Lab 6
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
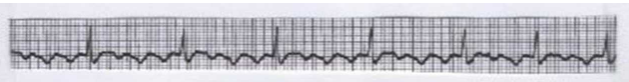
What is this?
Atrial flutter
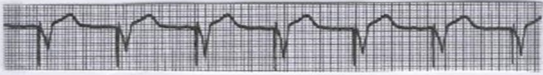
What is this?
Fixed ventricular pacemaker
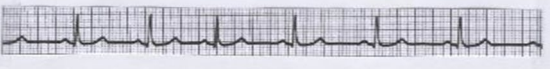
What is this?
Sinus arrhythmia
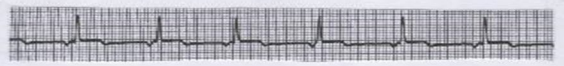
What is this?
Accelerated junctional rhythm
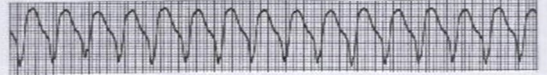
What is this?
Ventricular tachycardia
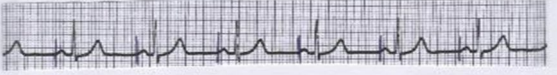
What is this?
Fixed atrial pacemaker
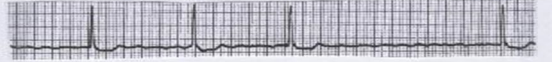
What is this?
Controlled Atrial fibrillation
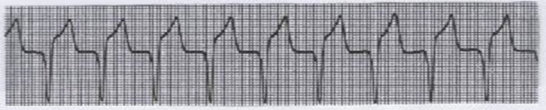
What is this?
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
What is the most important part of any ekg?
Identify the origin of the electrical impulse.
What are the 4 choices of identifying an ekg?
Sinus
Atrial
Junctional
Junctional
If there is more than one P wave on an ekg before the QRS what will the abnormality be?
An AV block
What type of rhythm will there be if you see a P wave that is different from the others on an ekg?
Atrial rhythm
What type of rhythm will there be if you see a wavy baseline (like flutter or fibrillatory waves) ?
Atrial rhythm
If an ekg has a flat baseline before the QRS complex and the QRS is complex is narrow what type of rhythm do you have?
Junctional rhythm
If an ekg has a flat baseline before the QRS complex and the QRS is complex is wide what type of rhythm do you have?
Ventricular rhythm
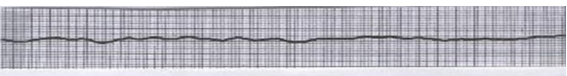
What is this?
fine ventricular fibrillation

What is this?
coarse ventricular fibrillation
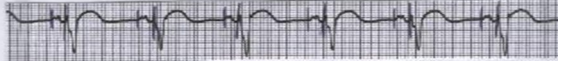
What is this?
fixed dual chamber pacemaker
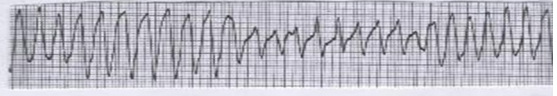
What is this?
Torsades de Pointes
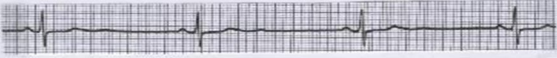
What is this?
sinus bradycardia
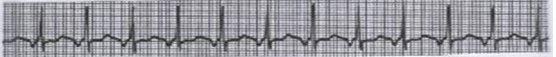
What is this?
junctional tachycardia
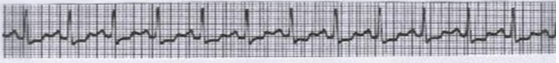
What is this?
sinus tachycardia (with some ST segment depression)
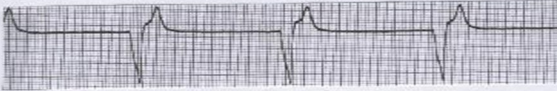
What is this?
idioventricular rhythm
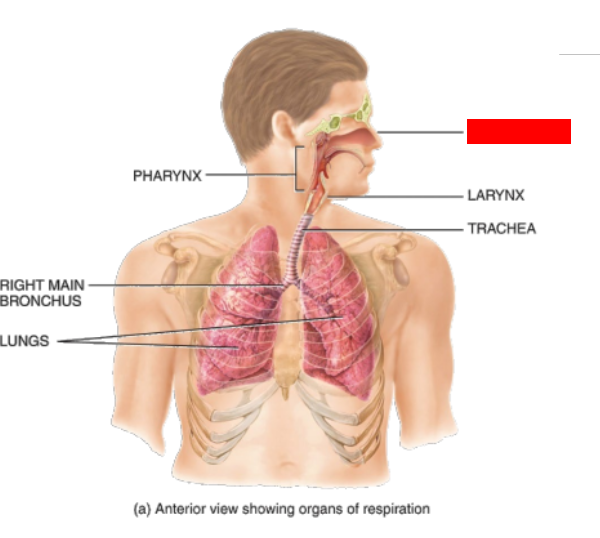
What is this?
Nose
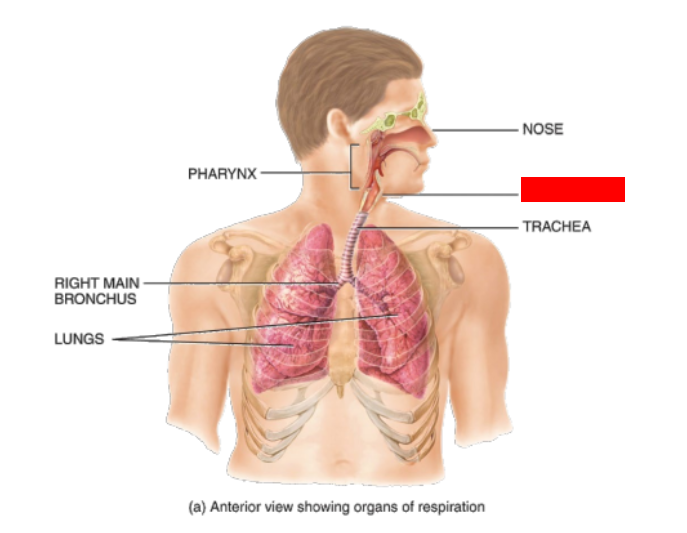
What is this?
Larynx
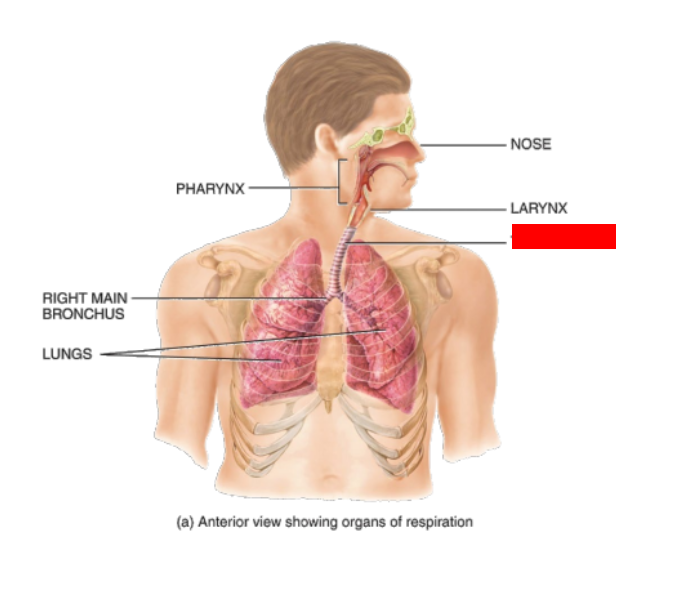
What is this?
Trachea
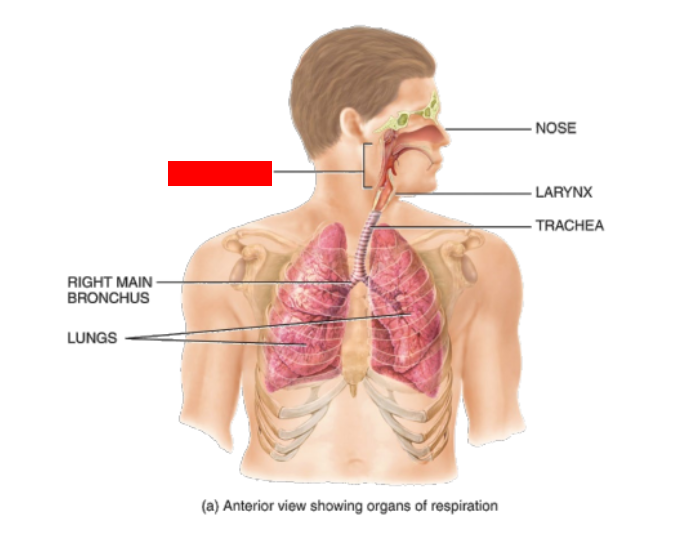
What is this?
Pharynx
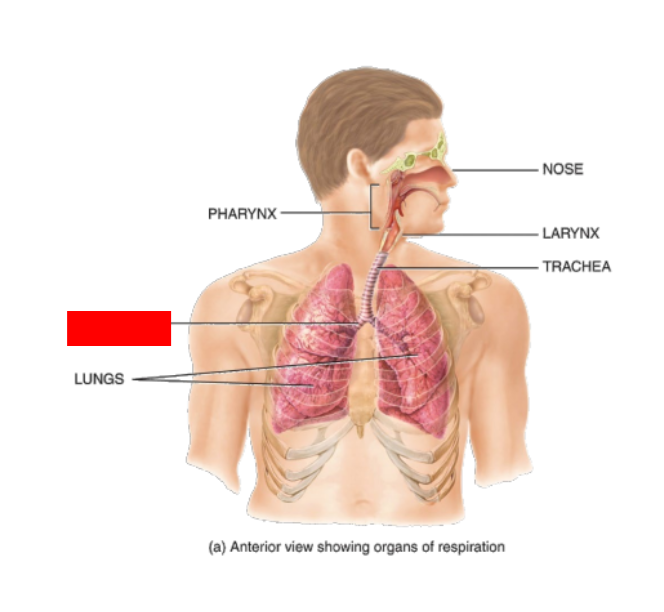
What is this?
Right main Bronchus
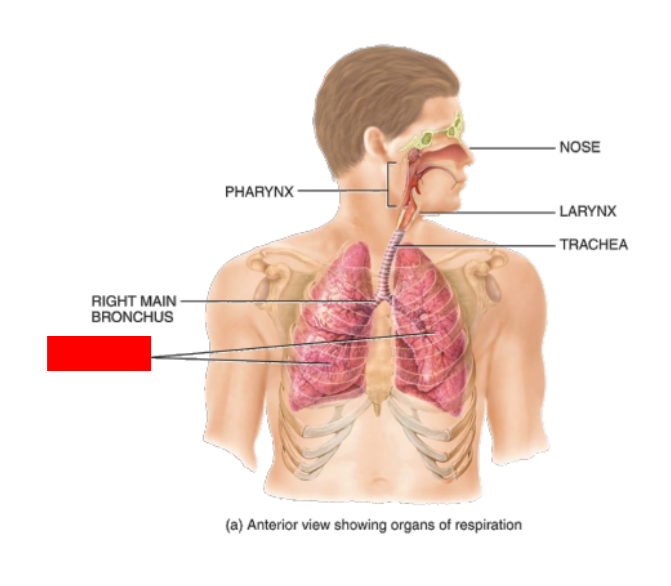
What is this?
Lung
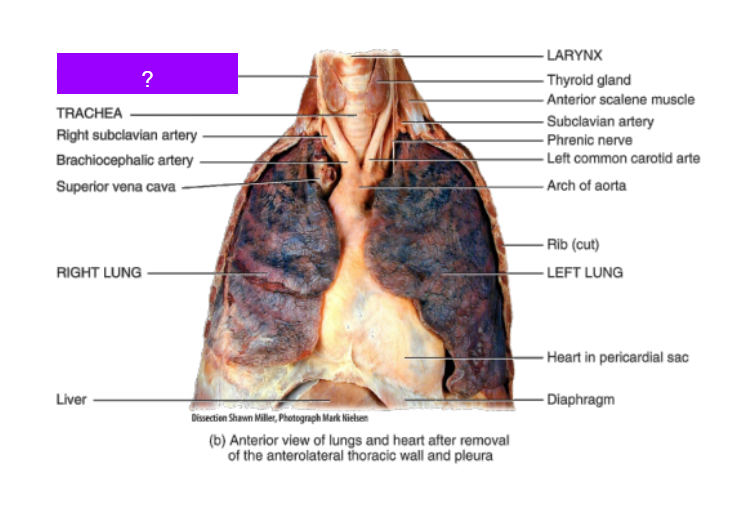
What is this?
Right common carotid artery
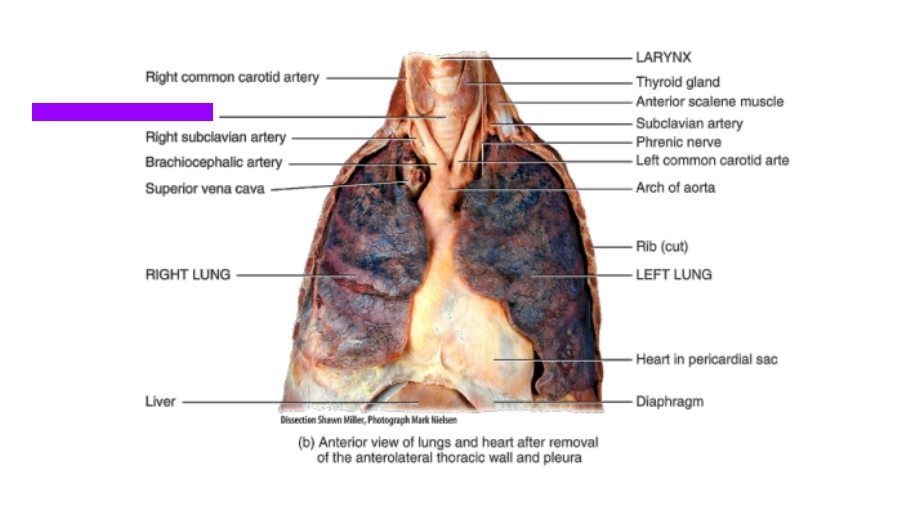
What is this?
Trachea
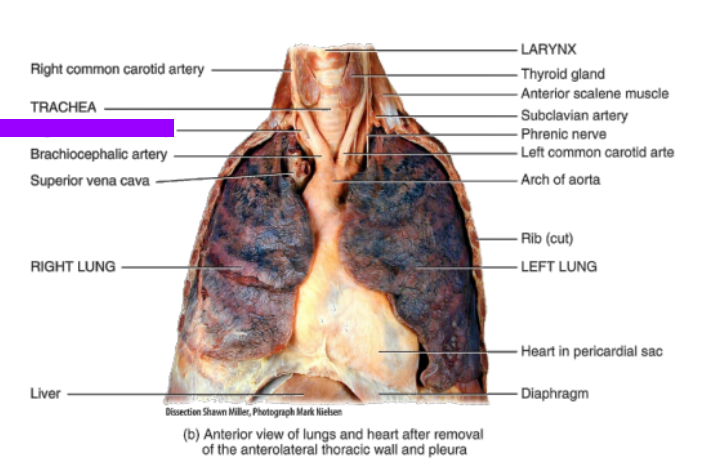
What is this?
Right subclavian artery
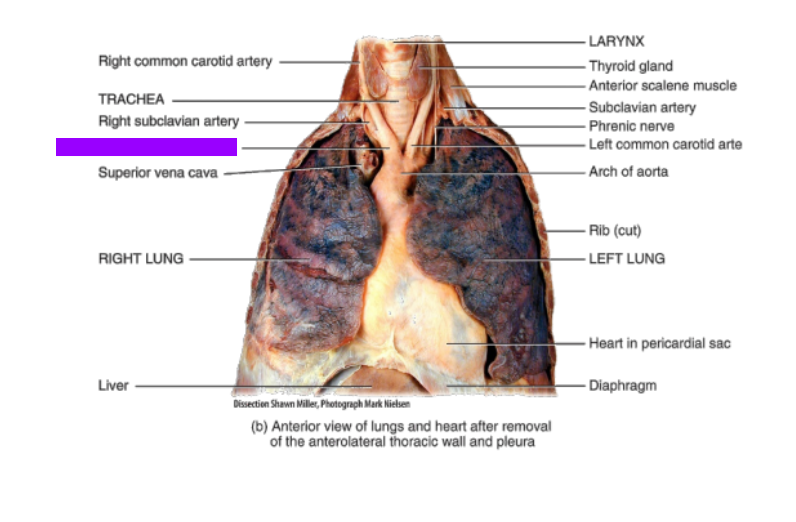
What is this?
Brachiocephalic artery
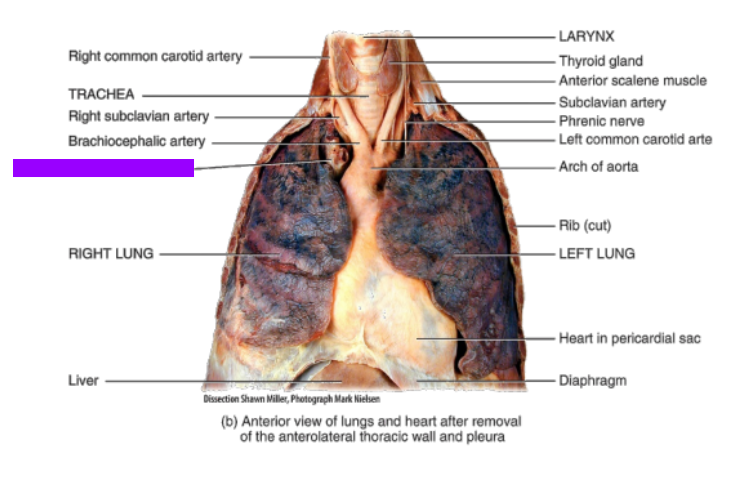
What is this?
Superior vena cava
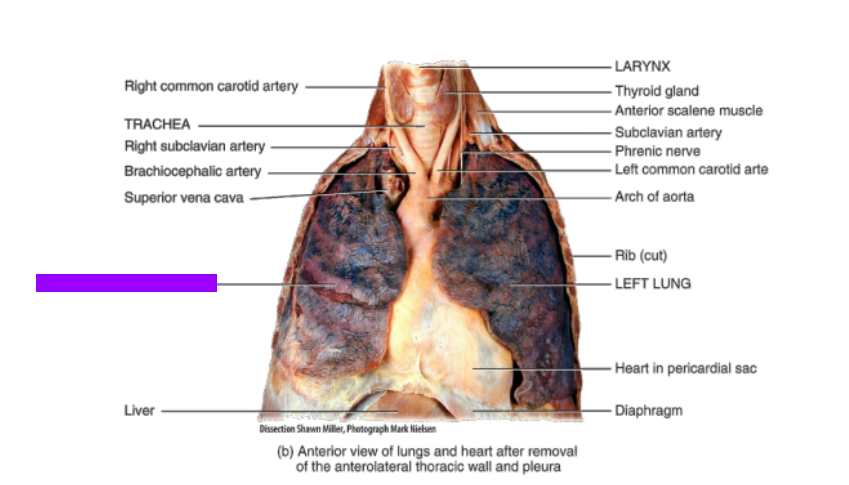
What is this?
Right lung
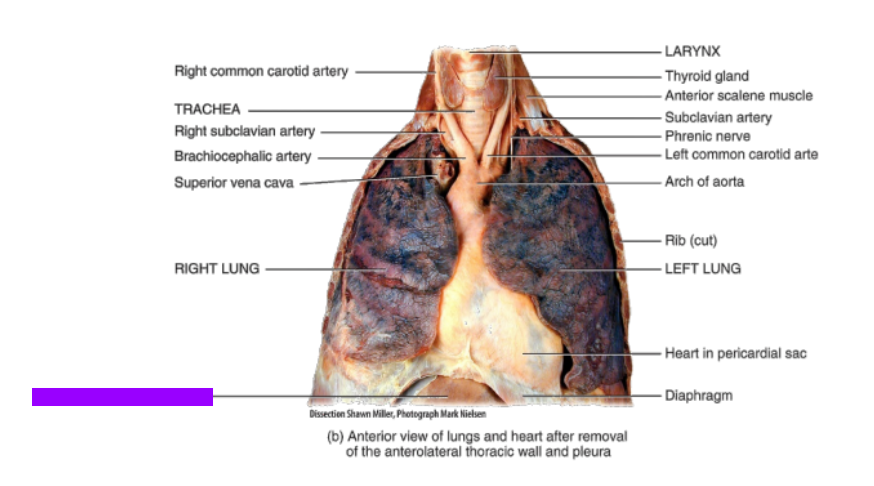
What is this?
Liver
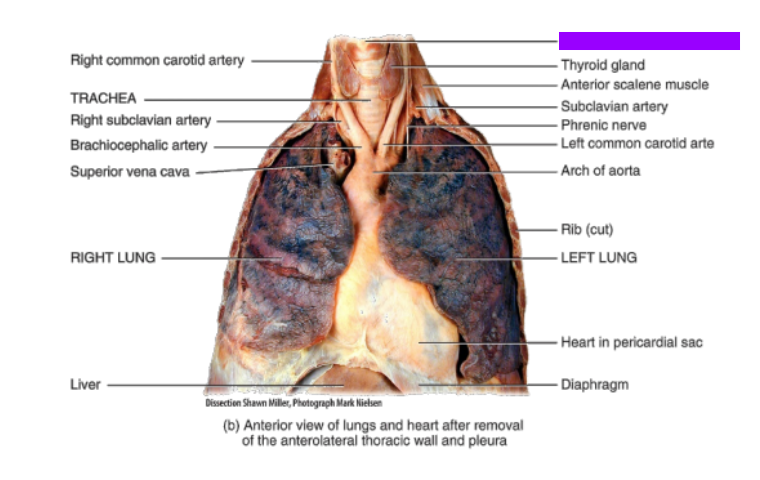
What is this?
Larynx
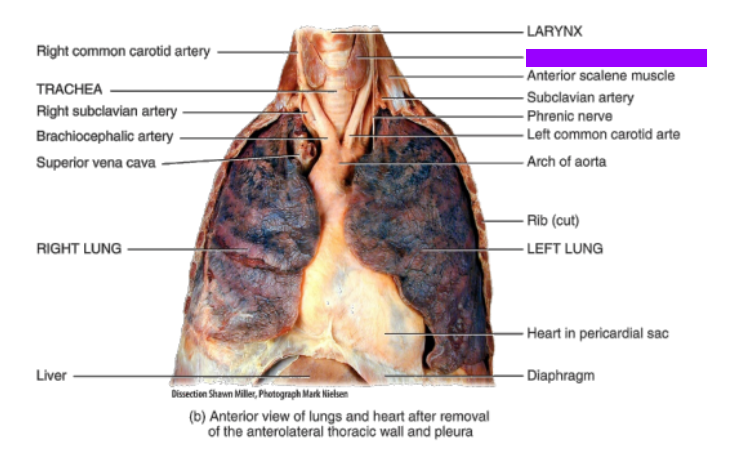
What is this?
Thyroid gland
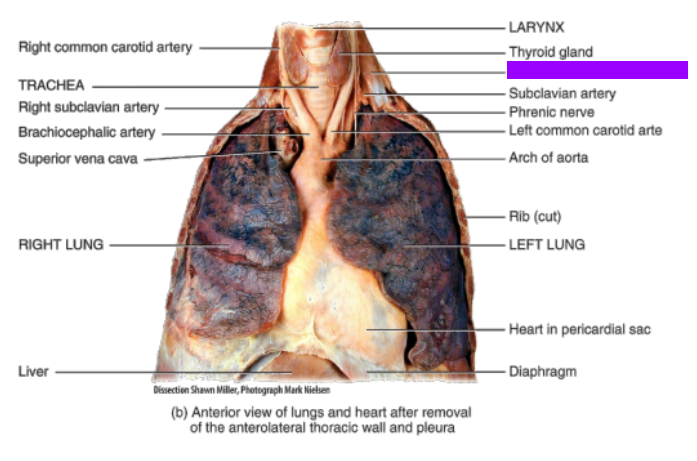
What is this?
Anterior scalene muscle
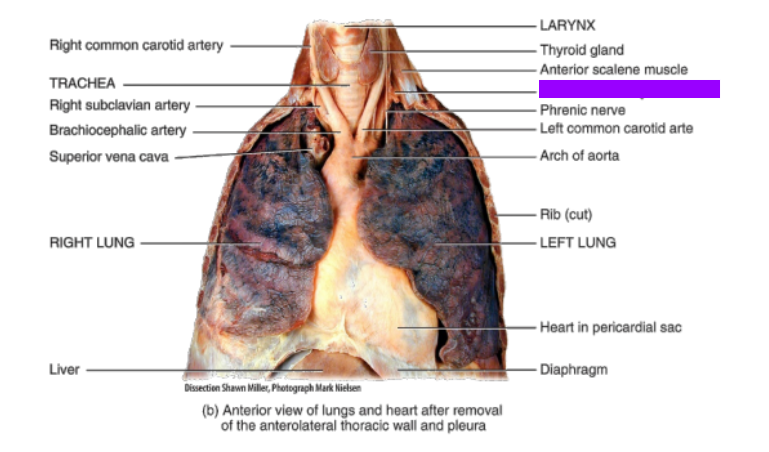
What is this?
Subclavian artery
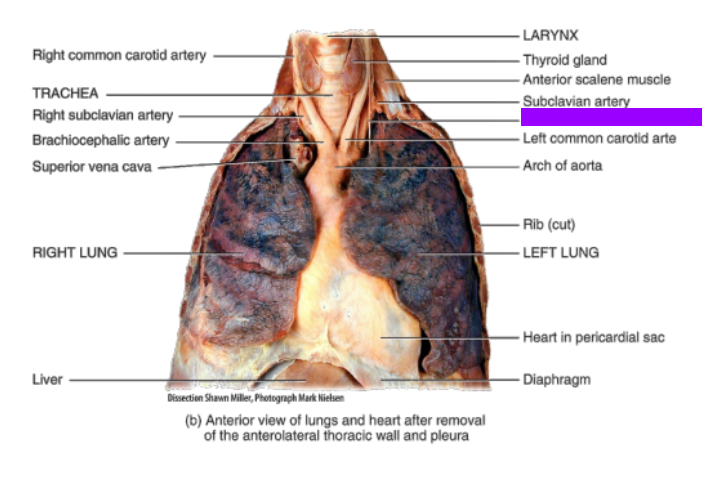
What is this?
Phrenic nerve
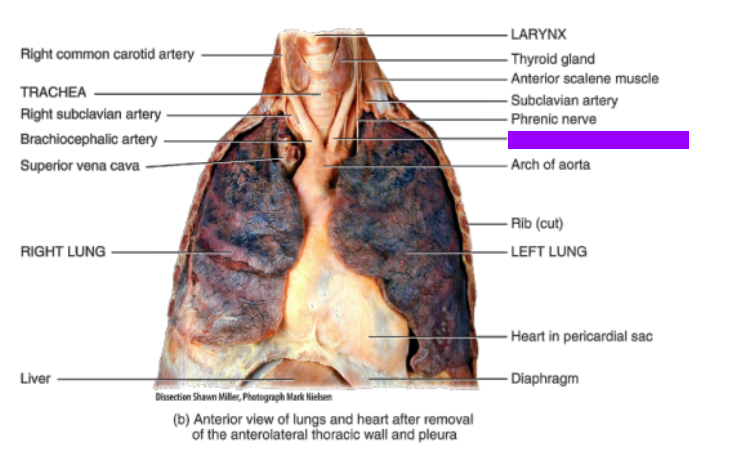
What is this
Left common carotid artery
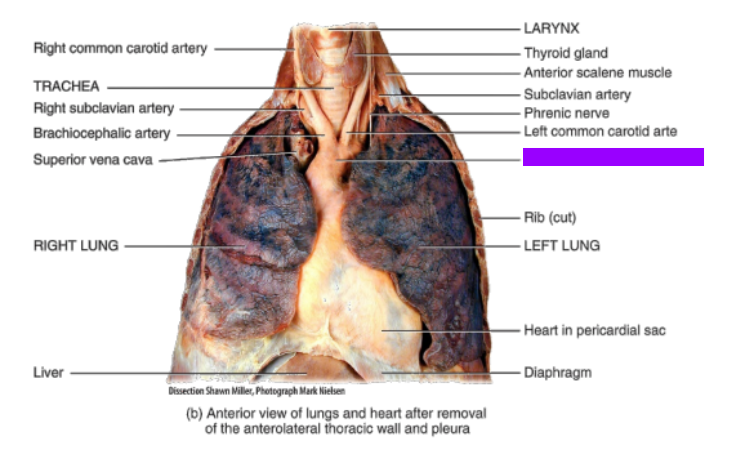
What is this?
Arch of aorta
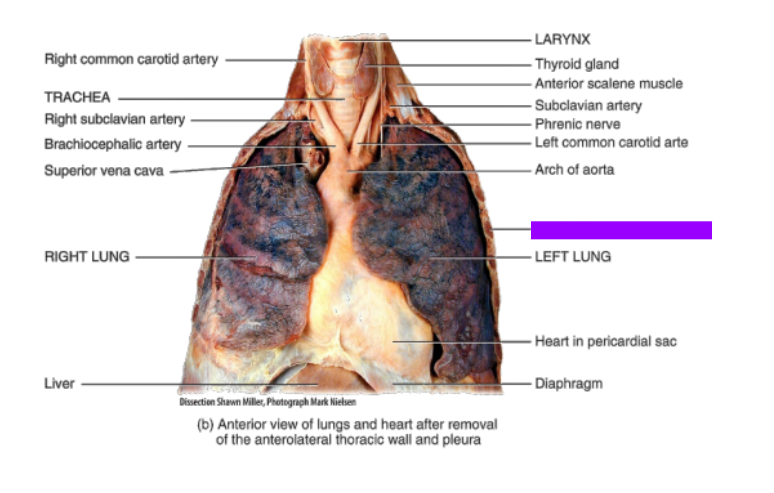
What is this?
Rib (cut)
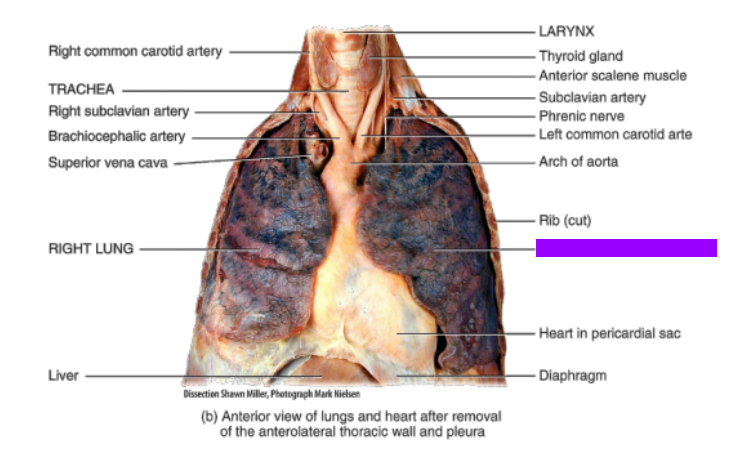
What is this?
Left lung
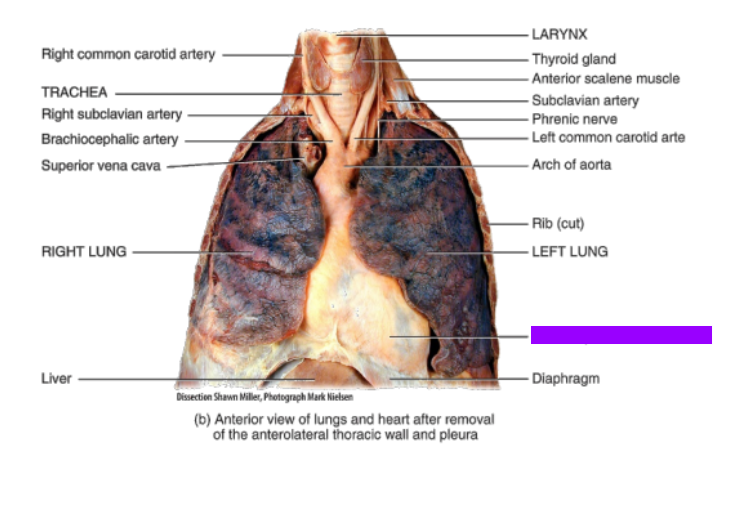
What is this?
Heart in pericardial sac
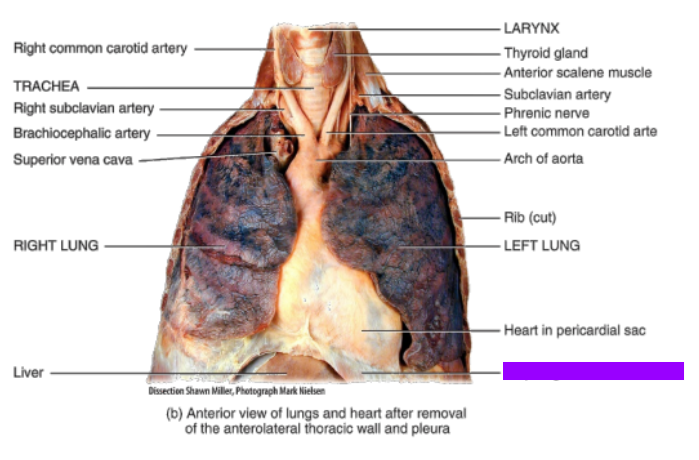
What is this?
Diaphragm
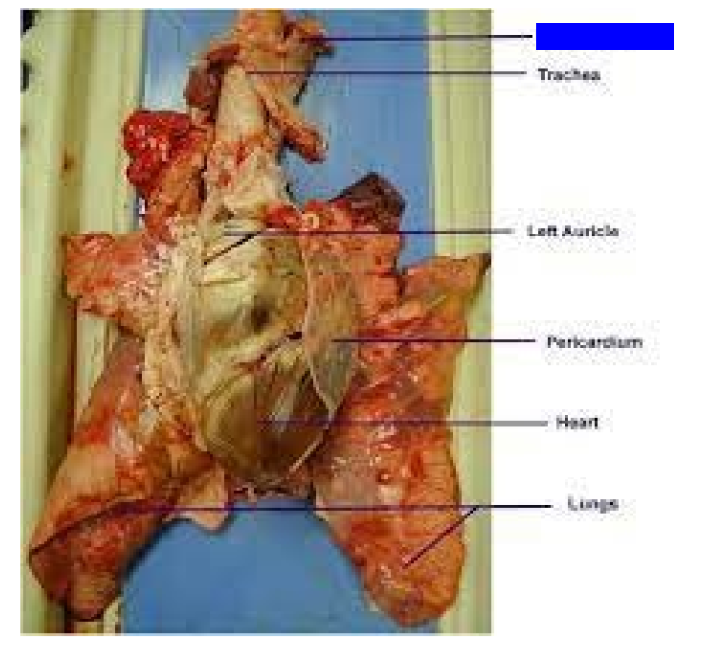
What is this?
Esophagus
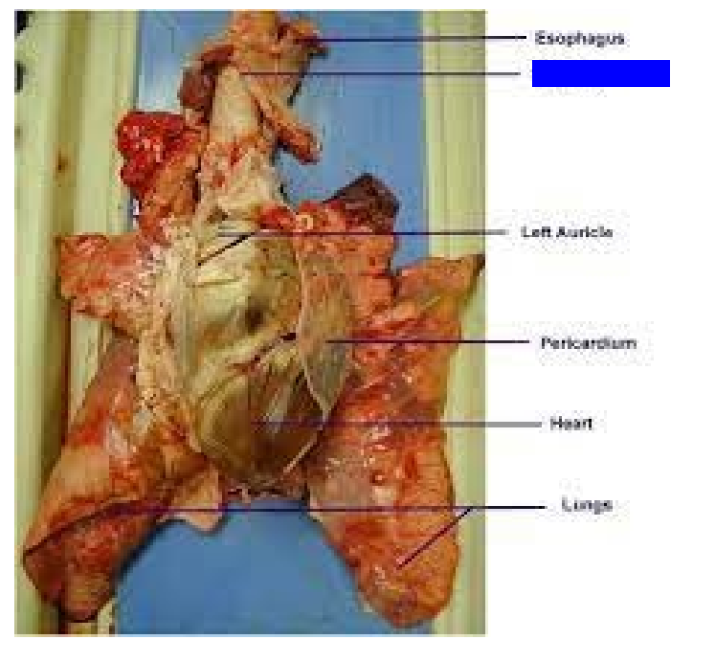
What is this?
Trachea
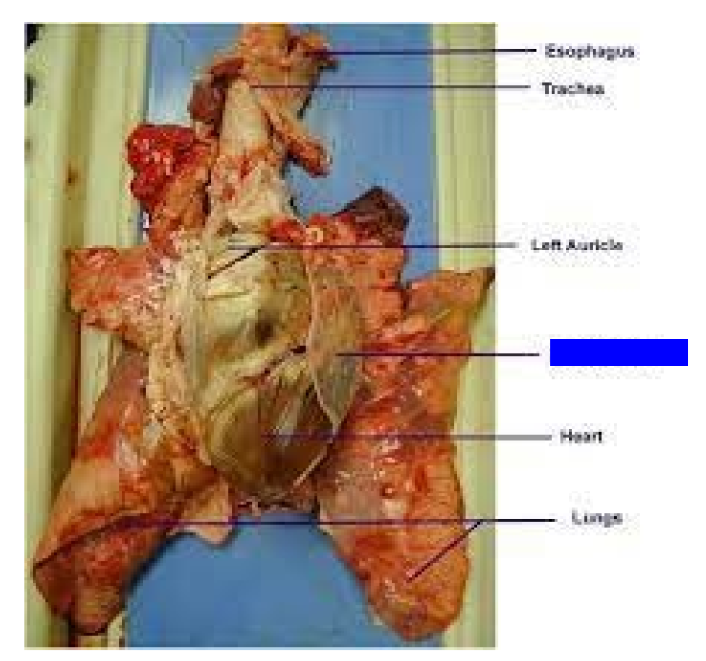
What is this?
Pericardium
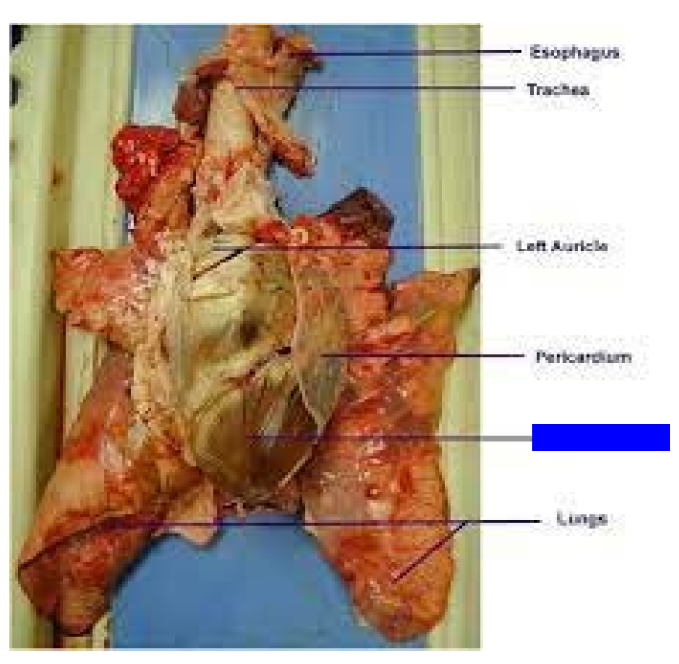
What is this?
Heart
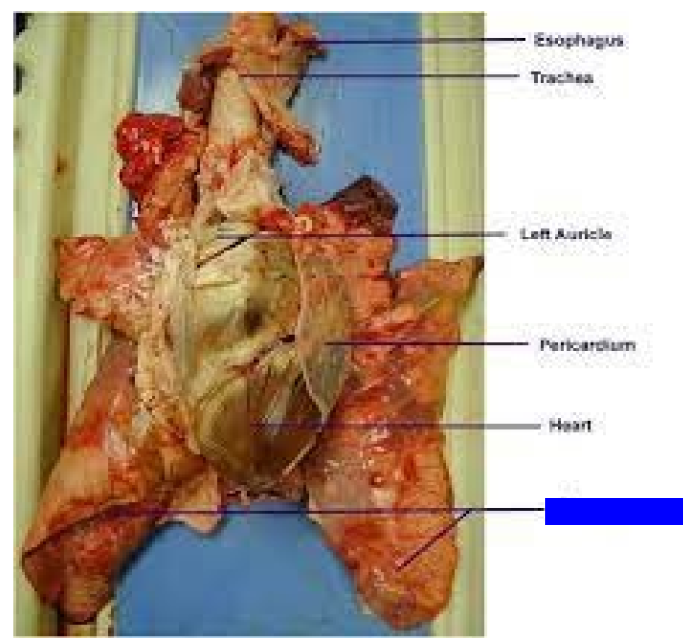
What is this?
Lungs
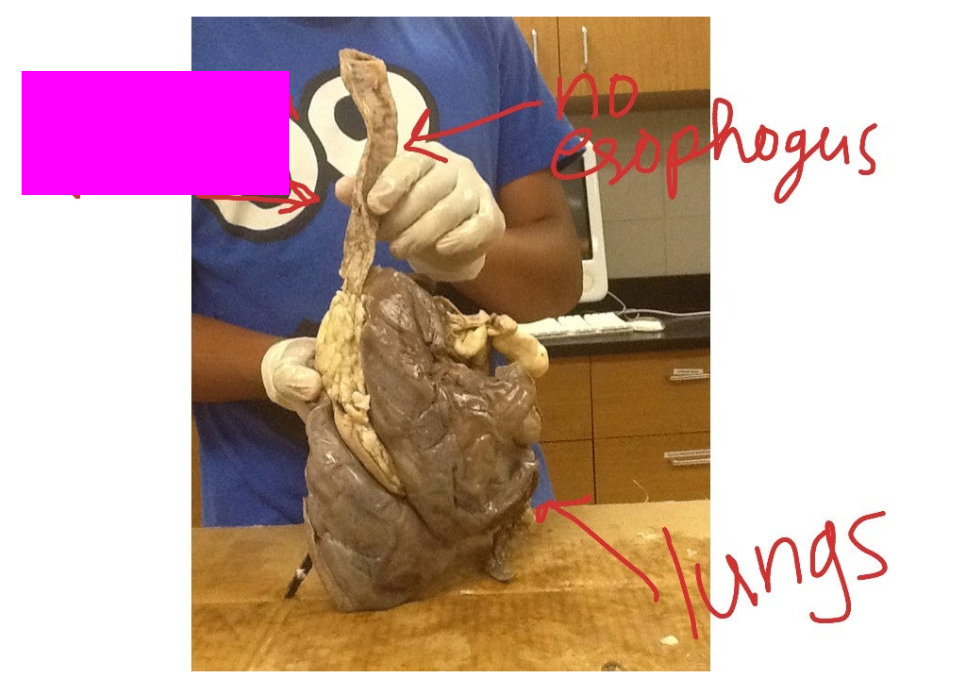
What is this?
Trachea
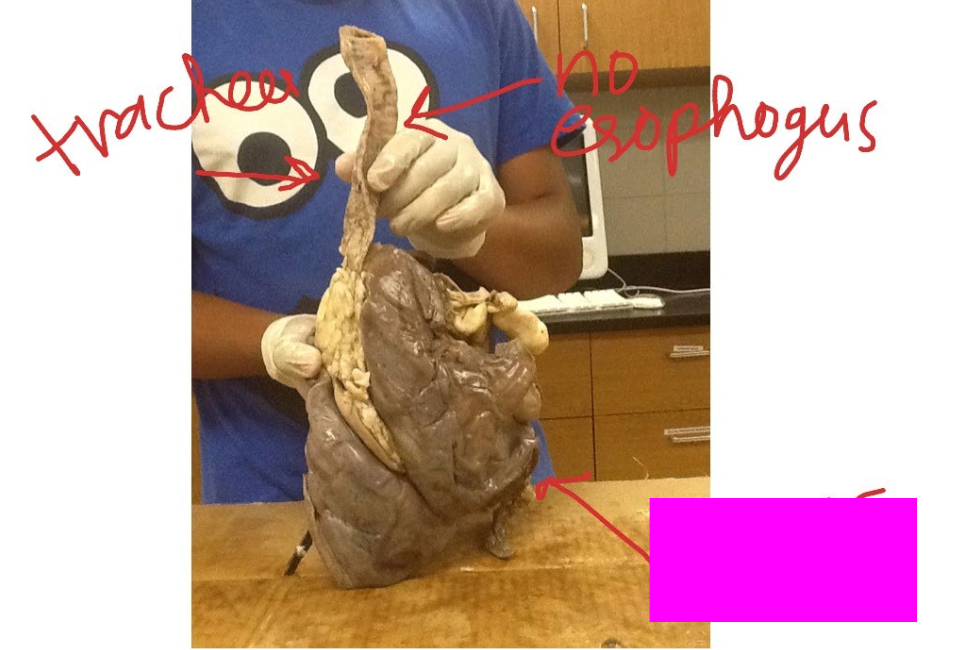
What is this?
Lungs
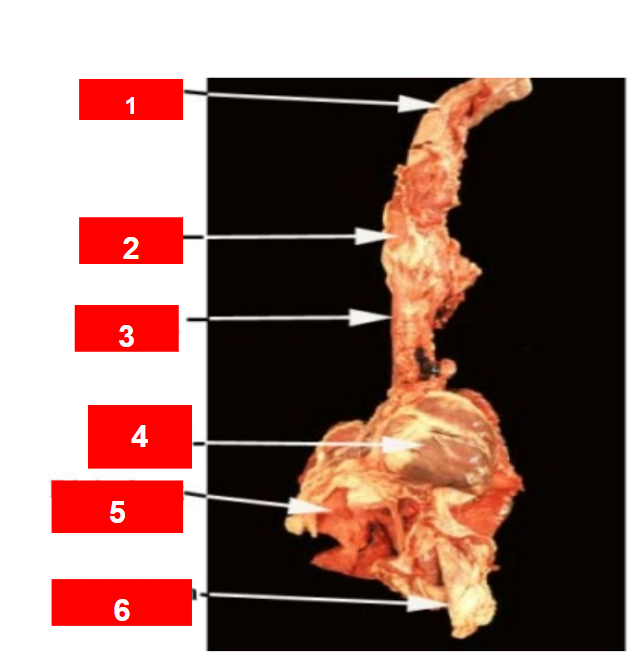
Label 1-6
Tongue
larynx
Trachea
heart
Right lung
Diaphragm
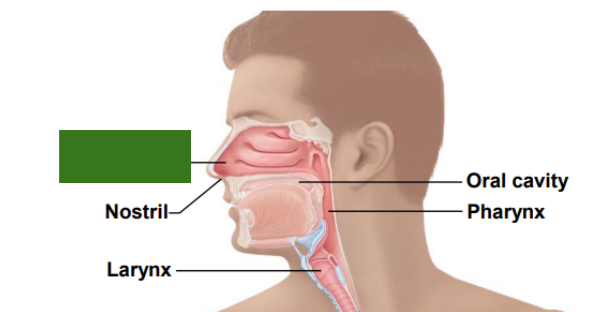
What is this?
Nasal cavity
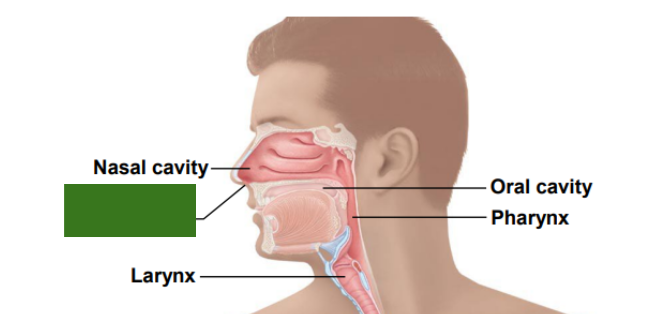
What is this?
Nostril
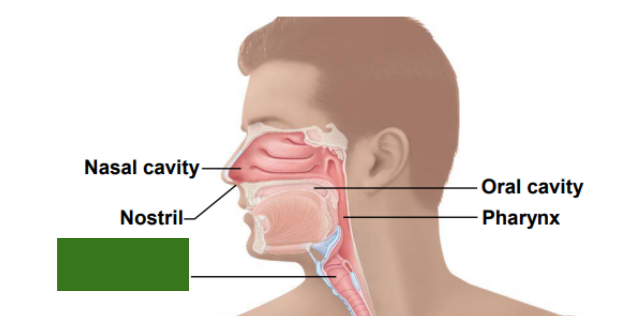
What is this?
Larynx
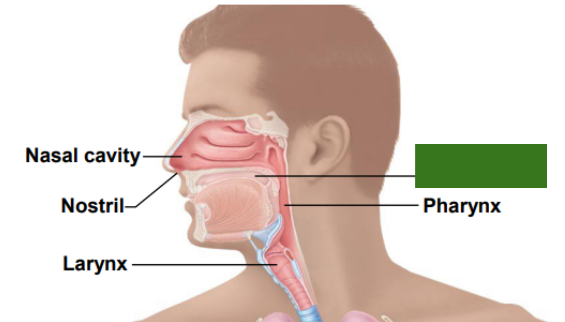
What cavity is this?
Oral cavity
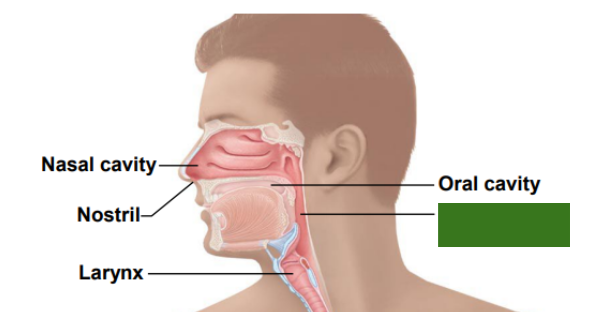
What is this?
Pharynx
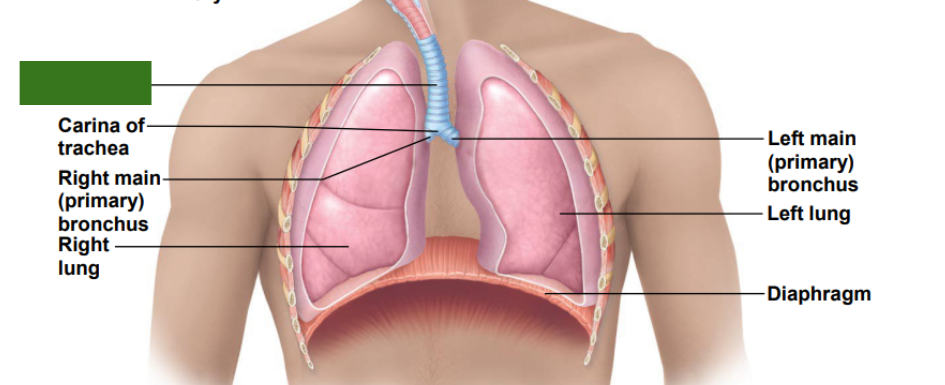
What is this?
Trachea
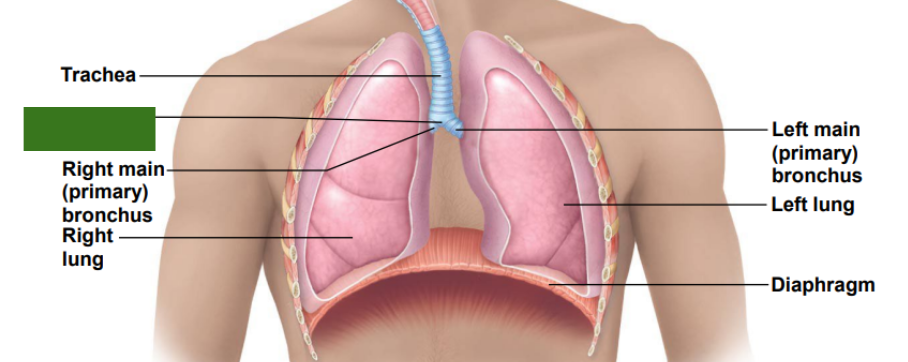
What is this?
Carina of trachea
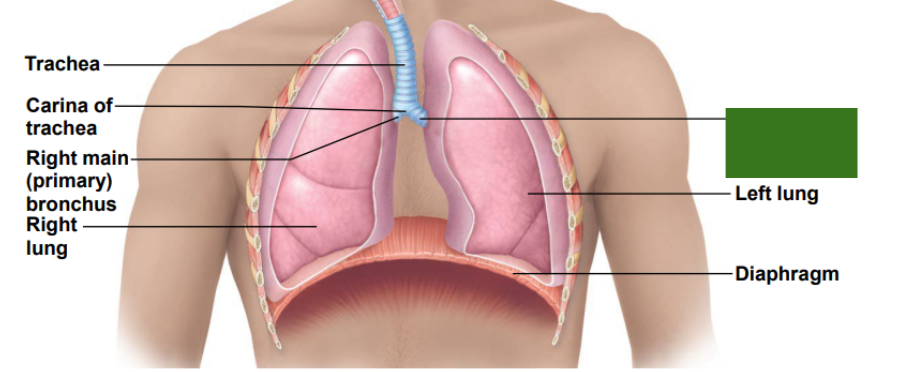
What is this?
Left main (primary) bronchus
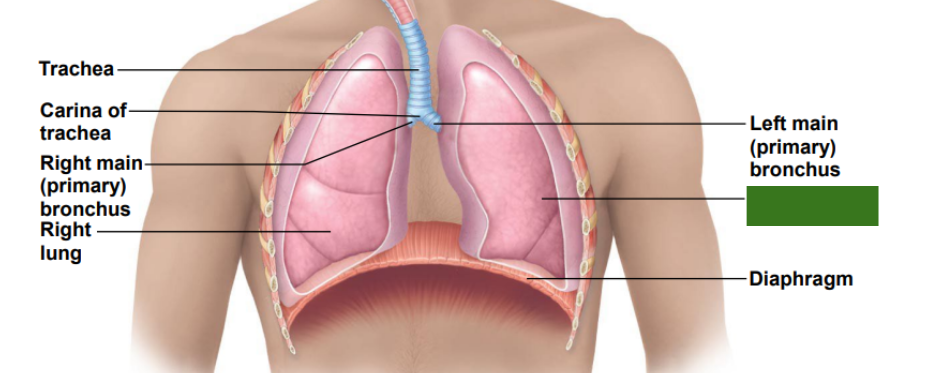
What is this?
Left lung
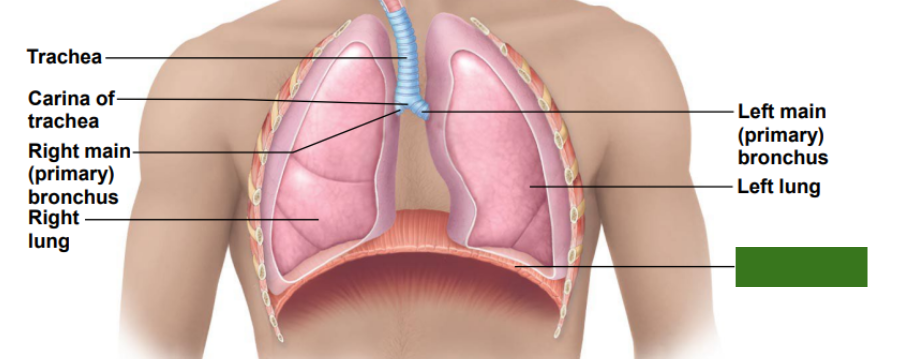
What is this?
Diaphragm
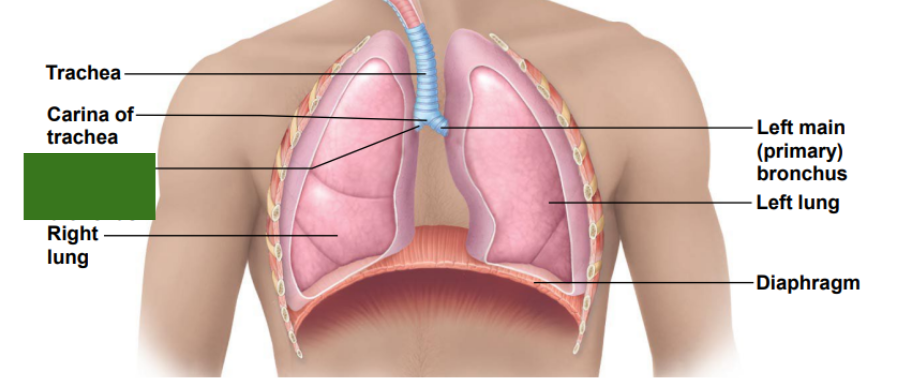
What is this?
Right main primary bronchus
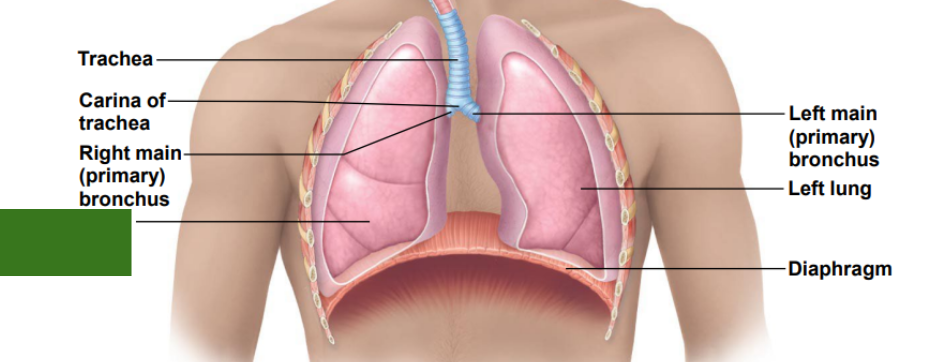
What is this?
Right lung
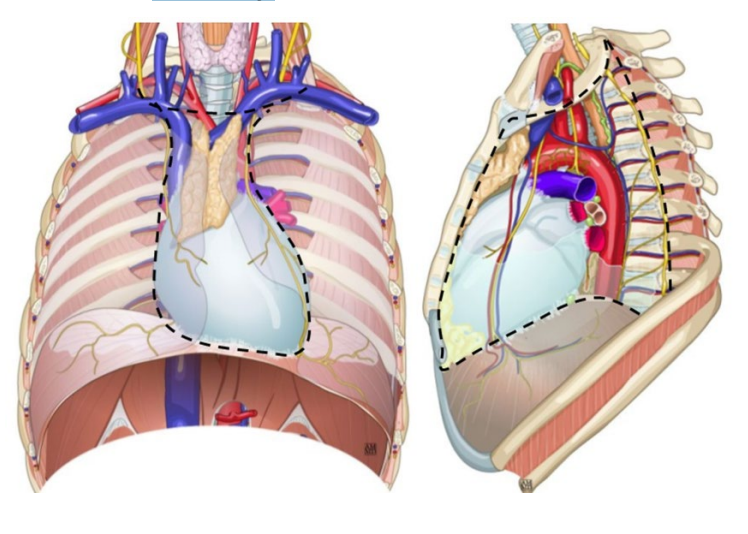
what is the central compartment in the thoracic cavity?
The mediastinum
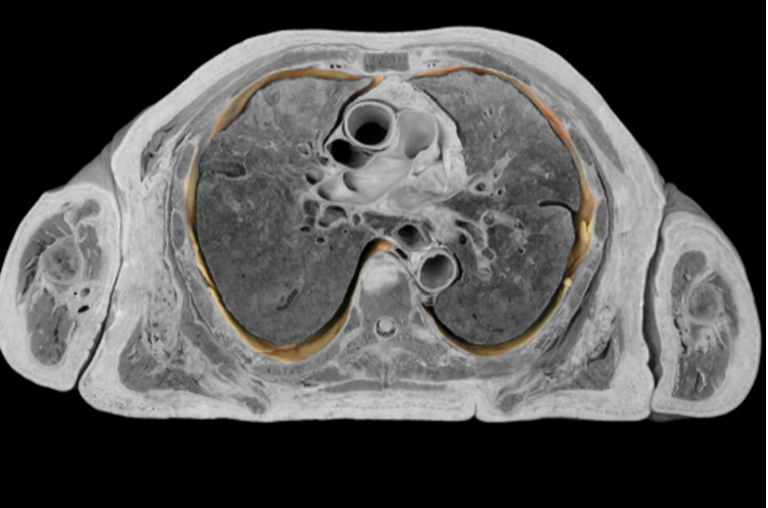
What is this?
PLEURA ( PARIETAL PLEURA)
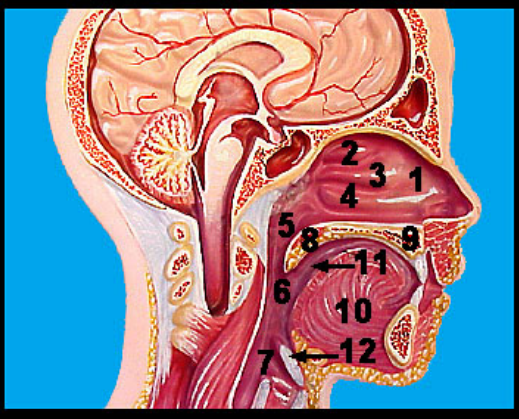
Label the upper respiratory tract 1- 12
1. Nasal cavity
2-4. Nasal conchae
5. Nasopharynx
6. Oropharynx
7. Laryngopharynx
8. Soft palate with uvula
9. Hard palate
10. Tongue
11. Oral cavity
12. Epiglottis
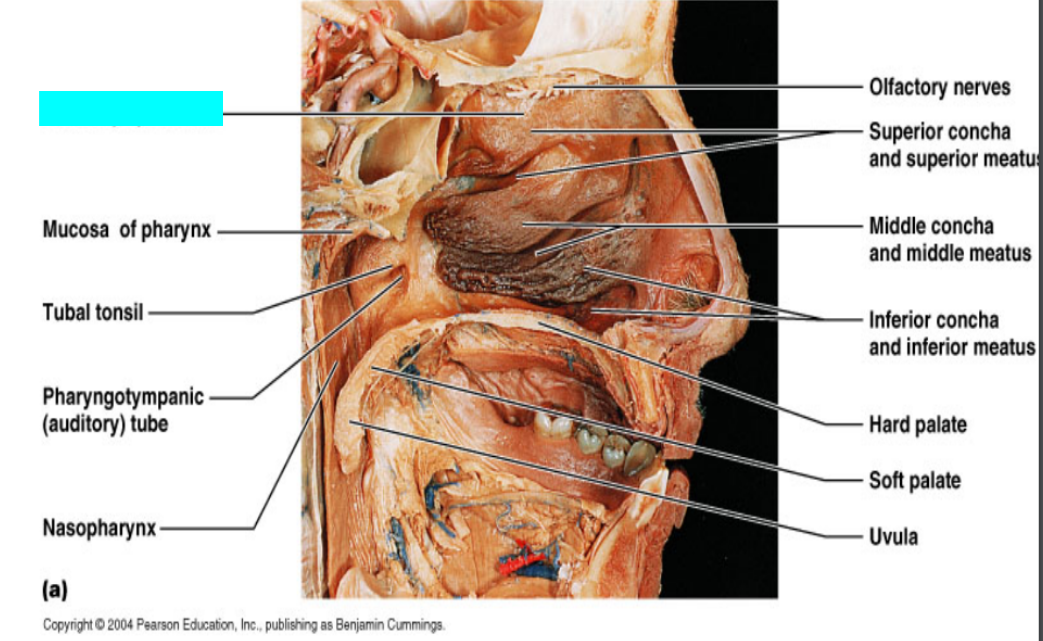
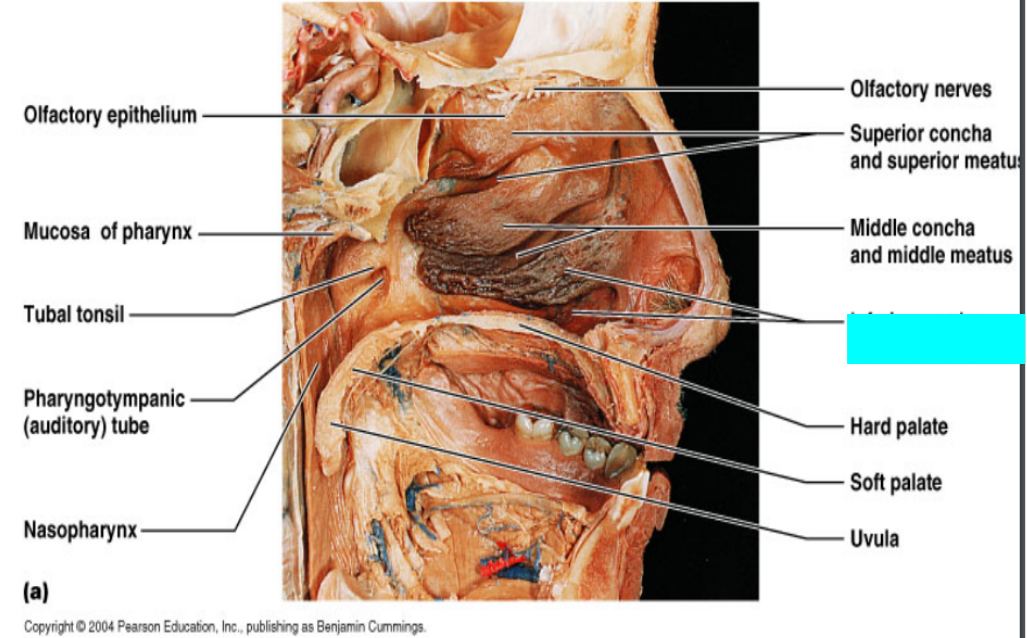
What is this?
Olfactory epithelium
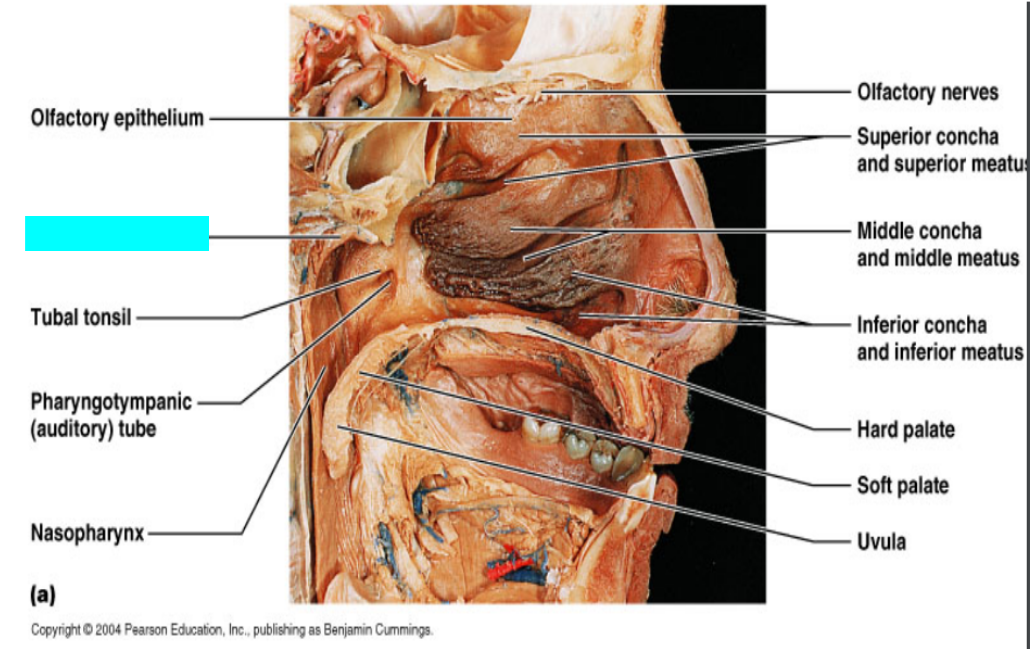
What is this?
Mucosa of pharynx
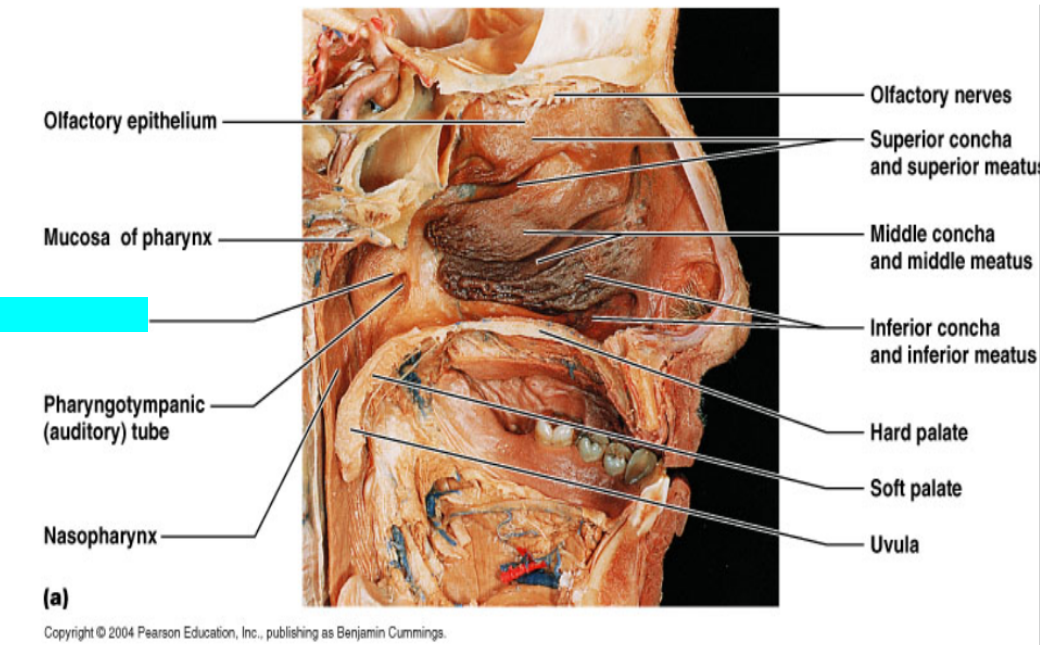
What is this?
Tuba tonsil
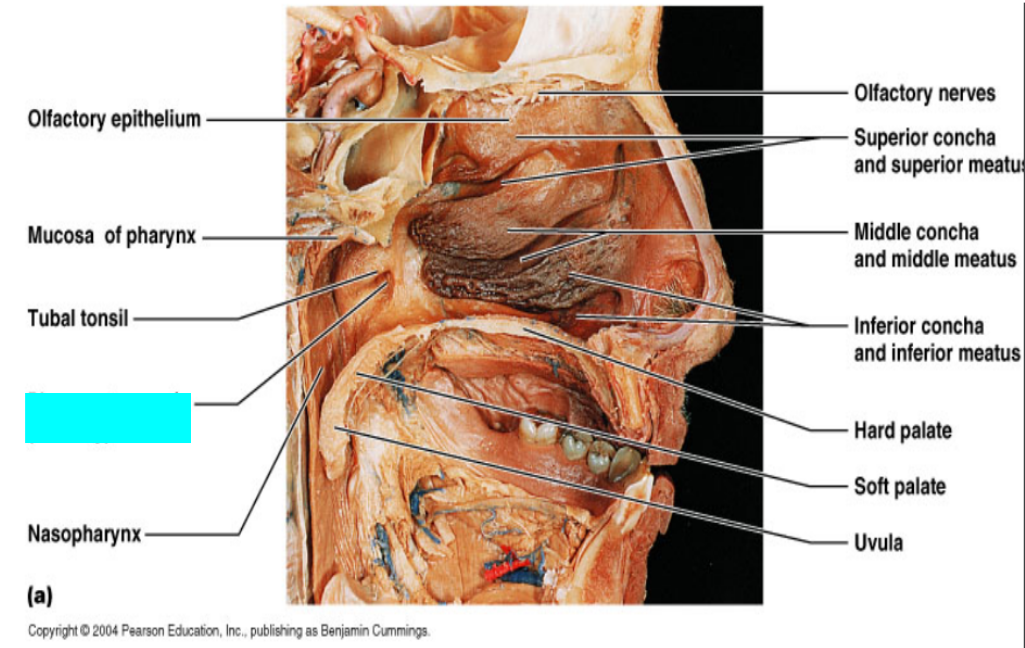
What is this?
Pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube
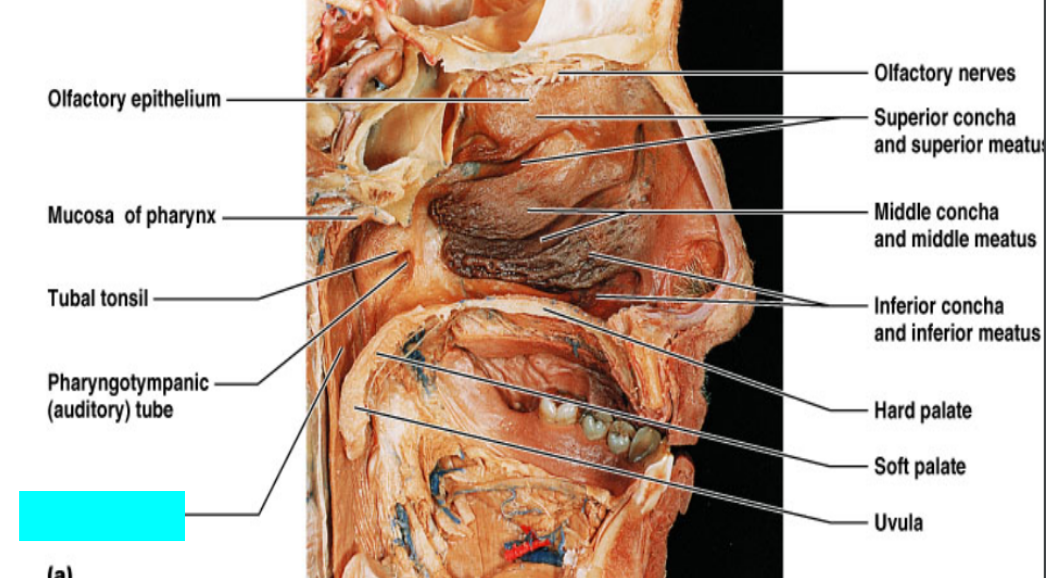
What is this?
Nasopharynx
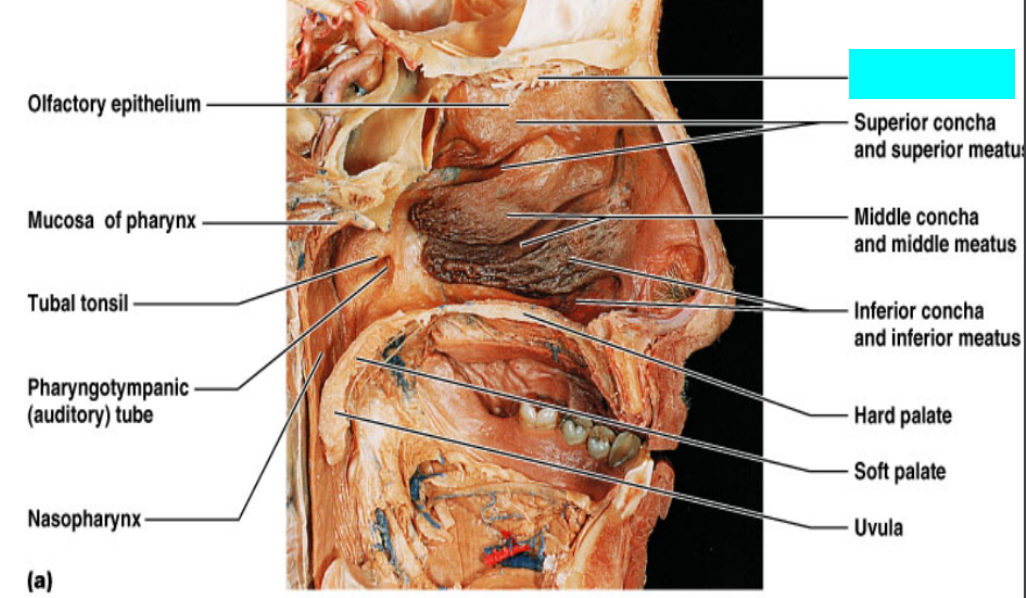
What is this?
Olfactory nerves
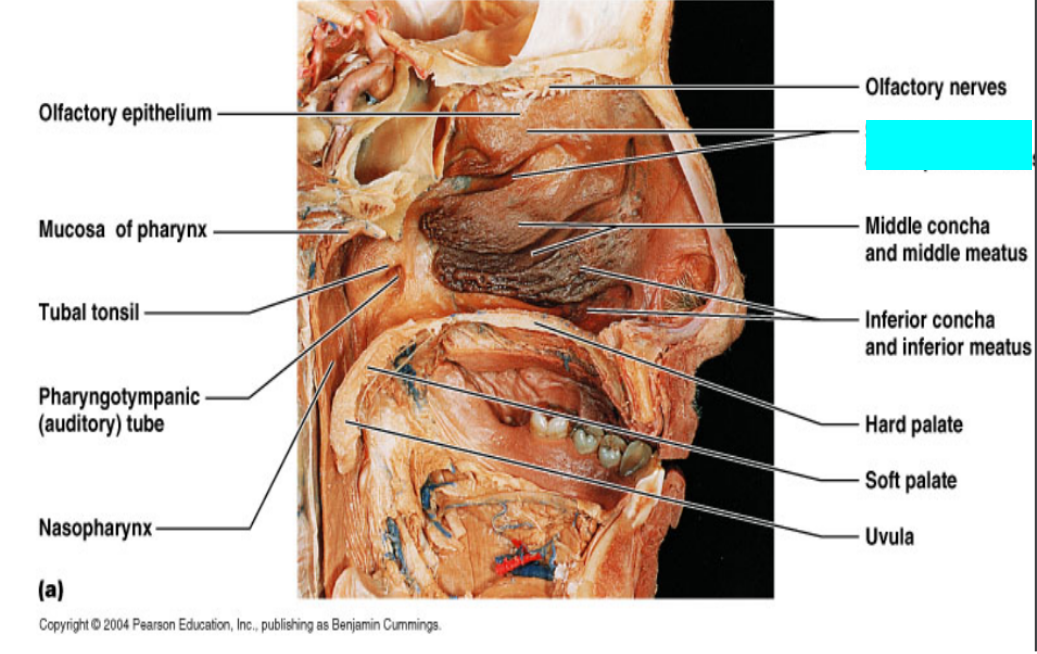
What is this?
Superior concha and superior meatus
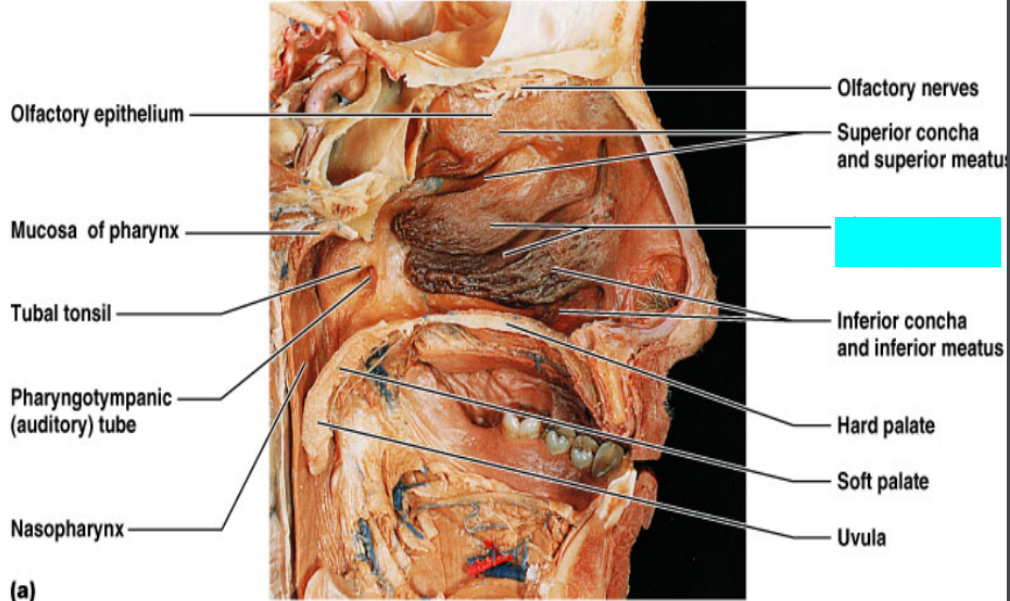
What is this?
Middle concha and middle meatus
What is this?
Inferior concha and inferior meatus
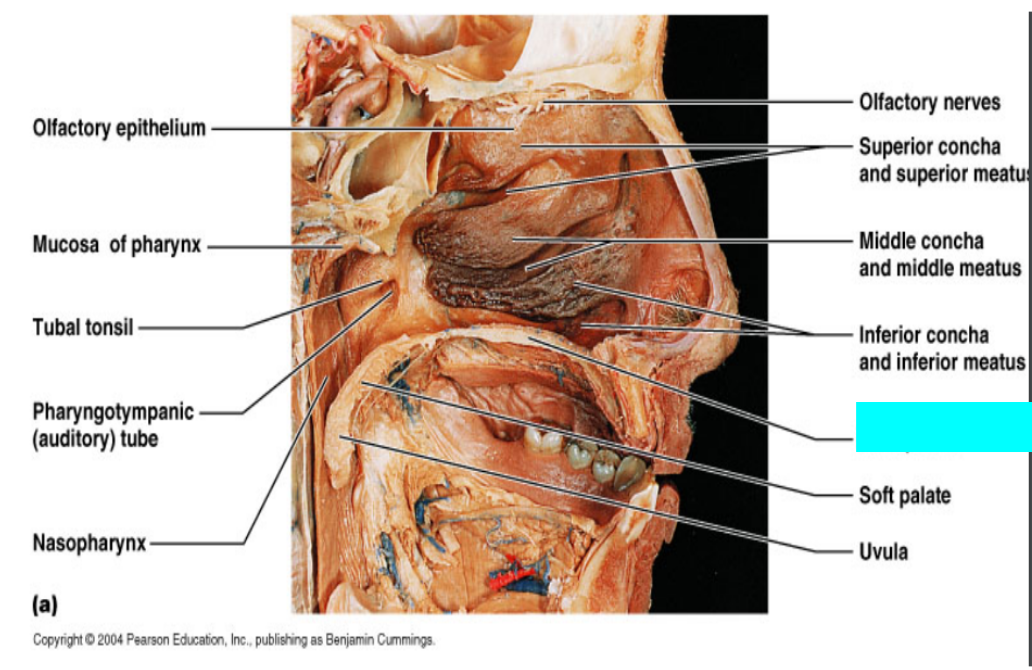
What is this?
Hard palate
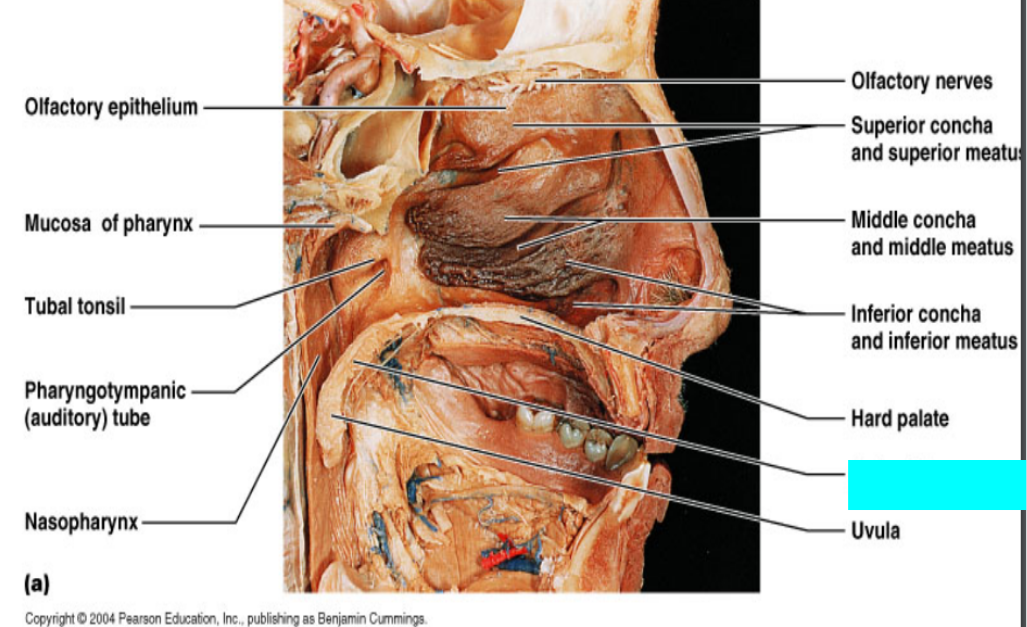
What is this?
Soft palate
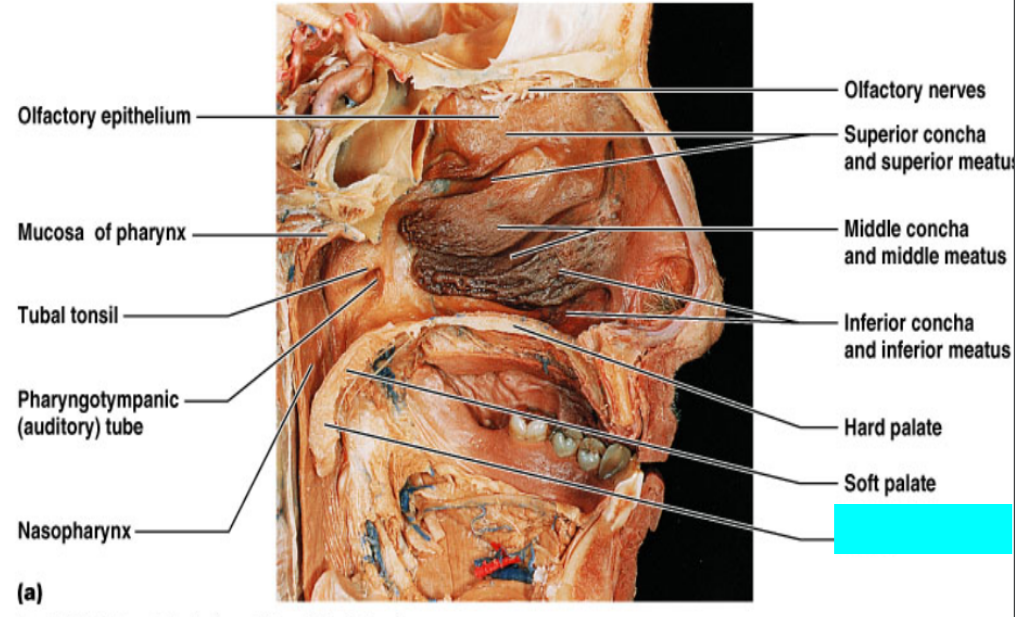
What is this?
Uvula
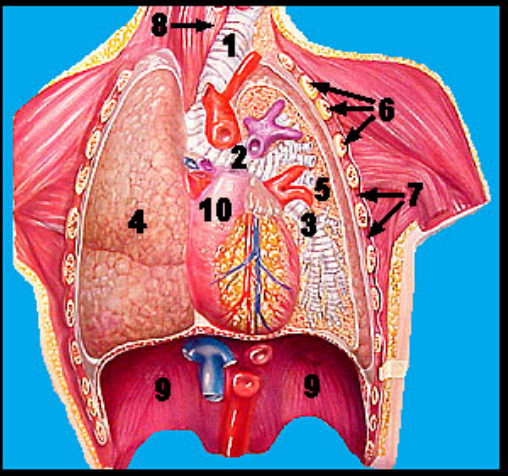
Label the upper respiratory tract 1-10
1. Trachea
2. left primary bronchus
3. Left secondary bronchus
4. Right lung
5. Left lung
6. Ribs
7. Intercostal muscles
8. Esophagus
9. Diaphragm
10. Heart
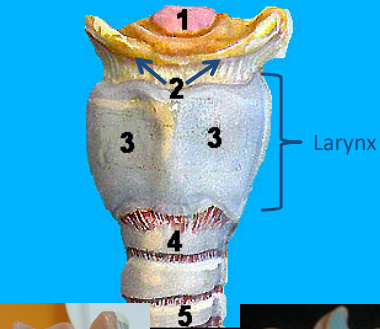
Label 1-5
1. Epiglottis
2. Hyoid bone
3. Thyroid cartilage
4. Cricoid cartilage
5. Trachea
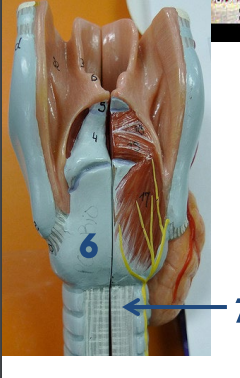
What is 6?
Cricoid cartilage posterior view
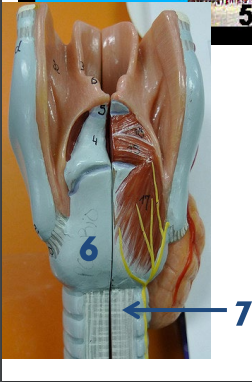
What is 7?
Trachealis muscle
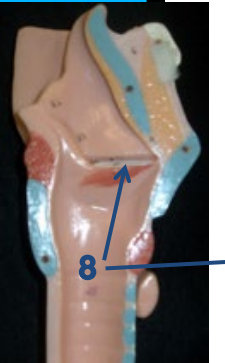
What is 8?
Vocal cords
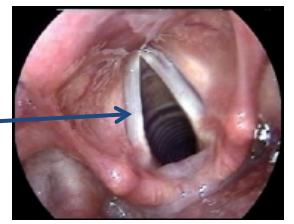
What is this?
vocal cords
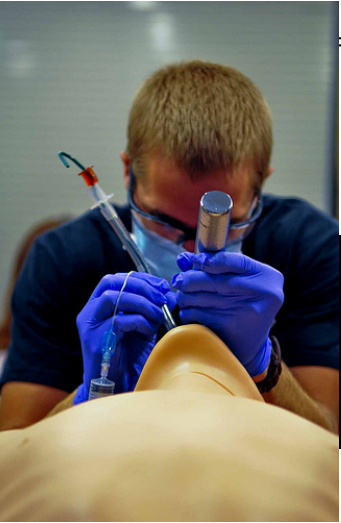
How do you Intubation a patient with a Laryngoscope
When intubating a patient, you need to visualize the vocal cords in the larynx to make sure that you insert the tube in the correct tube (trachea), not the esophagus

What is this?
Laryngoscope
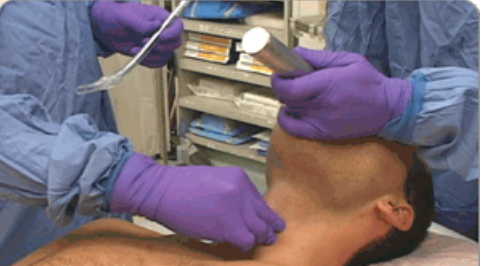
During cricoid pressure intubation, what do you do to the esophagus to minimize the chances of the tube entering the esophagus, and the patients stomach being pumped with air?
Temporarily pinch the esophagus during cricoid pressure.
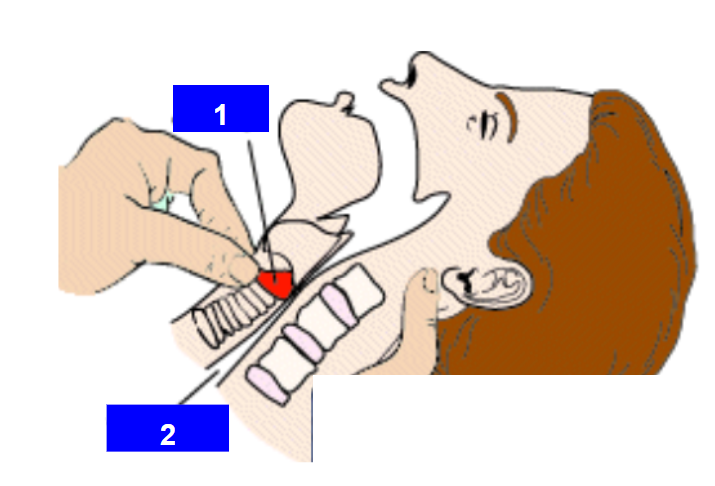
Label 1 & 2
Cricoid cartilage
Esophagus
What is this?
Pressure
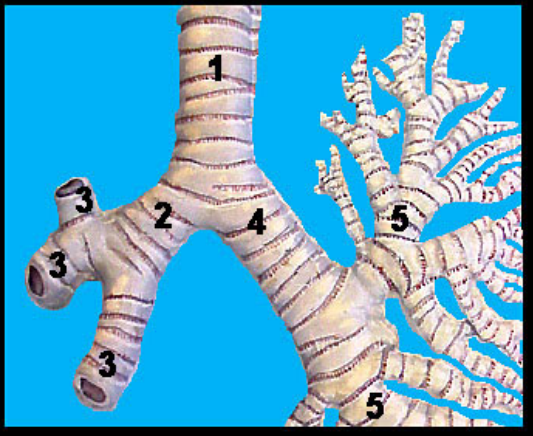
Label 1-5
1. Trachea
2. Right primary bronchus
3. Right secondary bronchi
4. Left primary bronchus
5. Left secondary bronchi
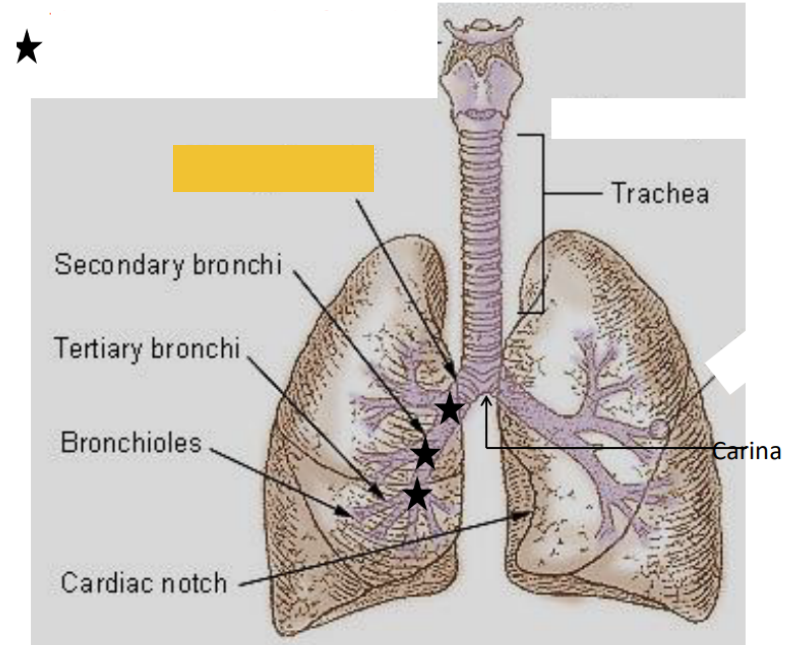
What is this?
Primary bronchi
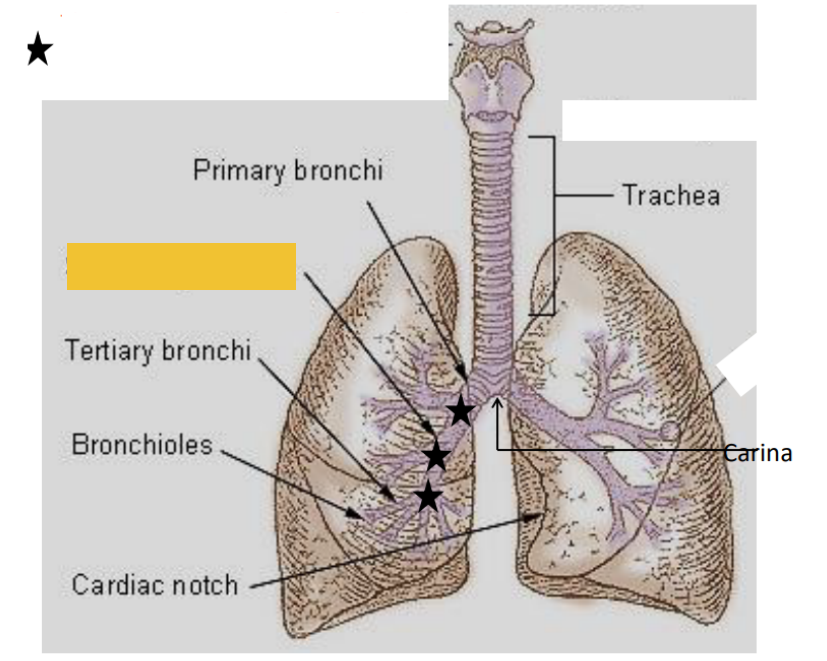
What is this?
Secondary bronchi
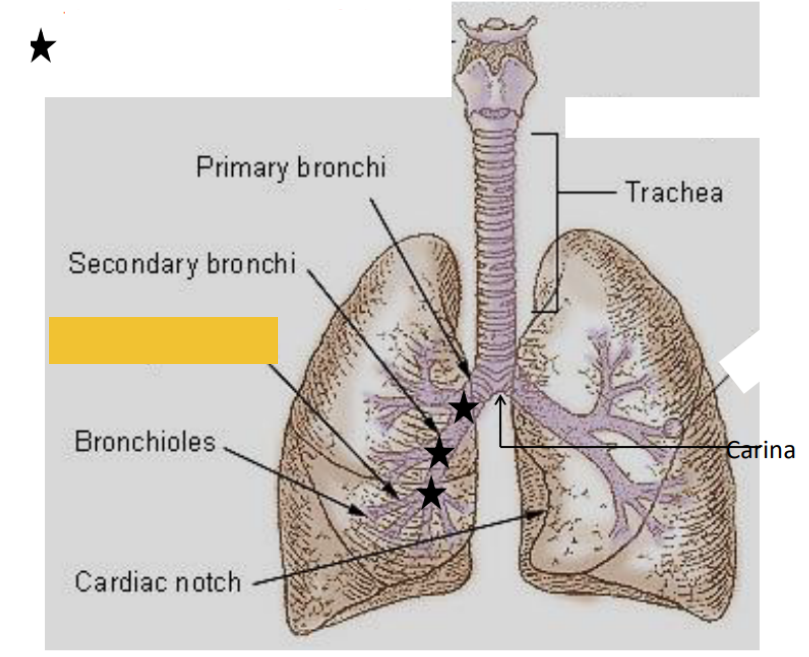
What is this?
Tertiary bronchi
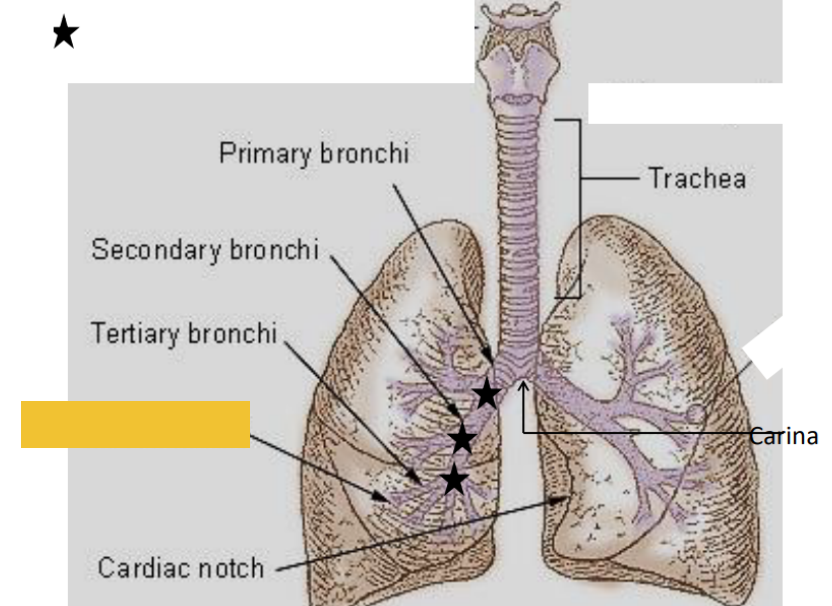
What is this?
Bronchioles
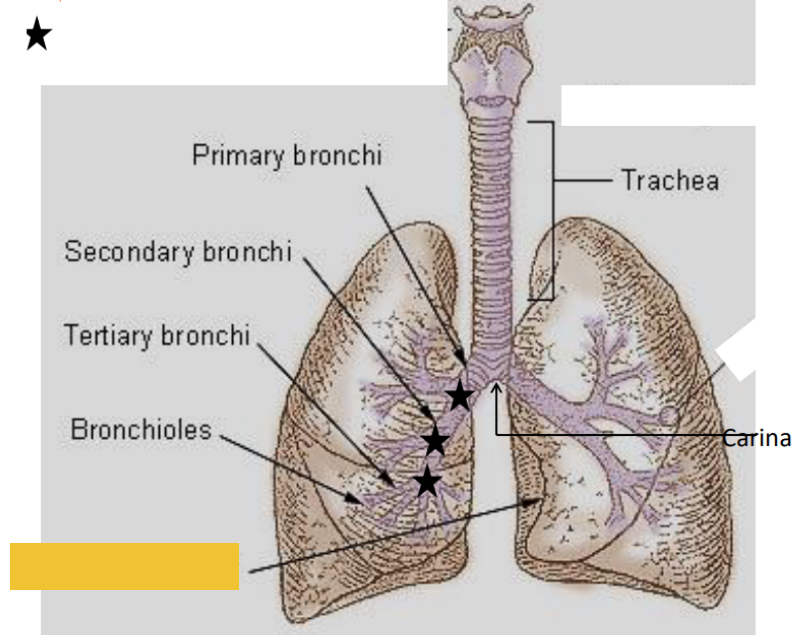
What is this?
Cardiac notch
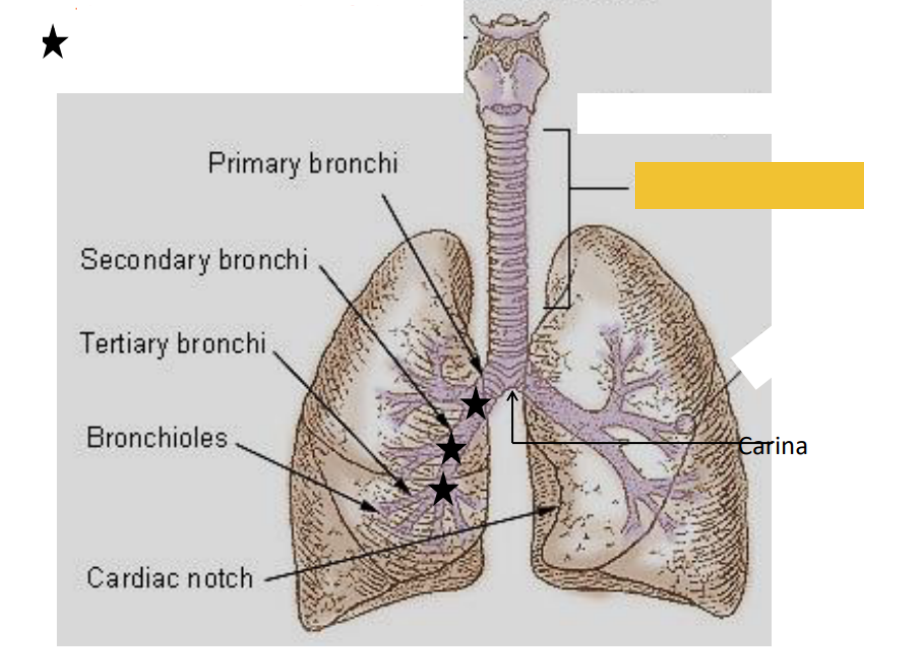
What is this?
Trachea