4.2b Mechanics of Breathing (pulmonary ventilation)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
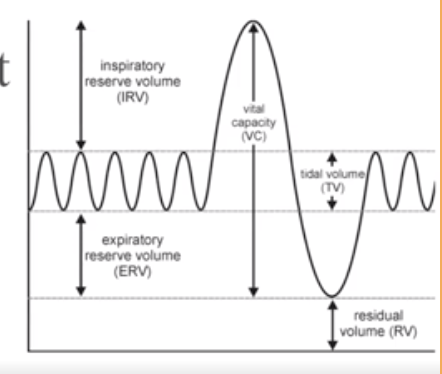
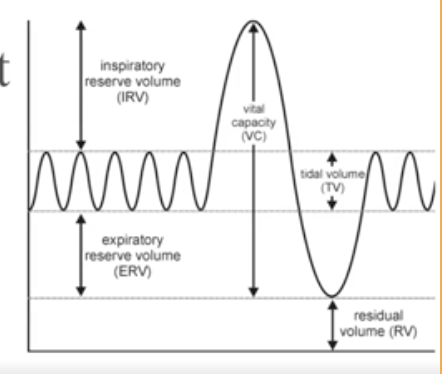
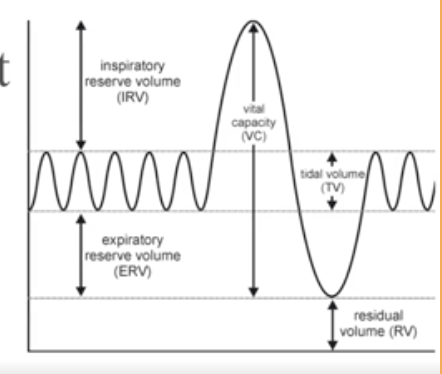
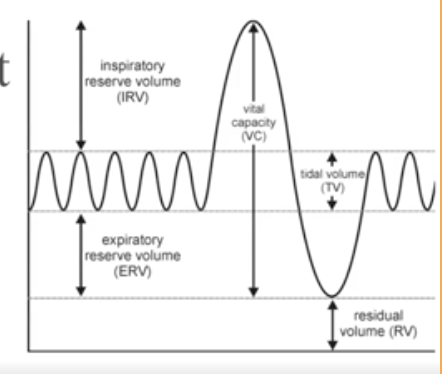
What is Tidal Volume?
Normal breathing moves about 500ml of air with each breath
2
New cards
What is Residual Volume?
after exhalation, about 1200 ml of air remains in the lungs
3
New cards
What is Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Amount of air that can be taken in forcibly over the tidal volume. (Usually between 2100 and 3200 ml)
4
New cards
What is Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled. (Approximately 1200 ml)
5
New cards
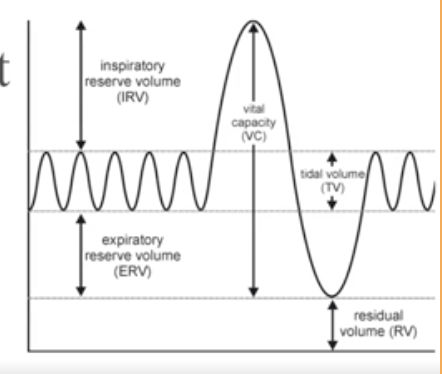
What is Vital Capacity
The total amount of exchangeable air.
Vital capacity = Inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + expiratory reserve volume
Vital capacity = Inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + expiratory reserve volume
6
New cards
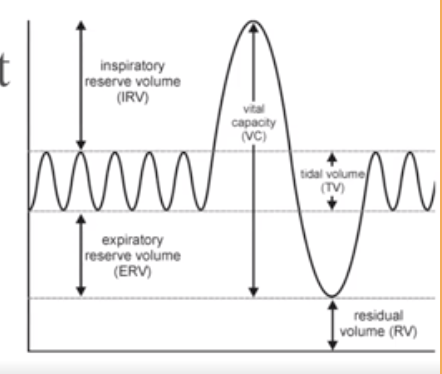
What is Total lung capacity?
The sum of all lung volumes.
Total Lung Capacity = Vital capacity + residual volume
Total Lung Capacity = Vital capacity + residual volume
7
New cards
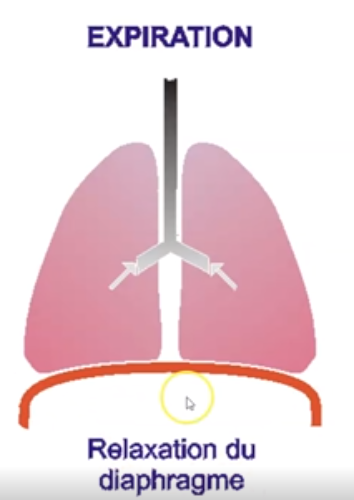
What is a diaphragm?
the dome-shaped skeletal muscle that forms the floor of the thoracic cavity
8
New cards
What happens to diaphragm during inspiration?
It contracts
9
New cards
When does a diaphragm relax?
during exhalation
10
New cards
Give some factors that can cause shortness of breath
1. advanced pregnancy
2. obesity
3. confining clothing
4. increased stomach size by impeding the descent of the diaphragm
11
New cards
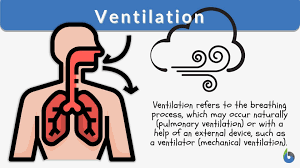
What is Pulmonary ventilation?
Moving air in and out of lungs
12
New cards
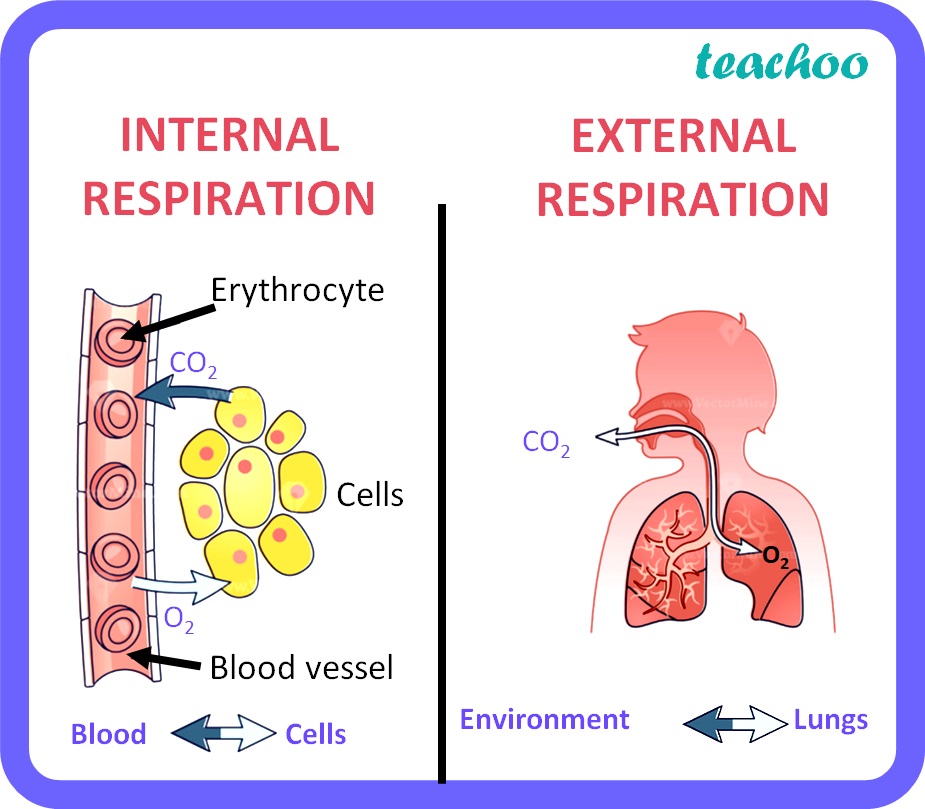
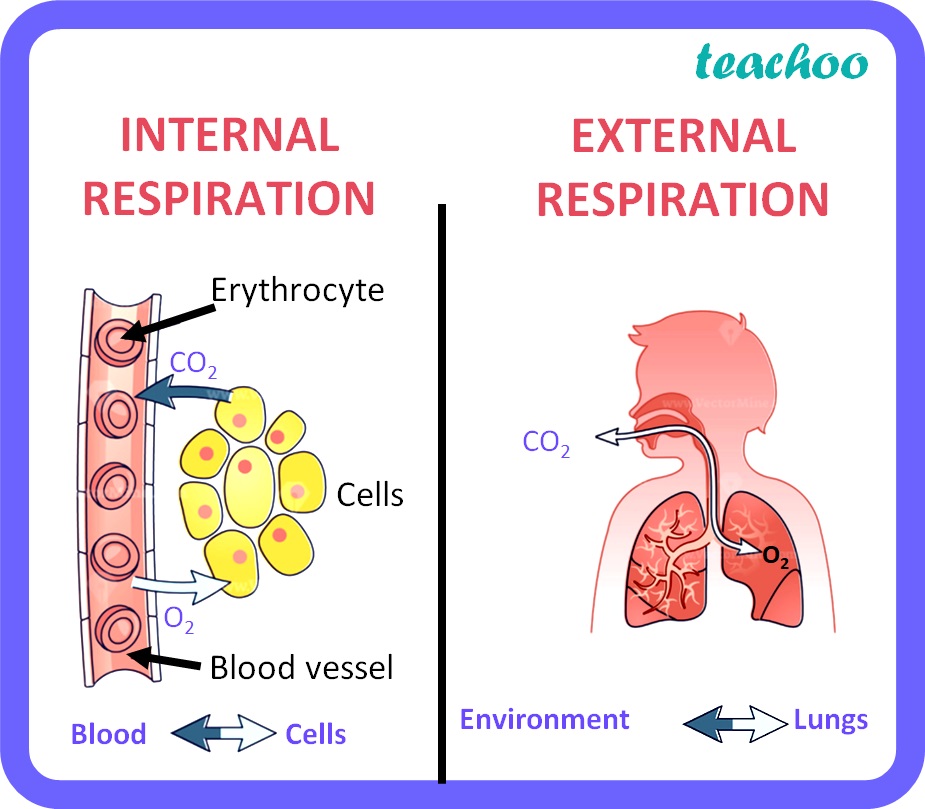
What is external respiration?
gas exchange between pulmonary blood and alveoli
13
New cards
What is internal respiration?
Gas exchange between blood and tissue cells in systemic capillaries
14
New cards
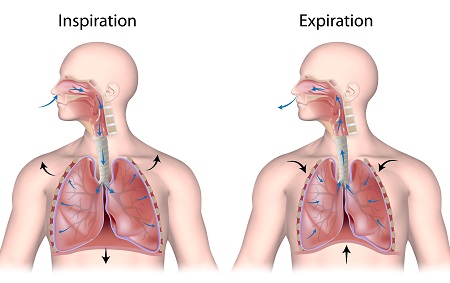
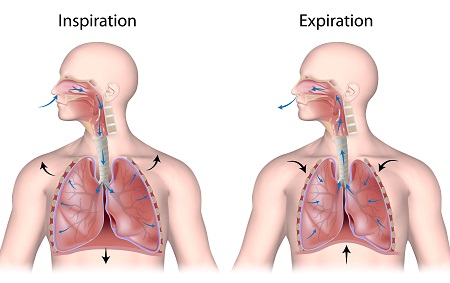
What is Inspiration?
the flow of air into the lung
15
New cards
What happens during inspiration?
* Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
* The size of the thoracic cavity increases
* External air is pulled into the lungs due to an increase in intrapulmonary volume
* The size of the thoracic cavity increases
* External air is pulled into the lungs due to an increase in intrapulmonary volume
16
New cards
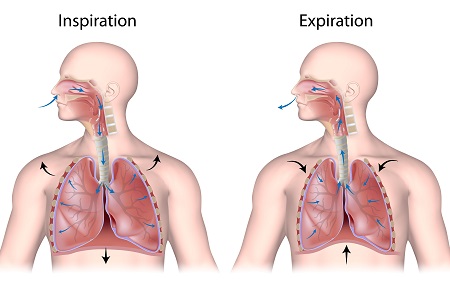
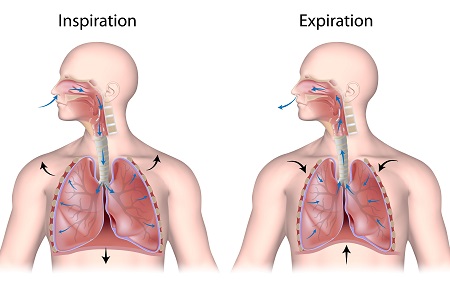
What is expiration?
air leaving lungs
17
New cards
What happens during expiration?
* Largely a passive process which depends on natural lung elasticity
* As muscles relax, air is pushed out of the lungs
* Forced expiration can occur mostly by contracting internal intercostal muscles to depress the rib cage
* As muscles relax, air is pushed out of the lungs
* Forced expiration can occur mostly by contracting internal intercostal muscles to depress the rib cage
18
New cards
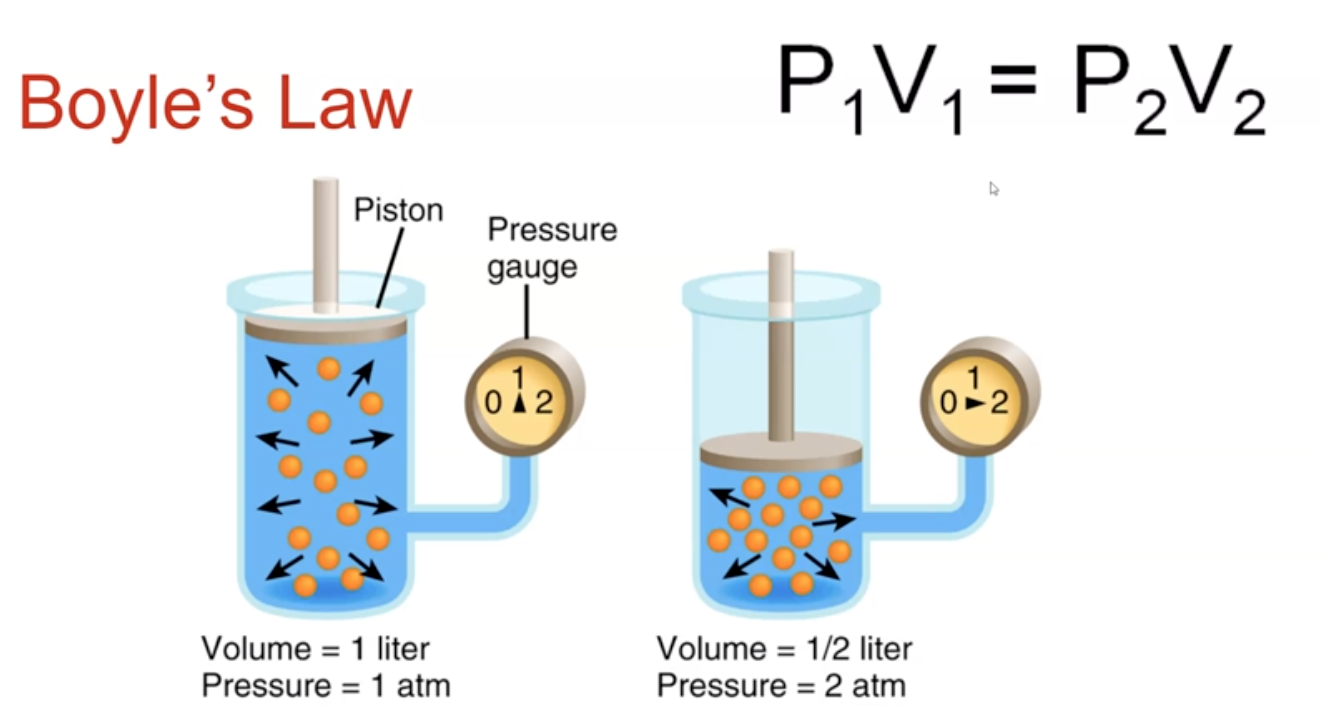
What is Boyle’s Law
P1v1 = P2V2