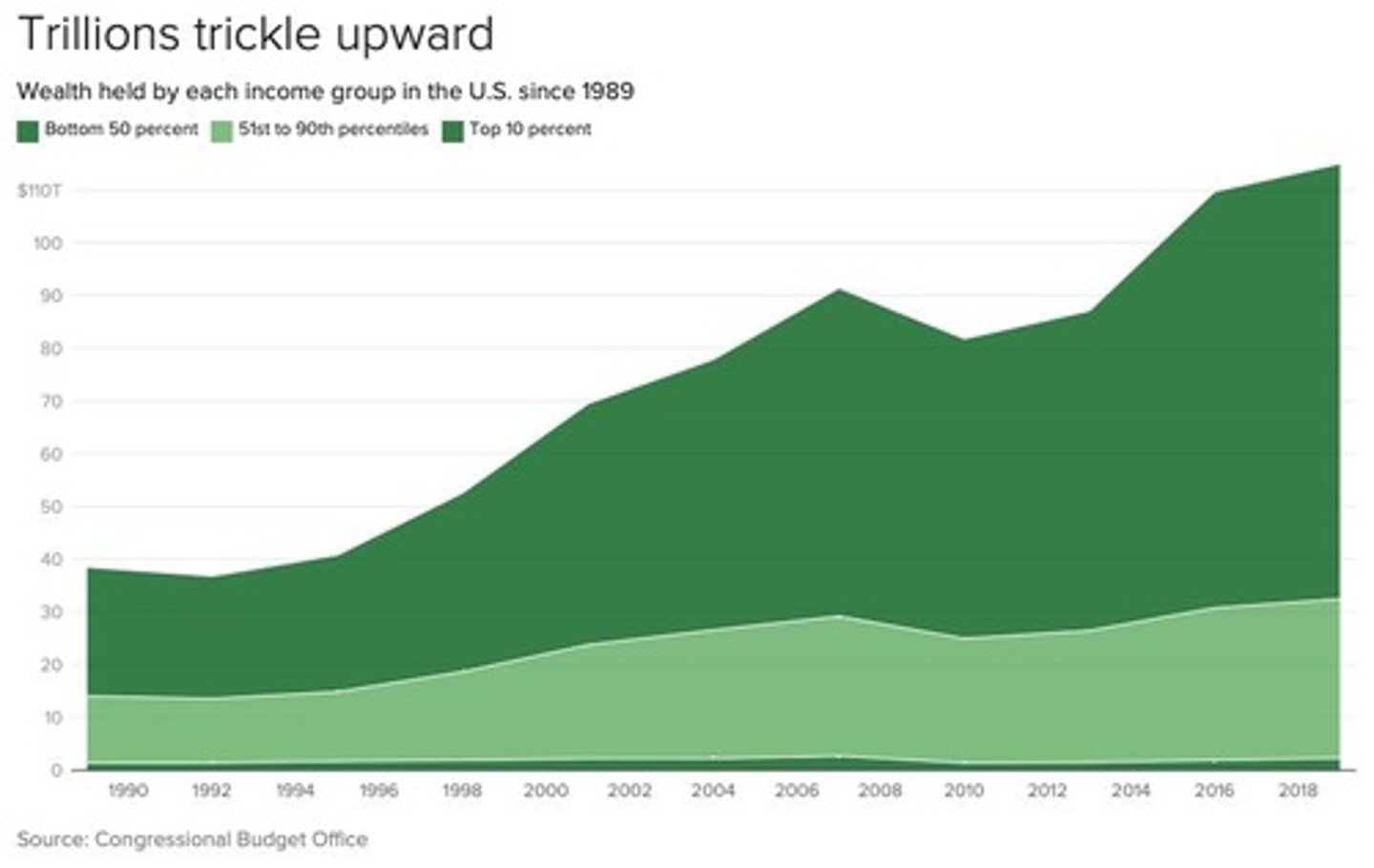
Economic inequality
A disparity in wealth and resources among different groups in society.
Ideology
A system of ideas and ideals that form the basis of economic or political theory.
Social change
The transformation of culture and social institutions over time.
Capitalist's commodity
Money used to generate profit.
Worker's commodity
Labour power that is exchanged for wages.
Simplify and deskill tasks
A strategy to make work easier and less specialized.
Intensify efficiency of the production process
Improving productivity, often exemplified by assembly lines.
Increase the workload, decrease staffing
A tactic to maximize output while minimizing labor costs.
Pit workers against one another to drive down wages
Creating competition among employees to reduce their pay.
Wage labour alienates us from the product we work on
Workers become disconnected from the items they produce.
Wage labour alienates us from the production process
Workers lose a sense of involvement in how products are made.
Wage labour alienates us from other people
Work conditions create barriers between individuals.
Wage labour alienates us from our own humanity
The labor system diminishes our sense of self and personal fulfillment.
Alienation degrades our human capacities for social & economic cooperation
Disconnection from work reduces our ability to collaborate effectively.
Class struggle ensues from the directly opposing interests of workers and owners
Conflict arises due to differing priorities between labor and management.

Solidarity
When a class collectively pursues its interests.
False consciousness
A mindset that accepts ideologies supporting the ruling class while undermining working-class unity.
Conflict theorists
Scholars who study the structures and beliefs that perpetuate social inequality.
Max Weber's critique of Marx
Weber analyzed how social beliefs influence economic changes.
Social class
A division based on economic status.
Party membership
Involvement in strategic social organizations.
Social status
A person's honor and prestige in society.
Functionalist lens
A perspective that views society as a complex system with interdependent parts.
Conflict lens
A viewpoint that emphasizes social struggles and power dynamics.
Collective consciousness
The set of shared beliefs and values within a society.
False consciousness
A misperception of one's social reality that supports the status quo.
Role of sociologist
To study social systems and contribute to social change.
Conflict lens
A perspective that does not assume people are antagonistic but considers how systems may pit individuals against one another.
Systemic Responses to Inequality
Approaches that address the root causes of inequality rather than focusing solely on individual beneficiaries of oppression.
Cycles of Inequality
Patterns where failures to address root causes lead to ongoing poverty and compounding problems.
Leverage Points for Change
Opportunities within systems that can be utilized to create effective policy changes to address inequality.
Cycle of Poverty
A situation where lack of resources leads to ongoing poverty, which is inefficient and expensive.
Life Expectancy Gap
A 21 year difference in life expectancy between Hamilton's poorest and richest neighbourhoods.
Canadian Pension Plan (CPP)
A program that reduced poverty among seniors from 33% in 1976 to 4% in 1994.
Unequal Opportunities
Variations in skills and knowledge that can disadvantage some individuals, perpetuating earlier inequalities.
Scholarly Skills Upgrade
An initiative to enhance vocabulary and writing skills, aimed at improving academic performance.
Systems of Injustice
Frameworks that highlight the underlying injustices and harms within societal structures.
Sociological Imagination
The ability to perceive the root causes for social stasis or change.
Functional lens
A perspective that views social order as harmony and institutions as serving societal needs.
Class Domination
A concept within the conflict lens that suggests societal structures facilitate oppression.
Relative Poverty
A condition where individuals lack the minimum income needed to maintain the average standard of living in their society.
Absolute Poverty
A condition where individuals do not have enough resources to meet basic needs for survival.