Lesson 21 Basic Organs and Structures in the Abdominal and Pelvic Cavity, the Kidneys
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
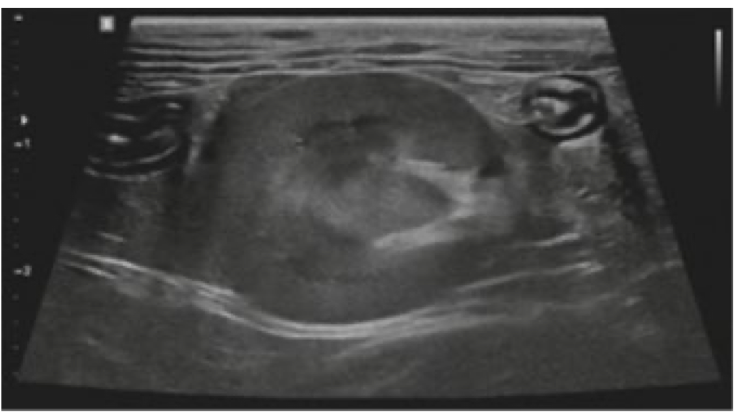
What diagnostic technique is used? What is the organ?
Ultrasound and Kidney
When estimating the size of the kidneys in dogs or cats on radiograph, what lumbar vertebrae is used as the reference?
L2
In dogs, which kidney is ventral to the last thoracic and first two/three lumbar vertebrae?
Right kidney
In dogs, which kidney is below the first/second to fourth lumbar vertebrae?
Left Kidney
Which kidney is more restricted by being deeply recessed within the caudate lobe of the liver?
Right
Is the right kidney more cranial or caudal to the left kidney?
Cranial
Why is it difficult to visualize the right kidney for imaging as well as to access for surgery?
Due to it being hidden in the recess of the liver and being more cranial, under the ribcage.
The cranial end of the right kidney is within the ribcage usually bisected by which rib?
T13
The right kidney is closely related to which gland?
right adrenal gland
The right kidney is medially close to which major blood vessel?
Caudal vena cava
The right kidney is ventrally in contact with what organs
right lobe of the pancreas
Descending duodenum
Ascending colon
The cranial end of the left kidney is in contact with which organs?
Spleen
Greater curvature of the stomach
Pancreas
Left adrenal gland
The left kidney is caudally in contact with which part of the colon?
Descending colon
The left kidney is medially related to which parts of the GI?
Descending colon
Ascending duodenum
Describe the location of the kidneys against the dorsal abdominal wall on either side of the vertebral column.
retoperitoneally
What does it mean to be retroperitoneally?
They sit behind the lining of the abdominal cavity
What is the shape of the kidneys in a dog and cat?
Bean shaped
How can you differentiate kidneys of a dog and cat?
Cats have more prominent Capsular veins in the surface of the kidneys
What is the lining of the kidneys called?
Renal capsule
The lateral border of the kidney is what shape?
Convexed
What is the shape of the medial border of the kidneys?
Concaved and indented at the hilus
Where does renal artery and vein, ureter enter the kidney?
The hilus
What are the two regions of the internal structure of the kidney?
Cortex
Medulla
What does the appearance of the renal cortex?
Granular
What is the appearance of the renal medulla?
Striated
In cows, the cortex remains unfused to form lobes while the medulla is undused and form medullary projections, what are these projections called?
Renal pyramids
What region of the kidney contains renal corpuscles and convoluted parts of the tubules?
Cortex
What region of the kidney contains the collecting ducts?
Medulla
What is the inner margin of the medulla where the ducts empty into the renal pelvis?
Renal crest
What is a false pyramids, and which species have this?
Pyramids will be seen in the paramedian sagittal section only but there are no true renal/medullary papillae present. This is seen in dogs and cats
What part of the kidney is a wide, funnel-shaped structure that collects the urine. It is the terminal dilated part of the ureter within the kidney.
Renal Pelvis
What part of the kidney is a depression caused by extension of the renal pelvis into the medulla on both sides of the crest?
Renal/pelvic recesses
What part of the kidney is a fat-filled space surrounding the renal vessels and the ureter?
Renal sinus
The kidneys are clearly seen in what percentage of the plain studies of the abdomen of the dog?
50%
What type of radiography is used for more detailed studies of the kidneys?
Contrast radiography
What type of views are usually performed to visulize the kidneys?
Lateral and VD
Which lateral is used more often to visualize the kidneys?
Right lateral
How sound the kidneys look on a radiograph of a cat/dog?
Bean shaped
Smooth
Homogenous
Stoft tissue opacity
The kidneys are often superimposed on one another, which kidney is more more cranial?
The right kidney
What is the normal canine kidney size?
2.5-3.5x of L2
What is the normal kidney size of a feline?
2.4-3x L2
In VD, the canines right kidney should lie in the area of which vertebrae?
T13-L2
In VD, the canines left kidney should lies in the area of which vertebrae?
L1-L3
In VD, the feline right kidney should lie in the area of which vertebrae?
L2-L4
In VD, the feline left kidney should lie in the area of which vertebrae?
L3-L5
While viewing an ultrasound of the kidneys how does the echotexture compare to the spleen?
Fine
Granular
Markedly hypoechoic much like the spleen
What is the echotexture of the renal cortex?
Hypoechoic or isoechoic ( much like liver)
hat is the echotexture of the renal medulla?
Hypoechoic or anechoic
What is it called when there is a presence of bright hyperechoic specks that represent the arcuate vessels?
Corticomedullary junction
What divides the renal medulla into segments on an ultrasound?
Diverticula and the vessels
Why is the renal pelvis hyperechoic?
The presence of fat and fibrous tissue
What makes the bovine kidney more primitive than a dog or cat?
The kidney is lobated (18-20 lobes), no renal crest or renal pelvis
What is the shape of the bovines right kidney?
Flattened
Oval
Which kidney’s cranial pole embeds in the liver?
Right Kidney
What is the shape of the bovines left kidney?
Slightly twisted, pointed cranially.
Which bovine kidney is displaced to the right by the rumen?
Left kidney
The lobes of the bovine kidney form pyramids that have what distinct structure?
Renal papillae
Where do the renal papillae drain into?
Minor renal calices
Where do the minor renal calices drain into?
Cranial/Caudal collecting ducts (Major Calyces)
The cranial and caudal calyces join to form what?
ureter
How is the small ruminant kidney similar to the canine?
Fusion of the cortex and medullary region
Bean shaped with renal hilus
medullary region fuses to form a single renal pyramid/renal crest
How is the porcine kidney different than any other species kidney?
No external lobation because the cortex is fused and smooth but has internal evidence of lobation.
What species is the only domesticated mammal whose kidneys are at the same level, meaning there is no contact between right kidney and liver?
Porcine
What are the internal features of the porcine kidney?
10 Medullary pyramids →10 minor calyces → two major calyces → renal pelvis → ureter
Where is the right equine kidney located in relation to what vertebrae?
T16-L1
The cranial pole of the equine right kidney makes what on the caudate process of the liver?
renal impression
What is the shape of the equine right kidney?
heart-shaped
flattened
small
transverse diameter = longitudinal diameter
Which organ is cranial to the horses right kidney?
The liver
Which organs are ventral to the horses right kidney?
Descending duodenum
Pancreas/base of cecum
Small colon/intestine
Which gland/blood vessels are medial to the horses right kidney?
Right adrenal gland and aorta
Where is the left equine kidney located in relation to what vertebrae?
T17-L2
What is the shape of the horses left kidney?
Flattened
bean-shaped or 6 shaped
What organs are cranial to the horses left kidney?
Spleen
Stomach
What organs/blood vessels are medial to the horses left kidney?
Aorta
Small colon
Small intestine
What makes the equine kidney more phylogenetically advanced than the bovine kidney?
It is a modified Unipyramidal type with a renal crest → renal pelvis → ureter
What structure of the equine kidney is unique to the equine species?
The terminal recess
What is the terminal recess?
Two polar recesses extend from the poles of the kidneys connecting the papillary ducts to the renal pelvis
Describe the vasculature of the kidney and its nephron going from the aorta to the kidney.
Aorta → Renal artery → Interlobar → Arcuate → Interlobular → cortex → Afferent arterioles→ renal corpuscles which will divide to form the capillary loop of the glomerulus
Describe the efferent vasculature of the kidney and its nephron from the glomerular to the tubules.
Glomerular capillaries→ Efferent arterioles (second capillary system) → peritubular capillaries that surround the tubules.
What is the renal pelvis?
The dilated terminal part of the ureter within the kidney
What blood vessel directly branches the afferent arterioles?
Interlobular artery
What is the renal sinus?
The region/space filled with fat that accommodates the ureter, renal artery, and vein
What is the renal papillary?
The terminal part of the renal pyramid within the kidney
What is the papillary junction?
The junction between the cortex and the medulla
What is the minor calices?
The parts that fuse to form the major calices