Glycolysis
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
In order to carry out both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, we need…
How many carbons does glucose contain?
glucose
6
Glycolysis is the first stage in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. This means that glycolysis…
Select all that apply
doesn’t require oxygen.
doesn’t require ATP.
doesn’t require carbon dioxide.
doesn’t require energy.
A
The first stage of respiration is…
Select all that apply
the link reaction.
glycolysis.
the Krebs cycle.
oxidative phosphorylation.
B
Glycolysis takes place in the…
Select all that apply
nucleus.
rough endoplasmic reticulum.
golgi apparatus.
cytoplasm..
D
Glycolysis produces molecules with...
Select all that apply
2 carbon atoms.
3 carbon atoms.
4 carbon atoms.
5 carbon atoms
B
During glycolysis, glucose is converted into two identical molecules containing three carbon atoms. These three-carbon molecules are called…
Select all that apply
glucose
phosphate
pyruvate
lactate
C
The first stage of respiration is called …………... This process takes place in the
…………….of the cell.
Since this is the first stage for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, the reactions in this process can take place without……………
At the end of this stage, two identical molecules are produced, called……………. These molecules each contain…………carbon atom(s).
glycoolysis
cytroplasm
oxygen
pyruvate
3
When glucose enters a cell’s cytoplasm, how many phosphate groups are added?
This produces a molecule called…
2
phosphorelated glucose/glucose phosphate
When glucose enters a cell’s cytoplasm, an enzyme adds two phosphate groups to it, producing a new molecule called glucose phosphate.
These phosphate groups are available due to...
Select all that apply
the breakdown of 1 ADP molecule.
the breakdown of phosphodiester bonds.
the breakdown of 2 ATP molecules.
the breakdown of phospholipids.
C
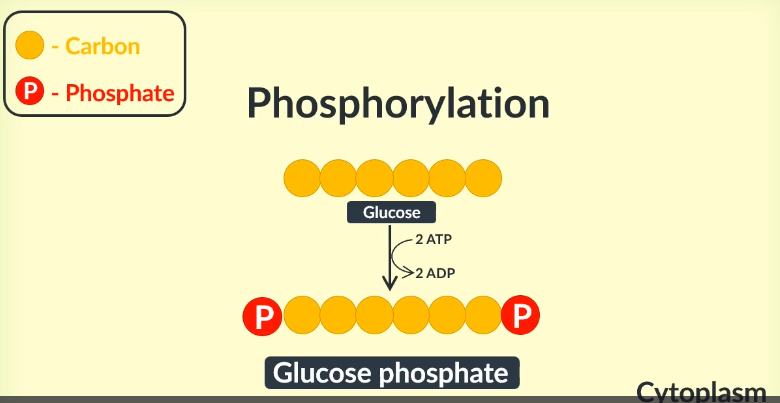
In the first stage of glycolysis, an enzyme adds …………phosphate groups to glucose. This process is known as………and produces a new molecule called….. ………
These phosphate groups are available due to the breakdown of two molecules of…….
2
phosphorelation
glucose phosphate
atp
Describe what happens in the first stage of glycolysis.
Glucose enters the cell’s cytoplasm.
Upon entry, an enzyme adds two phosphate groups to glucose in a process known as phosphorylation.
These phosphate groups are available due to the breakdown of two ATP molecules.
As a result, this produces a new molecule called glucose phosphate.

During glycolysis, for a single molecule of glucose, there’s an overall yield of…
2 ATP molecules.
In the second step of glycolysis, glucose phosphate breaks down into two molecules of…
triose diphosphate.
diose monophophate.
diose phosphate.
triose phosphate.
The conversion of a single triose phosphate molecule to pyruvate produces…
therefore for a single glucose molecule undergoing glycolyss, …. ATP moleucles are made (net)
D
2 ATP molecules.
2
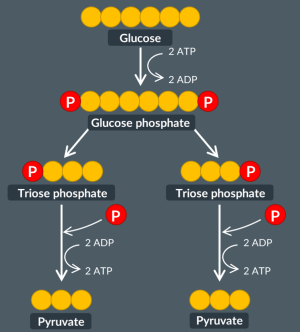
Earlier, in the first step of glycolysis, we saw that 2 molecules of ATP are broken down in the conversion of glucose to glucose phosphate.
In the second step of glycolysis, glucose phosphate breaks down into two molecules of ……. ………….
In the third step, each of these two molecules is converted to………….Each conversion separately produces….ATP molecules. Therefore, in the third step of glycolysis, there is an overall yield of….ATP molecules.
As a result, in glycolysis, for a single molecule of glucose there is an overall yield of….ATP molecules.
triose phosphate
pyruvate
2
4
2

Why Phosphate Groups Are Added in the First Step
to produce glucose phosphate→ more difficult to transport cf w origional glucose molecule
glucose enters cell through facillitated diffusion: requiring specific transport protein specific to glucose → which glucose phosphate cant travel through
if high conc outside cell cf in, glusose would leave cell ∴ not used for repsiration
Which of the following is an example of an oxidation reaction?
Select all that apply
A carboxylic acid gaining hydrogen.
Ammonia losing hydrogen.
Water splitting up into hydrogen and oxygen.
An aldehyde gaining hydrogen.
B
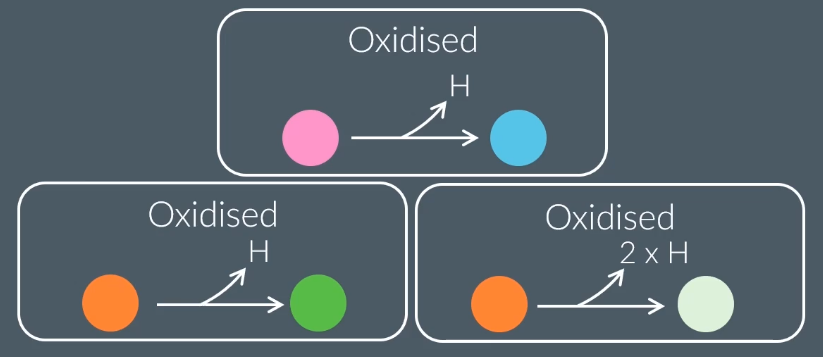
What substance is oxidised in this reaction?
Ethanol → Acetaldehyde + Hydrogen
Select all that apply
Ethanol
Acetaldehyde
Hydrogen
A
Which substances are being reduced in the following examples?
Acetaldehyde + Hydrogen → Ethanol
Nitrogen + Hydrogen → Ammonia
Methanol → Ethylene + Hydrogen
Select all that apply
Acetaldehyde
Ethanol
Nitrogen
Ammonia
Methanol
Hydrogen
A
C
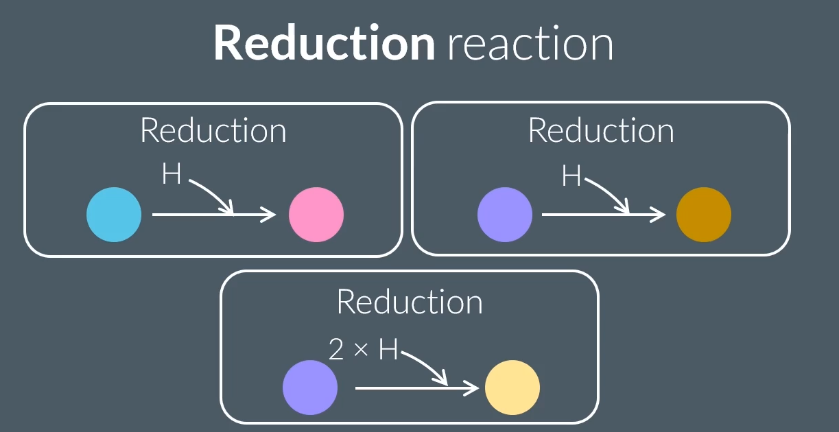
Identify the following as oxidation reactions, reduction reactions or neither.
a) Ammonia → Hydrogen + Nitrogen
b) Formaldehyde + Hydrogen → Methanol
oxidation
reduction
Oxidation and reduction reactions…
Select all that apply
always take place together.
cannot happen together.
always involve oxygen.
always result in oxygen being produced.
A
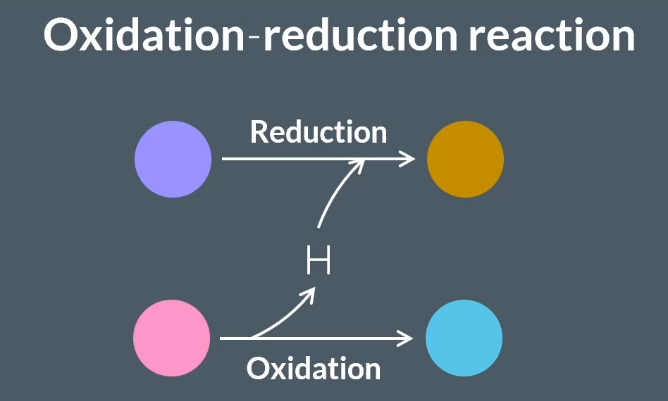
During the third step of glycolysis, triose phosphate loses a hydrogen.
So, during this reaction…
hydrogen is oxidised.
hydrogen is reduced.
triose phosphate is oxidised.
triose phosphate is reduced
C
During glycolysis, an oxidation-reduction reaction takes place.
Which substance is oxidised?
Select all that apply
triose phosphate
NAD
pyruvate
NADH
Which substance is reduced?
triose phosphate
NAD
pyruvate
NADH
Which forms ….. after …… a hydrogen
A
B
NADH
gaining
Out of the three steps in glycolysis, in which step does oxidation-reduction take place?
Name the molecule that is oxidised during glycolysis:……….
During the oxidation-reduction reaction in glycolysis,…is converted into…..
Step-3
triosphospate
NAD
NADH
Describe how oxidation-reduction is involved in glycolysis.
Triose phosphate loses hydrogen in the third step of glycolysis, so triose phosphate is oxidised.
This hydrogen is transferred to a molecule called NAD, forming NADH or reduced NAD.
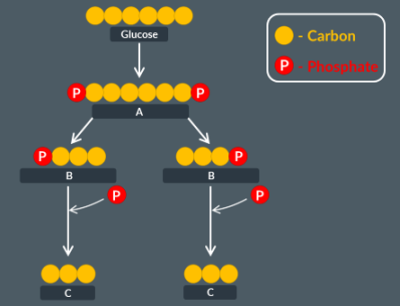
Here is a diagram of glycolysis. Identify A,B and C.
What is the overall yield of ATP?
Alongside pyruvate and ATP, what else is produced during glycolysis?
glucose phosphate
triose-phosphate
pyruvate
2
NADH
Describe the process of glycolysis. Ensure that all products formed are mentioned.
First, glucose enters the cell’s cytoplasm. Upon entry, an enzyme adds two phosphate groups to glucose in a process known as phosphorylation. These phosphate groups are available due to the breakdown of 2 ATP molecules. As a result, this produces a new molecule called glucose phosphate.
Second, hexose phosphate breaks down into two molecules of triose phosphate.
Third, triose phosphate is converted into pyruvate. In this step, 2 molecules of NADH and 4 molecules of ATP are formed.
The overall yield of ATP within glycolysis is 2 ATP.
