evaluating mechanism that support evolution of human cooperation [guest lecture]
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
recipe for success
the three Cs: cooperation, cognition, culture
human cooperation is unique
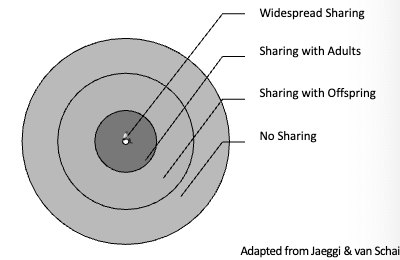
food sharing patterns in primates
unresisted transfer of food
widespread sharing
sharing with adults
sharing with offspring
no sharing
cooperation
cooperation largely limited to group members → kin and reciprocating partners
food sharing in other animals
chimpanzees transfer food to others but majority of it can be viewed as tolerated theft
widespread food sharing is absent
humans share food generously
forager food sharing is extremely generous
hawkes: Hadza hunters retain no more of their hunting income than anyone else
wood and marlowe: people retain less than majority of income
sexual division of labor
men target less reliable foods and those foods are shared more widely
human cooperation is a puzzle
evolutionary puzzle
social behavior of humans poses significant evolutionary puzzle
one of enduring puzzles in bio and social sciences is origin and persistence of intraspeciifc cooperation and altruism in humans
dictator game
evolution of cooperation — a mismatch
cooperation often occurs between anonymous strangers because we evolved in small, stable grps of mostly relatives
burnham and johnson: predict that human cooperative mechanisms include design features that modulate behavior in non anon and repeated environ and those mechnaims impact on empirical level of cooperation even in anon and final interactions
the hazda
1000 identify
social organization
live in camps
economic/political organization: sexual division of labor, high levels of egalitarianism
why study hazda:
cooperative grp living
absence of external monitoring and regulatory strcutures
opportunities for free riding
why study cooperation in hazda:
creation story: most do not know, few claimed haine created earth
after death: few claimed there is afterlife, few hazda discussed heaven
hazda cooperation
public goods game
4 sticks of honey; keep or donate
similarly cooperative people connected
generous hazda not necessarily more popular
cooperators live with other cooperators
clustering of them
cooperators preferentially form ties with each other
cooperative behavior is socially influence
no evidence for partner choice for cooperation
cooperators not more popular
cooperation is not table (no behavioral persistence)
weak agreement on rankings of cooperative character traits
humanc ooperative behavior flexible and affected be one’s local social enviornment