Topic 9 - Cloud Formation, Air Masses, and Where did that cold wind come from?
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How does a cloud form?
clouds form when moist air, that is air filled with water vapor, is lifted
water vapor cannot stay in what type of air ?
cold air
There are how many main types of clouds ?
4
what are the 4 main types of clouds?
high clouds, middle clouds, low clouds and vertical development clouds
what are some adjectives to help describe the clouds and what do they mean?
nimbus - rain, cumulo - puffy, strato - layered
what are high clouds?
almost always composed of ice crystals, wispy appearance, condensation trails form here, ex: cirrus clouds
what are middle clouds?
usually composed of liquid droplets, ex: alto+adjective (alto clouds)
what are low clouds?
layered clouds can cover several states at a time, they are white or grey in color. Don’t let thermal energy in, let all heat energy out. Ex: stratus clouds
what are vertical development clouds?
form when air is absolutely or conditionally unstable, ex:cumulus and cumulonimbus
what are cumulus clouds?
fair weather clouds, fluffy
what are cumulonimbus clouds?
very dark, produce intense thunderstorms, characteristic anvil shape
what is fog?
a cloud layer on or near the ground
how does fog form?
Forms when air temperature and dew point temperature are nearly the same
what are the three main types of fog?
radiation fog, advection fog and upslope fog or orographic fog
what is radiation fog?
Vertical fog, aka valley fog – cold air sinks into the valley
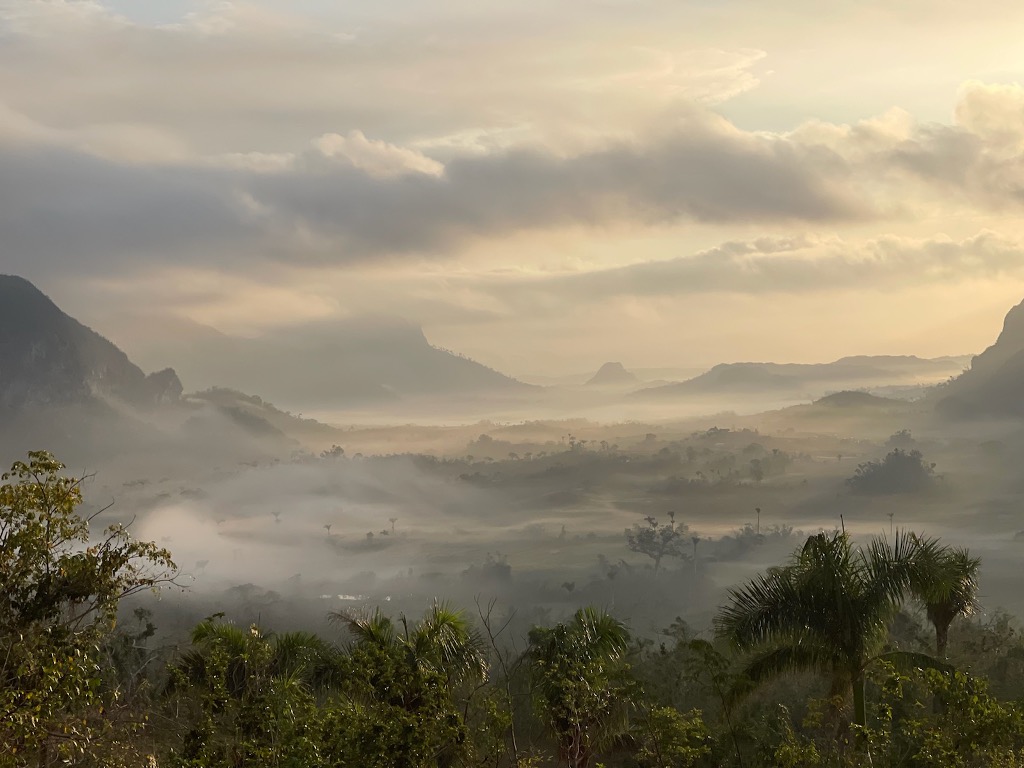

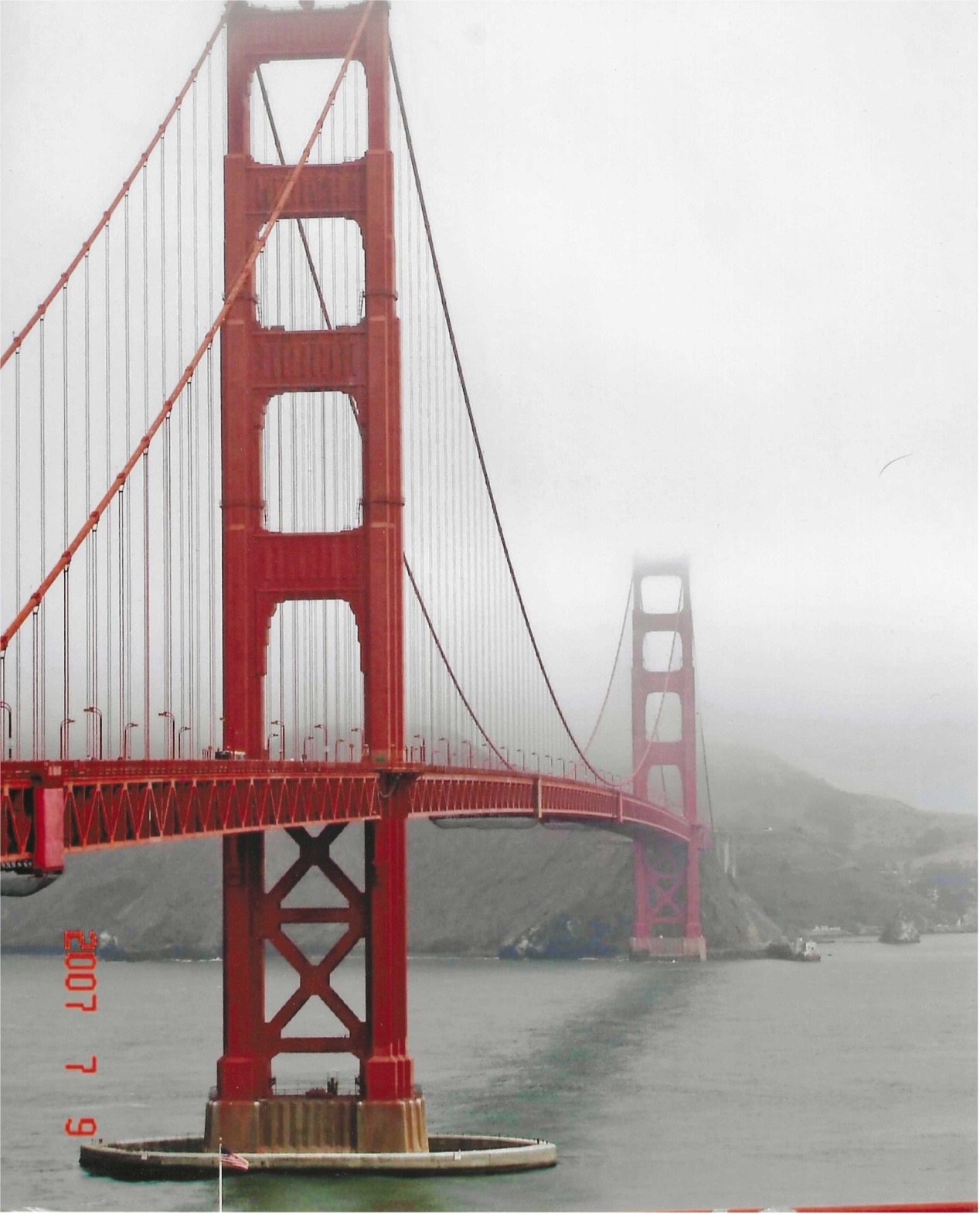
what is advection fog?
Forms horizontally, warm air flows over cold ground Eg: San Francisco and the golden gate bridge

what is upslope fog or orographic fog?
Forms in the mountains when air is forced over the mountains
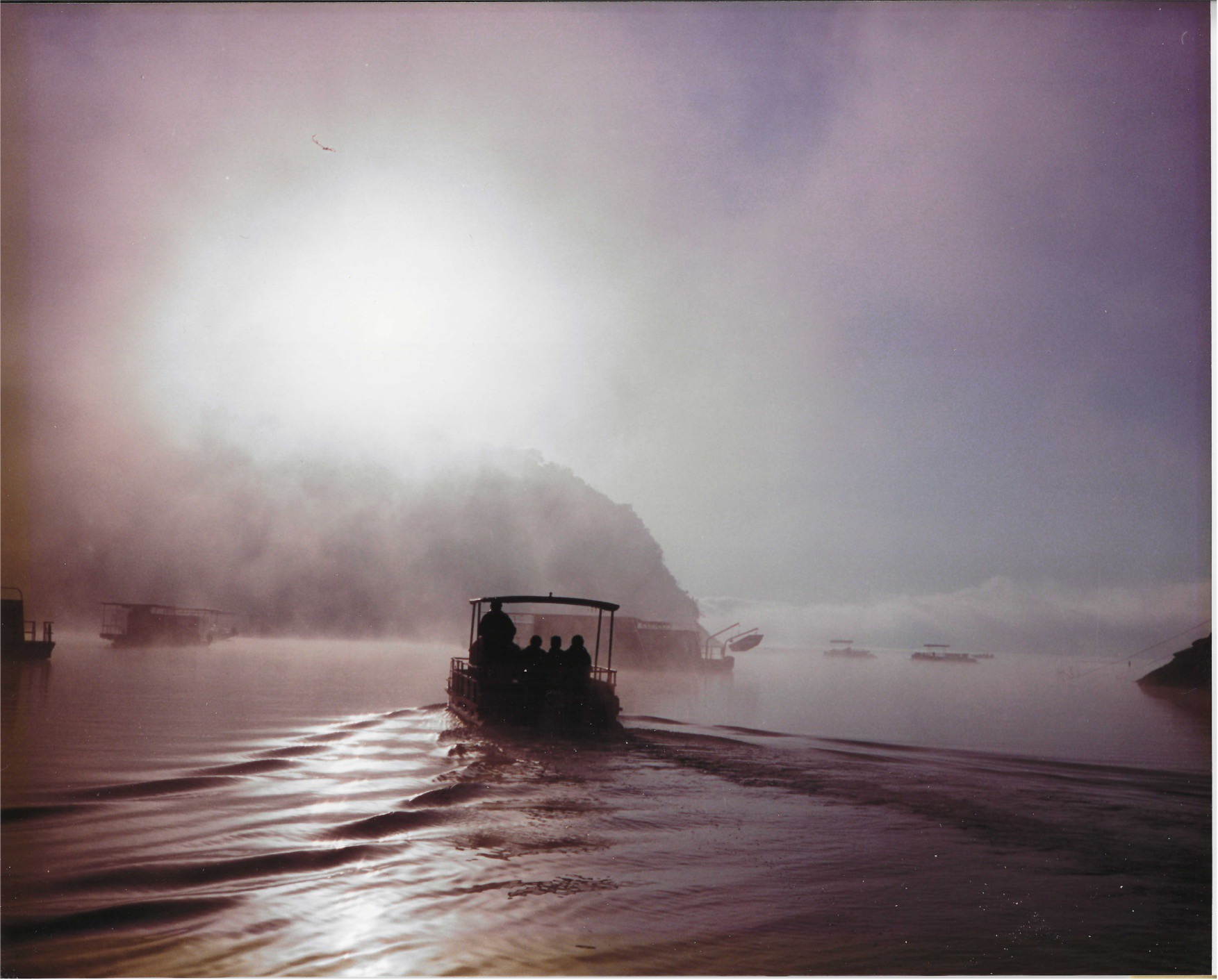
what is evaporation fog?
Horror film fog, aka steam fog – comes creeping in, often forms over water, aka sea smoke

How many masses are there?
there are 7 air masses that affect the weather across North America
what are the 7 air masses that affect the weather across America?
Continental Polar (cP), Continental Arctic (cA), Maritime Polar (mP), Maritime Tropical (mT), Continental Tropical (cT),
what are the characteristics of the air masses (7)?
these masses have specific temperature and water vapor
how are the air masses named ?
they’re named for the region (area) over which they form
the moisture of an air mass is described as ?
m for maritime or c for continental
what is m for maritime?
these form over large bodies of water(oceans), they are “wet” which means they have humidity
what is c for continental?
these form over land and they are “dry”
the temperature of an air mass is described as?
A - artic, P -polar, T - tropical, AA - antarctic
temperature is directly affected by ?
latitude
How and why do air masses change?
As they flow North, the air temperature decreases, WV content decreases (it has probably rained along the way), and at the final destination, the air mass is now cold and drier
How/why does it freeze in Florida?
The polar jet stream develops big Rossby waves, it allows cold air to move farther south and warm air to move farther north
what is the lake effect snow?
This occurs when cold air blows over a warmer area. Occurs with large temperature differences (ex: Wisconsin south to Chicago), or from land over water and back to land.
how do Air Masses cause changes in the weather?
The air masses must be lifted (move up) to cool down
what is convergent lifting?
air moves in from the sides (horizontally) to fill the space left by warm rising air
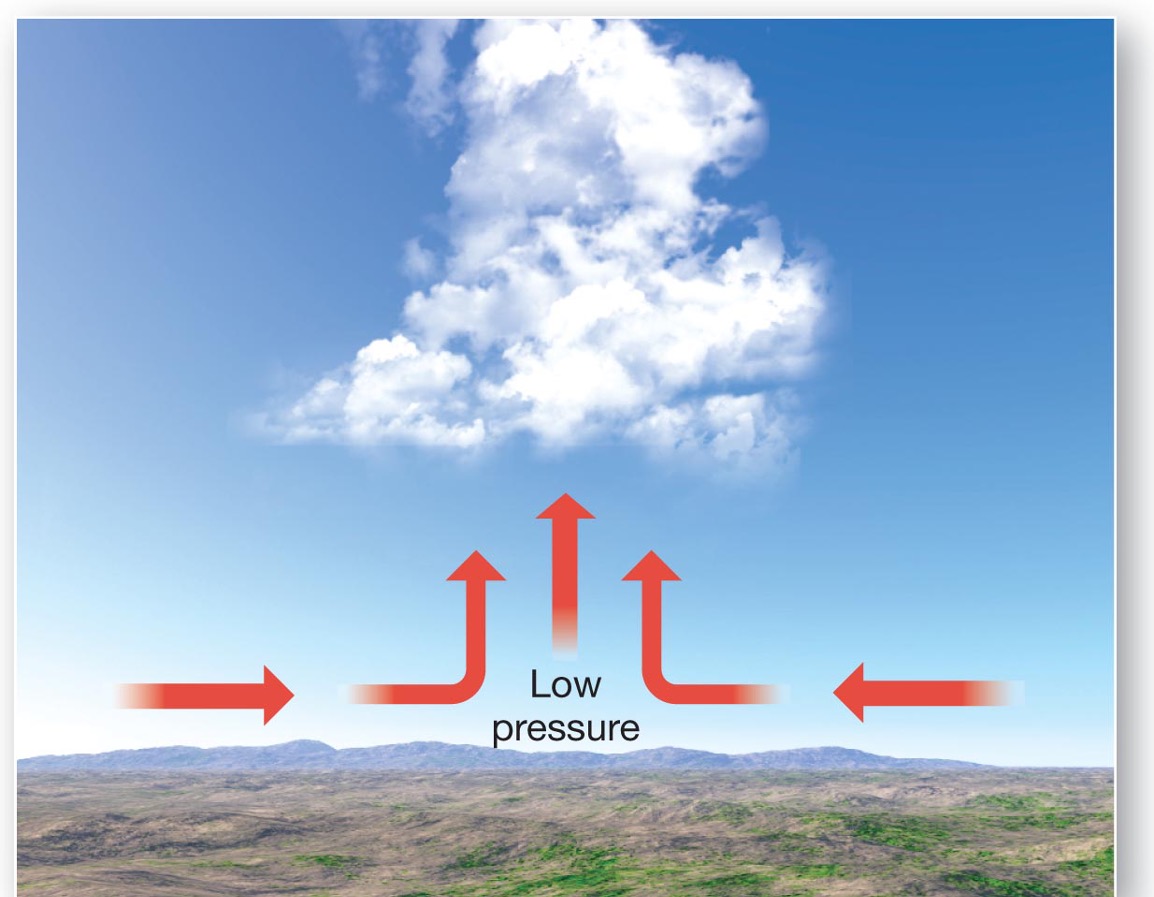
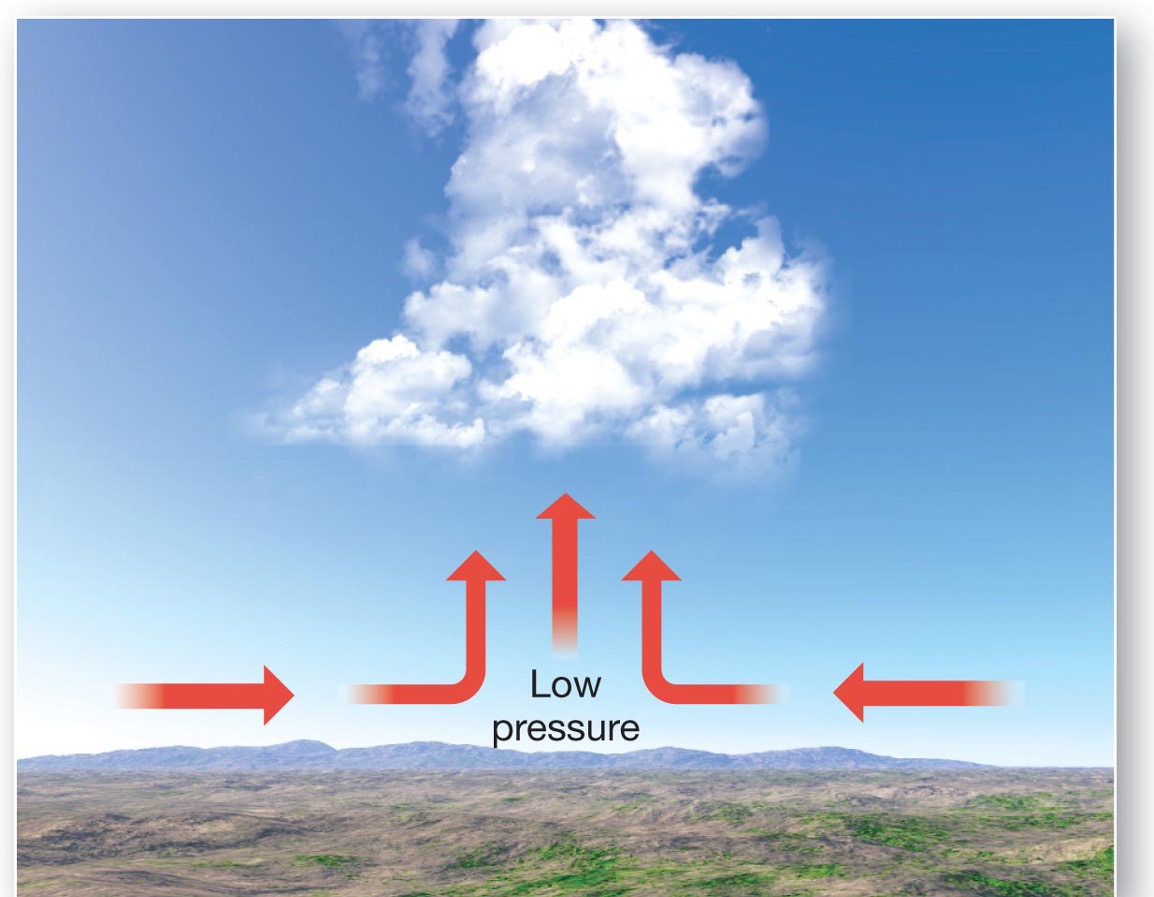
what forms in convergent lifting?
vertical development clouds form – cumulus clouds
what happens in convergent lifting?
Along the equator, trade winds meet, air rises, heavy rain. Great uplift occurs, towering cumulonimbus clouds form and high average annual precipitation.
what is convectional lifting?
occurs when air mass flows from maritime region to a continental region. This can even be over plowed land or even over a large urban area – heat island in cities

what happens in convectional lifting?
up and down movement of warm and cold air, there is unstable air (expect precipitation)

what is orographic lifting?
air rises when it meets a barrier, and the air cools, WV condenses etc
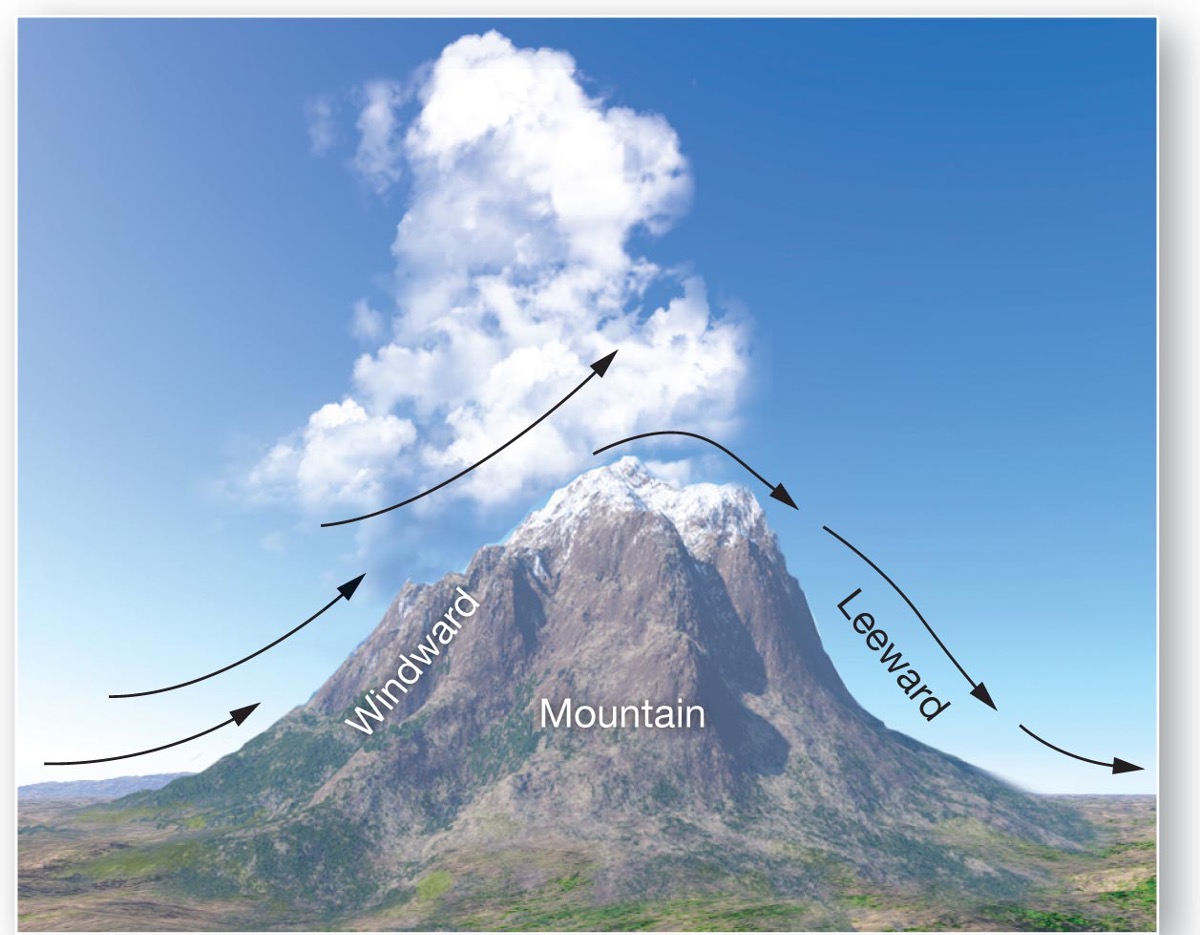
On what side of the mountain does a rain shadow form?
on the leeward side, the air is colder and dryer than the windward side
what is frontal lifting ?
due to incoming cold and warm air masses. The leading edge of an air mass is called the front, the front marks the difference between two distinctly different air masses (temperature, pressure, humidity, wind speed, wind direction and cloud development)
what happens in a frontal lifting (cold front)?
When a cold front forms the change in weather happens very quickly, the cold air pushes warm air up, air temperature decreases, WV decreases, vertical development clouds form – (cumulus) and likely rain. results: cumulonimbus clouds, heavy pptn, string winds, possible tornadoes, lightning and thunder, and maybe hail. The rain is short-lived
what is a squall line?
the line of thunderstorms that are approaching
what happens in a frontal lifting (warm front)?
The change in weather happens slowly, The warm air glides up over the cold air, As temp decreases, WV decreases, stratus clouds (not vertical), and likely pptn. Result: stratus rain clouds, steady pptn, unlikely to have strong winds, lightning thunder and hail. The rain is long lived.