ULSD Dental Terminology 1&2
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
What is dental anatomy?
dental morphology, positioning, nomenclature, development, and function
What's the purpose of learning dental anatomy?
to rebuild the lost tooth structure to where it satisfies function, force resistance, and aesthetics
What's the point of waxing?
to practice rebuilding the missing tooth structure
(crowns, partial dentures, and some other mouth restorations all start as a wax model then invested to a final restoration)
How is waxing helpful in practice?
emergencies, evaluation of aesthetics, evaluation of function and occlusion, patient's educational tool
The 2 different types of arches:
maxillary arch (upper U arch)
mandibular arch (lower L arch)
Where does the midline fall?
between central incisors
(dividing line between left and right)
What are the quadrants?
UR, UL, LR, LL
Occlusion refers to...
the movements of the mandible and the contacting of the maxillary and mandibular teeth
Mastication is...
the process of chewing
Heterodont...
teeth of different types (incisors, molars, canines...)
Homodont...
teeth of one kind (sharks, dolphins)
Monophydont...
having only one set of permanent teeth without the deciduous dentition
Diphyodont...
having two successive sets of teeth
1. deciduous teeth
2. permanent teeth
Polyphyodont...
teeth are continuously shed and replaced during the lifetime of an animal
What age range is primary dentition?
around 6mo to 6 years old
What age range is mixed dentition?
6-12 years old
What age range is permanent dentition?
12-21 years old
What kinds of teeth are involved in primary dentition? (aka deciduous teeth)
4 first molars
4 second molars
4 canines
4 laterals
4 centrals
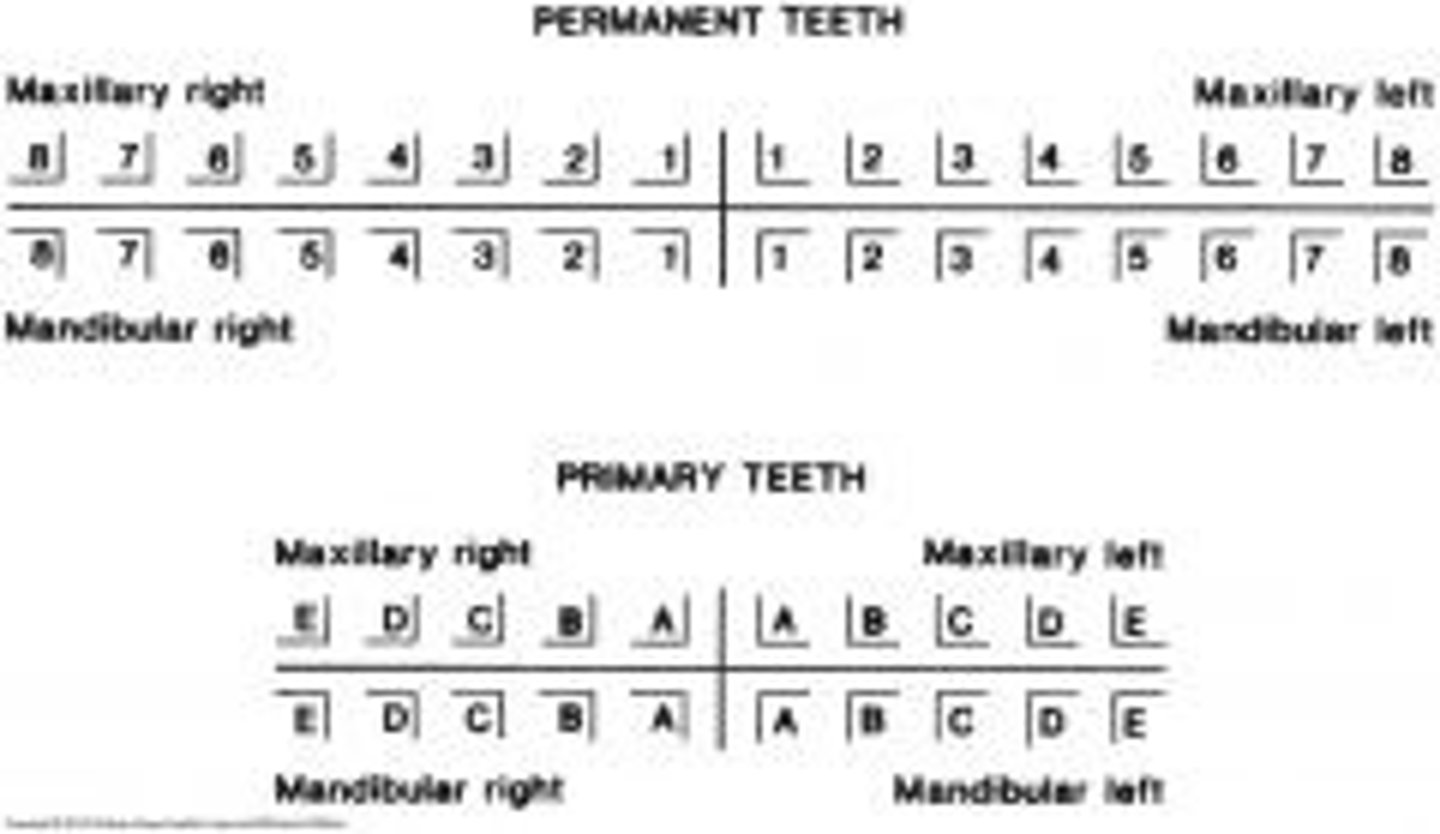
What letters is the maxillary arch for primary dentition?
A-J going right to left
What letters is the mandibular arch for primary dentition?
K-T going left to right
What kinds of teeth are involved in permanent dentition?
4 first molars
4 second molars
4 third molars
4 first premolars
4 second premolars
4 canines
4 laterals
4 centrals
What numbers is the maxillary arch for permanent dentition?
1-16 going right to left
What letters is the mandibular arch for permanent dentition?
17-32 going left to right
What is mixed dentition?
when permanent teeth start to erupt while primary teeth are still present
When does mixed dentition begin?
around 6 years old
What's the first tooth to erupt during mixed dentition?
first permanent molar
What tooth takes over the mandibular primary central tooth?
permanent mandibular central incisor
When does mixed dentition end?
when the last primary tooth falls off (usually canines) around 12 yo
List the order of permanent teeth erupting.
mandibular to maxillary
1st molar -> 1st molar ->
centrals -> centrals ->
laterals -> laterals ->
canines -> 1st premolars ->
1st premolars -> 2nd premolars ->
2nd premolars -> canines ->
2nd molar -> 2nd molar
At what age does each permanent tooth erupt for maxillary?
central incisor: 7-8 yo
lateral incisor: 8-9 yo
canine: 11-12 yo
first premolar: 10-11 yo
second premolar: 10-12 yo
first molar: 6-7 yo
second molar: 12-13 yo
third molar: 17-21 yo
At what age does each permanent tooth erupt for mandibular?
central incisor: 6-7 yo
lateral incisor: 7-8 yo
canine: 9-10 yo
first premolar: 10-12 yo
second premolar: 11-12 yo
first molar: 6-7 yo
second molar: 11-13 yo
third molar: 17-21 yo
Exfoliation means...
the normal loss of primary teeth after loss of their root structure
Resorption is...
breakdown/destruction (which leads to the loss of) the root structure of a tooth
Succedaneous teeth are...
the permanent teeth that replaces deciduous teeth
What teeth are considered succedaneous teeth?
permanent incisors, canines, and premolars
Deciduous teeth are...
the primary teeth that erupt first (baby teeth that will be replaced eventually)
Non-succedaneous teeth are...
all permanent molars
Why are all permanent molars considered non-succedanous?
molars didn't have previous teeth to replace
How are teeth identified?
Quadrant, dentition, and type
Ex: maxillary right (Q) permanent (D) canine (T)
Which teeth are considered anterior?
4 incisors, 4 laterals, and 4 canines
(canines and forward)
Which teeth are considered posterior?
8 premolars (4 first and 4 second premolars), and 12 molars (1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars)
What's the function of incisors?
- shaped and designed to cut food with the incisal edge
- the shape of the lingual surface help direct/guide foot to the back of the mouth for further chewing and grinding
What's the function of canines?
- longest teeth and roots (better anchored allowing for more stability)
- designed for holding/grasping/tearing food
- the position of canines guides other teeth into the best biting position
What's the function of premolars?
- chewing food
- pointed cusp on the cheek side holds the food while the cusp on the tongue side grinds the food
- have more of the characteristics of molars
What's the function of molars?
grinding food
How do you identify teeth using the numerical system?
start with maxillary right third molar #1 to left third molar #16
mandibular left third molar #17 to mandibular right third molar #32
- teeth numbers will not change whether teeth are missing in the arch or not
How do you identify teeth using the alphabetical system?
start with maxillary right primary second molar "A" to left maxillary primary second molar "J"
mandibular left primary second molar "K" to mandibular right primary second molar "T"
- teeth letters will not change whether teeth are missing or not
What's the palmer notation system?
a symbol is used to specify the arch and the eight teeth in each quadrant of the permanent dentition are numbered from the central incisor back to the third molar
(used in orthodontics)
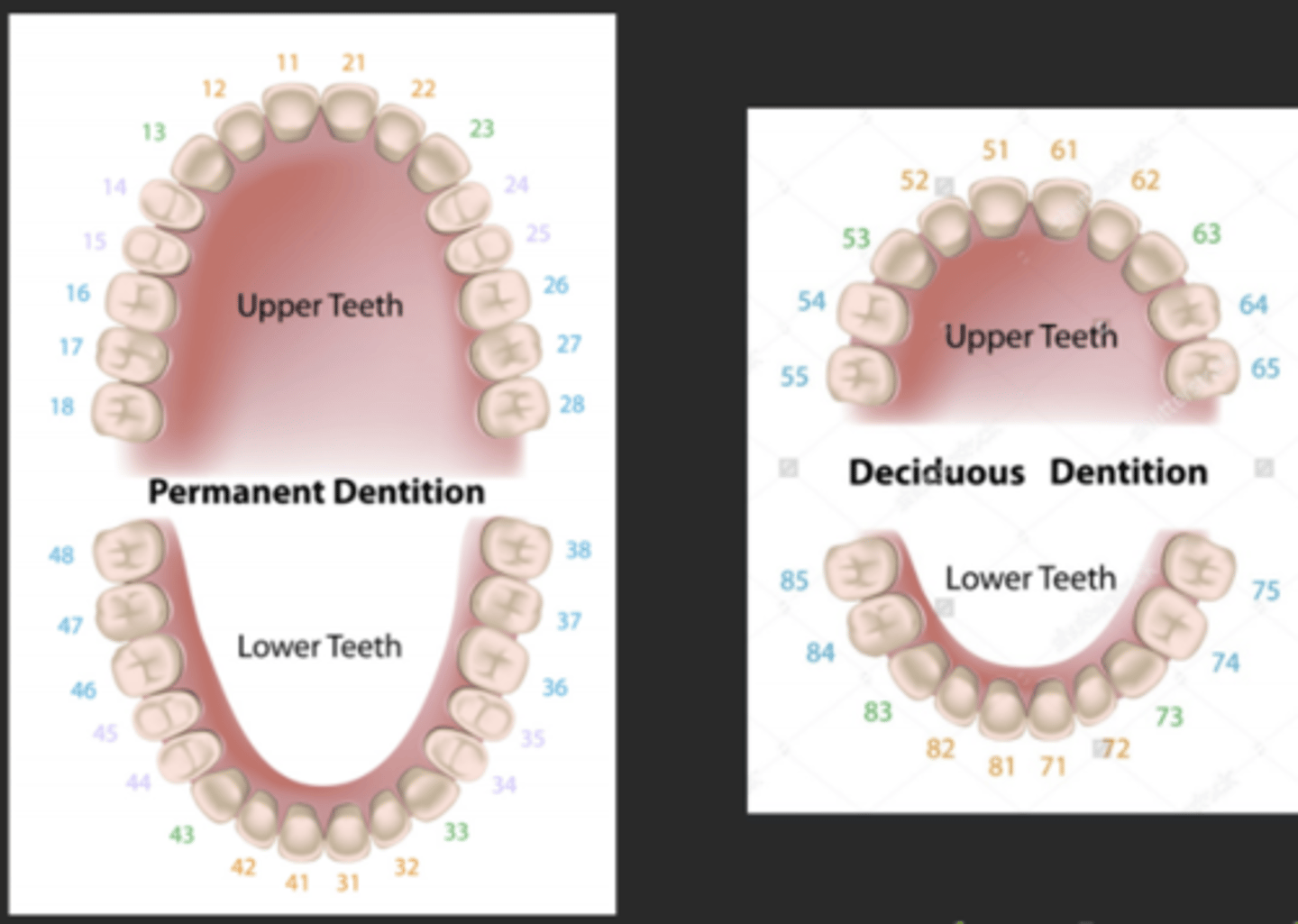
Federation dentaire international is a system where...
- number to each quadrant proceeds the tooth number used in palmer; a 2-digit system
- each quadrant is given a number: UR 1, UL 2, LL 3, LR 4
- for primary arches: UR 5, UL 6, LL 7, LR 8
Where's the facial surface?
towards the face
Where's the labial surface?
towards the lips (incisors + canines)
Where's the buccal surface?
towards the cheeks (premolars + molars)
Where's the lingual surface?
towards the tongue (mandibular)
Where's the palatal surface?
towards the palate (maxillary specific) (interchangeable w lingual)
What's the mesial surface?
towards the midline
What's the distal surface?
away from the midline (towards back of the mouth)
What's the proximal surface?
- the surface of the tooth that touches another tooth in the same arch (contact areas)
- flossing points
What's the occlusal surface?
the surface that comes in contact with the opposite arch (chewing surface of posterior teeth)
What's the incisal edge?
the cutting/biting surface of the anterior teeth (anterior teeth)
What are the tooth surfaces for anteriors?
facial/labial, lingual/palatal, mesial, distal, incisal
What are the tooth surfaces for posteriors?
buccal, lingual, mesial, distal, occlusal
What is the crown of a tooth?
- projecting out of the gum into the mouth
- covered w enamel
- clinical crown and anatomical crown
- small portion of the crown is covered with gingiva
What is the root of a tooth?
- embedded in the bone
- ends with the apical foramen (allows neurovascular bundle in the pulp)
- covered with cementum (calcification)
What does the enamel cover? What's it made out of?
- the crown portion of the tooth
- 90% inorganic material
Where's the cementum?
- outermost layer of the tooth
Where's the dentin?
- the middle layer of the tooth
- forms the majority of the tooth structure
- 70% inorganic material
Where's the pulp?
- innermost layer of the crown and root
- consists of blood vessels and nerve
- provides the nutrient and sensory supply to the tooth
Where's at the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)?
area where cementum meets enamel
What's a furcation?
space between roots
What's a trifurcation?
a 3-root tooth (maxillary molars)
(max = maximum roots)
What's a bifurcation?
a 2-root tooth (mandibular molars)
Where's the pulp chamber?
- the largest portion of the pulp
- in the crown of the tooth
- what you typically think of when you think "pulp"
Where's the pulp canals?
within the roots
Where's the pulp horns?
- extensions of the pulp chamber that project toward the cusp tips and incisal edges
- chicken have higher pulp horns
Where's the apical foramen?
- the apex of the tooth (in the root)
- nerves and blood vessels enter the pulp via apical foramen
What's the pulp cavity?
pulp chamber + pulp canals
What's the cervical?
- slightly restricted part of the tooth between te crown and the root
- "neck" of the tooth at the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)
Divide the crown of a tooth from top to bottom.
1/3 occlusal/incisal
1/3 middle
1/3 cervical
Divide the crown of a tooth starting from the side closest to the midline back.
1/3 mesial
1/3 middle
1/3 distal
Divide the crown of a tooth starting from the side towards the face back to the tongue.
1/3 buccal (post teeth)/ facial (anterior teeth)
1/3 middle
1/3 lingual
Divide the root of a tooth starting from the crown to the apical foramen.
1/3 cervical
1/3 middle
1/3 apical
What's a line angle?
- the junction of two surfaces
- aka the edge of a tooth
List the line angles for anterior teeth. Be able to know where they are on teeth.
- mesiolabial
- distolabial
- mesiolingual
- distolingual
- labioincisal
- linguoincisal
* mesioincisal and distoincisal are nonexistant because the teeth are rounded here
List the line angles for posterior teeth. Be able to know where they are on teeth.
- mesiobuccal
- distobuccal
- mesiolingual
- distolingual
- mesio-occlusal
- disto-occlusal
- bucco-occlusal
- linguo-occlusal
What's a point angle?
formed by the junction of 3 surfaces
List the point angles for anterior teeth. Be able to know where they are on teeth.
- mesiolabioincisal
- distolabioincisal
- mesiolinguoincisal
- distolinguoincisal
List the point angles for posterior teeth. Be able to know where they are on teeth.
- mesiobucco-occlusal
- distobucco-occlusal
- mesiolinguo-occlusal
-distolinguo-occlusal
What's convex?
curves outwards (like a bubble)
What's concave?
curves inwards (like a cave)
Whats's the contact area?
- where teeth touch one another
- essential for stabilizing the dental arches and protecting gingival tissue
- aka proximal surface
Where's the interproximal space?
- space formed cervical to the interproxmal contact (aka contact area/proximal surface)
- filled with tissue (gingival papillae aka gums)
- the triangle between the teeth and gum
What's an embrasure?
- space formed by the tooth curvatures next to the contact areas
- provides a spillway for food during mastication
- prevents food from being forced through the contact area
- if you put your tongue in the space where 2 teeth touch on the incisal side (to feel it more), your tongue is at an embrasure
List the embrasures.
- labial/buccal embrasures
- lingual embrasures
- incisal/occlusal embrasures
- cervical/gingival embrasures
What's the height of contour?
the greatest curve/bulge on a tooth on any surface
What's a cusp?
- rounded, pointed elevation of the occlusal surface of the tooth
- have enamel, dentin, and pulp
- vary in size, shape, number, and location
What's a cingulum?
- rounded elevation on the lingual surface of anterior teeth
- on the cervical 1/3
What's a mamelon?
- rounded prominence on the incisal edge of newly erupted incisors
- get shorter and smoother with function
What's a tubercle?
- small elevation on the tooth surface due to excessive enamel formation
- enamel only
What's a ridge?
any linear elevation on the tooth surface
What's the triangular ridge?
- descends from cusp tips to central part of occlusal surface
- the slopes of each ridge resemble a triangle