Chemistry Final Prep
5.0(2)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/65
Last updated 11:00 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
a cation has a ____ charge and is _____ than the atoms in which they are formed
postive, smaller
2
New cards
an anion has a ____ charge and is _____ that the atoms in which they are formed
negative, larger
3
New cards
as you move down on a group on the radius ______
increases
4
New cards
as you move across a period the radius _____
decreases
5
New cards
as you move down a group the ionization energy and electronegativity ______
decreases
6
New cards
as you move across a period the ionization energy and electronegativity ______
increases
7
New cards
the measure of attraction that an atom has for electrons in chemical bonds
electronegativity
8
New cards
how many valence electrons are in the electron dot notation for boron?
3
9
New cards
would it be easier to remove
10
New cards
calculate the empirical formula for C: 36.7%, H: 8.22%, F: 38.7%, O: 16.3%
C3H8OF2
11
New cards
Balance the following equation: __Ca+__HCL = __CaCl2+___H2
Ca+2HCL=CaCl2=H2
12
New cards
synthesis reaction
when two or more substances combine to form one substance
13
New cards
decomposition
a single reactant breaks down to form two or more products
14
New cards
combustion
a compound reacts with oxygen forming heat and light
15
New cards
single replacement
a reaction where an element replaces the atoms of another element
16
New cards
double replacement
a reaction where two compounds cations switch places
17
New cards
succinic acid is a substance produced by lichens. It is composed of 40.68% carbon, 5.08% hydrogen, and 54.24% oxygen and has a molar mass of 118.1 g/mol. What is the empirical formula and the molecular formula.
C2H3O2= empirical, C4H6O4=molecular
18
New cards
determine the limiting reactant of the chemical equation: Fe2O3+C= Fe+ CO2 (unbalanced)
Carbon
19
New cards
Who made the foundation to the periodic table?
Dimitri Mendeleev
20
New cards
Who solidifies the patterns in the periodic table to make periodic law?
Henry Mosely
21
New cards
Where are Alkali Metals on the periodic table?
group 1
22
New cards
Where are alkaline earth metals?
group 2
23
New cards
where are transition metals?
group 3-12
24
New cards
where are halogens?
group 17
25
New cards
where are noble gasses?
group 18
26
New cards
Who used the cathode ray tube to discover electrons?
JJ Thomson
27
New cards
Who used the gold foil experiment to discover the nucleus and protons?
Ernest Rutherford
28
New cards
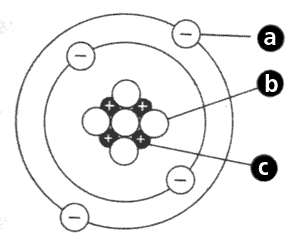
a.______ b._____ c.______
electrons, neutrons, protons
29
New cards
what is the mass number of an element equivalent to?
protons+neutrons
30
New cards
what is the electrons of an element equivalent to?
protons-electrons
31
New cards
atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
32
New cards
ion
an atom of an element that has lost or gained electrons, but still maintains the same number of protons
33
New cards
isotope
an atom of an element that has the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
34
New cards
what is the electron configuration for argon
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6
35
New cards
what is the noble gas notation for the electron configuration for krypton
[Ar], 4s2, 3d10, 4p6
36
New cards
Strontium has 4 isotopes with masses of: 84 (0.50% abundance), 87 (7%), 86 (9.9%), 88 (82.6%)
87.62
37
New cards
where are nonmetals on the periodic table
right side, C to Rn (and H)
38
New cards
where are metalloids
B down to Te
39
New cards
where are metals
left and middle side
40
New cards
find the energy used in the following equation: H2+F2= 2HF
-543kj (exothermic)
41
New cards
A metal weighting 59.047g was heated to 100C and then put it into 100ml of water (initially 23.7C). The metal and water were allowed to come to an equilibrium temperature of 27.8C. Calculate the specific heat of the metal.
q= .402J/g
42
New cards
A total of 54.0 Joules of heat are observed as 58.3g of lead is heated from 12.0°C to 42.0°C. From this data, what is the specific heat of lead?
Specific Heat (C): 0.03
43
New cards
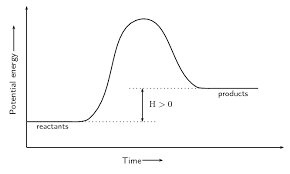
this graph is ______, because it is _____ energy
endothermic, gaining
44
New cards

this graph is _____, because it is _____ energy
exothermic, losing
45
New cards
hydrogen bonds occur between what molecules and hydrogen?
N, O, F
46
New cards
what is the weakest intermolecular force?
London Dispersion Forces (LDF)
47
New cards
An ionic compound cannot conduct as a ______,but can when__ ____.
Solid, dissolved
48
New cards
An ionic compound has a ____ melting point
High
49
New cards
Naming acids:
If the polyatimic ion ends in -ate, change it to ____
If the polyatimic ion ends in -ate, change it to ____
–ic (she ATE but I have an IC)
50
New cards
Naming acids:
If the polyatomic ion ends in –ite, change the ending to ____
If the polyatomic ion ends in –ite, change the ending to ____
\-ous
51
New cards
An ionic bond is between a metal and a _____
Nonmetal
52
New cards
A covalent bond is between two _____
Nonmetals
53
New cards
A gas occupies 12.3L at a pressure of 40 mmHg. What is the volume when the pressure is increased to 60mmHg?
8\.2
54
New cards
The density of a gaseous fluoride of phosphorus is 3.98 g/L at STO. The is the molar mass of this fluoride?
88
55
New cards
“Likes dissolves likes” means…
Polar molecules dissolve polar, and non polar can dissolve non polar molecules
56
New cards
If a bond is non polar it will only what imf?
Ldf only
57
New cards
In order for a bond to be non polar it must have what three things?
1\. Contain polar bonds (electro negativity difference)
2\. All atoms identical
3\. Symmetrical shape
2\. All atoms identical
3\. Symmetrical shape
58
New cards
AX4E0
Tetrahedral (symmetrical)
59
New cards
AX2E1
Bent (NOT symmetrical)
60
New cards
AX3E0
Trigonal planar (symmetrical)
61
New cards
AX2E0
Linear (symmetrical)
62
New cards
What imf would CH3Cl have? (Dipole dipole, hydrogen bond, ldf)
Dipole dipole (polar bonds)
63
New cards
A student needs to prepare a 75ml solution of .2M AgNO3. What mass of AgNO3 is needed?
2\.55g
64
New cards
A teacher needs to prepare a 500ml, 1M solution of HNO3 from a solution of 12M HNO3. What would the volume of the solution need to be?
41\.6ml
65
New cards
Calculate the PH of \[H+\] = 0.01M
2
66
New cards
Calculate the \[H+\] of pH=5.65
2\.2\*10^-6