Carbohydrates
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what are the four types of carbon based macromolecules?
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucelic acids
why is life carbon based?
because all of the large macromolecules are carbon based
what are covalent bonds
sharing of electrons between two atoms
what do carbohydrates contain
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
give examples of carbohydrates
sugars, starches like flour bread and past, cellulose and chitin
what are carb functions?
they are immediate energy sources
energy storage
structural materials
Sugars are…
immediate energy sources
the simplest carbs
monossacchraides and dissacharies
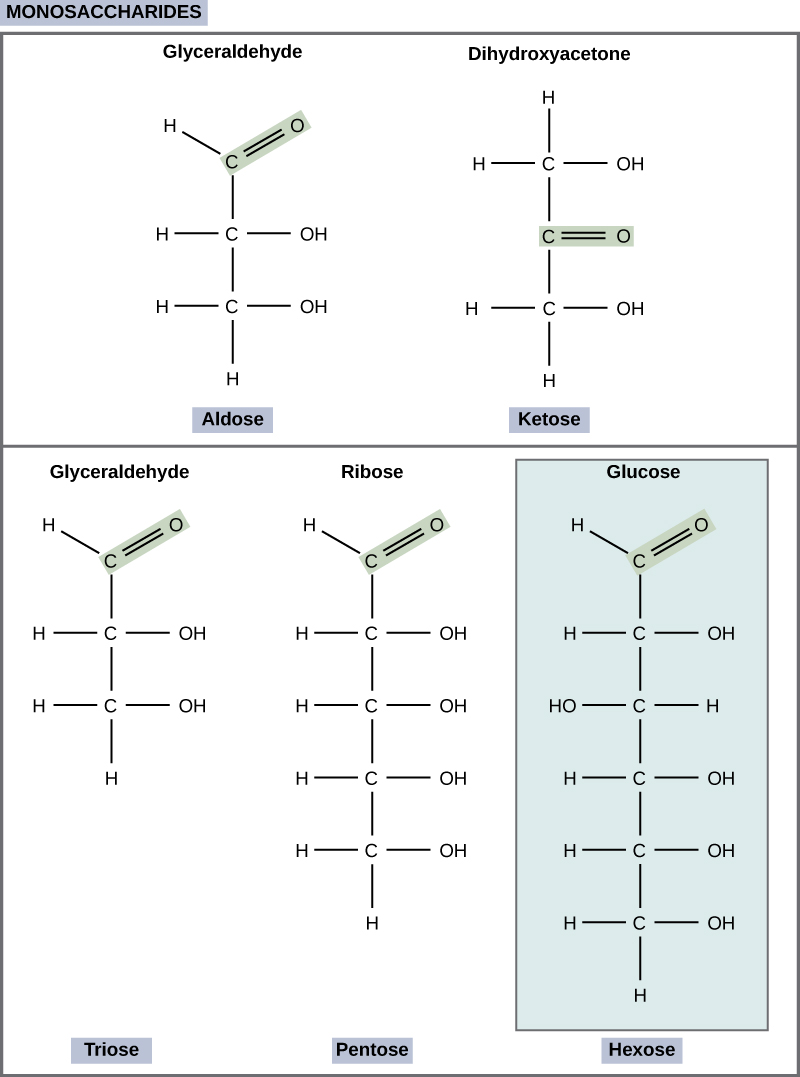
monosaccharides
C and H20
can be aldose or keytose based on position of carbonyl group
polar
conatin hydroxyl (-oH) groups
what is a hydroxyl group
functional group with one hydrogen and one oxygen (-OH)
what is a carbonal group?
double bond between carbon and oxygen
describe aldohydes + example
have carbonal group at end
glucose and galactose
aldose sugar
describe ketose base and examples
carbonal group in the middle
fructose
ketose sugars
in solutions what structures do sugars form
ring stuctures
what is a disaccharide
two monosacharides joined by glycosidic linkage
glycosidic linkage
links between two sugar molecules
what treactions causes glycosidic lunkage and explain
condensation
1 glucose + 1 glucose = dissacharide and water
they join together at the two OH and h20 is given off and the molecule shares the remaining O
what makes a sugar alpha or beta
in ring sturcture
the orientation of the hydroxyl group
if it is down it is alpha (opposite side from CH2OH group)
if it is up or the same side it is beta
what is 1-4 glycosidic linkage
between number 1 carbon of one monomer and number 4 carob of the other
what reactions break down polyssachrides
hydrolosis reactions
add water to break glycosidic linkage
what are storgae polysscahrides in plants
starch
found in the chloroplasts
low solubilty which makes it store
functional groups create bonds which makes it more stable
made of glucose
found in seeds and roots
coiled structure
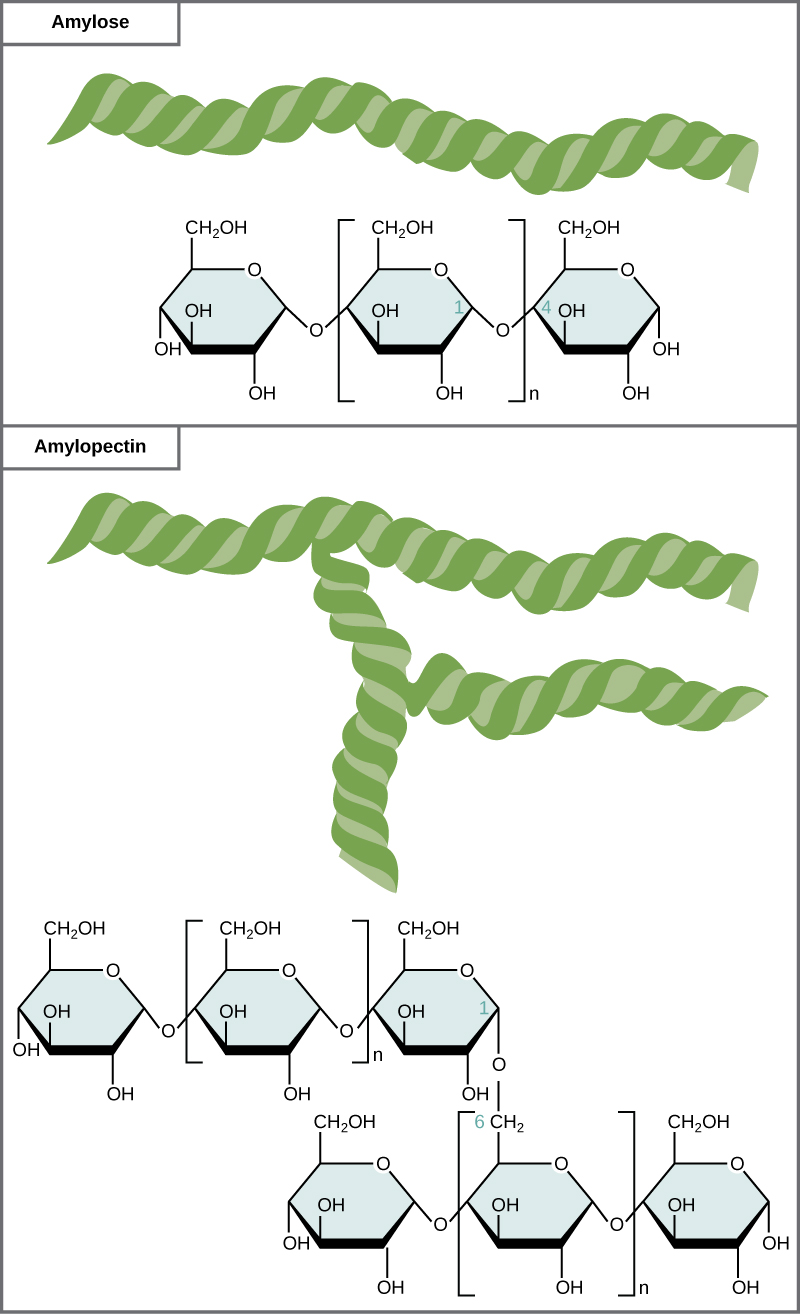
what are the two types of starch
amylose (basic and 1-4 glycosidic bonds)
amylopectin (alpha 1-4 links but with some alpha 1-6 links which makes branches)
what is the storage polysaccharide in animals
glycogen
found in the liver and the muscles
lots of branches
its a polymer of many carbon rings of glucose
coiled structure
liber uses it to mainatin glucose levels and muscles use it for energy for muscle contraction
what are structural polysaccharides + describe cellulose
cellulose
makes up plant cell walls
ghains of glucose molecules made up of 1-4 links but every second glucose is upside down
humans cant break it down
chains lie cluse together held by hydrogen bonds from O to H on chains
straight chain
beta glucose molecules
what is chitin
found in the exoskeleton of arthropods (insects) and fungilethery and becomes hard when touched with calcium carbonate
made of glucose units and nitrogen
how many bonds can carbon atoms form
4
the longer the chain of carbon carbom bonds…
the more stable the moleucle
what is the basis of nuecleic acids and proteins
double or single bonds of carbon with other carbon or non metalic elements
what makes up macromolecules
monomers that can link to form polymers
describe the hydrolysis of dissachride ….
breaks to glucose and fructose. the -OH group of the water molecule attahces to one of the monosscarhides while the -H arrahes to the other, which breaks the glycosidic bond
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/X7GZ8Jo9YQQ?si=25i7mSlRrHX1BS1s" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe>
why is glucose ppolar
because it has several -OH functional groups
the O atom in the glucose ring has a partial negative charge so the carbon hydrogen (CH) groups in it are partial positive
How does glucose dissolve in water
the -OH group of glucose makes a hydrogen bond with water
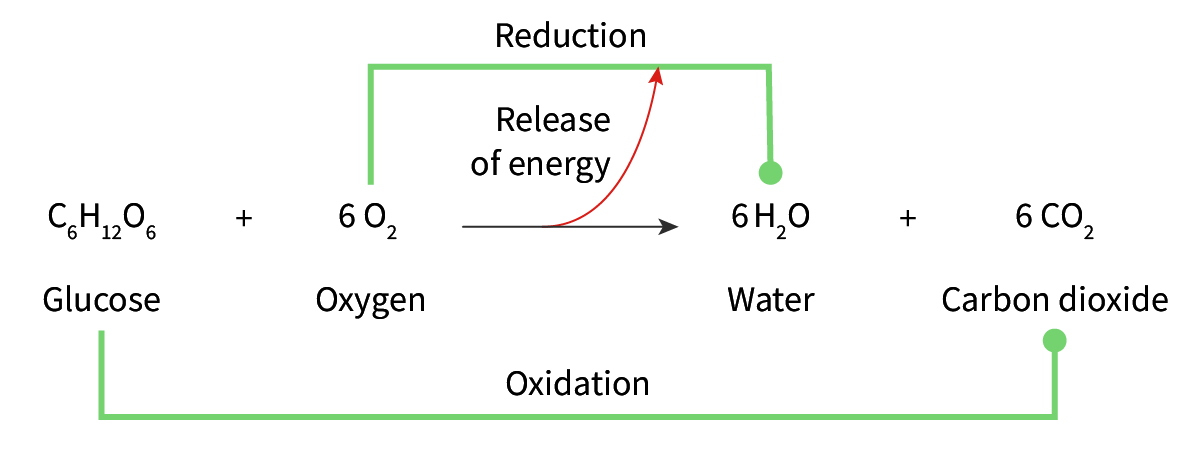
what is oxidation
the loss of electrons from a molecule
how is glucose oxidized
it loses electrons to oxygen and so it produces water and CO2 and energy is released to make ATP
what do hydrogen bonds do in cellulose
make stong and stable lattice tsructure of chains that are cross linked
why is cellulose necessary for the cell wall of plants
plants came withstand the forces of osmosis with it, or else they would collapse under their own weight
what is the role of glycoproteins in cell-cell recognition
they have carbs attached to them
they can be attached to amino acid residues in aprrotein or form branched linear chains from surface
they act as markers on the cell surface whuch means they identiy each other and foreign cells
can receive signals from cells (insluin binds to recpetor to give more glucose in cell)
ligans: bind to recpetors on cells to initate signalling pathways
structural supprot
ABO boold groups are an exaple of
glycoproteins found of the surface or red blood cells