Bio 103
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Last updated 3:46 AM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
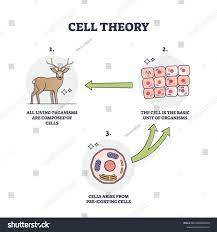
Cell Theory
States that: A cell is the smallest unit of life that makes up all living things. Cells can only come from preexisting cells.
2
New cards
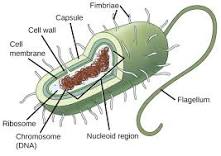
Prokaryotic cells
Don’t have a nucleus or plasma-bound organelles
Grows by binary fission and reproduces using conjunction pili.
Grows by binary fission and reproduces using conjunction pili.
3
New cards
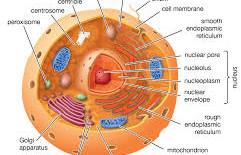
Eukaryotic cells
Have a nucleus (a plasma sack with DNA) and plasma-bound organelles (lysosomes and vacuoles) Grows by mitosis and reproduces using meiosis
4
New cards
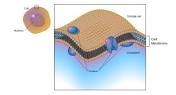
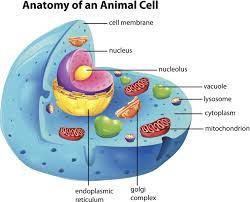
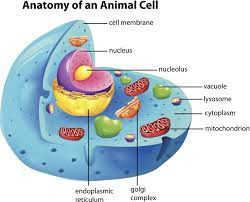
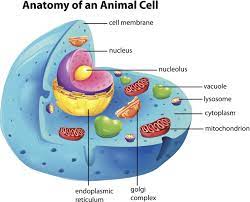
Cell membrane
Forms a boundary to control what goes in or out of a cell.
5
New cards
Cytoplasm
Biological goo with monosaccarides
6
New cards
Ribosomes
Reads mRNA and makes protien
7
New cards
DNA
Prokaryotic: Circular Plasmid
Eukaryotic: Linear Straight
Eukaryotic: Linear Straight
8
New cards
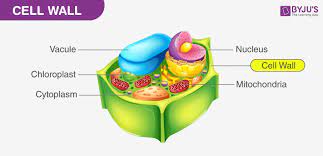
Cell wall
Only fungi and plants
9
New cards
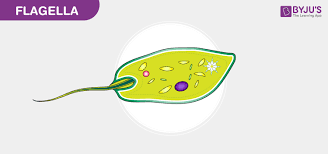
Flagella
For movement both cell type have this, but in eukarya its just sperm cells
10
New cards
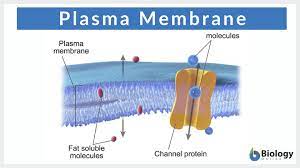
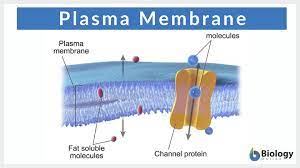
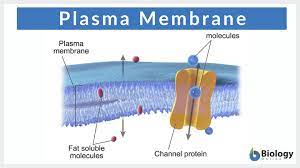
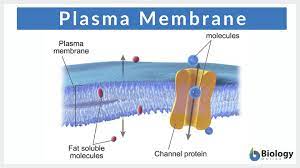
Plasma membrane
controls what goes in or out of the cell
11
New cards
Phospholipids
The most important part of the plasma membrane that has a bond at the tails causing a bilayer that allows water to cross pass.
12
New cards
Proteins
Controls what can cross the plasma membranes
13
New cards
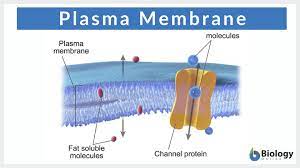
Channel protein
Makes the molecule a specific hole for a particle to pass through the membrane
14
New cards
Pump protein
Uses ATP to move big molecules like glucose
15
New cards
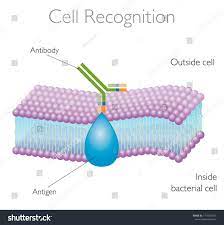
Cell recognition protein
Helps the immune system
16
New cards
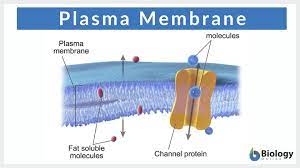
Receptor protein
binds molecules
17
New cards
Charbohydrates
help the immune system know self from nonself
18
New cards
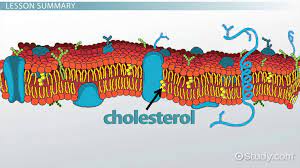
Cholesterol
Keeps plasma membrane stable
19
New cards
Fluid mosaic model
Explains how the plasma membrane functions

20
New cards
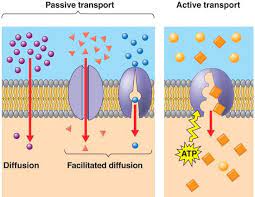
Simple diffusin
Moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration without using any ATP
21
New cards
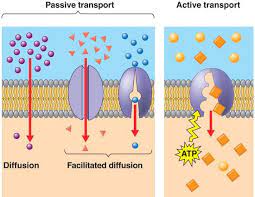
Facilitated diffusion
Moving from high concentration to low concentration with a protein and no ATP energy (Faster)
22
New cards
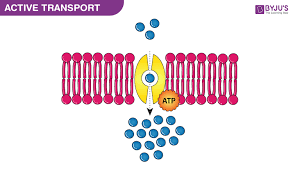
Active Transport
Using ATP to move things
23
New cards
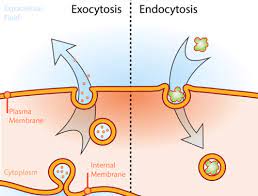
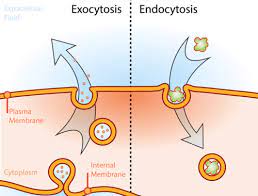
Endocytosis
Cell brings in a lot of molecules all at one time. The cell does this by using the cell membrane to pinch inward to make a vesicle
24
New cards
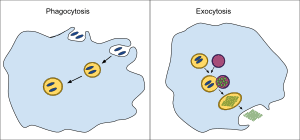
Phagocytosis
When a cell eats another organism
25
New cards
Exocytosis
Moving a lot of molecules out of a cell at one time
26
New cards
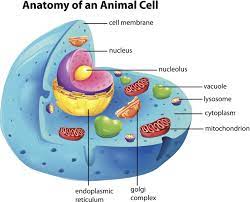
Organelle
Tiny organ inside a cell with a specific function
27
New cards
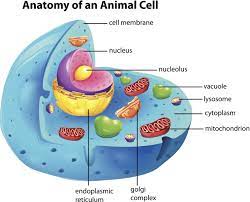
Nucleus
Plasma membrane sack of DNA. DNA can’t leave the nucleus
28
New cards
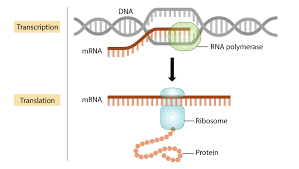
mRNA
Messenger RNA which can leave the nucleus
29
New cards
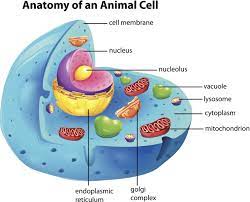
Endomembrane system
Plasma membrane-bound organelles inside the cell
30
New cards
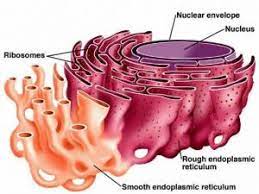
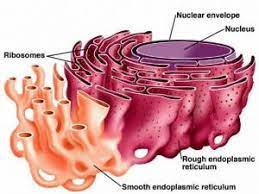
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Ribosome attached membrane sack for protein folding
31
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Plasma membrane sack that makes lipids and detoxifies cells
32
New cards
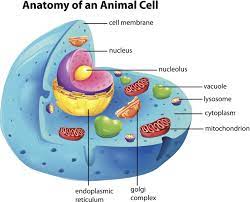
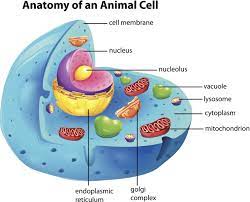
Golgi Apparatus
Folding proteins
33
New cards
Lysosome
Enzyme responsible for breaking down engulfed particles and old organelles.
34
New cards
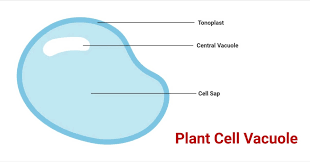
Vacule
Storing stuff i.e. Lipids and water
35
New cards
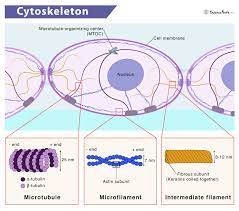
Cytoskeleton
Organelles giving cells their shape and structure
36
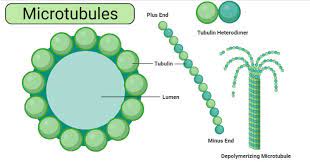
New cards
Microtubule
Protein rods that are made to be a highway for the motor proteins
37
New cards
Filament
Protein rod near cell membrane which helps give shape as well as muscle contractions
38
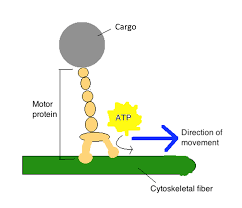
New cards
Motor Proteins
Move molecules across the cell (Each Step uses 1 ATP energy Molecule)
39
New cards
Energy Cells/System
Organelles making energy molecules
40
New cards
Chloroplast
Has 3 separate membranes and has its own DNA separate from the nucleus. This organ preforms photo synthesis
41
New cards
Mitochondrion
Has 2 separate membranes and has its own DNA separate from the nucleus. This cell performs Aerobic Cellular Respiration by turning glucose into ATP energy
42
New cards
Endosymbiosis Theory
Explains why some eukaryotic cells have chloroplasts and mitochondrion organelles
43
New cards
Brownian Motion Theory
All molecules are constantly moving and go from high to low concentration without using energy (simple diffusion)
44
New cards
Osmosis
Water moving
45
New cards
Green tube experiment
Water moves from low concentration to high causing osmosis
46
New cards
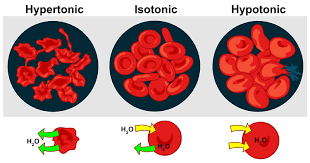
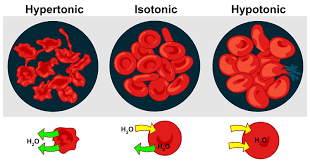
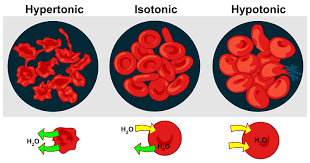
Isotonic
Same solute: water ratio on the inside and outside of the cell.
47
New cards
Hypertonic
One solution has more solute causing the water to flow out of the cells making them shrivel and die
48
New cards
Hypotonic
One solution has less solute and more water this is because the water flows into the cell. Plant cells will stay healthy, but animal cells will pop/burst.
49
New cards
Antibiotic
A chemical that kills prokaryotic and bacteria cells
50
New cards
Energy
Capacity to do work
51
New cards
Kinetic Energy
Motion energy
52
New cards
Potential Energy
Stored Energy
53
New cards
ATP
Adenine triphosphate most common form of energy
54
New cards
Thermodynamics
Energy laws that all biological systems follow
55
New cards
Law number 1
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can change from one form to another.
56
New cards
Law number 2
Energy cannot change from one for to another without loss of usable energy (Heat)
57
New cards
Cellular Motabolism
All chemical reactions inside a cell
58
New cards
Metabolic Pathway
Specific sequence of enzymes turning inputs into outputs
59
New cards
Big Theme
Biological systems are lazy and want to do the most work with the least amount of effort
60
New cards
Enzyme
protein with a specific shape that if broken won’t work anymore.
61
New cards
Denature
Changing the shape of an enzyme. Things that can cause denature are: Heat, pH, Salt/salinity
62
New cards
Catabolic
Bond breaking
63
New cards
Anabolic
Bond Making
64
New cards
Lactuse
Breaks lactose disaccharide into a monosaccharide
65
New cards
Trypsin
Turns milk protein casein into a morphine analog