Micro 12 | Gram-Negative Bacteria IV
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
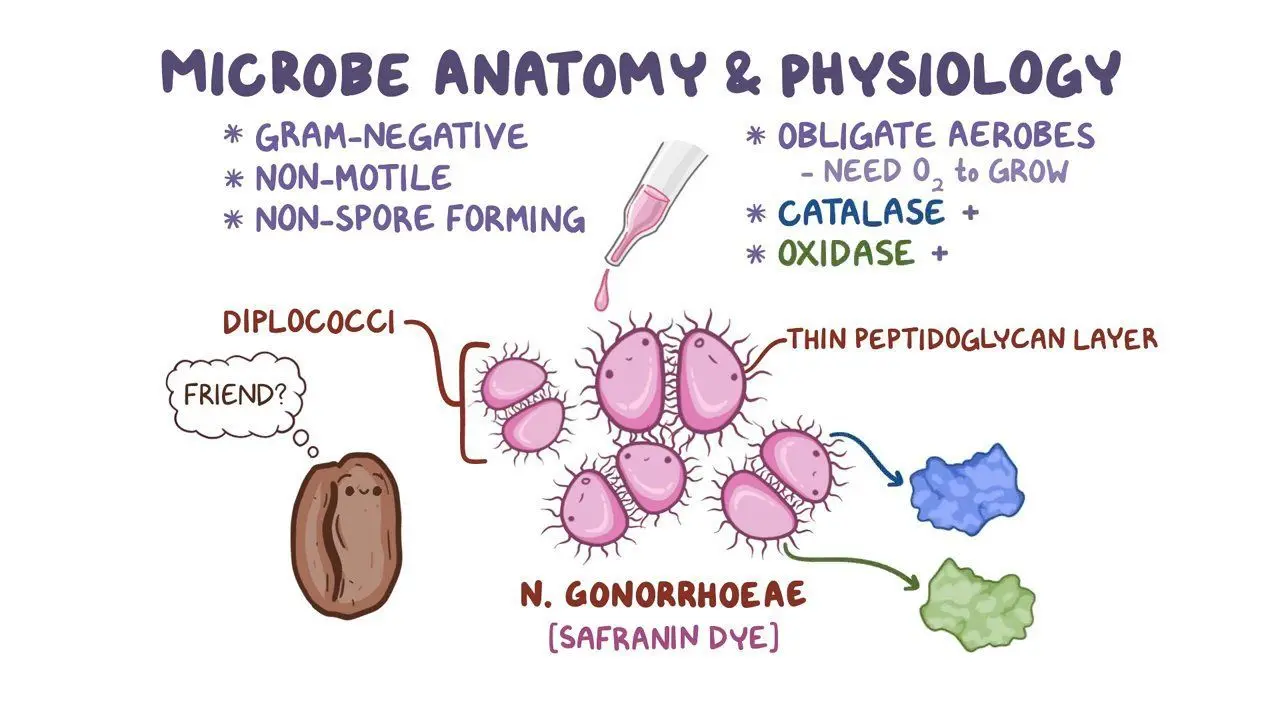
What is Neisseria gonorrhoeae?
A kidney bean-shaped, Gram-negative diplococci, and does not have a capsule.
How is Neisseria gonorrhoeae transmitted?
It is sexually transmitted and can also be passed from mother to baby at birth (perinatal transmission).
How can Neisseria gonorrhoeae be identified in the lab?
It is Gram-negative, oxidase-positive, and catalase-positive, ferments glucose (but not lactose or maltose), and is cultured on chocolate agar, Thayer-Martin, or Martin-Lewis agar in a CO₂ environment.
How to diagnose Neisseria gonorrhoeae?
Thayer-Martin agar (selective media in CO₂) or Martin-Lewis Agar (enriched and selective media)
Nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) is the best diagnostic method.
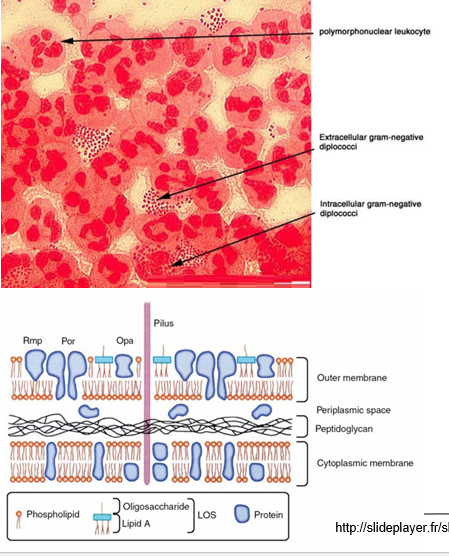
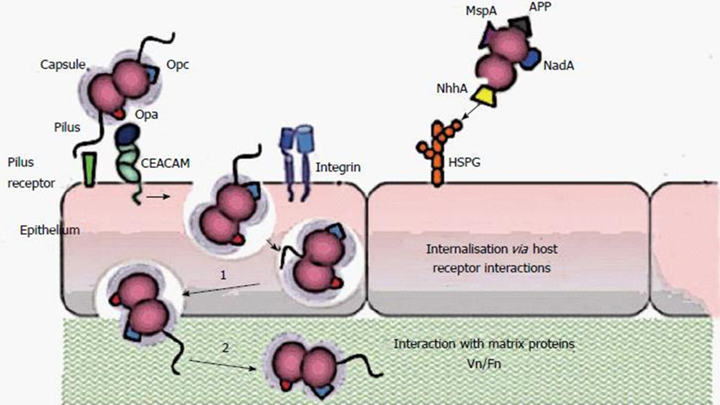
What are the virulence factors for N. gonorrhoeae?
Intracellular infection in polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs).
LOS (lipo-oligosaccharide) acts as an endotoxin.
Pilin proteins help with attachment but interfere with immune response.
IgA protease breaks down IgA, reducing mucosal immunity.
Antigenic variation in pili allows immune evasion.

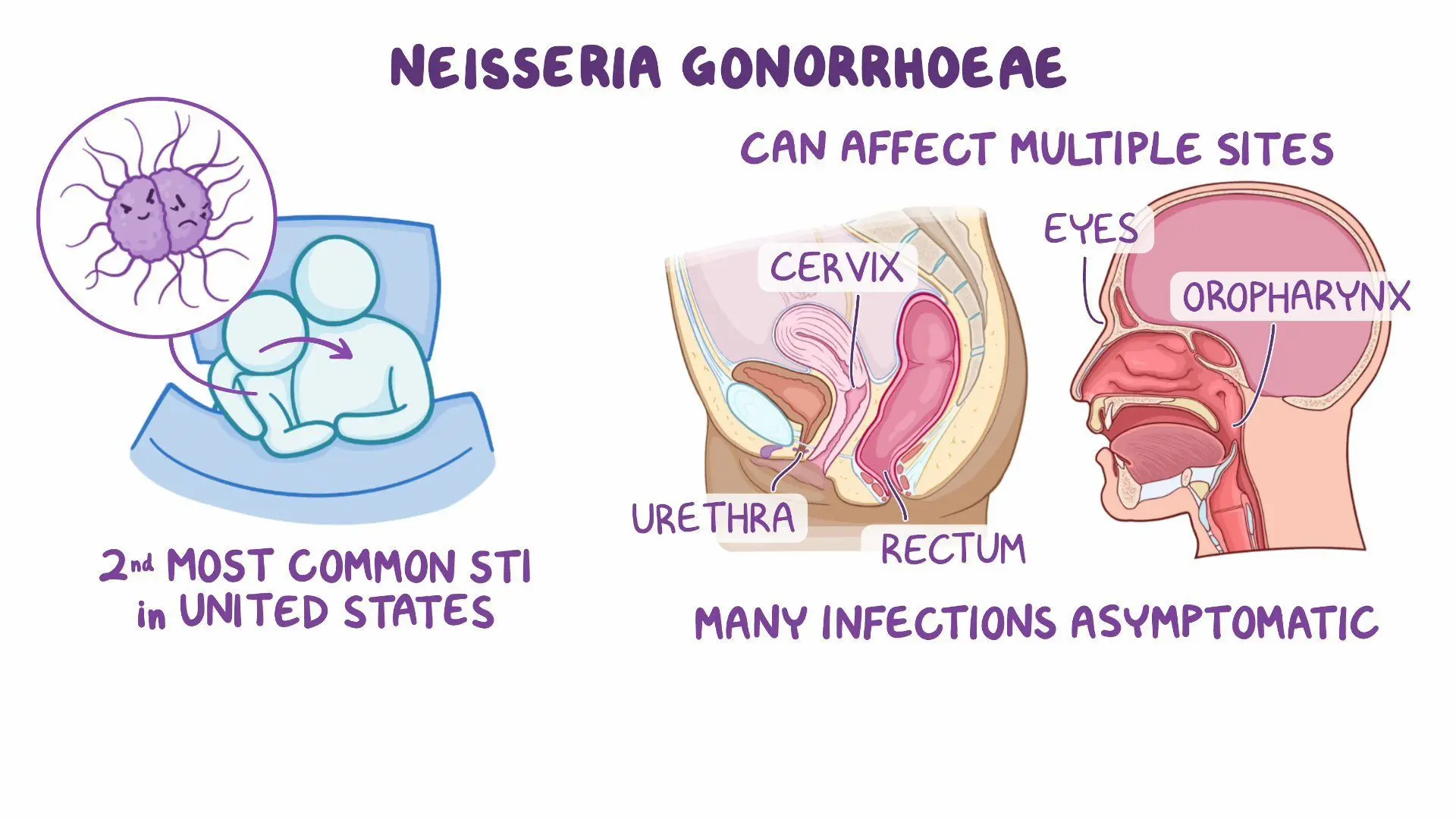
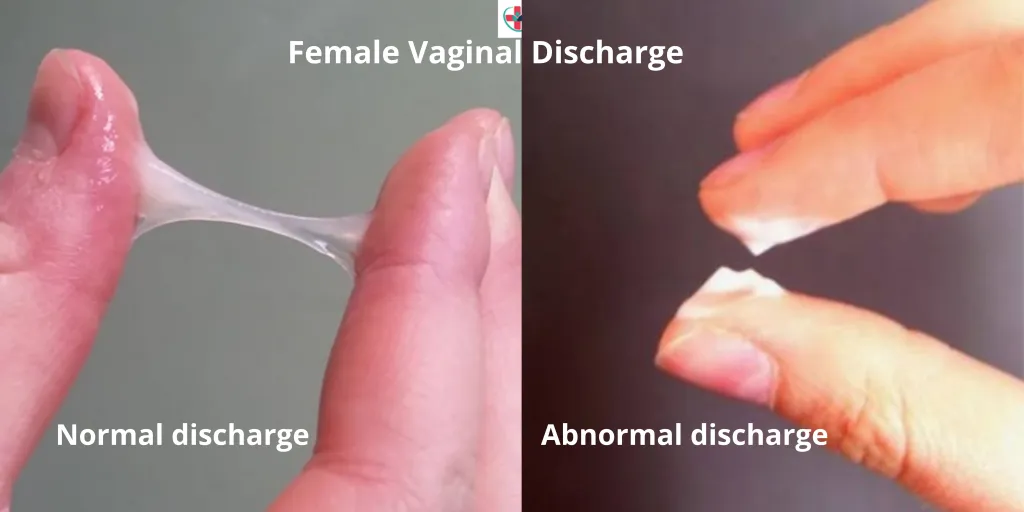
What is the main symptom of gonorrhea?
Creamy and purulent (pus-like) discharge from the urethra.
Primary site in women: cervix
Primary site in men: urethra
What are other diseases that can arise from gonorrhea?
Disseminated gonococcal infection: Can cause arthritis and septicemia (bacteria in the blood).
Purulent conjunctivitis: Affects newborns, transmitted during birth or in utero.
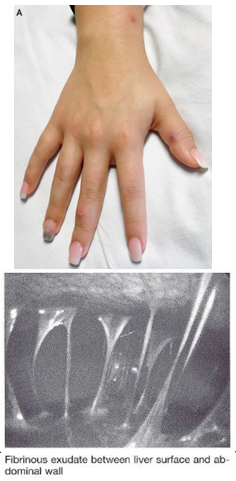
Fitz-Hugh Curtis syndrome: Inflammation of the liver capsule (perihepatitis) with fibrosis and adhesions, often due to pelvic inflammatory disease
Why is there no vaccine for gonorrhea?
The pilus protein of the bacteria undergoes frequent antigenic variation, making it difficult for the immune system to develop lasting protection.
What type of bacteria is Neisseria meningitidis?
An encapsulated, Gram-negative diplococcus, oxidase positive, and catalase positive.

What is the second most common cause of bacterial meningitis in all age groups except neonates?
Neisseria meningitidis
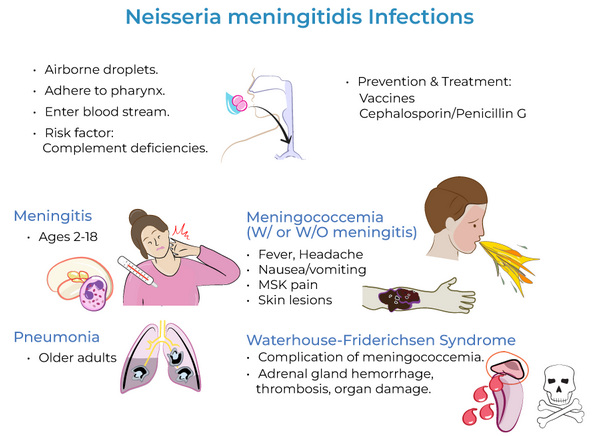
How is Neisseria meningitidis transmitted?
It spreads person-to-person through respiratory droplets and oral secretions, especially in crowded environments like dorms, military barracks, and family households.
Who is at high risk for Neisseria meningitidis infection?
Travelers to the "meningitis belt" in sub-Saharan Africa.
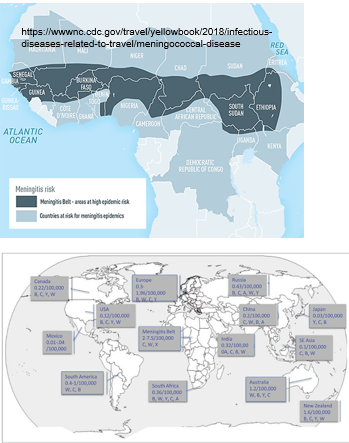
What sugars does Neisseria meningitidis oxidize?
It oxidizes glucose and maltose, but not lactose. Oxidase-positive
What culture media are used to grow Neisseria meningitidis?
It grows on chocolate agar (enriched, non-selective) and Martin-Lewis agar (selective).
What is the preferred method for diagnosing Neisseria meningitidis?
NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test)
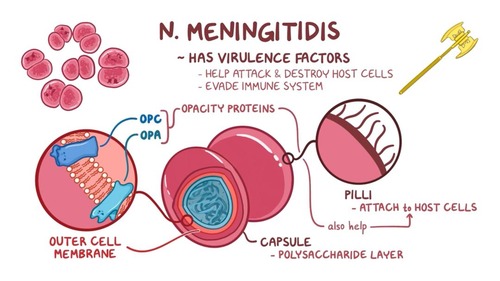
Virulence factors for N. meningitidis?
Polysaccharide capsule – Prevents phagocytosis and is used for serotyping. Major role in disease causation.
Pili proteins – Aid in attachment, facilitating disease spread.
LOS (lipo-oligosaccharide) – Acts as an endotoxin, causing endotoxemia. LOS endotoxin increases vascular permeability
IgA protease – Degrades IgA, helping the bacteria evade mucosal immunity.
How is Neisseria meningitidis prevented?
Prevention is through vaccination, which targets the polysaccharide capsule of the bacteria
How does LOS endotoxin act as a virulence factor?
LOS endotoxin damages blood vessels by making them more leaky, leading to inflammation, swelling, and severe complications like septic shock.
What are the main diseases caused by N. meningitidis?
Meningitis and meningococcemia
Characteristics of meningitis caused by N. meningitidis?
Progresses rapidly with symptoms like headache, fever, and vomiting (especially in young children).
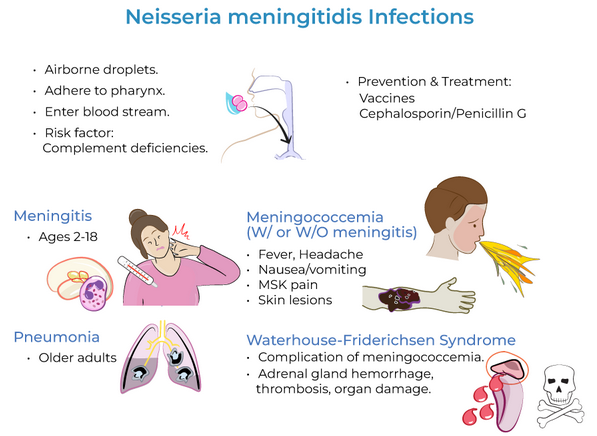
Characteristics of Meningococcemia caused by N. meningitidis?
A severe bloodstream infection resulting from LOS endotoxin and cytokine release, leading to blood vessel damage, excessive clotting, and widespread inflammation.
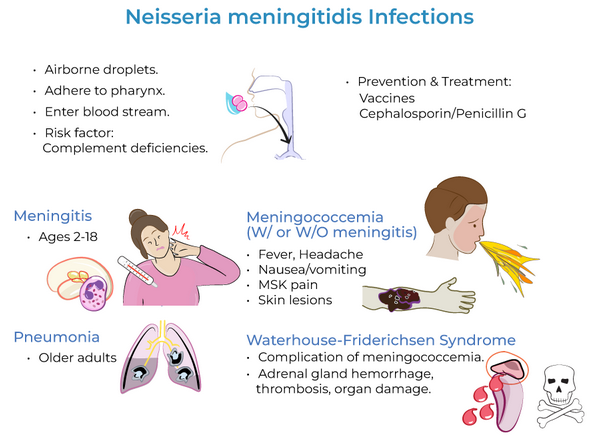
What complications can arise from Meningococcemia?
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, which causes septic shock, acute hypotension, tachycardia, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
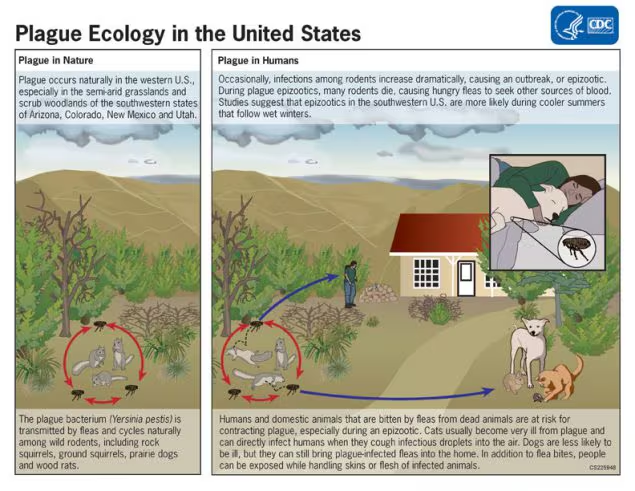
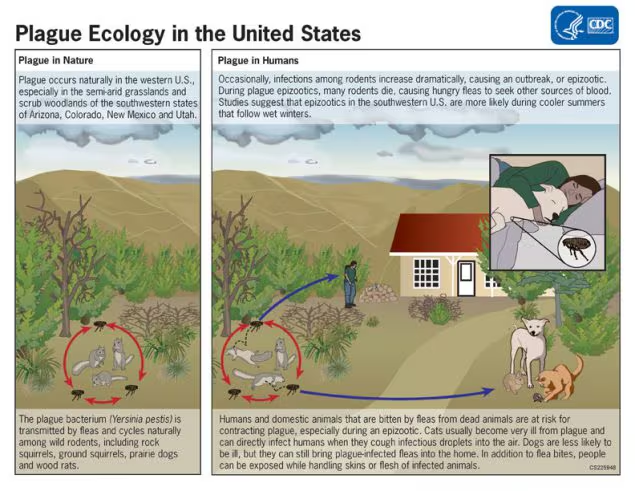
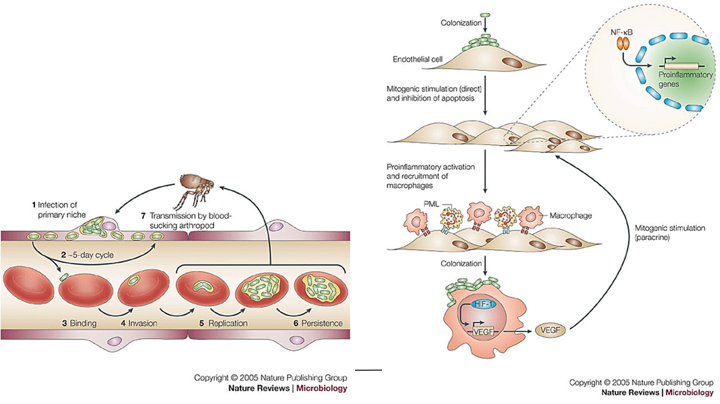
What is Yersinia pestis?
a Gram-negative coccobacillus that is oxidase-negative and has a protein-containing capsule. It is a zoonotic pathogen, with humans as accidental hosts.

How is Yersinia pestis transmitted?
Primarily through flea bites.
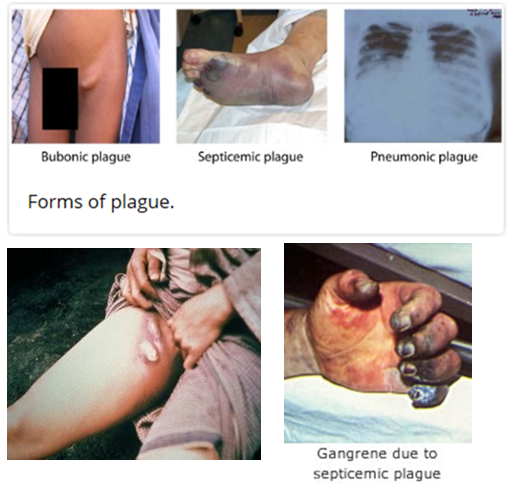
What are Yersinia pestis-associated diseases?
Bubonic plague – Most common form; spreads via flea bites or cutaneous exposure. Causes fever, chills, headache, weakness, and painful swollen lymph nodes (buboes).
Pneumonic plague – Most severe form, the only type that spreads person-to-person via inhaled droplets. Leads to rapidly progressing pneumonia, fever, and weakness.
Septicemic plague – Can result from flea bites or infected tissue handling. Symptoms include fever, shock, abdominal pain, and tissue necrosis (blackened fingers, toes, nose).
What are Bartonella species?
Bartonella species are Gram-negative coccobacilli that grow slowly (taking 2–6 weeks). They cause diseases like cat scratch disease (Bartonella henselae), trench fever (Bartonella quintana), and Carrion’s disease (Bartonella bacilliformis).
Transmission of Bartonella species?
Zoonotic, spread through direct contact with infected animals or arthropod vectors.
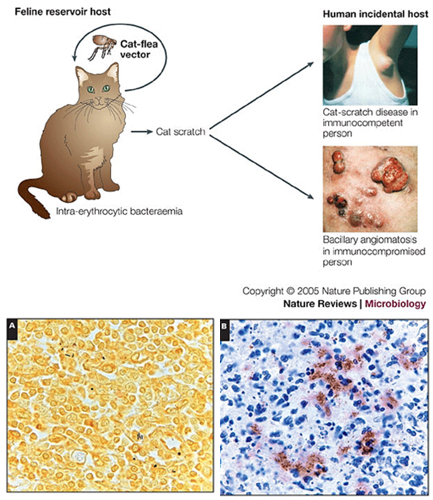
Which bacteria cause endothelial cell proliferation, leading to bacillary angiomatosis?
Bartonella henselae is the only bacteria known to cause this condition.
Bartonella henslae causes which two diseases?
Cat-scratch fever – Mild in healthy people, often in children, causing swollen lymph nodes near the scratch or bite. Can spread to organs in rare cases.
Bacillary angiomatosis – Affects immunocompromised patients, causing abnormal blood vessel growth in skin, lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
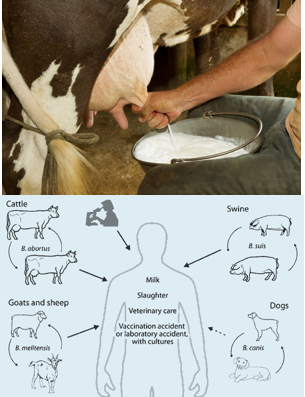
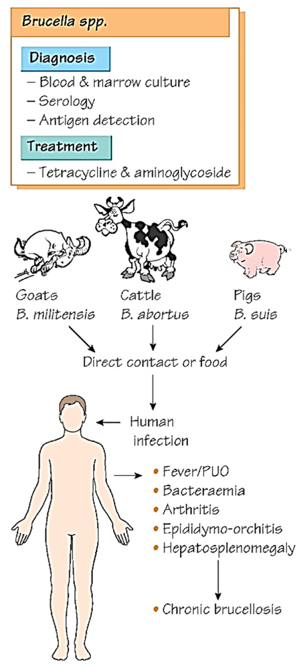
What is Brucella species?
Gram-negative bacteria that cause brucellosis, an infection that spreads from animals to humans. People get infected by eating contaminated dairy products, handling infected animals, or inhaling the bacteria.
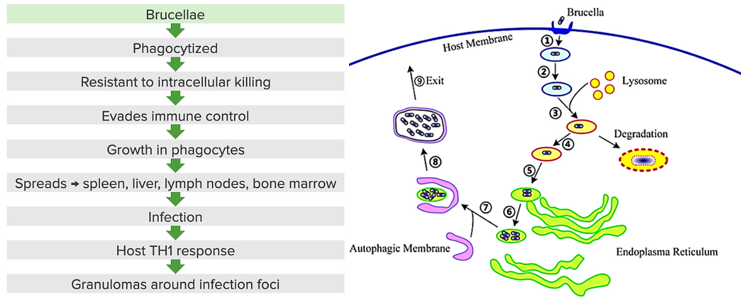
Virulence factors of Brucella species?
Intracellular infection – Hides inside immune cells to spread and avoid immune detection.
LPS (O Ag component)– Helps protect against immune response.
Immunosuppressive effects – Reduces MHC II expression, blocks cytokine production, and prevents infected cells from undergoing apoptosis, weakening immune defenses.
How is Brucellosis transmitted?
Contaminated food (especially unpasteurized dairy).
Inhalation of infected animal tissues (e.g., slaughterhouse exposure).
Rarely, person-to-person transmission.