SLPA 455 Test/Quiz questions
5.0(5)
5.0(5)
Card Sorting
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
1
New cards
(Q1) (T or F) The peripheral nervous system is composed of your brain and spinal cord.
False
2
New cards
(Q1) (T or F) Motor signals (going from the brain to the periphery) are conveyed along efferent neurons, and sensory information (from the periphery to the brain) is transmitted by afferent nerve fibers.
True
3
New cards
(Q1) (T or F) Passive forces are generated by contraction of chest wall muscles during inspiration.
False
4
New cards
(Q1) ( T or F) The primary function of the pulmonary apparatus is to support speech production.
False
5
New cards
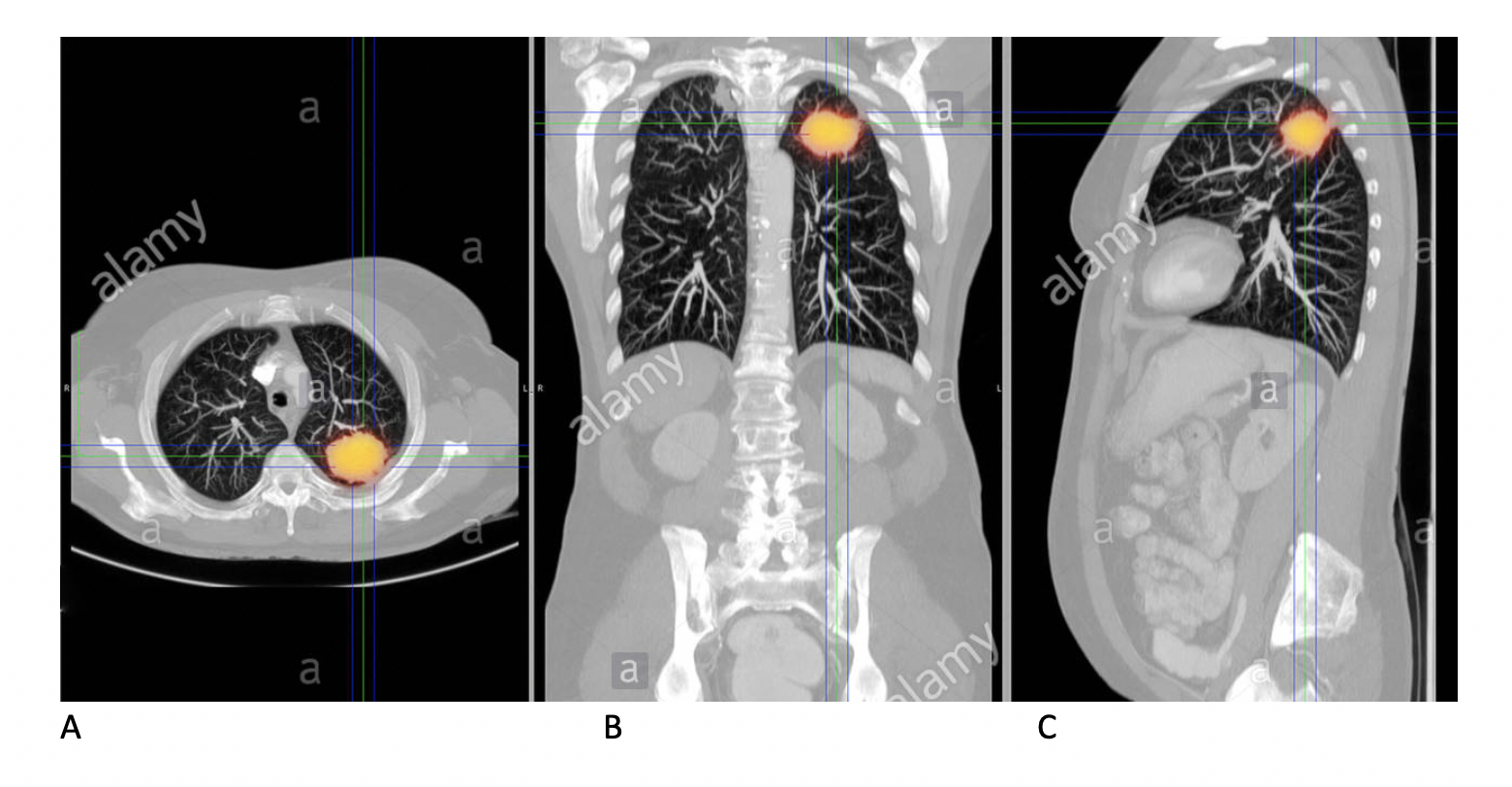
(Q1) The respiratory system are shown in what planes in images A to C?
A = Axial, B = Coronal, C = Sagittal
6
New cards
(Q1) (T or F) The ribcage and abdomen (AB) are regarded as components of the CHEST WALL, but are not essential for respiration, speech, and voice production.
False
7
New cards
(Q1) Muscles for inspiration versus muscles for expiration are examples of _________ muscles.
Antagonist
8
New cards
(Q1) (T or F) The ribcage is a rigid structure which consists of 18 pairs of immovable ribs made entirely of bone with immovable attachments to the sternum and vertebral column.
False
9
New cards
(Q1) Your thoracic spine is _________ to your sternum. (anatomical position)
Dorsal
10
New cards
(Q1) Pleural Pressure is ______. (check all that apply:)
* always positive
* always negative
* is fluctuating negative to positive
* is fluctuating positive to negative
* always positive
* always negative
* is fluctuating negative to positive
* is fluctuating positive to negative
ALWAYS Negative
11
New cards
(Q2) Assume lips/mouth open and vocal folds abducted. Now, a rapid increase in the vertical dimension of lung space within the rib cage is associated with:
a.) increased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and expiratory air flow
b.) increased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and inspiratory air flow
c.) decreased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and expiratory air flow.
d.) Decreased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and inspiratory air flow
a.) increased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and expiratory air flow
b.) increased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and inspiratory air flow
c.) decreased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and expiratory air flow.
d.) Decreased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and inspiratory air flow
d.) decreased alveolar pressure primarily due to active contraction of the diaphragm and inspiratory air flow.
12
New cards
(Q2) Which of the following helps decrease the surface tension in the alveoli to improve respiratory function?
* essential oils'
* surfactant
* synovial fluid
* pleural fluid
* essential oils'
* surfactant
* synovial fluid
* pleural fluid
Surfactant
13
New cards
(Q2) (pick the BEST answer) Sources of **passive force** in the chest wall include:
* The elasticity and contraction of the Pectoralis Major muscle
* Recoil of muscles, connective tissue, bone (ribs), cartilage (ribs), ligaments, surface tension of alveoli, and gravity
* Diaphragm muscle contraction
* Contraction of the scalenes muscles
* The elasticity and contraction of the Pectoralis Major muscle
* Recoil of muscles, connective tissue, bone (ribs), cartilage (ribs), ligaments, surface tension of alveoli, and gravity
* Diaphragm muscle contraction
* Contraction of the scalenes muscles
Recoil of muscles, connective tissue, bone (ribs), cartilage (ribs), ligaments, surface tension of alveoli, and gravity
14
New cards
(Q2) The costosternal and costovertebral joins make the following movements possible:
* Flexion of the cervical vertebrae
* Hip flexion relative to the lumbar spine
* “bucket-handle” and “pump-handle” rotation of the ribs
* Skull rotation
* Flexion of the cervical vertebrae
* Hip flexion relative to the lumbar spine
* “bucket-handle” and “pump-handle” rotation of the ribs
* Skull rotation
“bucket-handle and “pump-handle” rotation of the ribs.
15
New cards
(Q2) Increasing lung volume from 38% to 60% vital capacity in preparation for conversational speech likely involves activation of these muscles:
* interosseous internal intercostal muscles
* rectus abdominus muscles
* subcostal muscles
* external intercostal & diaphragm muscles
* interosseous internal intercostal muscles
* rectus abdominus muscles
* subcostal muscles
* external intercostal & diaphragm muscles
external intercostal & diaphragm muscles
16
New cards
(Q2) (T or F) The narrow space between the parietal pleura and visceral pleura is normally filled with air to facilitate coupling of the rib cage wall to the lungs, thereby allowing the lungs to expand during inspiration.
False
17
New cards
(Q2) Identify the muscle pairs listen below which are antagonists:
* levatores costarum and pectoralis major
* External intercostals and intercartilaginous internal intercostals
* Sternocleidomastoid and interosseus internal intercostals
* scalenes (all) and lateral iliocostalis cervicis
* Lateral iliocostalis lumborum and quadratus lumborum
* levatores costarum and pectoralis major
* External intercostals and intercartilaginous internal intercostals
* Sternocleidomastoid and interosseus internal intercostals
* scalenes (all) and lateral iliocostalis cervicis
* Lateral iliocostalis lumborum and quadratus lumborum
Sternocleidomastoid and interosseous internal intercostals
18
New cards
(Q2) Your functional residual (reserve) capacity is…
* IRV + VC
* TV + IRV
* IRV + ERV
* ERV + RV
* IRV + VC
* TV + IRV
* IRV + ERV
* ERV + RV
ERV + RV
19
New cards
(Q2) (T or F) In relation to breathing, contraction of the abdominal muscles (rectus abdominal, transversus and the external and internal obliques) serve to compress the abdominal contents and pull ribs downward, thus providing a forceful inspiratory drive.
False
20
New cards
(Q2) (T or F) The transversus abdominus muscles is deep to the internal oblique abdominal muscles, and is especially effective at compressing abdominal contents.
True
21
New cards
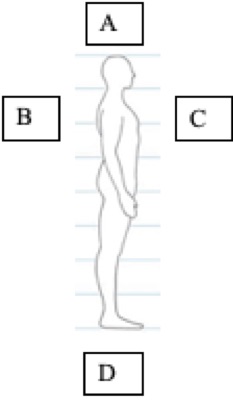
(T1) Identify the location term matching “c” in the diagram:
* Anterior and dorsal
* caudal and rostral
* posterior and dorsal
* posterior and ventral
* anterior and ventral
* Anterior and dorsal
* caudal and rostral
* posterior and dorsal
* posterior and ventral
* anterior and ventral
anterior and ventral
22
New cards
(T1) Which muscle has fibers from sternal, costal, and vertebral portions inserting into its central tendon?
* latissimus dorsi
* diaphragm
* quadratus lumborum
* sternocleidomastoid
* external oblique
* latissimus dorsi
* diaphragm
* quadratus lumborum
* sternocleidomastoid
* external oblique
Diaphragm
23
New cards
(T1) Which of the following monitors oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the arterial blood?
* terminal end buttons
* lewy body receptors
* central chemoreceptors
* peripheral chemoreceptors
* mechanoreceptors
* terminal end buttons
* lewy body receptors
* central chemoreceptors
* peripheral chemoreceptors
* mechanoreceptors
Peripheral chemoreceptors
24
New cards
(T1) A pneumothorax is primarily characterized by which of the following?
* air escaping from the lung into the pleural space causing positive pleural pressure
* aspiration of foreign material into the lungs
* low levels of surfactant production changing pleural pressure
* the replacement of lung tissue with stiff, scar-like tissure
* air escaping from the lung into the pleural space causing negative pleural pressure
* air escaping from the lung into the pleural space causing positive pleural pressure
* aspiration of foreign material into the lungs
* low levels of surfactant production changing pleural pressure
* the replacement of lung tissue with stiff, scar-like tissure
* air escaping from the lung into the pleural space causing negative pleural pressure
air escaping from the lung into the pleural space causing positive pleural pressure
25
New cards
(T1) The movement of the ribs that primarily helps increase transverse (side to side) thorax dimensions is the:
* bucket handle
* clavicual-sternal handle
* none are correct
* pump handle
* sternal handle
* bucket handle
* clavicual-sternal handle
* none are correct
* pump handle
* sternal handle
bucket handle
26
New cards
(T1) what structure forms the superior boundary of the chest cavity?
* pectoral girdle
* diaphragm
* larynx
* lumbar spine
* pelvic girdle
* pectoral girdle
* diaphragm
* larynx
* lumbar spine
* pelvic girdle
Pectoral girdle
27
New cards
(T1) Identify the four major abdominal muscles important for exhalation:
* rectus abdominus, transversus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques
* subclavius, rectus abdominus, levatores costarum, transversus abdominus
* external obliques, internal obliques, lateral iliocostalis lumborum, quadratus lumborum
* rectus abdominus, transversus abdominus, lateral iliocostalis cervicis, serratus posterior superior
* rectus abdominus, transversus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques
* subclavius, rectus abdominus, levatores costarum, transversus abdominus
* external obliques, internal obliques, lateral iliocostalis lumborum, quadratus lumborum
* rectus abdominus, transversus abdominus, lateral iliocostalis cervicis, serratus posterior superior
rectus abdominus, transversus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques
28
New cards
(T1) In contranst to quiet speech, loud speech is associated with higher targeted alveolar pressure in addition to:
* larger lung volumes and greater relaxation pressure
* larger lung volumes and lesser relaxation pressure
* smaller lung volumes and smaller relaxation pressure
* smaller lung volumes and greater relaxation pressure
* larger lung volumes and greater relaxation pressure
* larger lung volumes and lesser relaxation pressure
* smaller lung volumes and smaller relaxation pressure
* smaller lung volumes and greater relaxation pressure
larger lung volumes and greater relaxation pressure
29
New cards
(T1) The different layers of the meninges are:
* Parietal, visceral, pia
* Dura, Arachnoid, Pia
* Arachnoid, Alma, Dura
* Dura, Visceral, parietal
* Parietal, visceral, pia
* Dura, Arachnoid, Pia
* Arachnoid, Alma, Dura
* Dura, Visceral, parietal
Dura, Arachnoid, Pia (think DAP)
30
New cards
(T1) (T or F) Air pressure inside the lungs is known as pleural pressure.
False
31
New cards
(T1) Which of the following are True Ribs?
* 8-10
* 1-7
* 11-12
* none of these
* all of them
* 8-10
* 1-7
* 11-12
* none of these
* all of them
True ribs = 1-7!
32
New cards
(T1) Contraction of which muscle will produce expiratory force?
* inter-cartilaginous internal intercostals
* pectoralis minor
* masseter
* external intercostals
* interosseous internal intercostal
* inter-cartilaginous internal intercostals
* pectoralis minor
* masseter
* external intercostals
* interosseous internal intercostal
Interosseus internal intercostals
33
New cards
(T1) The thin tissue covering the surface of the chest wall that forms one side of the “pleural sandwich” is known as:
* abdominal pleura
* transverse pleural
* parietal pleura
* visceral pleura
* abdominal pleura
* transverse pleural
* parietal pleura
* visceral pleura
Parietal pleura
34
New cards
(T1) As people age, their vital capacity…
* fluctuates
* stays the same
* decreases
* increases
* fluctuates
* stays the same
* decreases
* increases
decreases
35
New cards
(T1) Quick changes in loudness, pitch and timing of the voice during running speech is known as:
* language fluctuation
* speech flow
* linguistic stress
* respiratory braking
* language fluctuation
* speech flow
* linguistic stress
* respiratory braking
Linguistic stress
36
New cards
(T1) Slurring of words due to decreased coordination and proprioception (awareness of body position and movement) is likely due to damage of the:
* cerebellum
* brain stem
* motor strip
* parietal lobe
* sensory strip
* cerebellum
* brain stem
* motor strip
* parietal lobe
* sensory strip
Cerebellum
37
New cards
(T1) Damage to the corticospinal tract will likely result in which of the following impairment(s):
* decreased movement of the tongue and face
* Decreased movement of the tongue during articulation
* Food entering the nasal cavity during swallowing
* decreased movement of the tongue during articulation and the diaphragm during respiration
* decreased movement of the diaphragm during respiration
* decreased movement of the tongue and face
* Decreased movement of the tongue during articulation
* Food entering the nasal cavity during swallowing
* decreased movement of the tongue during articulation and the diaphragm during respiration
* decreased movement of the diaphragm during respiration
Decreased movement of the diaphragm during respiration
38
New cards
(T1) In the supine position:
* there is no different in body shape of position that when upright.
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the head, meaning the person will shout quieter than when upright.
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the feet, meaning the person will shout quieter than when upright.
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the feet, meaning the person can shout louder than when upright
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the head, meaning the person can shout louder than when upright.
* there is no different in body shape of position that when upright.
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the head, meaning the person will shout quieter than when upright.
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the feet, meaning the person will shout quieter than when upright.
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the feet, meaning the person can shout louder than when upright
* the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the head, meaning the person can shout louder than when upright.
the abdominal wall falls in, and the diaphragm falls toward the head, meaning the person will shout quieter than when upright
39
New cards
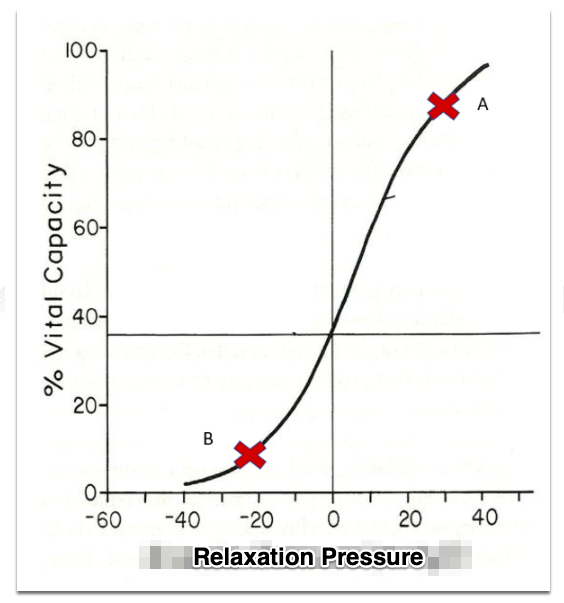
(T1) use the combined lung and chest wall relaxation pressure curve to answer the following question:
At 90% vital capacity (point a) the recoil/relaxation pressure is:
* positive for the chest wall and negative for the lungs
* negative for the chest wall and positive for the lungs
* positive for both the chest wall and lungs
* negative for both the chest wall and lungs
At 90% vital capacity (point a) the recoil/relaxation pressure is:
* positive for the chest wall and negative for the lungs
* negative for the chest wall and positive for the lungs
* positive for both the chest wall and lungs
* negative for both the chest wall and lungs
Positive for both the chest wall and lungs
40
New cards
(T1) The lungs and larynx are considered to be part of the ______ for speech
* source / generator
* oral system
* filter
* source / generator
* oral system
* filter
Source / generator
41
New cards
(T1) in which neural structure is the central pattern generator for respiration located
Medulla of the brain stem
42
New cards
(T1) A client with spinal cord injury resulting in poor control of muscles of the ribcage and diaphragm may have to resort to which type of non-typical breathing pattern?
Clavicular breathing
43
New cards
(T1) Which of the following is an example of running speech?
* sustain vowel production
* repeated syllable production (eg la la la)
* singing a note
* public speaking
* sustain vowel production
* repeated syllable production (eg la la la)
* singing a note
* public speaking
public speaking!
44
New cards
(T1) An injury impairing an individual’s ability to move their tongue would affect which of the four subsystems?
* pharyngeal-oral
* velopharyngeal nasal
* respiratory
* laryngeal
* pharyngeal-oral
* velopharyngeal nasal
* respiratory
* laryngeal
pharyngeal - oral
45
New cards
(T1) When the lungs are removed from the body, they rest and are at equilibrium:
* slightly open
* not enough info to answer
* collapsed
* fully open
* slightly open
* not enough info to answer
* collapsed
* fully open
collapsed
46
New cards
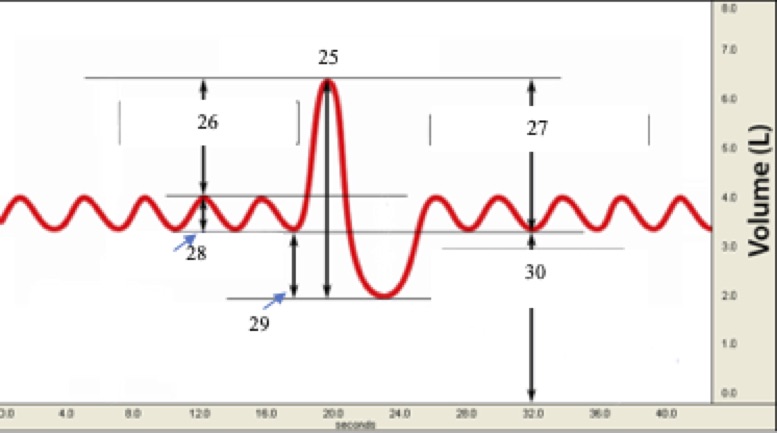
(T1) Label #26 on the graph below
* tidal volume
* expiratory reserve volume
* vital capacity
* inspiratory capacity
* inspiratory reserve volume
* tidal volume
* expiratory reserve volume
* vital capacity
* inspiratory capacity
* inspiratory reserve volume
inspiratory reserve volume
47
New cards
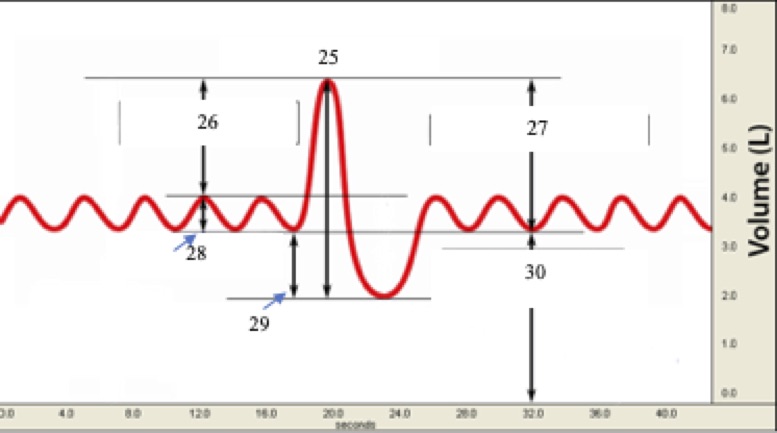
(T1) Label #27 on the graph below.
* inspiratory capacity
* tidal volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* vital capacity
* expiratory reserve volume
* inspiratory capacity
* tidal volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* vital capacity
* expiratory reserve volume
Inspiratory capacity
48
New cards
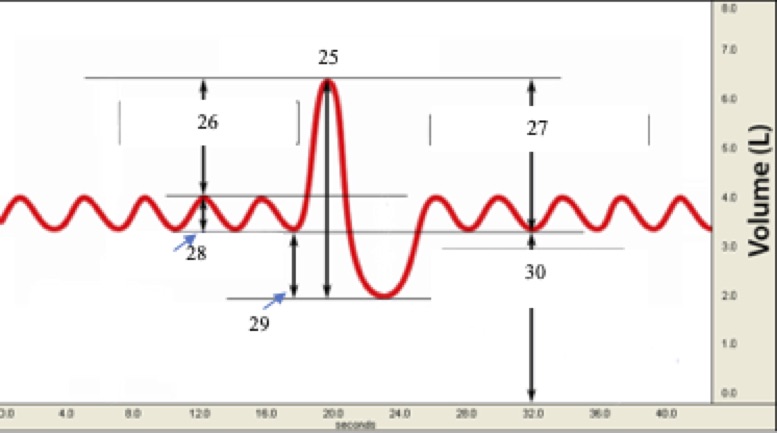
(T1) Label #28 on the graph below
* inspiratory reserve volume
* residual volume
* tidal volume
* functional residual (reserve) capacity
* expiratory reserve volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* residual volume
* tidal volume
* functional residual (reserve) capacity
* expiratory reserve volume
tidal volume
49
New cards
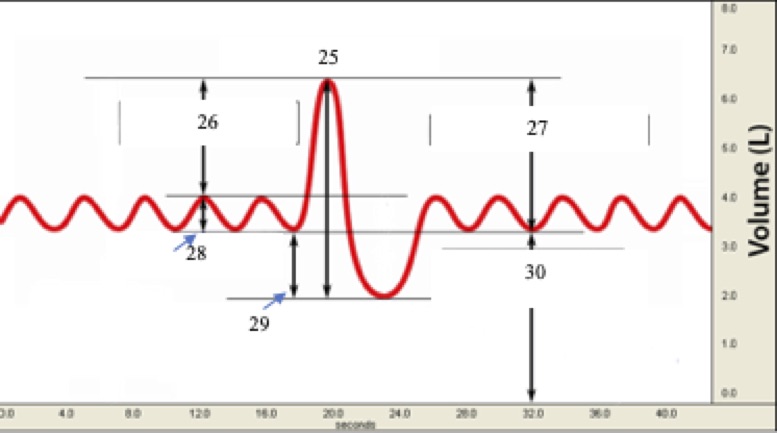
(T1) Label #29 on the graph below
* tidal volume
* residual volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* expiratory reserve volume
* functional residual (reserve) capacity
* tidal volume
* residual volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* expiratory reserve volume
* functional residual (reserve) capacity
Expiratory Reserve volume
50
New cards
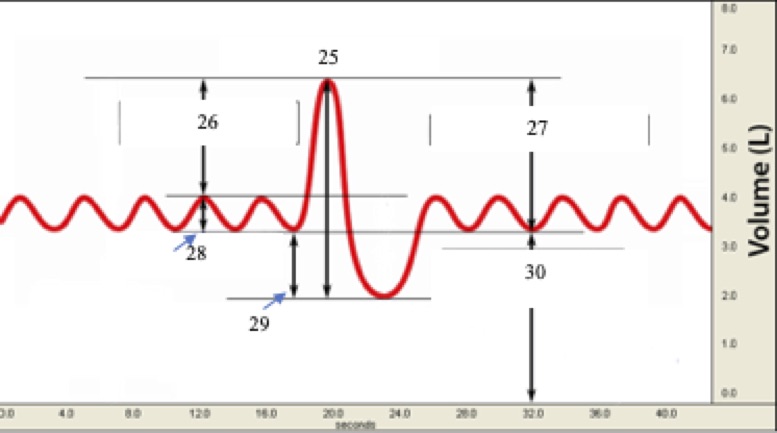
(T1) Label #30 on the graph below (the vertical line by the 30 should be continuous)
* tidal volume
* functional residual (reserve) capacity
* expiratory reserve volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* residual volume
* tidal volume
* functional residual (reserve) capacity
* expiratory reserve volume
* inspiratory reserve volume
* residual volume
Functional residual (reserve) capacity
51
New cards
(T1) When you are laying on your front, you are said to be in the _____ position.
Prone
52
New cards
(T1) The plane that would split your body into left and right lateral sides is known as the:
Sagittal plane
53
New cards
(T1) During respiratory braking, active forces are working ________ relaxation/recoil pressures.
* in synergy with
* in opposition to
* to enhance
* to multiply
* in synergy with
* in opposition to
* to enhance
* to multiply
in opposition to!
54
New cards
(T1) The electrical signal that travels down the axon is known as
an action potential
55
New cards
(T1) running speech usually occurs in the mid-range (60%) of:
* inspiratory volume
* tidal volume
* inspiratory capacity
* expiratory capacity
* vital capacity
* inspiratory volume
* tidal volume
* inspiratory capacity
* expiratory capacity
* vital capacity
vital capacity
56
New cards
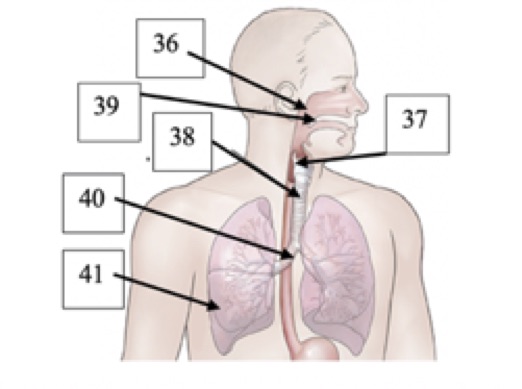
(T1)Label #36 in the picture below
* bronchus
* trachea
* larynx
* nasopharynx
* oropharynx
* bronchus
* trachea
* larynx
* nasopharynx
* oropharynx
nasopharynx
57
New cards
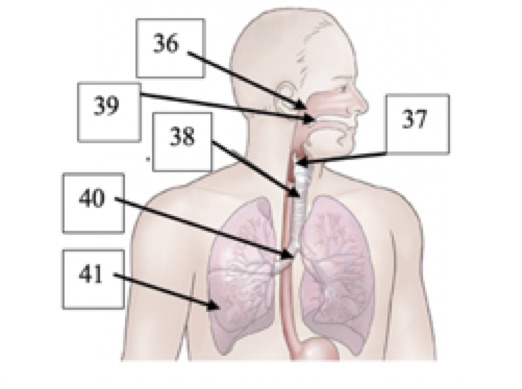
(T1) Label #37 in the picture below
* oropharynx
* bronchus
* nasopharynx
* trachea
* larynx
* oropharynx
* bronchus
* nasopharynx
* trachea
* larynx
larynx
58
New cards
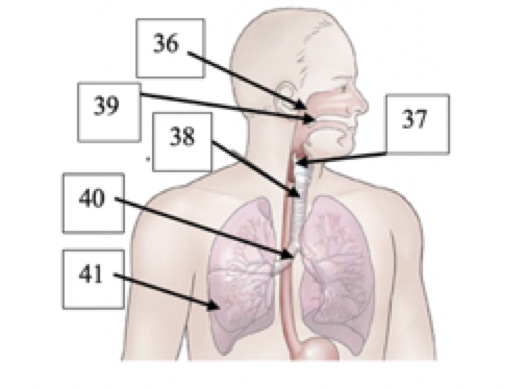
(T1) Label #38 in the picture below
* oropharynx
* trachea
* larynx
* nasopharynx
* bronchus
* oropharynx
* trachea
* larynx
* nasopharynx
* bronchus
trachea
59
New cards
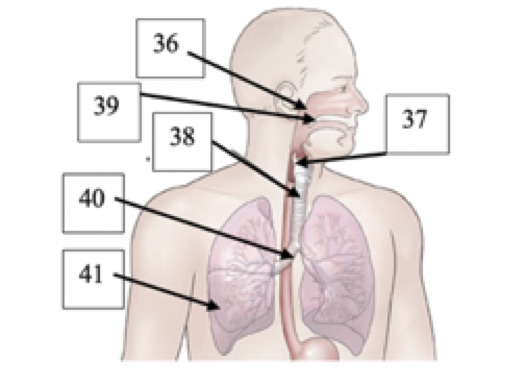
(T1) Label #39 on the picture below
* epiglottis
* velum
* bronchus
* alveoli
* bronchioles
* epiglottis
* velum
* bronchus
* alveoli
* bronchioles
velum
60
New cards
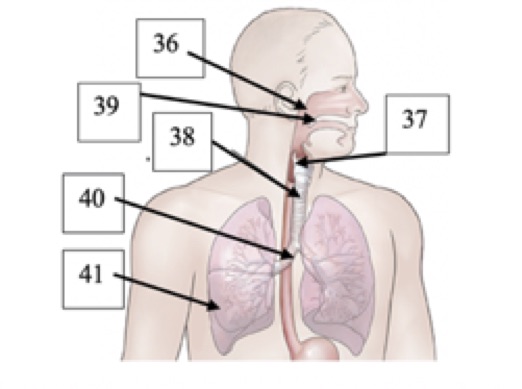
(T1) Label #40 on the picture below
* bronchioles
* epiglottis
* bronchus
* velum
* alveoli
* bronchioles
* epiglottis
* bronchus
* velum
* alveoli
bronchus
61
New cards
(T1) (T or F) A person cannot have impaired speech but intact language as both speech and language are synonymous terms (ie. speech and language are the same thing)
False
62
New cards
(T1) Which muscle is most effective at compressing abdominal contents like a belt?
Transverse abdominis
63
New cards
(T1) An adult with respiratory injury that results in a reduction in vital capacity would most likely…
* speak in long sentences
* speak louder
* produce more words/syllables per breath
* produce less words/syllables per breath
* speak in long sentences
* speak louder
* produce more words/syllables per breath
* produce less words/syllables per breath
produce less words/syllables per breath
64
New cards
(T1) The lateral iliocostalis group contains ___ muscle groups, containing the ______,__ _______,__ and _____ sections.
Three; Cervicus, Lumborum, Thoracis
65
New cards
(T1) The sternocleidomastoid and the pectoralis major are:
* antagonists for expiration
* synergists for inspiration
* antagonists for inspiration
* synergists for expiration
* antagonists for expiration
* synergists for inspiration
* antagonists for inspiration
* synergists for expiration
synergists for inspiration
66
New cards
(T1) (T or F) Active forces come from the elastic recoil of connective tissues (eg. cartilage), lung tissues, surface tneison, and gravity.
False
67
New cards
(T1) When the chest wall is at rest, intra-pleural pressure is:
* fluctuating above and below atmospheric pressure depending upon the phase of the respiratory cycle
* positive, above atmospheric pressure
* the same as atmospheric pressure
* negative, below atmospheric pressure
* fluctuating above and below atmospheric pressure depending upon the phase of the respiratory cycle
* positive, above atmospheric pressure
* the same as atmospheric pressure
* negative, below atmospheric pressure
negative, below atmospheric pressure
68
New cards
(T1) Alveoli pressure changing to a level below atmospheric pressure results in…
* expiration
* inspiration
* both inspiration and expiration
* depends on the task
* expiration
* inspiration
* both inspiration and expiration
* depends on the task
inspiration
69
New cards
(T1) (T or F) Intra-oral pressure would be higher for a stop consonant sound like “p” than for a vowel sound like “ahhhh”
True
70
New cards
(T1) If a person has damage to their right Phrenic nerve, you would expect the person to have:
* impairment to the movement of the pectoralis major’s left side
* impairment to the movement of the diaphragm’s left side
* none are correct
* impairment to the movement of the pectoralis major’s right side
* impairment to the movement of the diaphragm’s right side
* impairment to the movement of the diaphragm on both sides
* impairment to the movement of the pectoralis major on both sides
* impairment to the movement of the pectoralis major’s left side
* impairment to the movement of the diaphragm’s left side
* none are correct
* impairment to the movement of the pectoralis major’s right side
* impairment to the movement of the diaphragm’s right side
* impairment to the movement of the diaphragm on both sides
* impairment to the movement of the pectoralis major on both sides
impairment to the movement of the diaphragm’s right side
71
New cards
(Q3) (T or F) Abduction of the vocal ligaments results primarily from contraction of the Pars rectus muscle.
False
72
New cards
(Q3) The primary movement of the arytenoid cartilage is:
Rocking
73
New cards
(Q3) (T or F) The conus elasticus is a thinning of the cricothyroid ligament, and gives rise to the vocal ligament.
False (conus elasticus is a THICKENING of the CT ligament)
74
New cards
(Q3) The larynx has multiple functions including:
* prevent debris/food from entering airway
* creating thoracic (sub glottal) pressure
* increase subglottal pressure
* All are correct
* prevent debris/food from entering airway
* creating thoracic (sub glottal) pressure
* increase subglottal pressure
* All are correct
All of are correct!
75
New cards
(Q3) Which muscle primarily serves to lower medial compression of the vocal folds and widen the glottis?
Posterior Cricoarytenoid
76
New cards
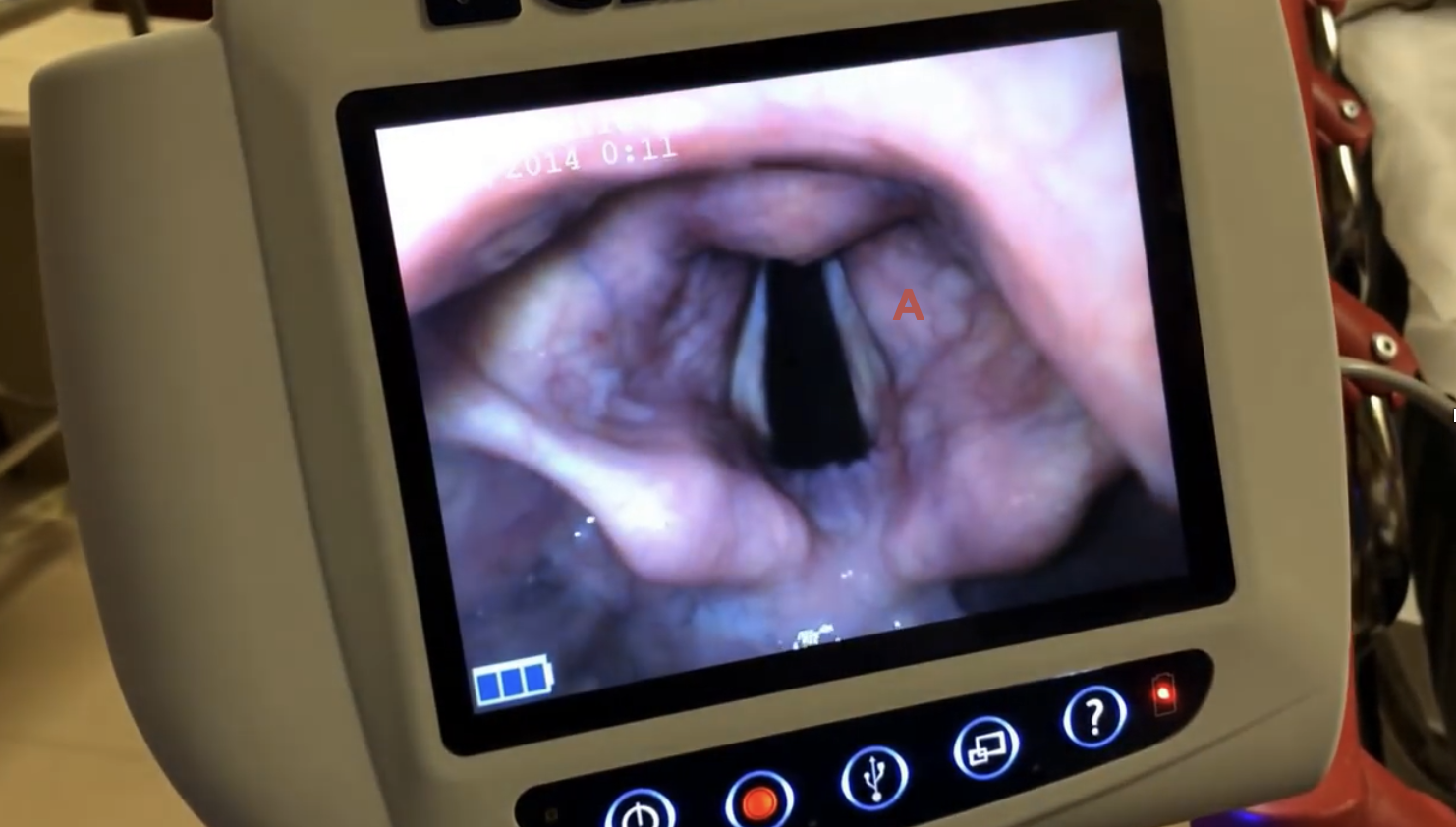
(Q3) Which of the following best describes the location of Letter “A” in this image:
False vocal folds
77
New cards
(Q3) During running speech, quick changes in pitch are primarily facilitated by joints lubricated with
* surfactant
* ligamental fluid
* mucosal fluid
* synovial fluid
* none of the above
* surfactant
* ligamental fluid
* mucosal fluid
* synovial fluid
* none of the above
synovial fluid
78
New cards
(Q3) (T or F) If you want to help someone with a tracheotomy tube speak, it is important to find a 2-way valve to place on the tracheostomy tube so air can move freely in and out through the tracheostomy tube.
False
79
New cards
(Q3) (T or F) The intrinsic muscles of the larynx primarily function to change the location/position of the laryngeal housing
False
80
New cards
(Q3) The ventricular folds (false vocal folds) are
* located inferior to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are used to generate voice
* located superior to the true vocal folds. ideally, the ventricular folds are used to generate voice
* Located inferior to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are not used to generate voice
* Located superiorly to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are not used to generate voice.
* located inferior to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are used to generate voice
* located superior to the true vocal folds. ideally, the ventricular folds are used to generate voice
* Located inferior to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are not used to generate voice
* Located superiorly to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are not used to generate voice.
located superiorly to the true vocal folds. Ideally, the ventricular folds are NOT used to generate voice
81
New cards
(Q4) An expected fundamental frequency range for a male is
* 85-180 Hz
* 165-255 Hz
* 85-180 dB
* 165-255 dB
* 85-180 Hz
* 165-255 Hz
* 85-180 dB
* 165-255 dB
85-180 Hz
82
New cards
(Q4) The muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage serves as the insertion for:
* vocalis muscle and omohyoid muscle
* posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and stylohyoid muscle
* posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytneoid muscle
* rectus and oblique heads of the cricothyroid muscle
* vocalis muscle and omohyoid muscle
* posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and stylohyoid muscle
* posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytneoid muscle
* rectus and oblique heads of the cricothyroid muscle
posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
83
New cards
(Q4) A soft/breathy vocal attack is associated with:
* extreme contraction on the LCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* light contraction on the LCA to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* Extreme contraction on the PCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* extreme contraction on the PCA to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* extreme contraction on the LCA to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* Light contraction on the LCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* Light contraction of the CT muscle to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* extreme contraction on the LCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* light contraction on the LCA to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* Extreme contraction on the PCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* extreme contraction on the PCA to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* extreme contraction on the LCA to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* Light contraction on the LCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
* Light contraction of the CT muscle to create high laryngeal opposing pressure
* to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
light contraction on the LCA to create low laryngeal opposing pressure
84
New cards
(Q4) (T or F) Contraction of the PCA abducts the vocal folds, and are active during deep inspirations
True
85
New cards
(Q4) Falsetto voice (high pitch) is voice supported by
* increased levels of vocal fold tension, and a slow vibration frequency
* low levels of vocal fold tension, and a rapid vibration frequency
* increased levels of vocal fold tension, and a rapid vibration frequency
* Increased levels fo vocal fold tension, and a slow vibration frequency
* increased levels of vocal fold tension, and a slow vibration frequency
* low levels of vocal fold tension, and a rapid vibration frequency
* increased levels of vocal fold tension, and a rapid vibration frequency
* Increased levels fo vocal fold tension, and a slow vibration frequency
increased levels of vocal fold tension, and a rapid vibration frequency
86
New cards
(Q4) (T or F) During a hard glottal attack, expiratory airflow precedes vocal fold vibration
False
87
New cards
(Q4) (T or F) Muscles above the hyoid bone are antagonistic with those below the hyoid bone.
True
88
New cards
(Q4) Activation of which muscle(s) would best support my ability to shout loudly?
* a - lateral cricoarytenoid
* b- posterior cricoarytenoid
* c- interarytenoid
* d- cricothyroid
* a and d
* c and c
* a and c
* a - lateral cricoarytenoid
* b- posterior cricoarytenoid
* c- interarytenoid
* d- cricothyroid
* a and d
* c and c
* a and c
a and c (lateral cricoarytenoid and interarytenoid
89
New cards
(Q4) Which nerve/branch controls the cricothyroid muscle?
External superior laryngeal nerve
90
New cards
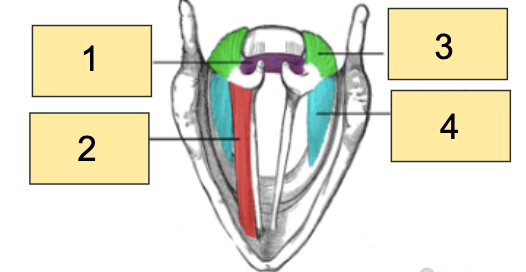
(Q4) Number 2 in the image below refers to the:
Thyroarytenoid muscle
91
New cards
(T2) In the source-filter theory of voice production, the larynx services as the:
source/generator
92
New cards
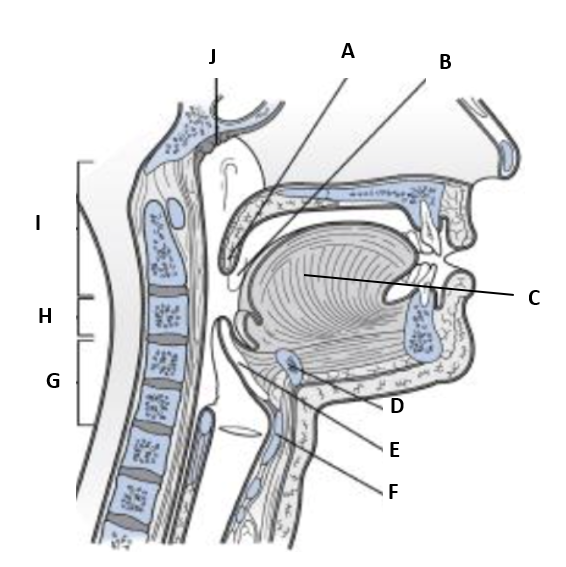
(T2) Label D on the diagram
* treu vocal folds
* false vocal folds
* cricoid cartilage
* thyroid cartilage
* hyoid bone
* treu vocal folds
* false vocal folds
* cricoid cartilage
* thyroid cartilage
* hyoid bone
hyoid bone
93
New cards
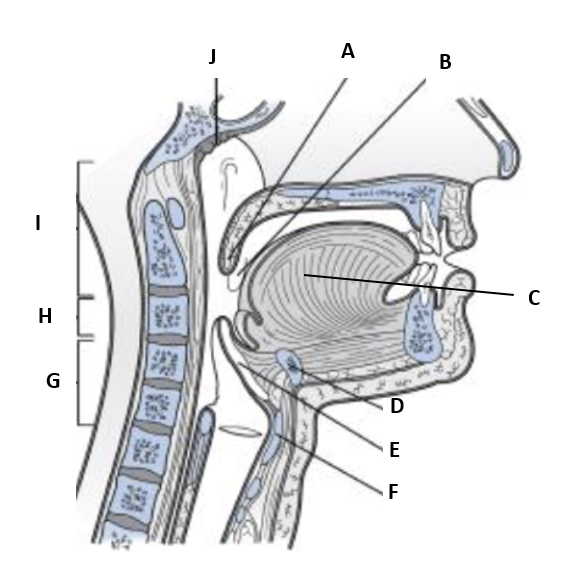
(T2) Label F on the diagram
* cricoid cartilage
* posterior pharyngeal wall
* epiglottis
* hyoid bone
* thyroid cartilage
* cricoid cartilage
* posterior pharyngeal wall
* epiglottis
* hyoid bone
* thyroid cartilage
thyroid cartilage
94
New cards
(T2) Which of the following extrinsic muscles or muscles would best support increased pitch?
* A- thyrohyoid
* b - sternohyoid
* c - omohyoid
* A and C
* A and B
* B and C
* A- thyrohyoid
* b - sternohyoid
* c - omohyoid
* A and C
* A and B
* B and C
A - Just Thyrohyoid
95
New cards
(T2) Which of the following may best help someone speak after a total laryngectomy?
* walkie talkies
* electrolarynx
* masako maneuver
* vocal attacks
* gentle onsets
* none of the above
* walkie talkies
* electrolarynx
* masako maneuver
* vocal attacks
* gentle onsets
* none of the above
electrolarynx
96
New cards
(T2) which intrinsic laryngeal muscle is regarded as the primary pitch/fundamental frequency controller for voice?
* posterior cricoarytenoid m.
* cricothyroid m
* interarytenoid m
* vocalis m
* posterior cricoarytenoid m.
* cricothyroid m
* interarytenoid m
* vocalis m
Cricothyroid m
97
New cards
(T2) (T or F) The arytenoid cartilages are located immediately superior to the cricoid cartilage
True
98
New cards
(T2) (T or F) Vocal fold oscillations are the result of rapid, alternating, muscular contractions of the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle and posterior cricoarytenoid muscles
false
99
New cards
(T2) Your perception of vocal fold vibration amplitude is known as:
Loudness
100
New cards
(T2) Damage to the superior laryngeal nerve (external branch) would impair which of the following muscles (or muscle)?
* a - cricothyroid muscle
* b - vocalis muscle
* c - lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* d - posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
* a and b
* a nad c
* b and d
* c and d
* a - cricothyroid muscle
* b - vocalis muscle
* c - lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* d - posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
* a and b
* a nad c
* b and d
* c and d
a - just cricothyroid muscle