Bacteriology and Oral Diseases; pptx 1 & 2(PRE QUIZLET)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
bacteriology
study of bacteria and archaea
Mycology
study of fungi
Parisitology
study of parasites
virology
study of viruses and prions
what are prions?
misfolded versions/mutated protein that can cause disease
what is the size of Bacteria & Archaea
0.5 - 5µm
conversion from micrometer(µm) to millimeter(mm)
1µm = 0.001mm
what is the size of Protozoa?
5-1,000 µm
What is the size of fungi?
5-100µm
what is the size of viruses?
0.002 - 0.05µm
how did bacteria allow the production of other living organisms?
-used photosynthesis
-produced oxygen
-recycling of elemental nutrients
-allow for nitrogen fixation
-break down organic matter(shit)
how do bacteria help animals?
-prevent potential pathogens form gaining a foothold
-help digest good
-provide essential nutrients
- can break down cellulos
what essential nutrients do bacteria help provide?
vitamin K and B
what is passing gas the biproduct of?
bacteria breaking down food in an organisms stomach
bovine rumen
organ that harbours bacteria that digest cellulose and other polysaccharides
bacteria allow cow to obtain nutrients from grass/grain diets. Cow provides habitat for bacterial growth and a continual food supply
Beneficial cultural impact of microbes
-production of biofuels
-production of fermented foods
-production of antibiotics and drugs
-sewage treatment
Detrimental cultural impact of microbes
-Industrial biofouling
-food spoilage
-Disease
Robert Hooke
-reported that living things were composed of little boxes or cells
-The first to describe microorganisms
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
first to describe bacteria, further progress required development of more powerful microscopes
Discoveries by Leeuwenhoek
-Bacteria
-Yeast
-Protozoa
-Blood Cells
-Capillaries
-blood circulation
-spermatozoa
-muscle fibers
-dust mites
-nematodes
-rotifers
Louis Pasteur's experiments
-Disproved spontaneous generation. Said that all cells come from preexisting cells (Cell Theory)
-microbes cause fermentation
-Pasteurization
Studies on fermentation
-Alcoholic fermentation is caused by living yeast cells
-Fermentation does not require oxygen
-Wine is spoiled by lactic acid-producing bacteria
Pasteurization prevents the spoilage of wine
Spontaneous generation
the mistaken idea that living things can arise from nonliving sources, disproven by Pasteur through his experiment with 1 sterile and one non sterile broth
Robert Koch
-Development of pure culture methods
-Microbes cause disease
-streak plate
Who suggested the use of agar instead of gelatin for streaking?
Dr. Hess's wife
Why is agar a better solidifying agent than gelatin?
it has a higher melting point
what is agar made from?
seaweed
Koch's Postulates
a sequence of experimental steps for directly relating a specific microbe to a specific disease
What are Koch's postulates?
1. The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease.
2. The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
3. The pathogen from the pure culture must cause the disease when it is inoculated into a healthy, susceptible laboratory animal.
4. The pathogen must be isolated from the inoculated animal and must be shown to be the original organism.
Alexander Fleming
discovered penicillin
Age of molecular biology
1944-1966 and included:
-DNA
-mRNA
-Ribosome
-tRNA
-Codon
-Genetic code
-Gene
-Operon
Age of genetic engineering
1973-1977 and included:
-Restriction endonuclease
-Recombinant RNA
-DNA sequencing
Age of genome sequencing
1995-present and includes:
-First bacterial genome sequence
-First metagenomic sequence
-Bacterial genomes sequenced
660,00 bacterial genomes sequenced
Willoughby B. Miller
-chemo-parasite theory of caries
-Focal infection theory
-Bacteria produce acid in oral cavity that causes tooth decay
focal infection theory
A hypothesis that bacteria existing in a primary site-the focus-may gain entry into the circulatory system and cause diseases elsewhere in the body.
What kinds of bacteria usually have a pigment? why?
Bacteria that grow in the air because it protects them from light (UV radiation)
If a bacteria reflects light
that usually means that they have a capsule
Polymorphic bacteria
Bacteria which change their structure depending on environment and gene expression
coccus
round
Rod (bacteria)
bacillus, rod shaped
Spirillum
spiral shaped bacteria
spirochete
A bacterium having a spiral shape (plural = spirochetes)
appendaged bacteria
possess extensions of their cells as long tubes or stalks
filamentous bacteria
form long, thin cells or chains of cells
Scientific names for organisms
genus and species
what are the rules when writing the names of organisms?
The names are italicized of underlined. The genus is capitalized and the species if lower case. After first use, can be abbreviated with the first letter of genus and the species e.g. Escherichia coli --> E. Coli
Pathogenesis
ability for disease to develop
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
An electron microscope used to study the internal structure of thin sections of cells
pepdidoglycan
the polymer made of sugars and amino acids found in the cell wall of bacteria.
What is the composition of the cell membrane of bacteria?
Composed of phospholipids similar to that of eukaryotes
What are the functions of the cell membrane in bacteria?
-permeability; prevent leakage and functions as a gateway for transport of nutrients into and out of the cell
-protein anchor; site of many proteins involved in transport, bioenergetics, and chemotaxis
-energy conservation; site of generation and use of the proton motive force(the gradient)
Would a antibiotic that is designed to attack the cell membrane on a bacteria also attack our(human) cells?
Yes, it can damage our cells as well since they are composed of the same structure
can antibiotics bypass the cell membrane easily?
No
gram-negative
Describing the group of bacteria that have a cell wall that is structurally more complex and contains less peptidoglycan. Often more toxic than gram-positive bacteria.
gram positive
Describing the group of bacteria that have a cell wall that is structurally less complex and contains more peptidoglycan. Usually less toxic than gram-negative bacteria.
LPS (lipopolysaccharide)
A molecule consisting of lipids and polysaccharide moieties that is a major component of the cell wall of gram negative bacteria.
Which bacteria type is it harder to produce antibiotics for? why?
gram-negative, because it has 2 cell membranes
peptidoglycan structure
Chains of sugars (NAG and NAM) which are connected by a β 1-4 cross link which also has a peptide interbridge link between 2 NAMs from with the other chains on either side connecting them together to make a mesh like structure
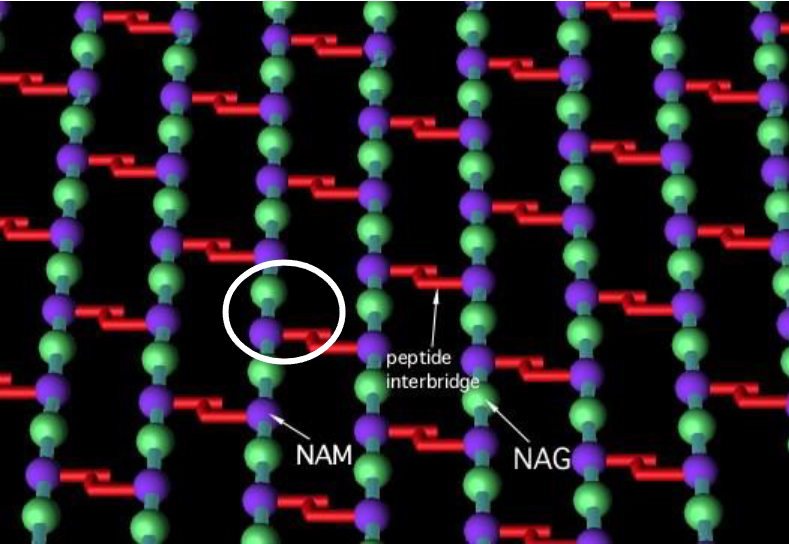
peptidoglycan transpeptidase