MCAT Physics and Math - Circuits
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
current
the flow of positive charge
metallic conductivity
seen in solid metals and the molten forms of some salts; sea of electrond
electrolytic conductivity
seen in solutions; depends on the strength of a solution; measured by placing the solution as a resistor in a circuit and measuring changes in voltage across the solution
Conductance
reciprocal of resistance
unit: siemens (S)
conductivity
act as a medium through which current can pass
Siemens per meter (S/m)
metallic bond
visualized as a sea of electrons flowing over and past a rigid lattice of metal cations; equal distribution of the charge density of free electrons across all of the neutral atoms within the metallic mass
current (I)
amount of charge Q passing through the conductor per unit time ∆t
unit: ampere (1 A = 1 C/s)
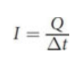
direct current (DC)
charge flows in one direction only
ex. household batteries
alternating current (AC)
flow changes direction periodically
ex. supplied over long distances to homes and other buildings
potential difference (voltage)
produced by an electrical generator, a galvanic (voltaic) cell, a group of cells wired into a battery,
electromotive force (emf or ε)
no charge is moving between the two terminals of a cell that are at different potential values; “pressure to move” that results in current
units: volts or joules/coulomb
Kirchhoff’s Junction Rule
At any point or junction in a circuit, the sum of currents directed into that point equals the sum of currents directed away from that point.
Iinto junction = Ileaving junction
Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule
Around any closed circuit loop, the sum of voltage sources will always be equal to the sum of voltage (potential) drops
Vsource = Vdrop
Resistance
opposition within any material to the movement and flow of charge
unit: ohms (Ω)
resistors
Conductive materials that offer amounts of resistance between conductors (no resistance) and insulators (very high)
where ρ is the resistivity, L is the length of the resistor, and A is its cross-sectional area
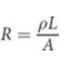
resistivity (ρ)
number that characterizes the intrinsic resistance to current flow in a material; greater resistance at higher temperatures
unit: ohm–meter (Ω · m)
conduction pathways
number of pathways through the resistor; inversely proportional to resistance
Ohm’s Law
basic law of electricity because it states that for a given magnitude of resistance, the voltage drop across the resistor will be proportional to the magnitude of the current
V = IR
where V is the voltage drop, I is the current, and R is the magnitude of the resistance
internal resistance (rint)
wires and emf sources often have some small amount of resistance
V = Ecell – irint
where V is the voltage provided by the cell, Ecell is the emf of the cell, i is the current through the cell, and rint is its internal resistance
secondary batteries
can be recharged; external voltage is applied in such a way to drive current toward the positive end of the secondary battery; galvanic (voltaic) cell when it discharges and as an electrolytic cell when it recharges
Power
ratio of work (energy expenditure) to time; rate at which energy is dissipated by a resistor;interconverted by substitution using Ohm’s law
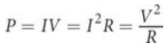
Resistors in Series
voltage drops are additive
Rs = R1 + R2 + R3 + ⋯ + Rn
equivalent/resultant resistance
set of resistors treated as a single resistor with a resistance equal to the combination of the individual resistances, in series or parallel
Resistors in Parallel
inverse relationship between the portion of the current that travels through a particular pathway and the resistance offered by that pathway; when n identical resistors are wired in parallel, the total resistance is given by R/n
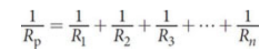
Capacitors
hold charge at a particular voltage; charge on the capacitor increases
ex. defibrillator
discharging
releasing charge
capacitance
ratio of the magnitude of the charge stored on one plate to the potential difference (voltage) across the capacitor
unit: farad (1 F = 1 C/V)
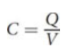
parallel plate capacitor
where ε0 is the permittivity of free space A is the area of overlap of the two plates, and d is the separation of the two plates
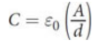
uniform electric field
separation of charges between the capacitor plates with parallel field vectors from the positive plate toward the negative plate
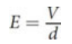
potential energy stored in a capacitor
dielectric material
insulation; decreases capacitance
C′ = κC
where C′ is the new capacitance with the dielectric present and C is the original capacitance
dielectric constant (κ)
measure of insulating ability; a vacuum has a dielectric constant of 1, by definition
Capacitors in Series
total capacitance decreases in similar fashion to the decreases in resistance seen in parallel resistors
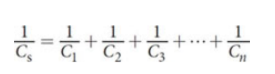
Capacitors in Parallel
resultant capacitance that is equal to the sum of the individual capacitances
Cp = C1 + C2 + C3 + ⋯ + Cn
meters
devices that are used to measure circuit quantities in the real world
Ammeters
measure the current at some point within a working circuit; wired in series; ideal no resistance
voltmeter
used to measure the voltage drop across two points in a circuit; wired in parallel; ideal infinite resistance.
ohmmeter
calculate resistance by knowing the ohmmeter’s voltage and the current created through another point in the circuit; does not require a circuit to be active