Bacteriology test 1
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes: single celled, no nucleus, simple chromosome structure, divides by binary fission, peptidoglycan cell wall, one type of ribosome
Eukaryotes: nucleus and membrane bound organelles, formed by bacteria and archaea relationship, less permeable cytoplasmic membrane with sterols, cell division my mitosis or meiosis, chitin or cellulose cell wall,
Bacteria vs archaea
Bacteria: larger domain, some photosynthetic, none form methane, medically important, membrane lipids- ester linked, flagella grow at tip, contain peptidoglycan
Archaea: smaller domain, not photosynthetic, none are known pathogens, occupy extreme habitats, methane formers, membrane lipids - ether linked, flagella assemble at base, contain pseudomurein,
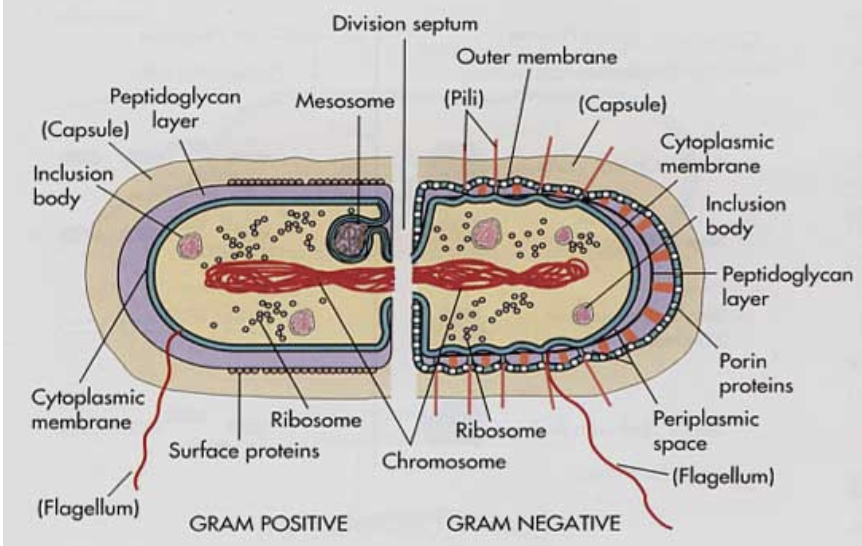
Gram positive vs gram negative bacteria
Gram positive: thick peptidoglycan layer! have mesosome, surface proteins, stain purple for gram stain
Gram negative: thin peptidoglycan layer! Lipopolysaccharide layer with high amounts of endtoxins. pili, periplasmic space as well as cytoplasmic space, porin proteins as outer membrane, stain red or pink for gram stain.
Adhesion to host cells is from
pili, proteins, teichoic acid
immune recognition by host
all outer structures and secreted proteins create immune response from host
how do bacteria escape host cell recognition
antigenic variation, m proteins, capsule
how are bacteria adhesive?
pili, outer surface proteins
Controls for protein synthesis
DNA
transcription- mRNA synthesis
protein synthesis
inducers- IPTG, Arabinose
Repressors
Nutrients/ energy source
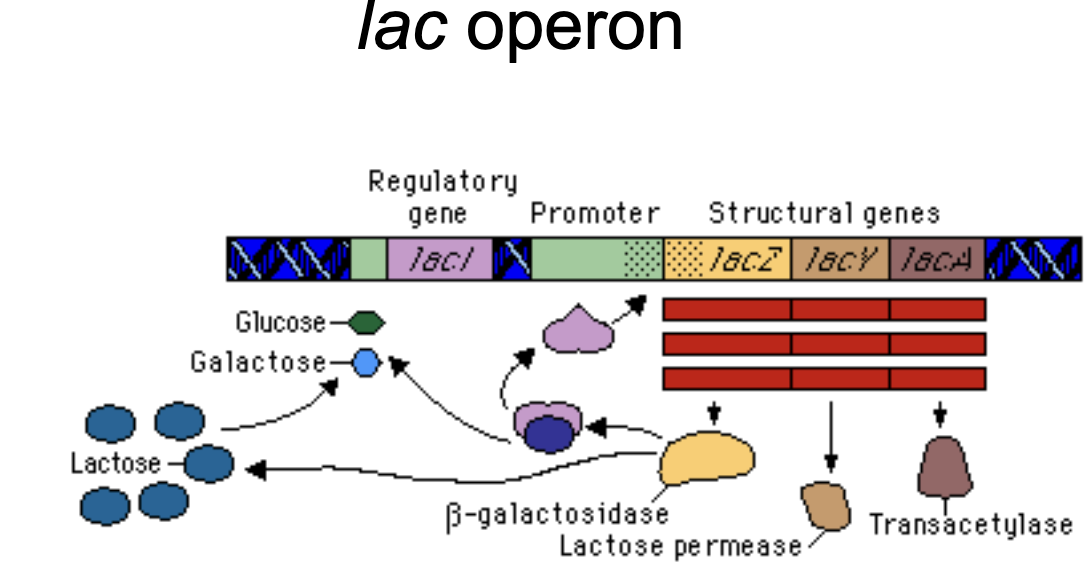
lac operon
Lactose metabolism. The genes in the operon allow bacteria to process lactose.
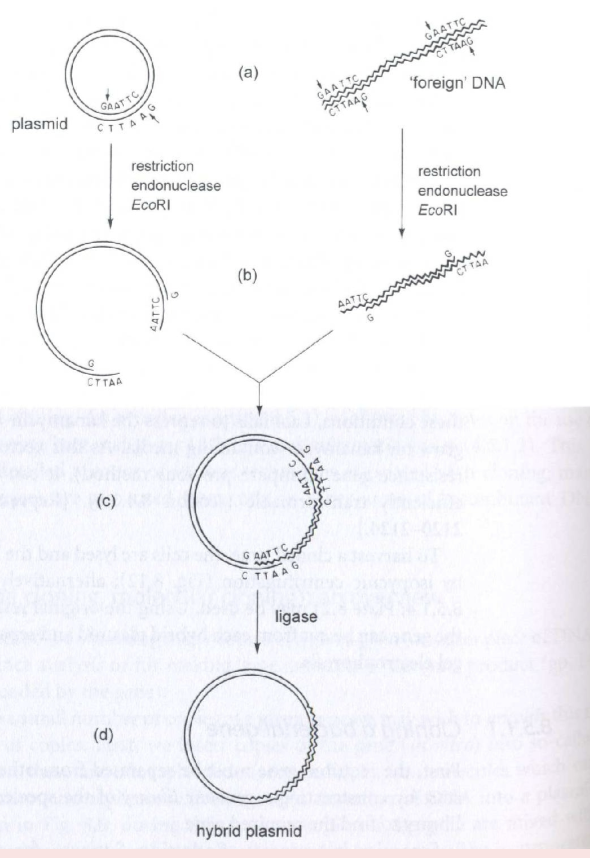
Cloning of foreign DNA for expression
several different types of plasmids, antibiotics, inducers, and bacterial strains
Plasmid features
Origin of replication
Promoters- inducible or constitutive
structural or fusion genes
ribosome binding sites
multiple cloning sites
transcriptional terminator
antibiotic resistance markers
How will you exploit a plasmid to modify what a bacterial cell does?
You can clone foreign DNA for expression! Have plasmid + “foreign DNA”. Knick plasmid and foreign DNA using restriction endonuclease. Add DNA to plasmid, seal with ligase to form hybrid plasmid which now modifies what the bacterial cell does.
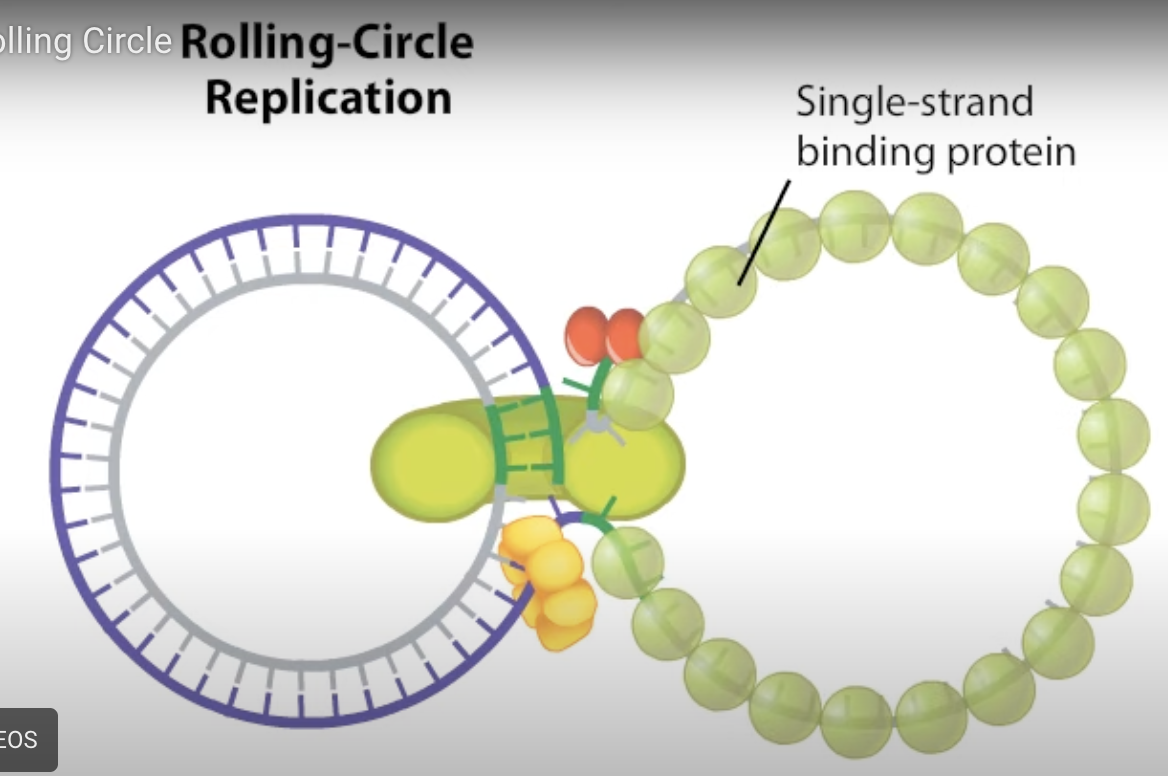
Rolling circle replication
Replication initiator protein binds to origin of replication to nick the 5’ end so DNA polymerase III can bind to 3’ and replication can begin when helicase binds to prevent tangling of DNA. The original initiator protein will cut the strand once finished and ligase will fix the nick. Once strand is complete a loop is formed and RNA polymerase will bind and form complementary strand
Purification of recombinant protein
identify protein of interest
identify source of protein
identify gene that encodes protein
amplify gene
clone amplicon using PCR
transform bacteria to identify plasmids
reclone gene to expression plasmid
transform expression host
express recombinant protein
purify protein
use protein
Purposes to make recombinant protein
to get information about protein
difficult to isolate and purify protein in native organism
Bacterial population benefits from phages
exposure drives population diversification
phages can function as weapons against foreign bacterial populations
facilitate genetic material transfer via horizontal gene transfer
phages that are released by prophage induction interact with cells of metazoan host which can lead to expression changes
practical application using phages and process
Phages can be used to neutralize or block antibodies against a virus (example SARS- CoV-2)
Infect mice with COVID 19, they produce antibodies
take the b cells from infected mice and isolate the mRNA from the b cells then amplify by PCR.
Clone PCR fragments into phage and then the phage infects bacteria to express heavy and light chains of cloned particles.
Do multiple times until desired phage is acquired
convert phage DNA to circular plasmid
Insert plasmid into bacteria transform bacterial cells to have the Antibodies
On your trip to Hawaii you collected some soil samples and plan to identify a new bacteria- how will you do it
Collect soil
Dilute soil
lawned on plate
isolate colonies
lawn with target bacteria
added isolated colonies to plate
observe for zone of inhibitions
if yes then microbe for soil sample produced antimicrobial against target bacteria
List specifically what recombinants proteins will you make example a specific cheese
identify protein
identify source
identify gene encoding protein
amplify gene
clone amplification in PCR cloning vector (add distinguishing factor like antibiotic resistance)
transform e. coli to make plasmids that hold the gene for specific cheese (in order to select e. coli containing plasmid add to plate that contains the antibiotic target)
reclone gene of interest in expression plasmid
transform expression host ( the bacteria that reads expression plasmid) to express recombinant protein ( the flavor of cheese)