Exam 3 flashcard but with funny shitposts
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For the best experience for learn and practice in the in options in the top right put answer with definition , idk if this gonna work 💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀💀 This set only covers the bolded sections of Cantus PowerPoints so please go over the non- bolded sections for full coverage. Sorry to whoever got a bad grade thought he would ask more about the bolded stuff like he said.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Mesoderm function
Skeletal and muscular system

Endoderm function
construct linings of two tubes within the body.

Ectoderm Function
Give rise to external body parts/Hormone regulation

What does it mean to be multicellular ?
Have many cells

Who can’t produce their own food ?
Heterotrophs

Unicellular
One Cell

Some animals will consume autotrophs (plants)
Herbivores

Other animals will consume other animals
Carnivores

Some animals will consume both plants and animals
Omnivores

Originally unicellular heterotrophs are called:
Protists

What do animals lack?
Rigid cell walls

What is the replacement of that animal cells are held together by?
Extracellular frames of proteins like collagen

What are the 5 Key innovations that animals have evolutionized by?
Symmetry, Tissues, Body Cavity, Embryonic development, Segmentation.
Animals tend to have a definite shape and symmetry… what are the main 2 types of symmetry?
Radial, Bilateral
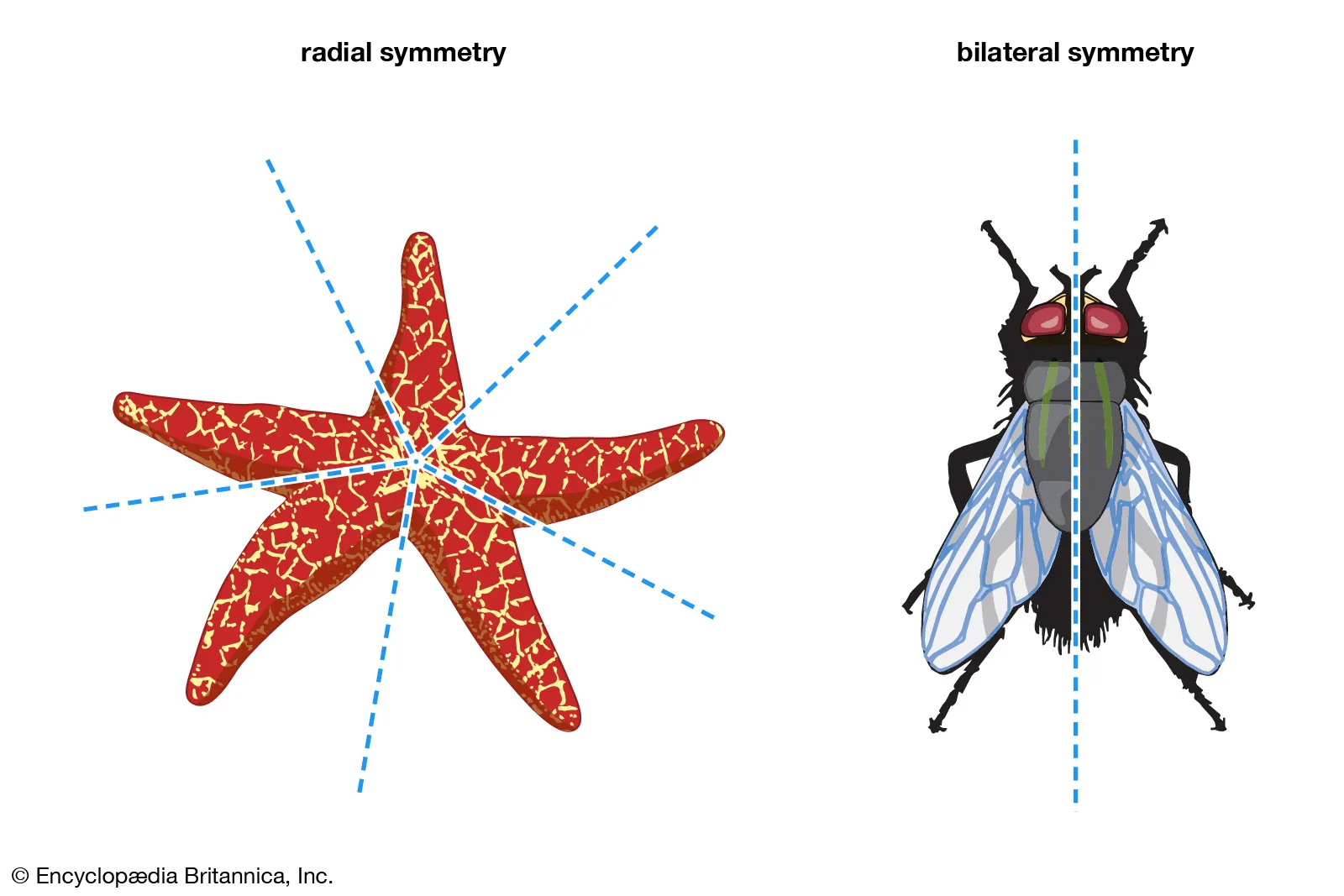
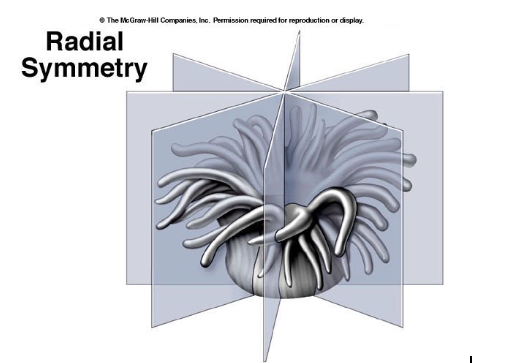
Radial Symmetry is most similar to…
A pie because you can separate it In multiple different ways


Is where the body has a distinct left or right, Known to have their brain and sensory structures located in one end
Bilateral Symmetry
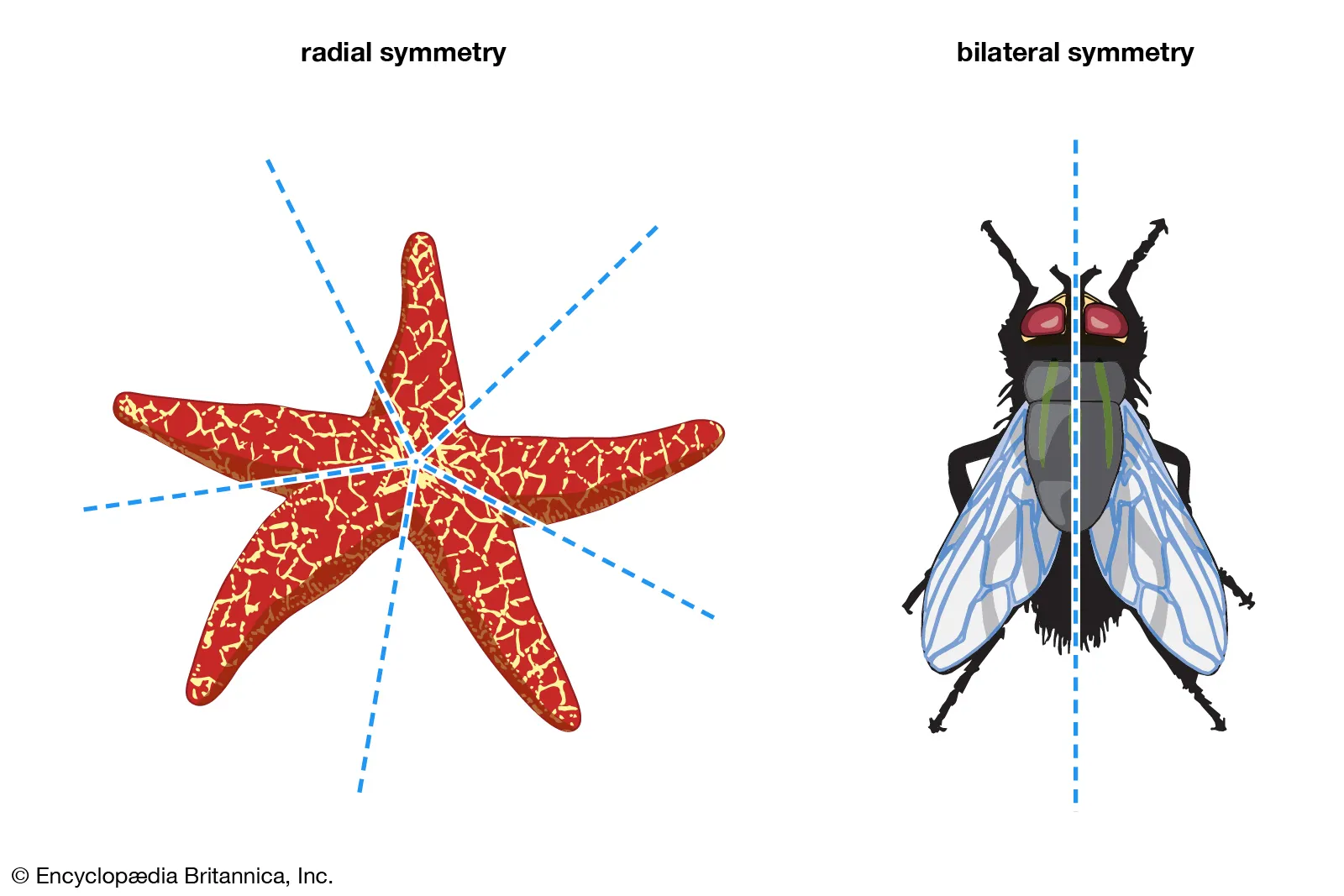

During Early Embryo Development, there are two type of patterns… What are those two called?
Protostomes, Deuterostomes


Protostomes consist of…
Flatworms, Roundworms, Annelids, Molluscs, and Arthropods.


Deuterostomes consist of…
Echinoderms, and Chordates

What is Common between/ Found in Both Protostomes and Deuterostomes
The First Embryonic opening called a Blastopore
Where does Blastopore turns in protostome
into the mouth

Deuterostomes turn in…
into the Anus


During Embryonic Development, most Animal cells divide themselves into three layers… What are those three layers names?
Ectoderm, Endoderm, Mesoderm

What is the endoderm..
Innermost layer,

What is the Ectoderm
outer most layer

mesoderm
intermediate layer

Sponges do not have tissues instead they have…
Germ layers


Cnidarians do not have what layer
Mesoderm


What do some Protostomes not have but are instead packed with?
Acoelomate- No body Cavity

Protostomes that are not completely lined by mesoderm
Pseudocoelomate

Their body cavity is entirely lined with mesoderm
Coelomate

Sponges lack what…
Lack tissues

What are sponges classified as…
PARAZOANS (beside the animal)

Multicellular, aquatic animals that lack organized tissues are called
Porifera: The Sponges

What is the interior of the sponge is…
Choanocytes
The whip of the flagella causing the water current through the sponge is called
Choancytes

Describe the sexual Reproduction of the Sponge
Sponges will release sperm into its central cavity to float out
The sperm finds the egg in another sponge and fuses with it to create a Zygote
the Zygote will turn into a larvae and then will swim to a new area
Describe the Asexual Reproduction
A Small Protuberance will grow until it’s a new complete organism

What will all the other animals classified as…
Eumetazoans

The ancient group of aquatic invertebrates that are radially symmetrical and capture their prey with a ring of stinging tentacles
Cnidarians

How do Cnldocytes get their prey?
They trap their prey and penetrates prey and injects toxin

Cnidarians have two main bodies… what are their names?
polyp, Medusa

What is the Polyp-
Cylindrical with mouth surrounds by tentacles, mouth faces up.

What is the Medusa?
Umbrella Shape with mouth surrounded by tentacles on one side

Cnidarians are divided into 5 Classes, what are those 5 classes… What are those 5 classes?
Anthozoa, Cubozoa, Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Staurozoa

Define the Anthozoa?
Usually sessile (Attach to the sea bed), Larvae form is free swimming,

What are Adult Anthozoa labels as
Polyps

What does the Anthozoa include
Sea anemones and corals

What is coral bleaching?
When corals are stressed by changes in conditions such as temperature,

Define Cubozoa…
They have a box shaped medusa stage with 4 sets of tentacles equidistant apart (some of the most venomous marine animals are in this group)

Hydrozoa
many live in colonies, can be floaters

What is the Hydrozoa similar to?
to coral

What is a prime example of Hydrozoa
Freshwater hydra species

The stalked jellies, They stay in their medusa form, but they look like a polyp they have a stalked medusa form
Staurozoan

What is the name of a stalked medusa form jelly fish
Staurozoan

Which group contains the True Jellies?
Scyphozoan

What stays in there medusa forms in adulthood?
Scyphozoan

Which group is pelagic and free swimming
Scyphozoan

What does the phylum Playhelminthes contains
20,000 Ciliated, soft bodied, flattened animals

Describe the Flatworm
Are bilateral in symmetry and are acoelomate

What does a Platyhelminthes lack or not have
Nervous systems incomplete digestive system only one opening

what are the three classes of Platyhelminthes
turbellaria, cestoda , Trematoda

What is Turbellarias function
Excretion of metabolic waste.

What is cestodas function
Absorb nutrients from the host's alimentary tract

Turbellaria
Free living flatworms

Cestoda
Tapeworms

Trematoda
Flukes

What is Trematoda function
Protects organism for the enviorment

Endoparasites that vary in size well developed regions called scolex,
Parasitic Tapeworms

What is a scolex
Bears hooks and suckers for attachment

The smallest bio unit of life
Cells

Group of similar cells preforming similar functions
Tissue

Types of Tissue each together to preform a specific action with an organisms
Organ
Group of organs that work together to perform a specific action within an organism
Organ system

Covers the body surfaces and lines body cavities
Epithelial Tissue

Binds and supports body parts
Connective tissue

Moves the body and its parts
Muscular Tissue

Receives stimuli and conducts nerve impulses
Nervous tissue

Flattened cells, lines blood vessels and areas of gas exchange
Squamous

Cube shaped, lines the lumen (a portion of the kidney)
Cuboidal

Rectangular columns: have nuclei located in the bottom of the pillar, lines the digestive tract
Columnar

Maintenance of the relatively constant conditions of the internal environment
Homeostasis

Primary mechanism behind homeostasis,
Negative feedback

The product dampens the original stimulus
Negative feedback

What’s one example of negative feedback
Pancreas detects blood sugar is too high
2 components to negative feedback:
Sensor, Control Center

Sensor
Detects internal change

Control Center
Initiates the effect to bring conditions back to normal

4 types of tissues?
Connective, Epithelial, Nervous, Muscular

How do you differentiate the muscle tissues?
Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac

What are neuroglia?
Any of the cells that hold nerve cells in place and help them work the way they should.

What is our fat storage tissue called?
Adipose tissue
What is the most rigid type of connective tissue?
Bone

What is active movement?
Voluntary and independent muscle contractions

Coelomates with a complete digestive tract
Molluscs

Internal Organs
Visceral Mass

Muscular portion for movement
Foot

Envelopes but does not enclose visceral mass
Mantle

Nudibranchs, conchs, and snails
Gastropods
Octopuses, squids, and nautiluses
Cephalopods
