STATISTICS
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are mutually exclusive events?
If events are mutually exclusive, it means that if one of them occurs, the other event cannot occur. Either one or the other can occur, but not both.
how to prove mutual exclusivity
P(A or B) = P(A)+P(B)
what are independent events
When the outcome for one event doesn't depend on the outcome for another event
how to prove independant events
P(A and B) = P(A) X P(B)
what is the actual significance level
The probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis
what are the two ways of representing a probability distribution
- probability table
- probability mass function
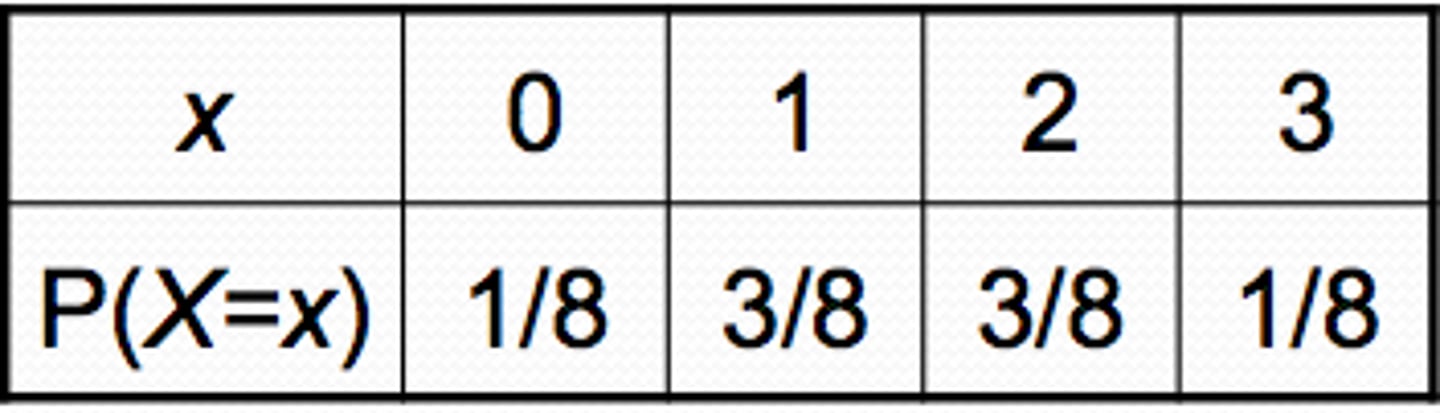
what does a probability table look like
what does a probability mass function look like
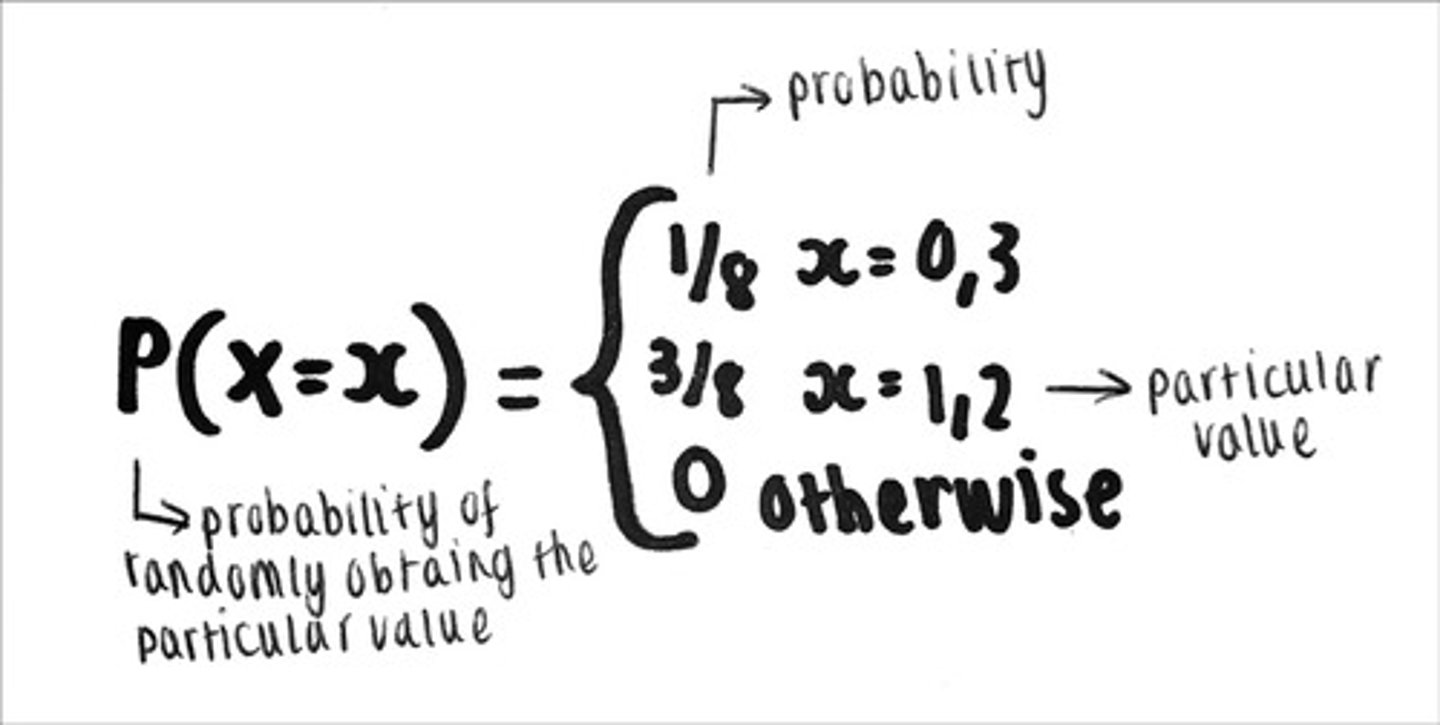
how to find frequency on a histogram
class width x frequency density
why is there a scale factor multiplier on histograms
the area of the bar is proportional to the frequency of each class
how to calculate mean in a cumulative frequency table
- mean = ∑xf/∑f
-∑fx is the sum of products of the data values and their frequencies
-∑f is the sum of the frequencies
when coding, what operations affect measure of location and measure of spread
- multiplication/division AND addition/subtraction for measure of location
- ONLY addition/subtraction for measure of spread
define population
The whole set of items that are of interest
define census
Observes or measures every member of a population
define sample
A selection of observations taken from a subset of the population which is used to find out information about the population as a whole
define sampling units
Individual units of a population
define sampling frame
list of all sampling units
advantages of a census
Completely accurate result
disadvantages of a census
-Time-consuming and expensive
-Cannot be used when the testing process destroys the item
-Hard to process large quantities of data
advantages of a sample
-Less time-consuming and expensive than a census
-Fewer people have to respond
-Fewer data to process than in a census
disadvantages of a sample
-The data may not be as accurate
-The sample may not be large enough to give information about small sub-groups of the population
Advantages of simple random sampling
Free of bias
Easy and cheap to implement for small populations and small samples
Each sampling unit has a known and equal chance of selection
disadvantage of simple random sampling
Not suitable when the population size or the sample size is large
A sampling frame is needed
What is systematic sampling?
The required elements are chosen at regular intervals from an ordered list
how do you carry out systematic sampling using a population, sample size and random num generator
-population/sample size = regular intervals
-first observation chosen at random using random num generator
-go up in the regular intervals calculated before
advantages of systematic sampling
Simple and quick to use
Suitable for large samples and large populations
disadvantages of systematic sampling
A sampling frame is needed
It can introduce bias if the sampling frame is not random
fundamentally, what is stratified sampling
dividing the population into subgroups (strata) that share similar characteristics then carry out simple random sample in each from each stratum
how do you carry out stratified sampling
-divide the population in strata according to their characteristics
-to calculate the number sampled from each sample:
(num in stratum/num in population) x overall sample size
-carry out simple random in each stratum
advantages of stratified sampling
-Sample accurately reflects the population structure
-Guarantees proportional representation of groups within a population
disadvantages of stratified sampling
-Population must be clearly classified into distinct strata
-Selection within each stratum suffers from the same disadvantages as simple random sampling
What is quota sampling and how to carry out
-dividing the population into strata according to characteristics
-predefined quota from each sample is filled using convenience sampling
Advantages of quota sampling
-Allows a small sample to still be representative of the population
-No sampling frame required
-Quick, easy and inexpensive
-Allows for easy comparison between different groups within a population
Disadvantages of quota sampling
-Non-random sampling can introduce bias
-Population must be divided into groups, which can be costly or inaccurate
-Increasing the scope of study increases the number of groups, which adds time and expense
-Non-responses are not recorded as such
what is opportunity/convenience sampling
Sample taken from people who are available at time of study, who meet criteria.
Advantages of opportunity sampling
Easy to carry out
Inexpensive
Disadvantages of opportunity sampling
-Unlikely to provide a representative sample
-Highly dependent on individual researcher
what is quantitative data
numerical data
What is Qualititative data
Qualitative data is information about qualities; information that can't actually be measured - non-numerical data
what is a continuous variable
A variable that can take any value in a given range
What is a discrete variable?
A variable that can take only specific values in a given range
what is the standard deviation and mean of the standard normal distribution (the Z distribution)
Mean = 0
std = 1
conditions for a binomial distribution to be approximated to a normal distribution
- probability must be close to 0.5
- n (num trials)must be large
if approximating a binomial distribution to a normal distribution, how do you calculate 𝜎 & µ
- µ = np
- 𝜎 = √np(1-p)
if you are using a normal approximation to a binomial distribution, what must you do when calculating probabilities?
apply a continuity correction
for a random sample of size 'n' taken from a random variable normally distributed, what is the normal distribution for the sample mean
x̄ ~ N ( µ , (𝜎^2/n) )