Module 2 Abnormal ECGs
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
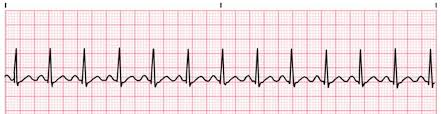
sinus tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is common, but usually reflects systemic illness or injury (such as
sepsis, trauma or dehydration), rather than a primary cardiac condition. The electrical
conduction through the heart is normal, albeit accelerated. The ECG appearances of
ST include:
■ regular rate, usually less than 120 bpm in an otherwise healthy person
■ normal appearance of P, QRS and T waves
■ QRS may be widened if an associated conduction defect is present—bundle branch
block (BBB)
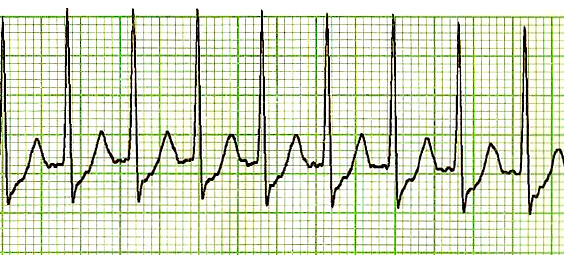
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
SVT includes several tachycardias arising from the AV node or above. The two most
common forms are AV node re-entry tachycardia and tachycardia associated with
accessory conduction pathways, such as Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW)3.
In both forms, an alternative electrical pathway is present which allows repeated
rapid conduction of atrial impulses to the ventricles and subsequent ventricular
stimulation.
The ECG appearances of SVT are characterised by:
■ hidden or absent P waves
■ regular QRS complexes (ventricular rate)—typically 120–180 bpm
■ normal QRS complexes in the absence of associated BBB (QRS may be widened
in WPW with conduction along the accessory pathway)
■ normal T waves.
what is Tachycardia
Tachycardia’ is an all-encompassing term that refers to a fast heartrate, usually in
excess of 100 bpm. Tachycardia may be classified as ‘regular’ or ‘irregular’, and may have a ‘narrow’ or ‘wide’ complex.
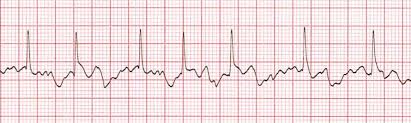
Atrial fibrillation
An irregular tachycardia in a conscious patient is almost always atrial fibrillation (AF).
AF is the result of chaotic electrical current flow in the atria resulting in independent
muscle fibre contraction (fibrillation), rather than a synchronous contraction of all
muscle fibres. The sino-atrial (SA) node no longer acts as a pacemaker for the heart.
The ECG appearances of AF are characterised by:
■ variable ventricular rate (QRS complexes)
■ absence of P waves
■ erratic baseline between QRS complexes
■ narrow QRS complexes in most cases, but these may be wide if an associated
BBB is present (aberrant conduction)
■ normal T waves
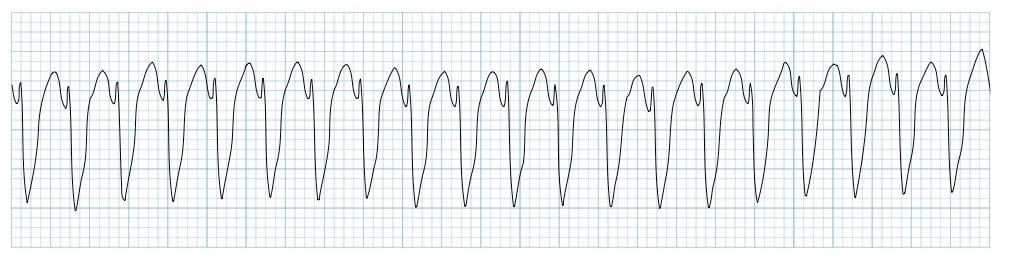
Ventricular Tachycardia
Atrial fibrillation
An irregular tachycardia in a conscious patient is almost always atrial fibrillation (AF).
AF is the result of chaotic electrical current flow in the atria resulting in independent
muscle fibre contraction (fibrillation), rather than a synchronous contraction of all
muscle fibres. The sino-atrial (SA) node no longer acts as a pacemaker for the heart.
The ECG appearances of AF are characterised by:
■ variable ventricular rate (QRS complexes)
■ absence of P waves
■ erratic baseline between QRS complexes
■ narrow QRS complexes in most cases, but these may be wide if an associated
BBB is present (aberrant conduction)
■ normal T waves
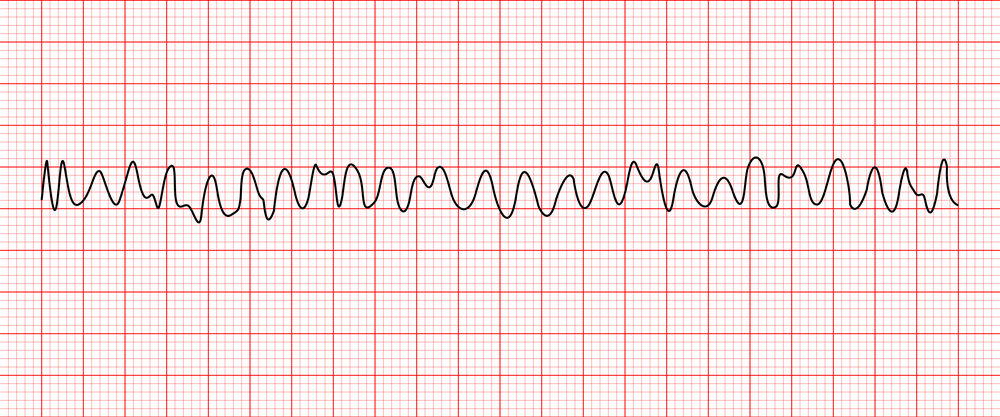
Ventricular fibrillation
VF is an asynchronous chaotic ventricular rhythm that follows no regular pattern and
produces no cardiac output. The patient will be unconscious.
The ECG appearances of VF are characterised by:
■ irregular undulations
■ no clear-cut ventricular complexes
■ varying ECG amplitude.
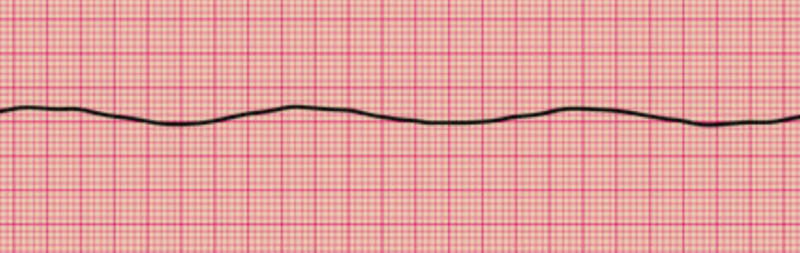
Asystole
Asystole is the term used to describe a lack of cardiac activity and contraction as a
result of a lack of any detectable electrical activity. It is usually a prelude to death.
The ECG appearances of asystole are:
■ lack of any P, QRS or T waves
■ lack of any irregular undulations
■ a ‘flat line’ appearance.
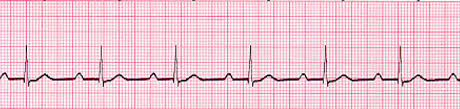
First-degree heart block
In first-degree heart block, conduction through the AV node is delayed, but all
impulses are conducted. The ECG in first-degree heart block is characterised by:
■ normal P waves
■ prolonged PR interval > 20 ms (5 mm)
■ normal QRS complexes and T waves.
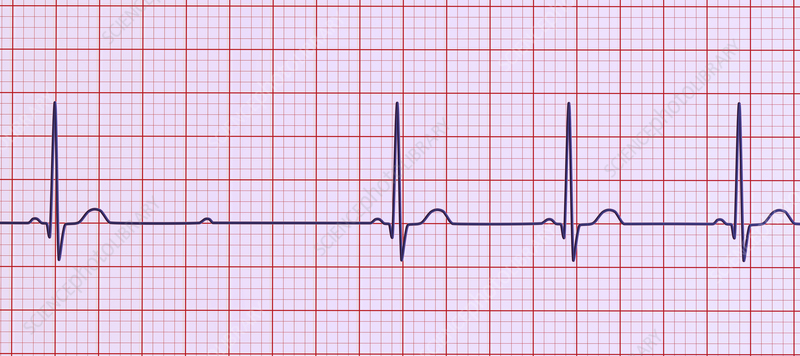
Second-degree heart block (Mobitz type1) (wenckebach)
In second-degree heart block, some—but not all—impulses are conducted through
the AV node. Second-degree heart block may be either Mobitz Type 1 (Wenckebach)
or Mobitz Type 2
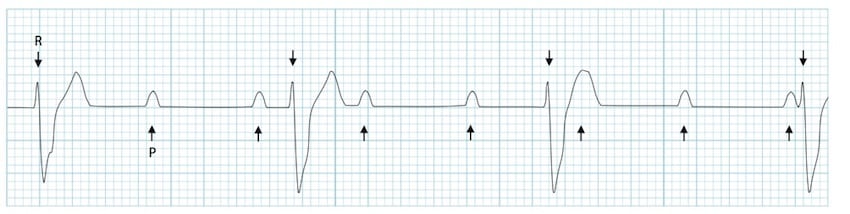
Third-degree (complete) heart block
Third-degree heart block is characterised by complete failure of atrial impulses to be
conducted through the AV node to the ventricles. The ECG in complete heart block is
characterised by:
■ normal regular P waves present, unless AF present
■ lack of association between P waves and QRS complexes (AV dissociation)
■ regular ventricular rate (QRS) 30–50 bpm
■ QRS complexes may be narrow or broad, depending on the level of block and origin
of ventricular pacemaker focus.