Orgo II Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:18 PM on 10/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
1
New cards
IMPORTANT things to remember for MC exam
\-For select all that apply questions, make sure you look at every option carefully. (If ==**charge**== is correct, if arrows are going the correct direction, configurations)
2
New cards
common electrophile
carbonyl
3
New cards
how to calculate oxidation state fast
Pick an atom that changes
If its connected to an atom more electronegative than +1
If its connected to an atom less electronegative than -1
(count double bonds twice)
add it all up: if oxid # went up, then it was oxidized
If its connected to an atom more electronegative than +1
If its connected to an atom less electronegative than -1
(count double bonds twice)
add it all up: if oxid # went up, then it was oxidized
4
New cards
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Benzene is nucleophile
5
New cards
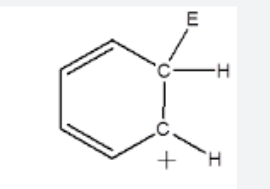
general name of this structure
benzenium ion/cyclohexadienyl cation/ wheland intermediate
6
New cards
Rate determining step is
formation of benzenium
7
New cards
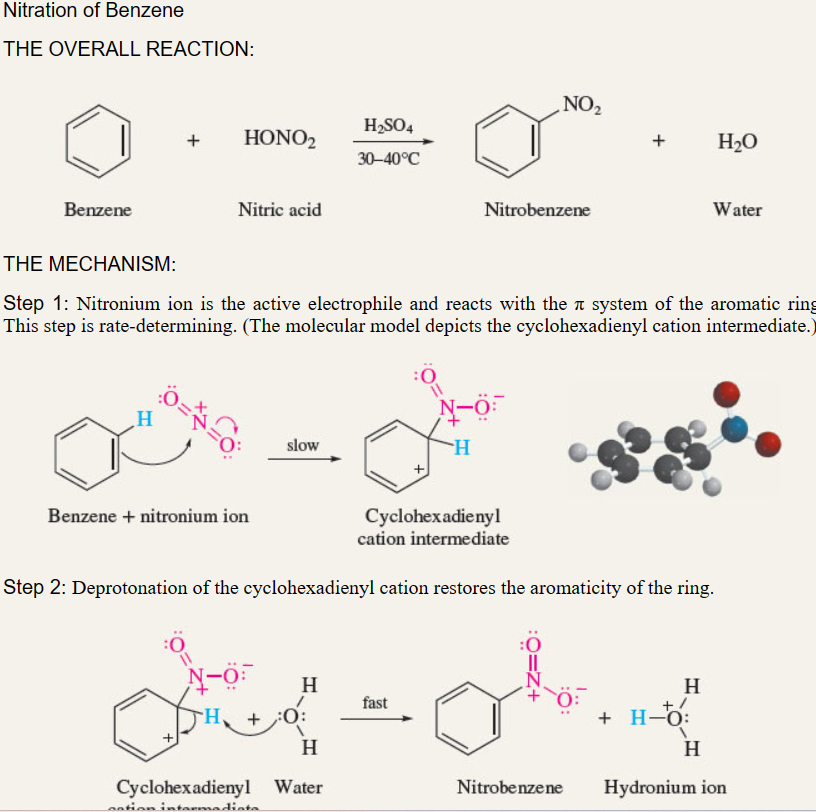
Nitration of benzene
benzene + HNO3 and H2SO4 → nitrobenzene
\
electrophile is NO2+
\
electrophile is NO2+
8
New cards
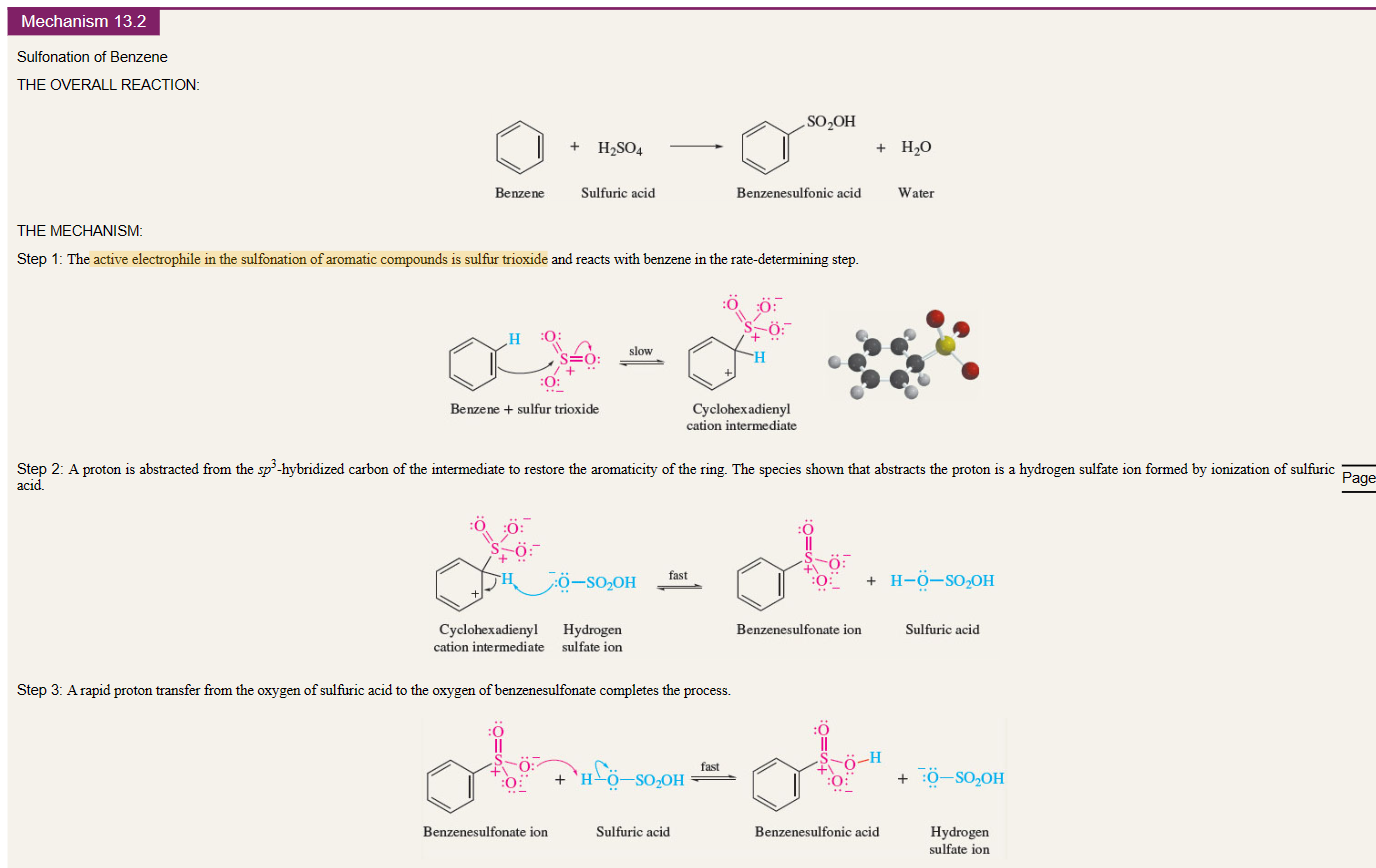
Sulfonation of benzene
benzene + H2SO4 →
electrophile is SO3
electrophile is SO3
9
New cards
Halogenation of benzene
benzene + Fe + Br2
electrophile is Bromine-Iron (III) Bromide complex
electrophile is Bromine-Iron (III) Bromide complex
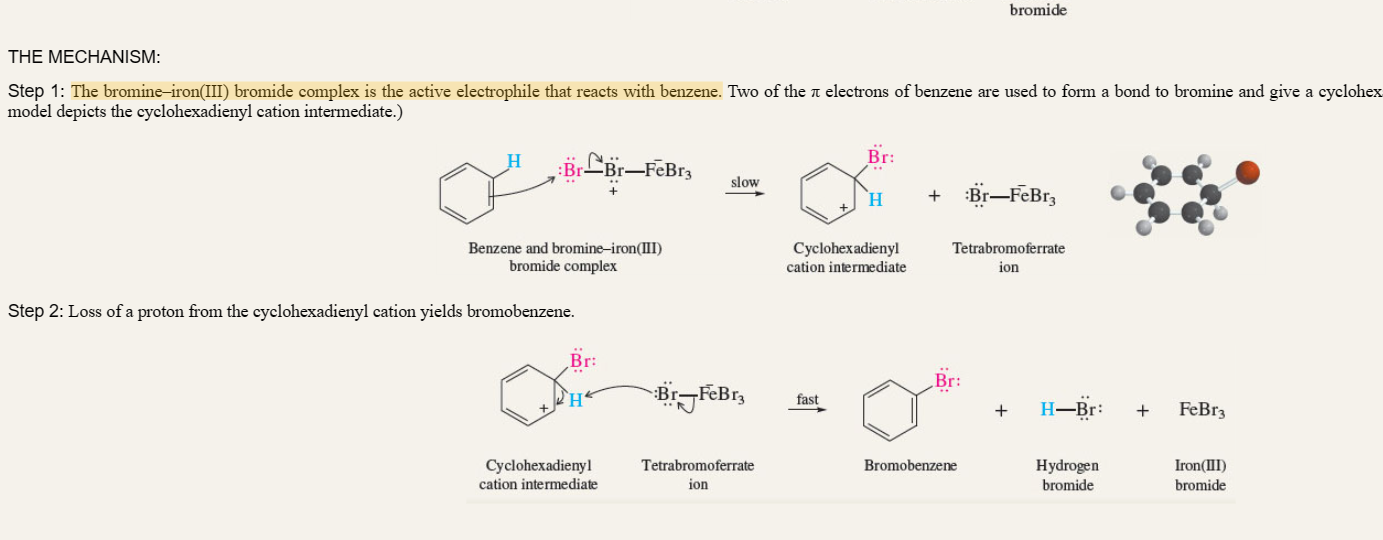
10
New cards
Friedel Crafts Alkylation
benzene + secondary halide or tertiary halide
electrophile is carbocation
==note:== subject to rearrangement
electrophile is carbocation
==note:== subject to rearrangement
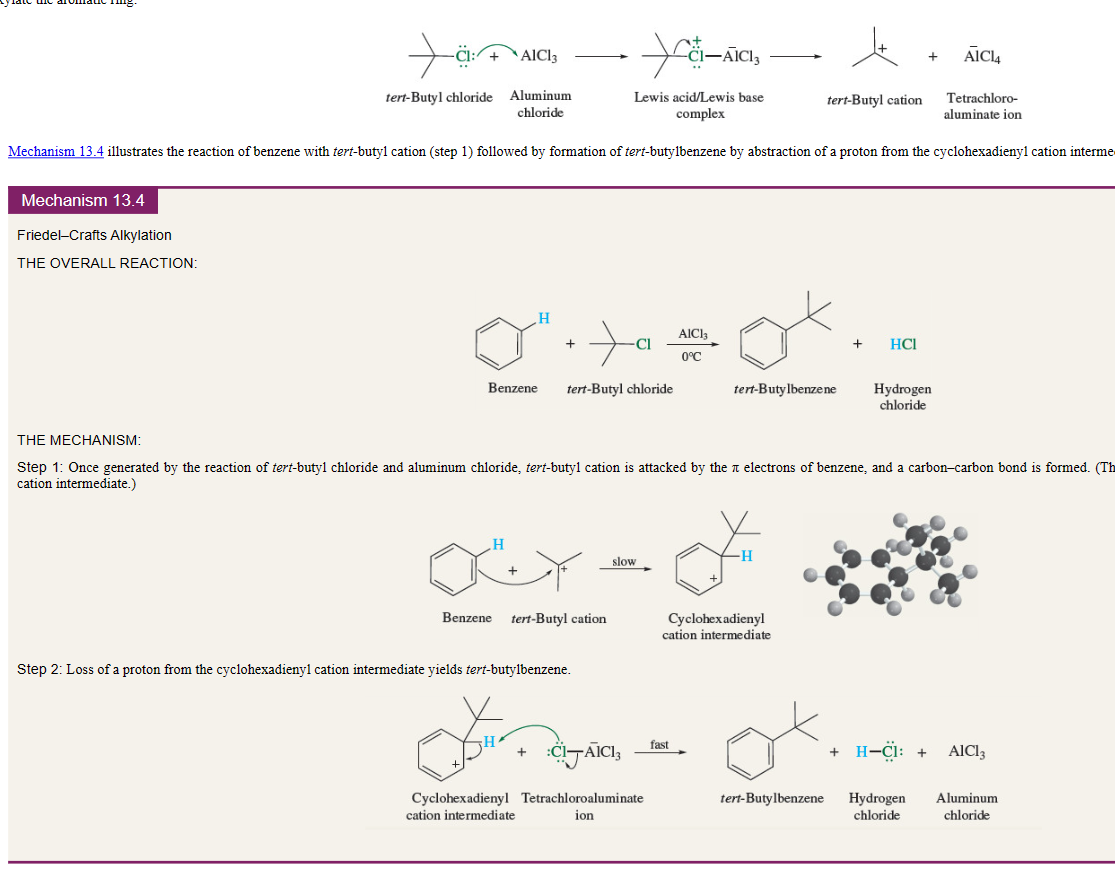
11
New cards
alkenes, which are converted to carbocations by protonation can be used to alkylate benzene
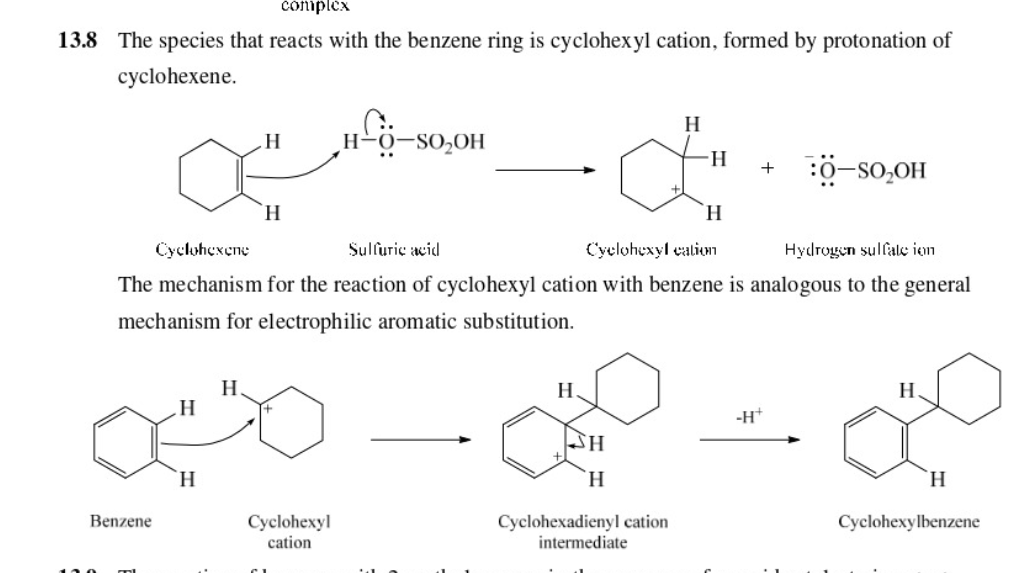
12
New cards
Freidel’s Crafts of Acylation
electrophile is acyl cation
==Do not rearrange==
==Do not rearrange==
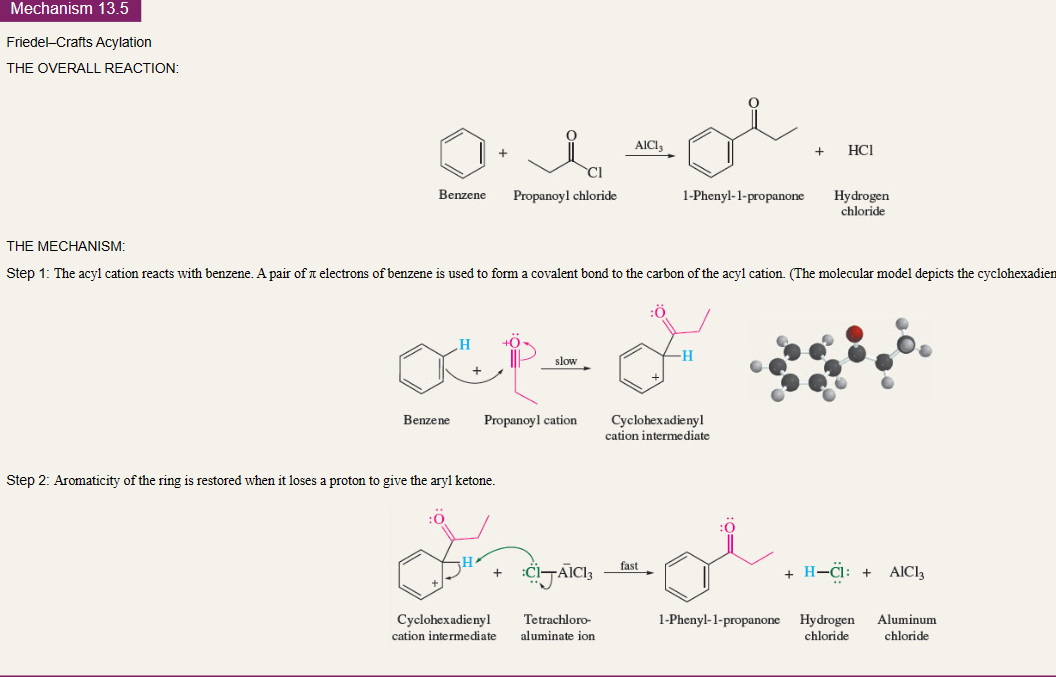
13
New cards
Preparation of acyl chlorides
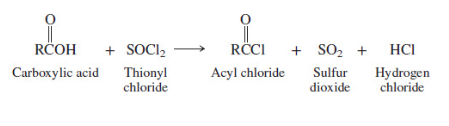
14
New cards
Freidel’s Crafts Acylation using anhydrides
no issue of rearrangement
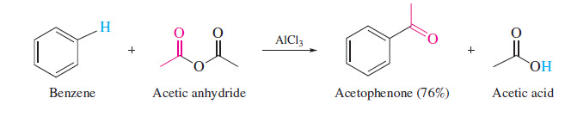
15
New cards
Acylation-reduction
no issue of rearrangement
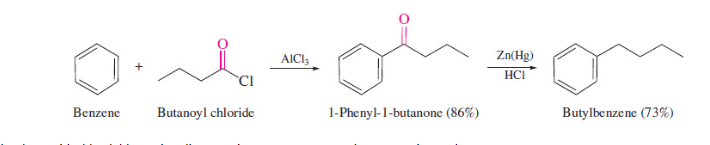
16
New cards
Substituent effect
\-To make a stronger nucleophile, put more electron density
\-To make weaker nucleophile, add more electronegativity
\-To make weaker nucleophile, add more electronegativity
17
New cards
Electron Drawing Group (activating)
Ortho-Para Director
18
New cards
Electron Withdrawing group (deactivating)
Meta Director
examples: -CF3, -NO2, -SO3H, electropositive carbon
examples: -CF3, -NO2, -SO3H, electropositive carbon
19
New cards
Halogens are…
deactivating but Ortho/Para directing
20
New cards
If multiple substituents,
Stronger EDG will dictate regiostreochemistry
21
New cards
EDG ranks highest to lowest
R2N-
RO-
R-
Cl,Br
RO-
R-
Cl,Br
22
New cards
Nucleophilic aromatic Substitution
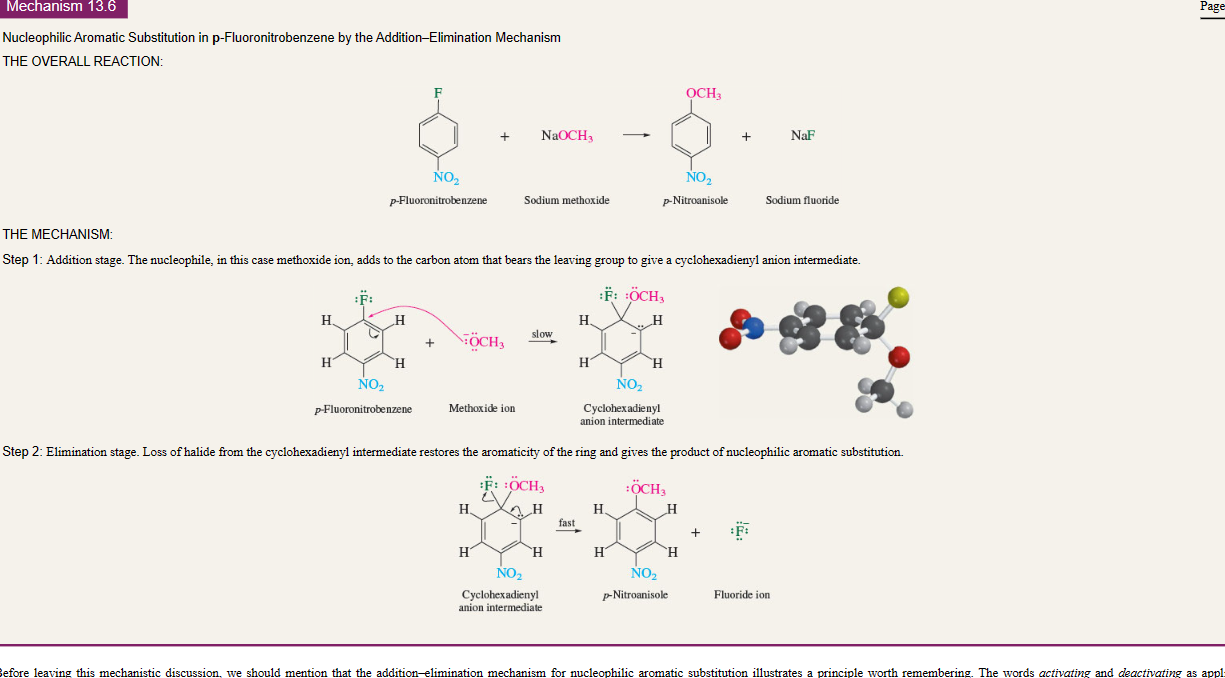
23
New cards
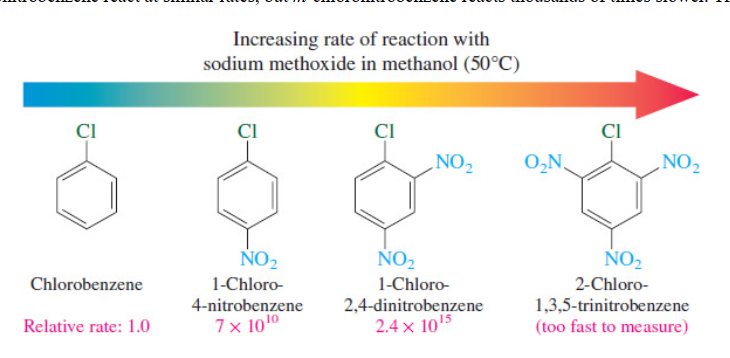
Nucleophilic substitution
ortho and para sites of EWG react way faster
24
New cards
Tip for retrosynthesis
"An aromatic ring more deactivated than a monohalobenzene cannot be alkylated or acylated under Friedel–Crafts conditions."
25
New cards
organometallic nomenclature
attached alkyl group is prefix, metal is the parent
when metal bears two substituents, treat it as it was a anion
when metal bears two substituents, treat it as it was a anion
26
New cards
Grignard reagents
organomagneisum compounds
27
New cards
RX + 2Li with diethyl ether
RLi + LiX
28
New cards
RX + Mg with diethyl ether
RMgX
29
New cards
Reaction of organic halide with metal is ox-redox reaction
metal is oxidized/ reducing agent
30
New cards
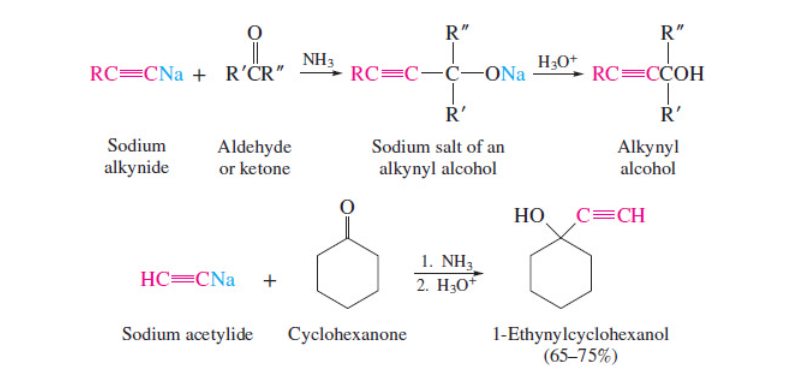
synthesis of acetylenic alcohols
use terminal alkynes
31
New cards
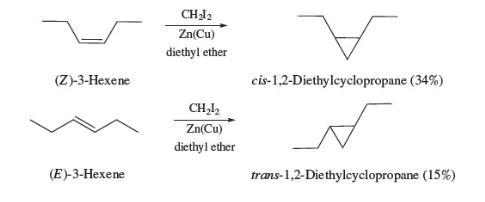
orgozinc reagents for epoxides
ICH2ZnI is electrophile (due to empty p orbital)
32
New cards
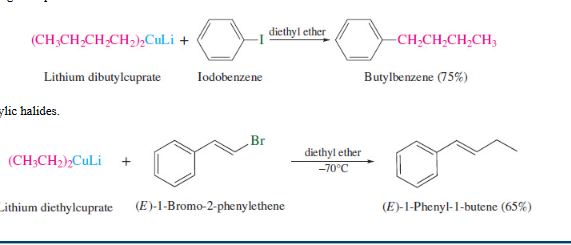
Lithium dialkylcuprate (Gilman reagent)
33
New cards
P-toluenesulfonates
displaces halide as well, same sterochemistry
34
New cards
alkene to alcohol (OH to most substituted)
Use H2SO4 and H2O
35
New cards
alkene to alcohol (OH to least substituted)
1\.B2H6, diglyme
2. H2O2, OH-
\
2. H2O2, OH-
\
36
New cards
3 ways for reduction
First way: NaBH4 and methanol/H2O/ethanol
\
Second way:
1. LiAlH4, diethyl ether
2. H2O
\
Third way:
H2, Pt, ethanol
\
Second way:
1. LiAlH4, diethyl ether
2. H2O
\
Third way:
H2, Pt, ethanol
37
New cards
LiAl4 and NaBH4 are
nucleophiles/reducing agents
38
New cards
reduction of carboxylic acid
turns to primary alcohol (turns to aldehyde first)
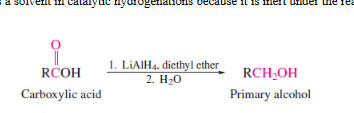
39
New cards
Diol nomenclature
alkane + #,# diol
40
New cards
dihydrooxylation of alkene
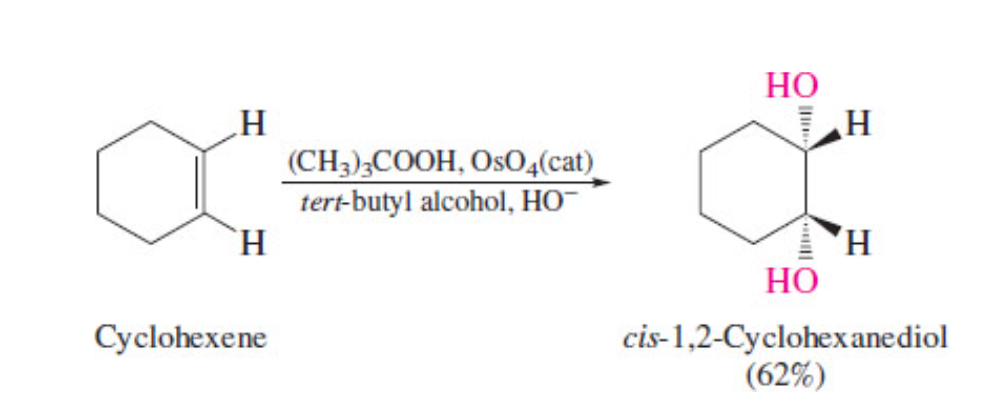
41
New cards
conversion of alcohols to ethers
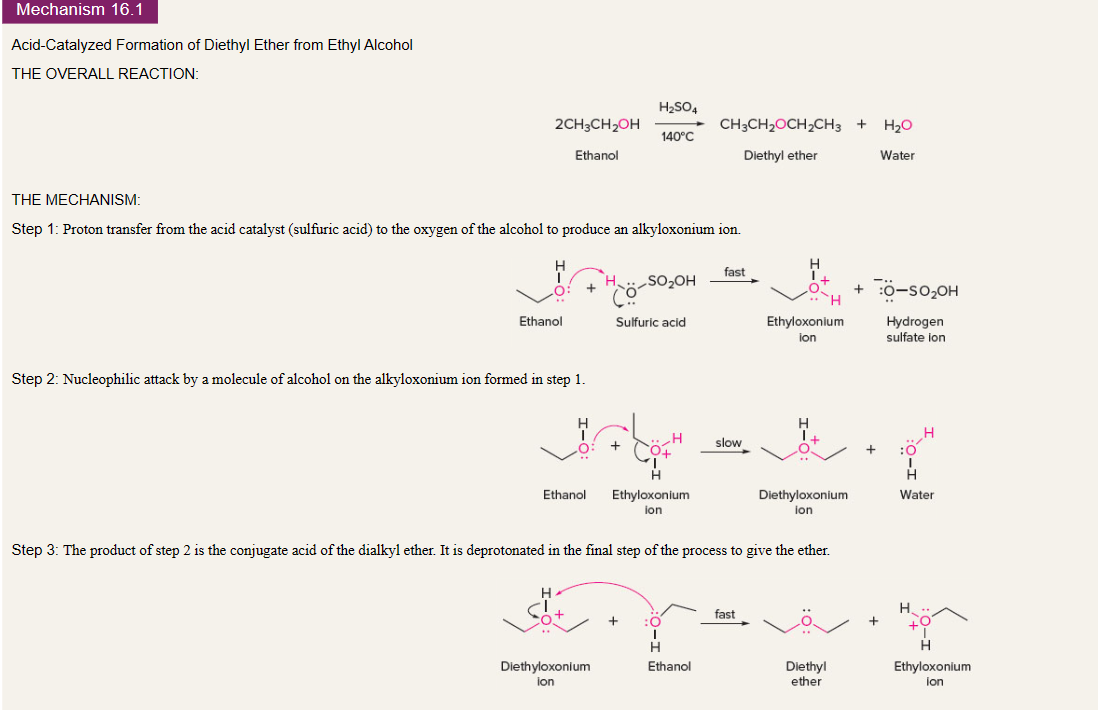
42
New cards
Esterfication
retention of configuration
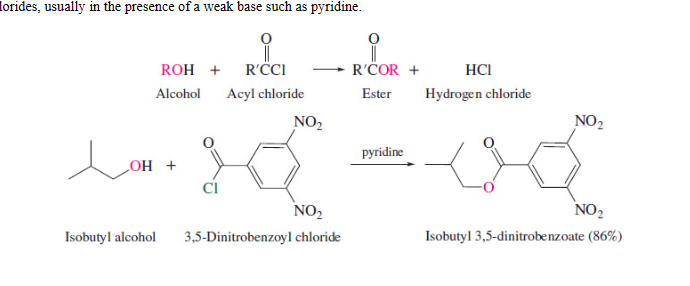
43
New cards
Primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
use K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4, and H2O
44
New cards
Primary alcohol to aldehyde
PCC and CH2Cl2
45
New cards
Secondary alcohol to ketone
First way: Na2Cr2O7, H2O and H2SO4
\
Second way: PCC, CH2Cl2
\
Second way: PCC, CH2Cl2
46
New cards
oxidizing tertiary alcohols
Tertiary alcohols are NOT readily oxidized → No reaction
47
New cards
Swern Oxidation
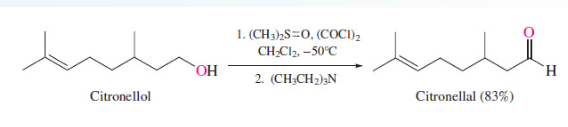
48
New cards
oxidative cleavage of vicinal diols
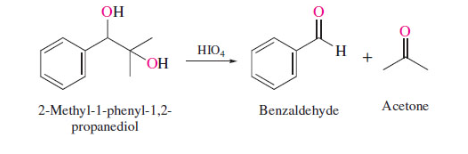
49
New cards
thiol nomenclature
similar to diol, it OH group present, then use prefix sulfonyl- or mercapto-
50
New cards
thiols are
strong smelling (skunk fluid)
51
New cards
alkyl halide with -SH
change of configuration
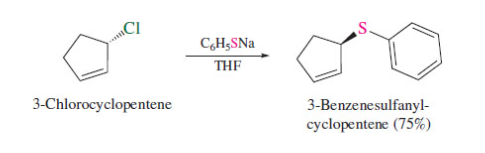
52
New cards
Disulfide formation
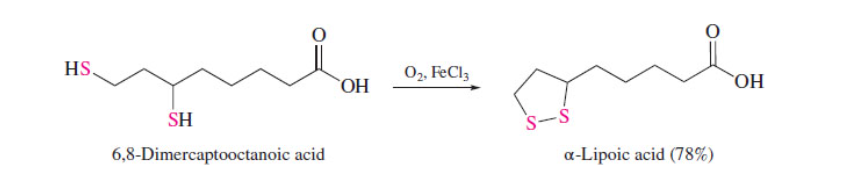
53
New cards
Ether nomenclature
list the two alkyl groups and add ether at the end
54
New cards
ether oxygen is a hydrogen bond acceptor
which means soluble in water
55
New cards
Crown nomenclature
Total # of atoms-crown-# of oxygens
56
New cards
18-crown-6 solubilizes
potassium salts
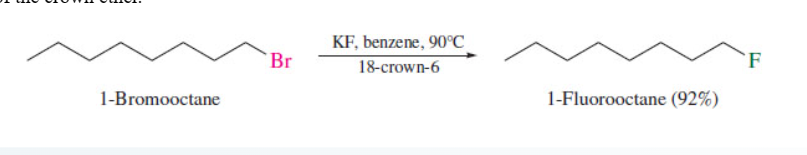
57
New cards
Ethers from alcohol and alkene
1. protonation
2. add O group
3. deprotonation
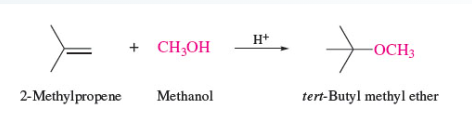
58
New cards
make vicinal halohydrins from alkene
trans addition
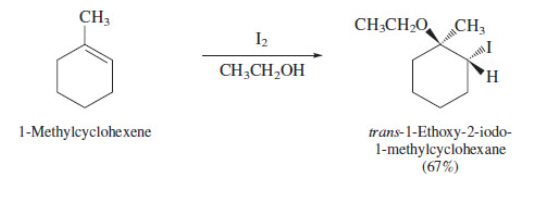
59
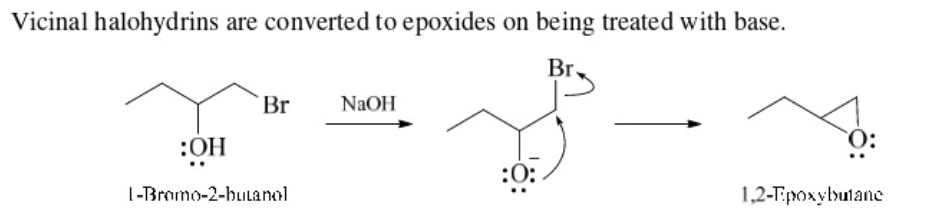
New cards
vicinal halohydrins to epoxide
Use NaOH and H2O
60
New cards
Williamson ether synthesis
ONLY primary halides,
secondary halides undergo E2
secondary halides undergo E2
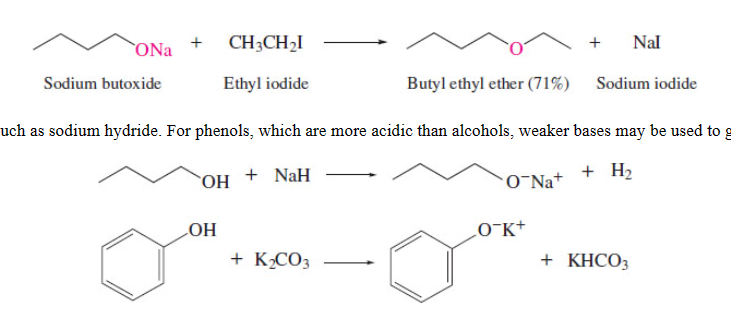
61
New cards
preparing sulfides
change of configuration
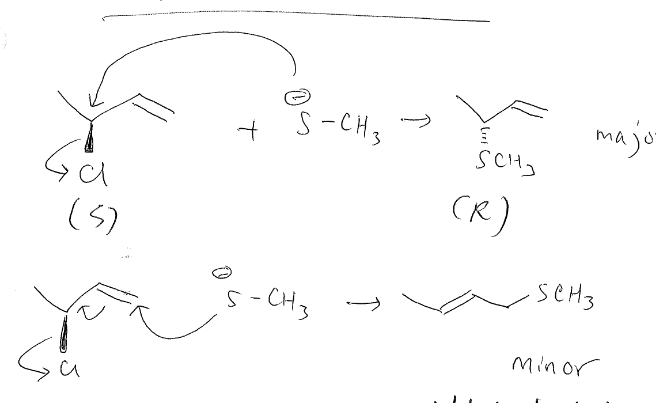
62
New cards
acid catalyzed cleavage of bonds
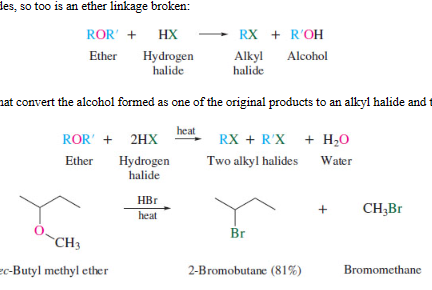
63
New cards
formaldehyde
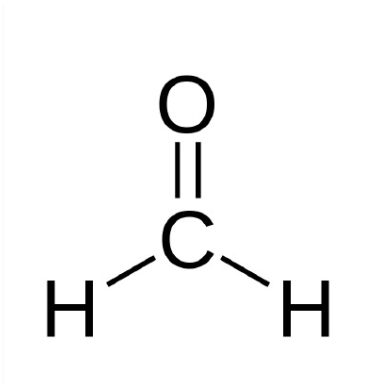
64
New cards
PCC
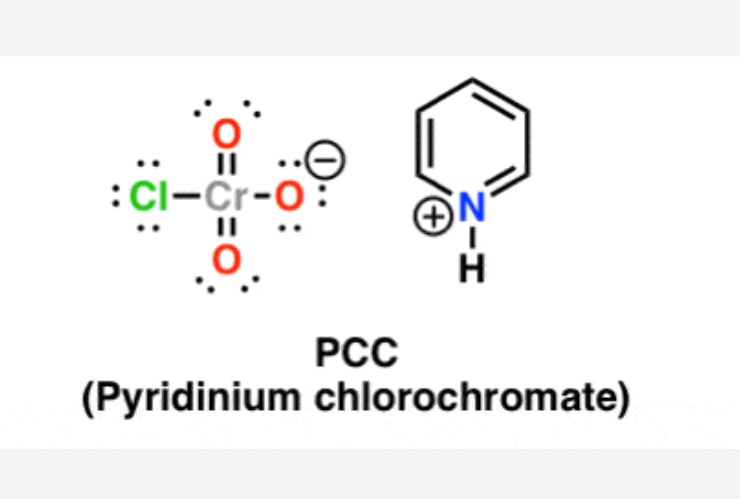
65
New cards
PDC
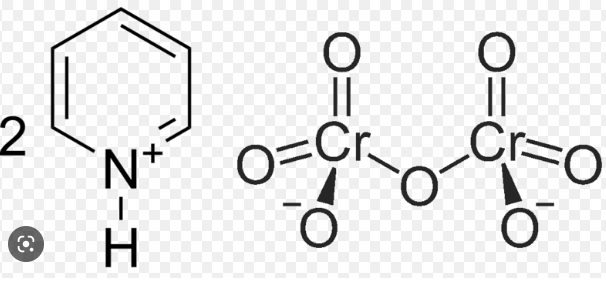
66
New cards
acyl chloride in ester formation mechanism
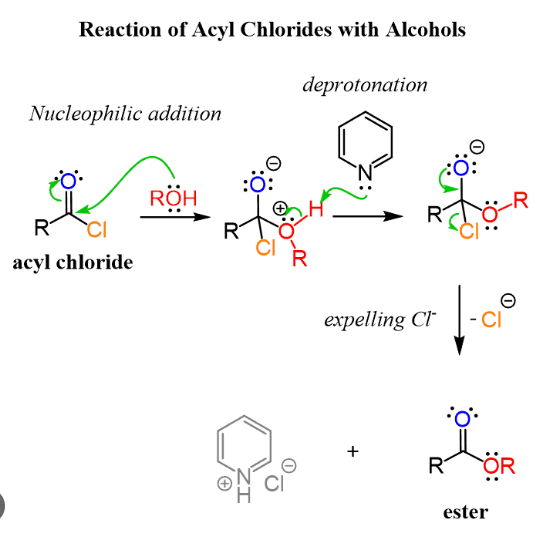
67
New cards
dehydrobromination
use base for secondary and tertiary bromides
68
New cards
anhydride ester formation
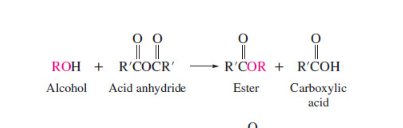
69
New cards
ethylene oxide
hint: if you see two carbons added on, (LLOK AT QUIZ
70
New cards
most electronegative atoms
F, O, N, Cl
71
New cards
condensation
two molecules come to form one larger one and some smaller molecule
72
New cards
previous alcohol reactions table in ch 16
73
New cards
use of NBS
74
New cards
allyl vs vinyl
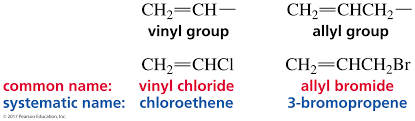
75
New cards
sp2 carbons
SN2 reactions cannot occur with leaving groups (X) bonded to sp2-hybridized carbons
76
New cards
17\.8
77
New cards
primary alcohol using a Grignard reagent
Use Formaldehyde
\
\
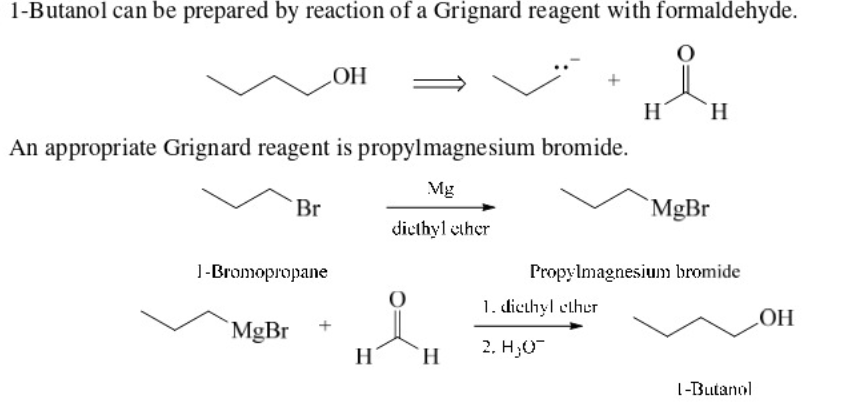
78
New cards
As with carboxylic acids, esters may be reduced using lithium aluminum hydride to give primary alcohols
\
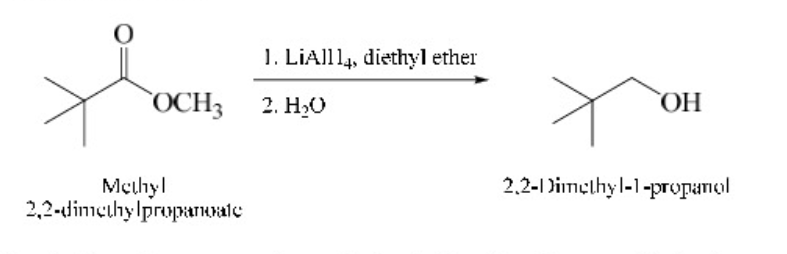
79
New cards
Bromobenzene into 2-phenylethanol
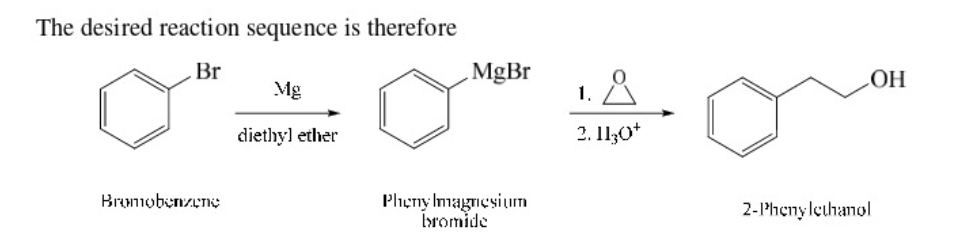
80
New cards
If you see two added carbons to make a primary alcohol hints to
1\.ethlyene oxide
2\. H3O+
2\. H3O+
81
New cards
hydroboration-oxidation
syn addition, OH to least substituted
82
New cards
primary alcohol to carboxylic acid use
use HCrO4
or Na2Cr2 O7 in sulfuric acid
or Na2Cr2 O7 in sulfuric acid
83
New cards
primary alcohol to aldehyde
PCC (or PDC) and CH2Cl2
84
New cards
hydroboration-oxidation of 1-phenylcyclobutene
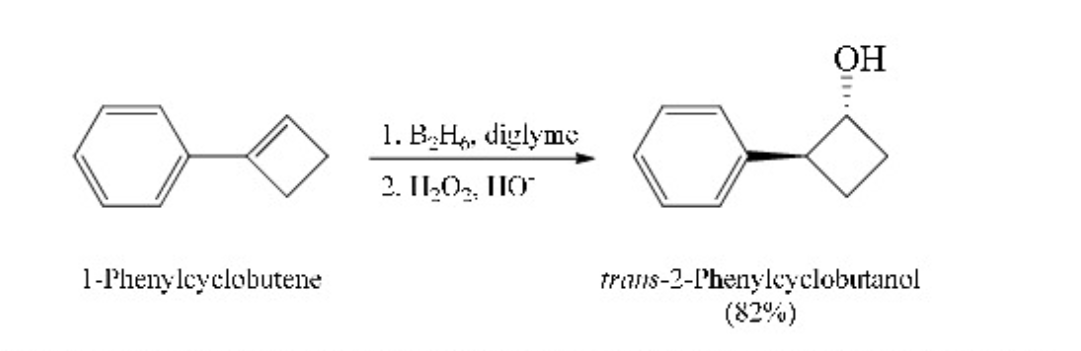
85
New cards
alkyne to alkane
86
New cards
alkyne to trans alkene
87
New cards
alkyne to cis alkene
88
New cards
For addition, usually makes the most stable carbocation.
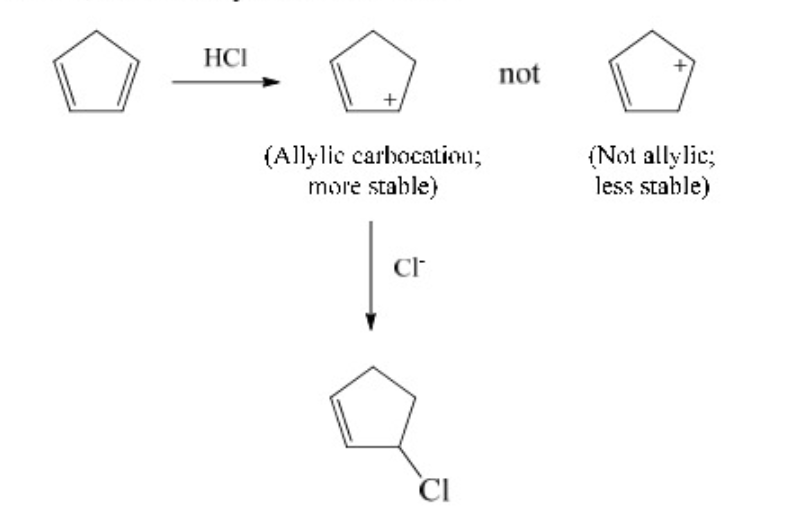
89
New cards
hydrolysis
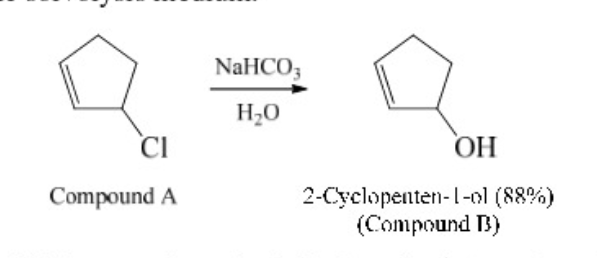
90
New cards
ozonolysis
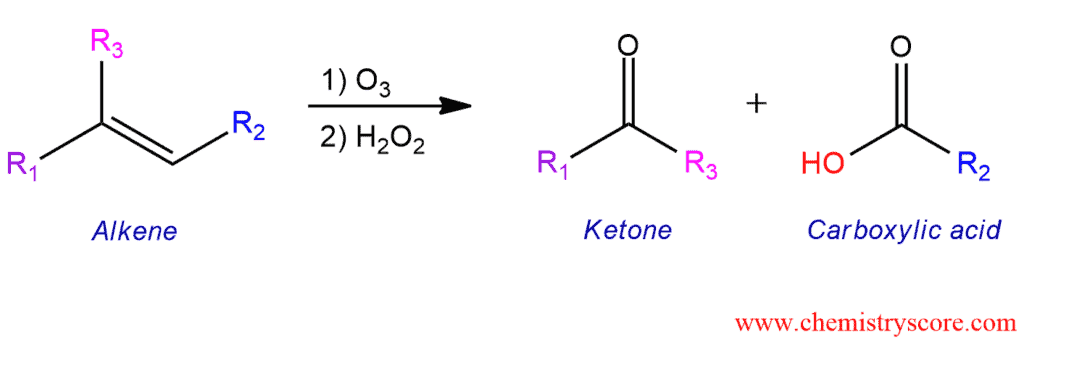
91
New cards
ozonolysis intramolecular
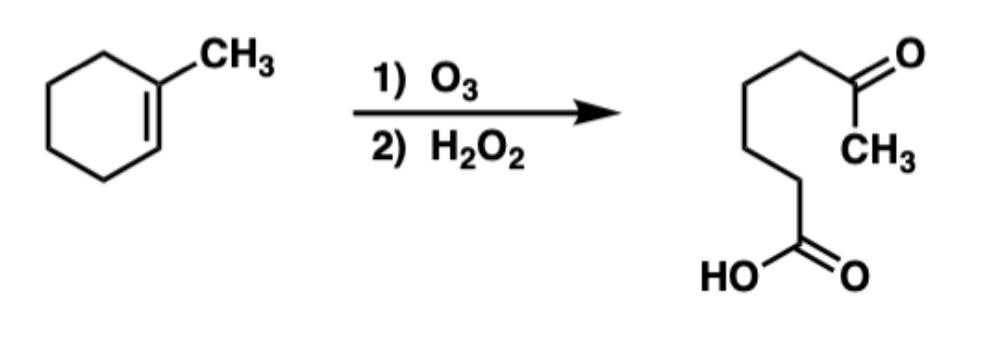
92
New cards
NMR of alcohol
The broad band in the IR spectrum at 3300 cm-1 is the O—H stretching vibration of an alcohol. The presence of an alcohol is confirmed by the disappearance of a peak following addition of D2O as the hydroxyl proton undergoes rapid exchange with deuterium. "
93
New cards
stereochemistry of Williamson ether synthesis
the ether product has the same absolute configuration as the starting alkoxide because no bonds to the chirality center are made or broken in the reaction
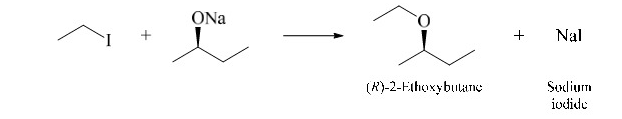
94
New cards
vicinal halohydrins with base
turn into epoxides (intramolecular Williamson ether synthesis)