Injury, Pathology, & Remodeling and Perimortem Trauma Mechanisms
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Pathology
study of disease
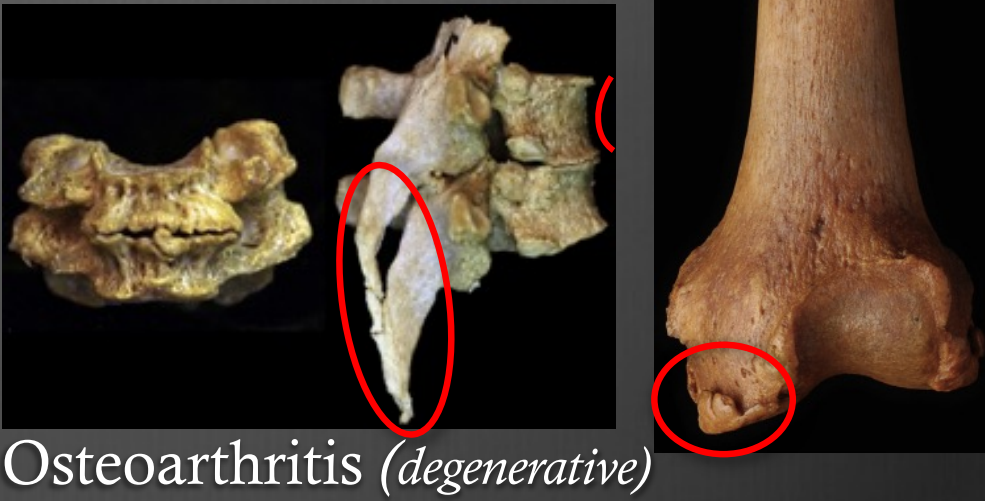
Osteoarthritis (degenerative)
(degenerative)
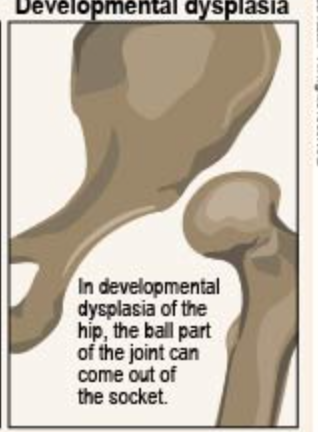
hip dysplasia
(congenital/ developmental)
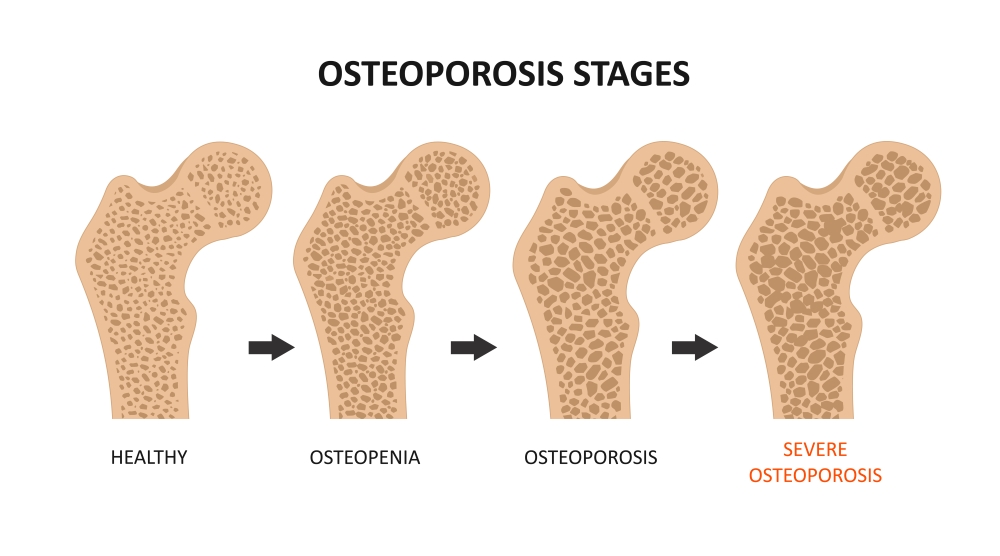
Osteoporosis
(degenerative)
Antemortem Trauma
trauma that occurred during life
osteogenesis
healing, reactive bone
macroscopic phases of healing
inflammatory, reparative, remodeling
inflammatory
ossifying callus begins 2-10 days
reparative
woven bone: bridges fracture by about 2-3 months
remodeling
organized cortical bone replaces woven bone: takes months - years
Postmortem trauma
after death/ taphonomic
postmortem trauma characteristics
breaks are more jagged and brittle and color differentiates from surrounding bone
Perimortem trauma
at or around death
Perimortem trauma morphology
sharp edges, smooth surfaces, no color differentiation relative to surrounding surface
Young’s modulus
relationship of stress and strain and their effect on bone deformation
Elasticity
returns to shape
plasticity
permanent deformation
fracture/ break
too much load to bear
perimortem biomechanics
bone has plasticity and elasticity
postmortem biomechanics
bone lacks plasticity: fractures more easily
trauma mechanisms
blunt force, sharp force, gunshot wound
Cause of death (COD)
event leading directly to death
Manner of death (MOD)
legal distinction for how the COD occurred
Types of MOD
Natural, homicide, accidental, suicide, undetermined
types of perimortem bone fracture
complete vs incomplete
Trauma mechanism
fracture pattern can tell us the direction of the force
fracture path
follows the path of least resistance
Gunshot wounds
High velocity impacts
Entrance wound
clean, round/ oval surface
Exit wound
external beveling
beveling
“cone-shaped” defect in the bone; angle is always in the direction of the projectile
Keyhole- shaped entrance wound
combination of internal and external beveling
gsw - cranium fractures
radiating and concentric fractures
gsw - long bones
entrance wound but no exit wound
Slow velocity
Blunt and sharp force trauma
blunt force trauma characteristics
slightly jagged edges, and flaking off of bones
blunt force examples
falls (from heights), blows with blunt object, car accidents
sharp force trauma
created by tool with a point or beveled edge
alterations
straight line incision, punctures, gouges, and clefs
striations on bone
serrated blades are distinctive from non serrated blades
saws
dismemberment - sharp force trauma on bone
hacking trauma
combination of blunt and sharp force trauma (machete)
thermal alterations
burn trauma
pugilistic posture
normal burning patterns of body
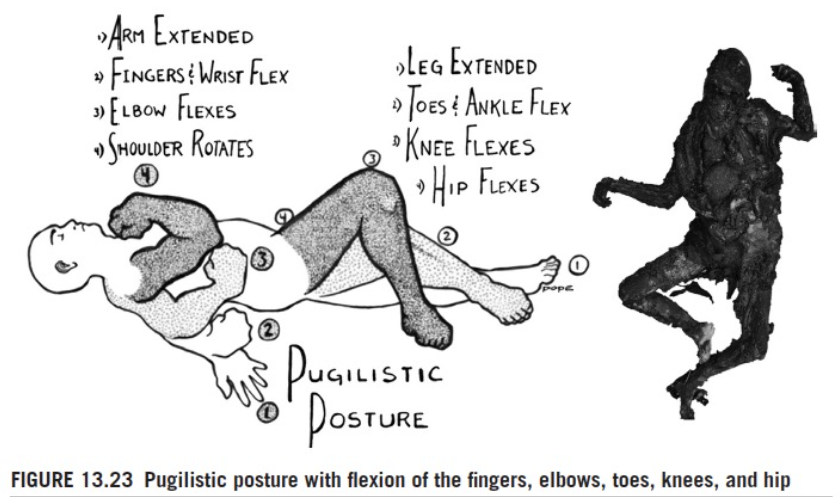
burn pattern characteristic
skeletal region with less soft tissue will typically be exposed first
color changes in burn patterns
typically first to occur in heat-altered bone
unaltered bone
pale yellow
heat border
white line - altered bone tissue
charred bone
bone directly exposed to fire
gray to white
calcined - lost all organic content and moisture
cremation
body completely calcined, disintegrates to ash
ancestry estimation
methods perpetuated racism in varying fields
scientific racism/ polygenism
samuel morton
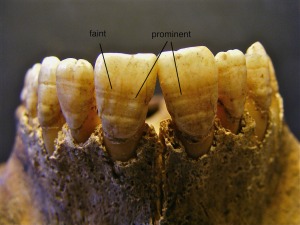
shovel-shaped incisors
native american/ northeastern asians
morphometric methods
scores features, and applies discriminant function analysis
carabelli’s cusp
european
structural violence
evidence of poverty and racialized capitalism in bone
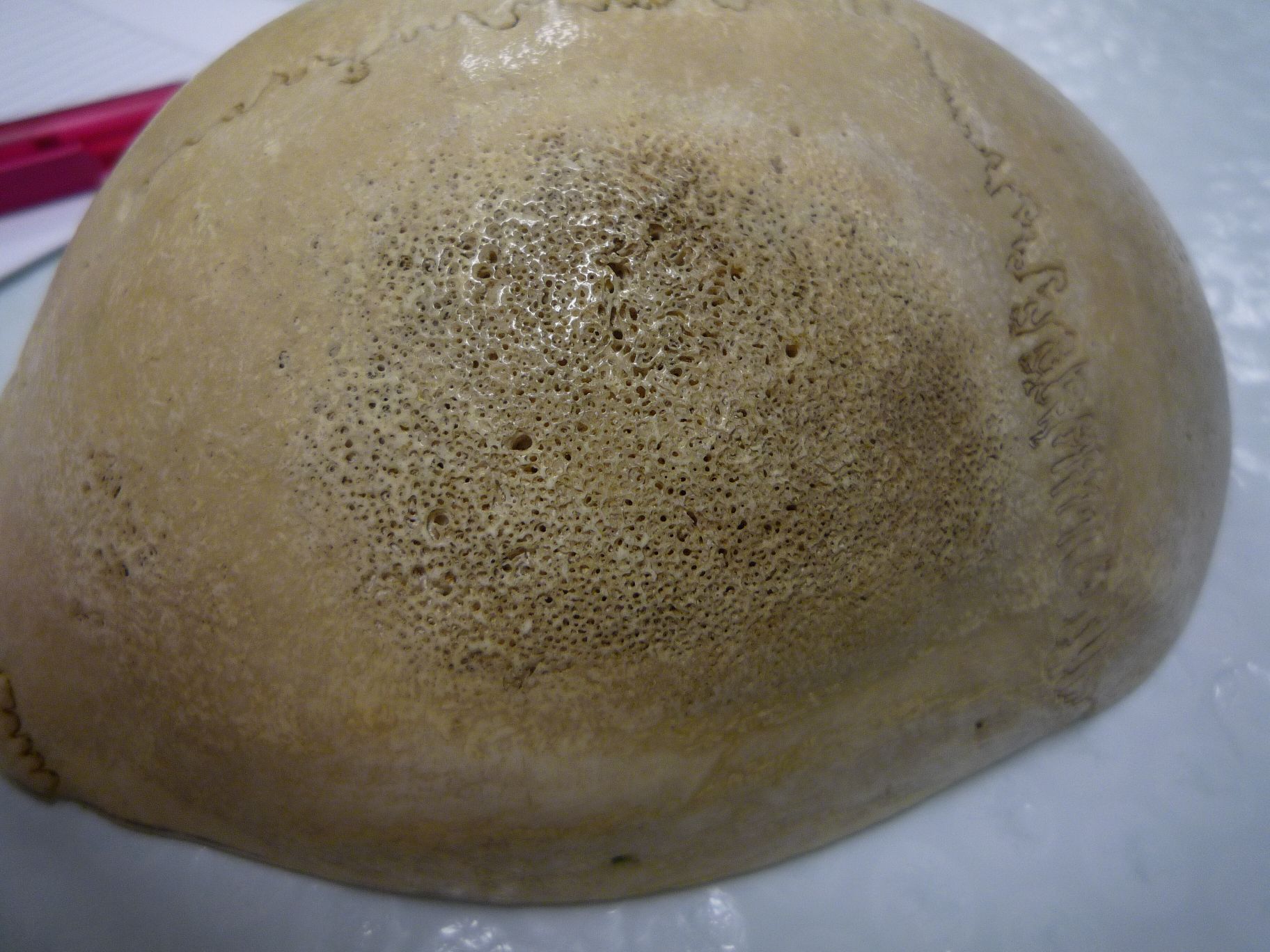
porotic hyperostosis
iron deficiency

linear enamel hypoplasia
malnutrition especially in younger years