Multi-store model of memory (Atkinson and Shiffrin, 1968)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
page 6-7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
storage
retention of information within stores of memory
retrieval
movement of info from long-term store to concious awareness
encoding
form in which information is stored
decay
fading of memory over time
capacity
max amount of info able to be stored at a given time
duration
length of time info can be stored for
what is the multi-store model of memory and its features
Atkinson and Shiffrin theorised information flows through 3 storage systems (the 3 working components of memory) which are sensory register, short-term memory, and long term memory. they are connected to each other through attention, rehersal, and retrieval processes
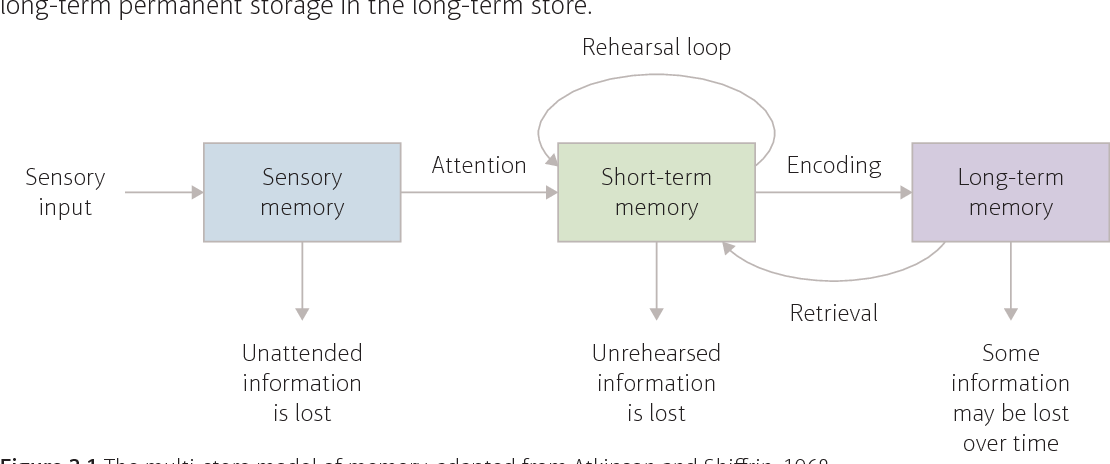
what are the 3 components of the multistore model of memory?
Sensory register, Short-term memory, and long-term memory
what is the sensory register
where sensory info is briefly held before decaying or transfering to short term store. this is where info first enters. info not attended to decays rapidly. the reception of sensory information here is unconcious and automatic
how is sensory information stored in the sensory register (How Long)
Atkinson and Shiffrin theorised that there were likely seperate stores for each of our senses. they mainly focused on visual and auditory. visual information is held for 0.2-0.4 seconds in the iconic store. auditory information remains in the echoic store 3-4 seconds
what is the short term memory
temporary memory store for limited info recieved from sensory register and long-term store. sensory info attended to transfers to short-term (working memory). a trace of the memory still remains in the sensory register where it then decays. Info in the short term store is mainly encoded acoustically
how many pieces of information can the short term store hold and how quick does decay occur
capacity of 5-9 pieces of information which decays ~15-30 seconds unless unless rehersal and coding processes occur, which either hold the information for longer, or allow for encoding into the long term store.
Long term memory
relatively permanent memory store for a limitless amount of information that sends and recieves info via short term memory
unlimited amount of info can be stored. some decay does occur over time, however the info is mostly permanent
how is information encoded in the long-term store?
mainly encoded semantically (unless the information is meaningful, they will decay over time
what is the difference between encoding and retrieval?
Encoding is the receiving and interpretation of information. Retrieval is the process used to recall stored information.
identify the differences between the sensory register and the long-term memory in terms of duration, capacity, and coding
the sensory register only lasts for a few milliseconds (0.2-0.4 visual, 3-4 auditory), unlimited capacity, and sensory information from the 5 senses is encoded differently (echoic - audio, iconic - visual, olfactory - smell, haptic - tactile, gustatory - taste) encoding is visual and acoustic
information in the long-term memory is relatively permanent (decay theory), the long term has an unlimited capacity, info is encoded semantically,