histology- cardiovascular system
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
arterial system
capillary system
venous system
the heart
what are the 4 parts of a CV system?
lymphatic capillaries
small and medium sized lymphatic vessels
big lymphatic vessels and collecting ducts
the lymphatic vascular system is made up of...
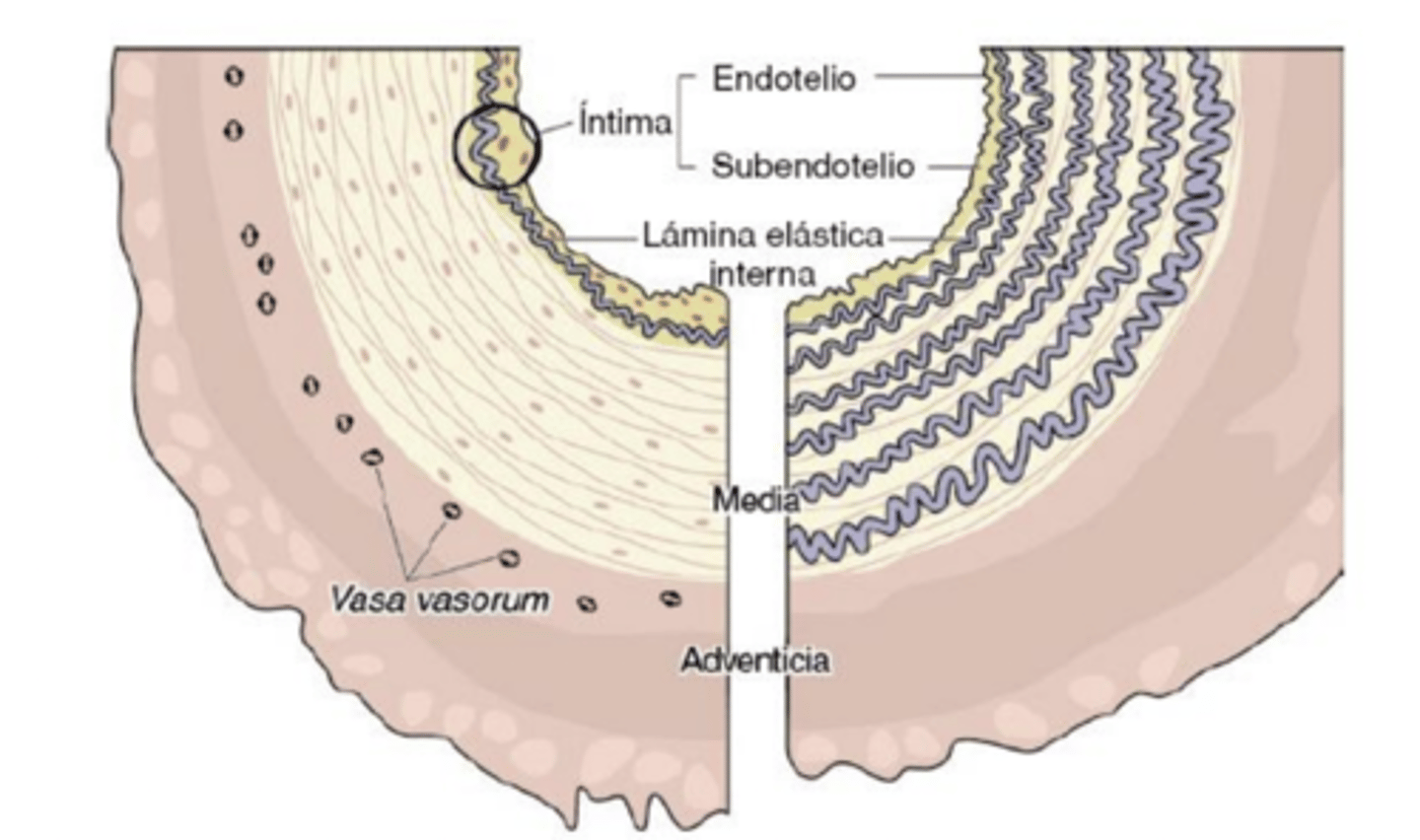
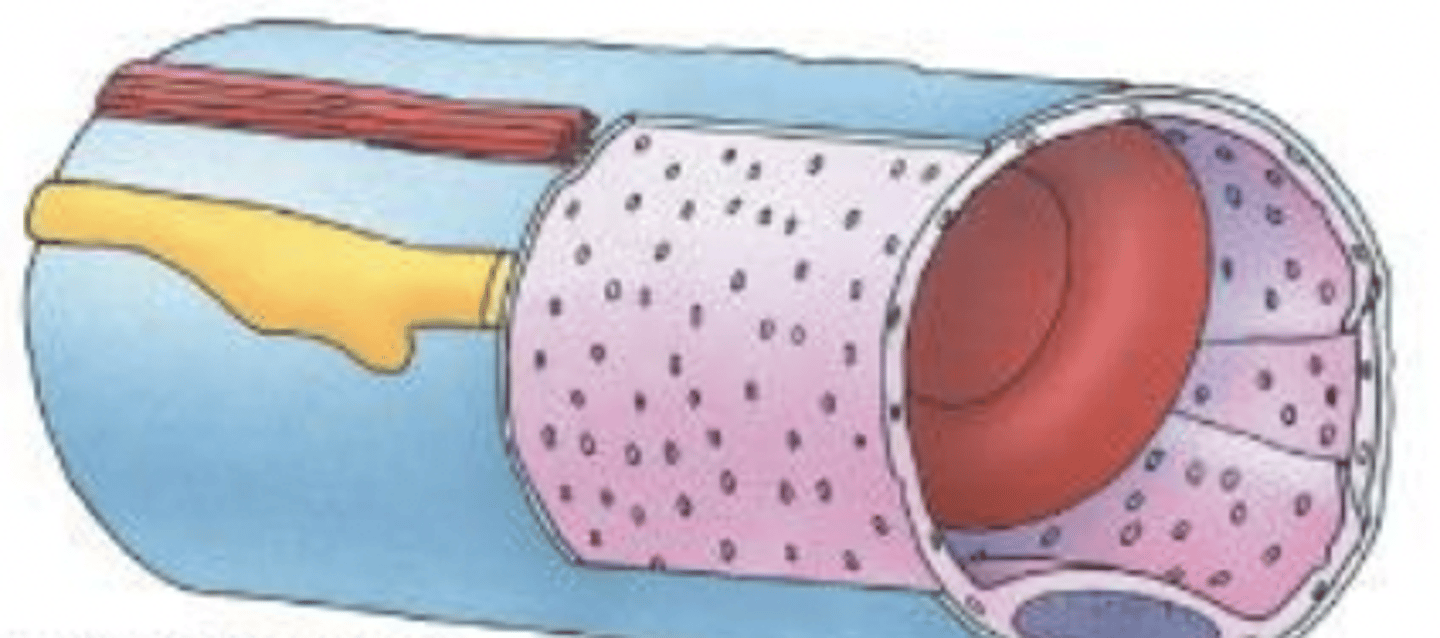
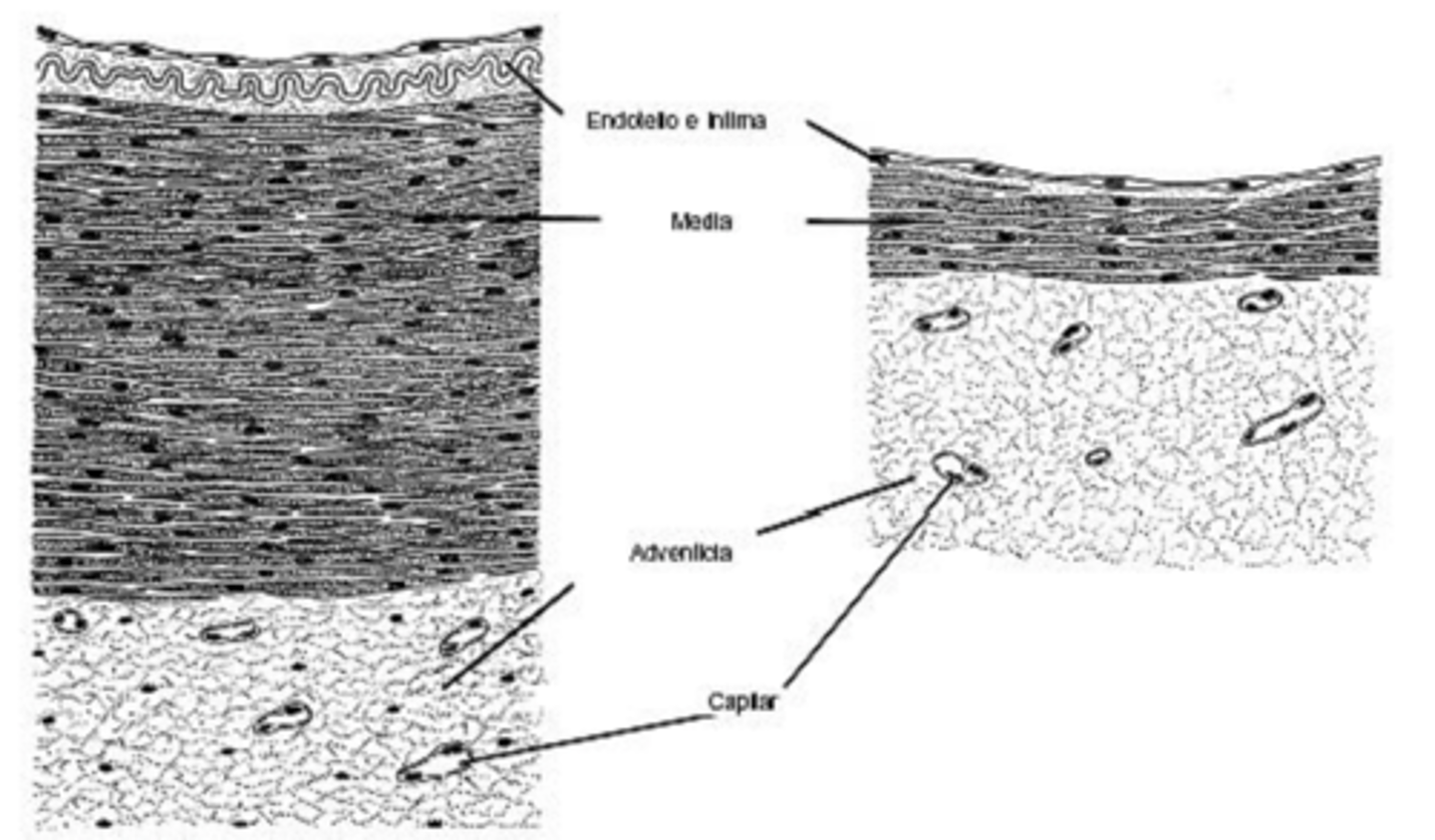
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
what are the 3 main layers of the vessels?
tunica intima
which is the most internal layer of the vessel called?
external
tunica adventitia is the most _____ layer of the vessel
tunica intima
which layer of the vessel is in direct contact with the blood?
endothelium
connective tissue
internal elastic lamina
what is in the tunica intima layer?
simple squamous epithelium
the endothelium in the tunica intima is usually which morphology?
smooth muscle
connective tissue
external elastic membrane
the tunica media is made up of...
elastic arteries
muscular arteries
arterioles
what are the 3 types of arteries in the arterial system?
elastic artery
which is the biggest type of artery- elastic, muscular, arteriole?
elastic
the aorta is an example of a ________ artery
to control the high pressure blood that they are receiving
why do elastic arteries need elasticity?
contract
when the heart dilates, what do the elastic arteries do?
dilate
the elastic arteries ______ when the heart contracts
continuous
do the elastic arteries face a continuous or intermittent blood flow?
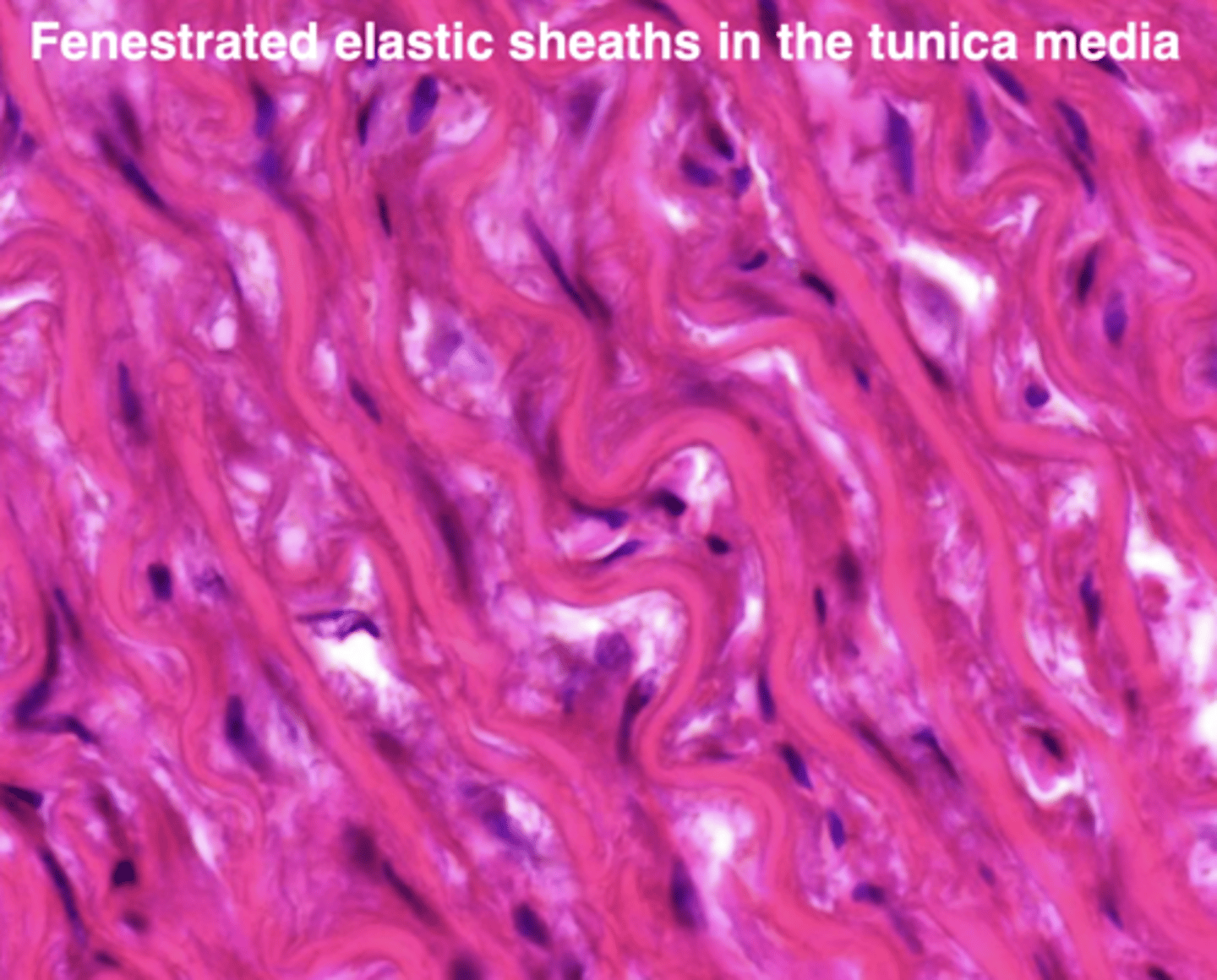
it has fenestrated sheaths of elastic fibers
what is unique about the tunica media of elastic arteries?
media
in elastic arteries, which layer is this thickest- intima, media, adventitia?
lots of collagenous tissue
what type of tissue is found in the tunica intima?
controlling of high pressure blood by distending and recoiling
the very thick elastic layer in elastic arteries is for...
distend
when in systole, do the elastic arteries distend or recoil?
recoil
when in diastole, do the elastic arteries distend or recoil?
elastic
what type of artery is this- elastic, muscular, or arteriole?
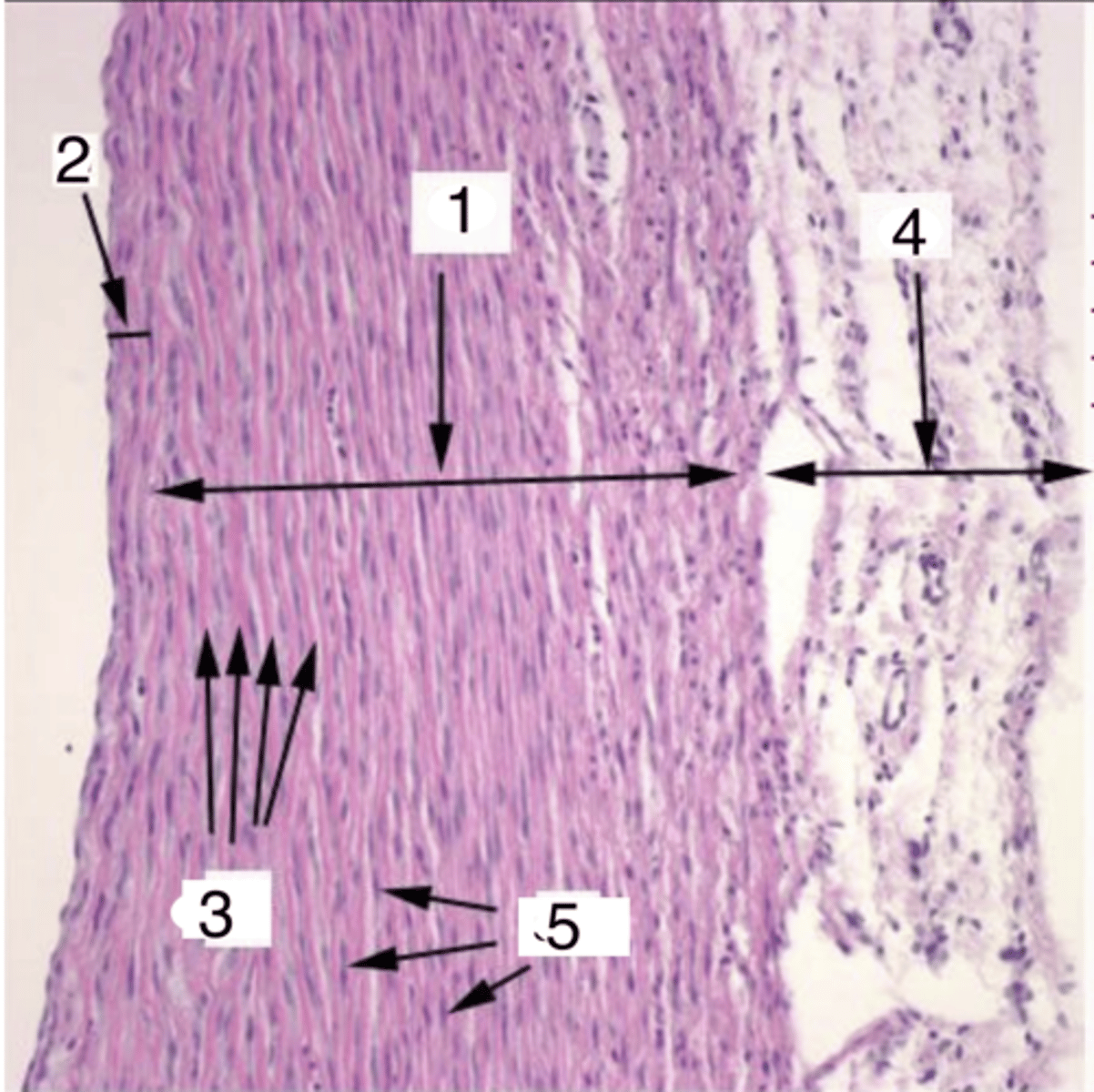
2
where is the tunica intima?
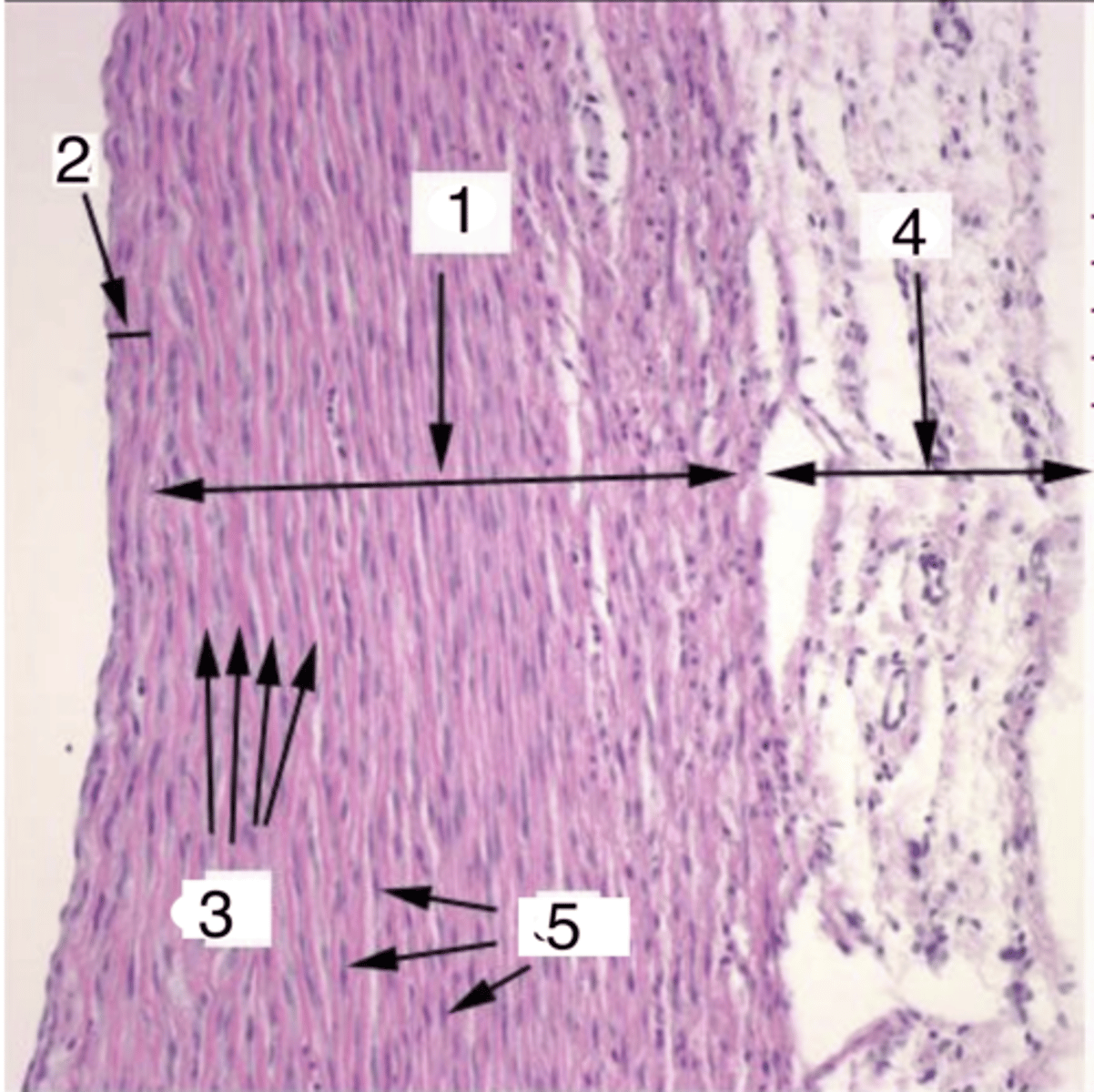
tunica media
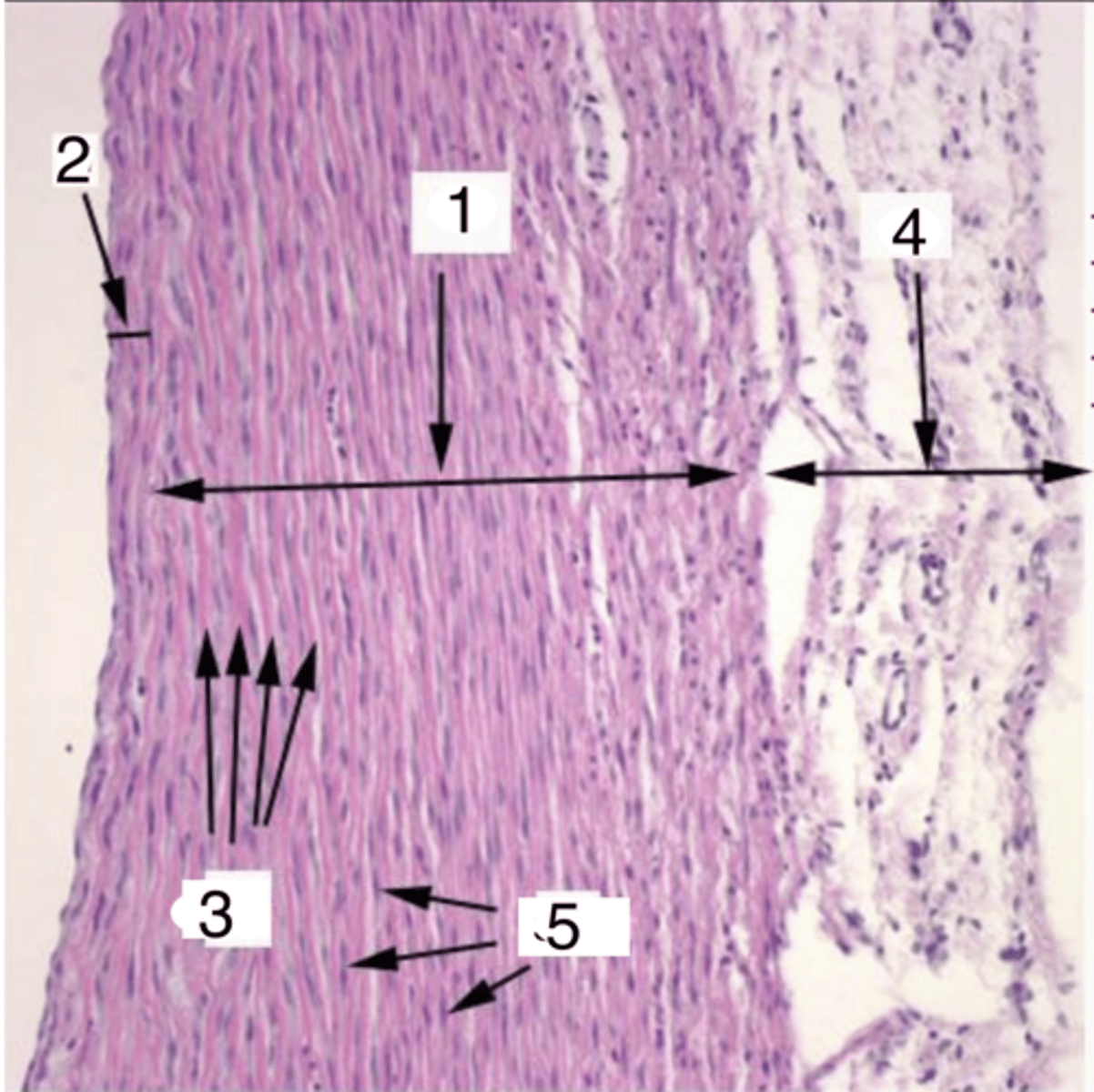
what is 1?
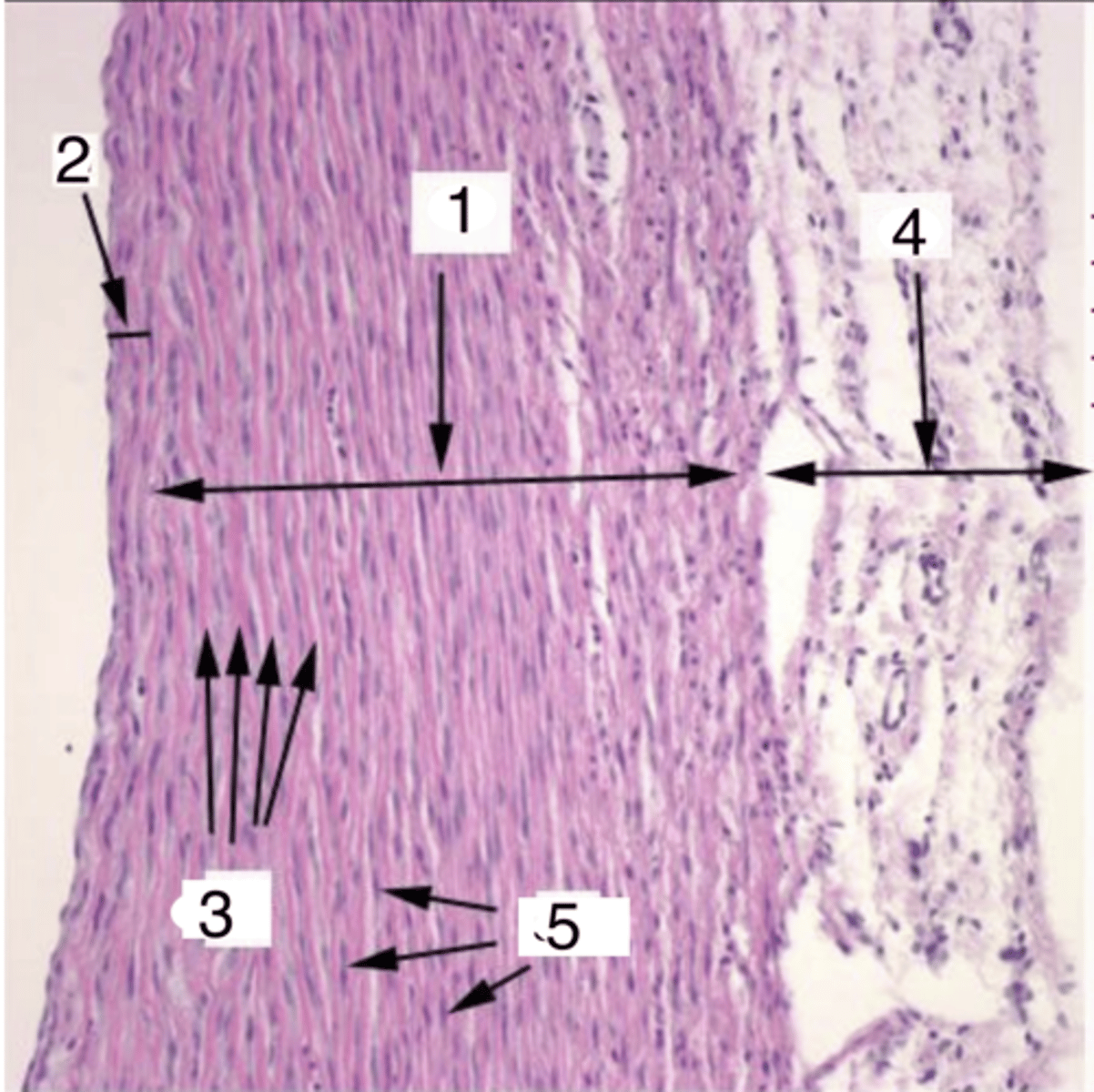
elastic membranes
what structures are at 3?
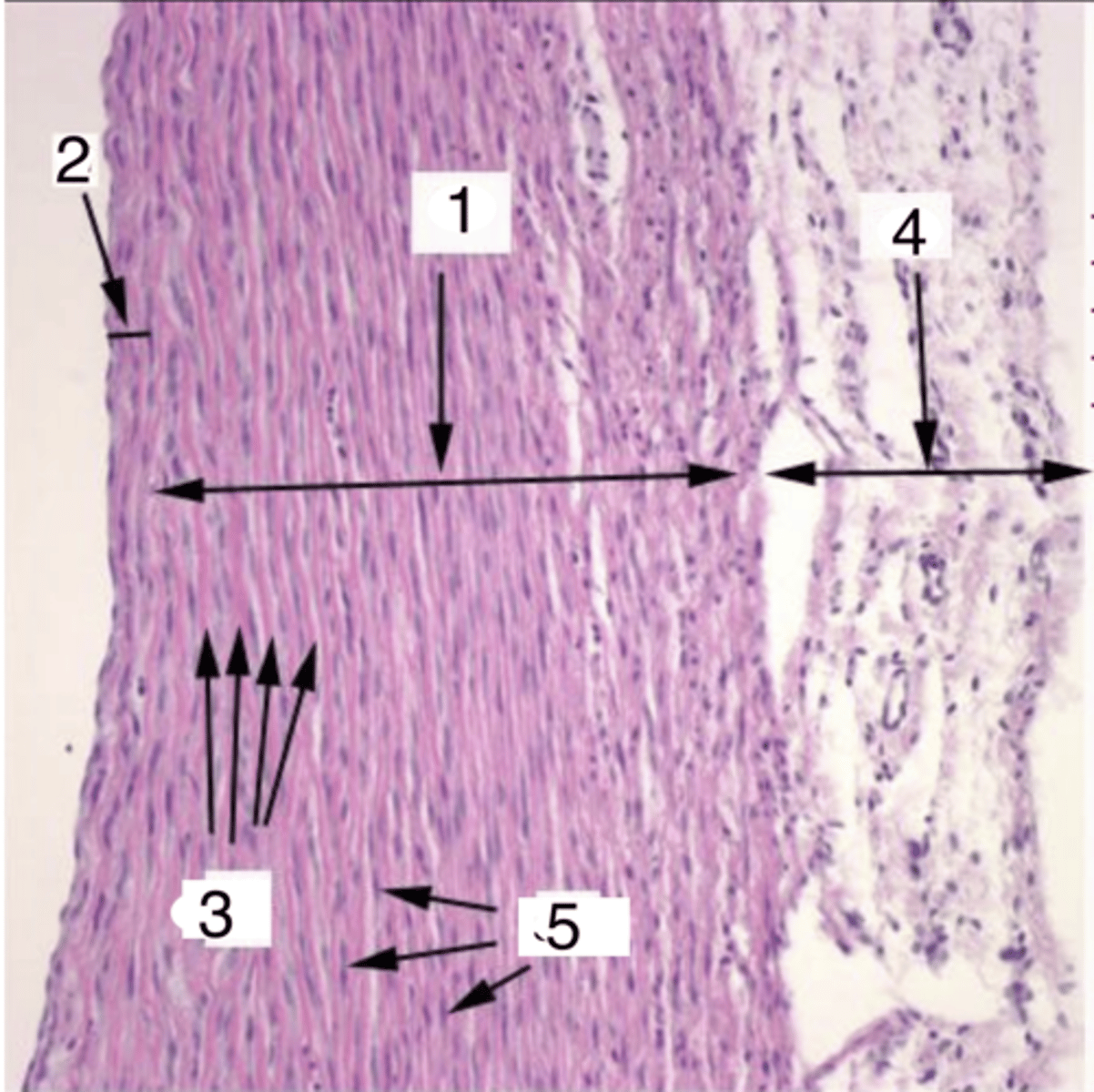
smooth muscle cells
what cells make up the tunica media at 5?
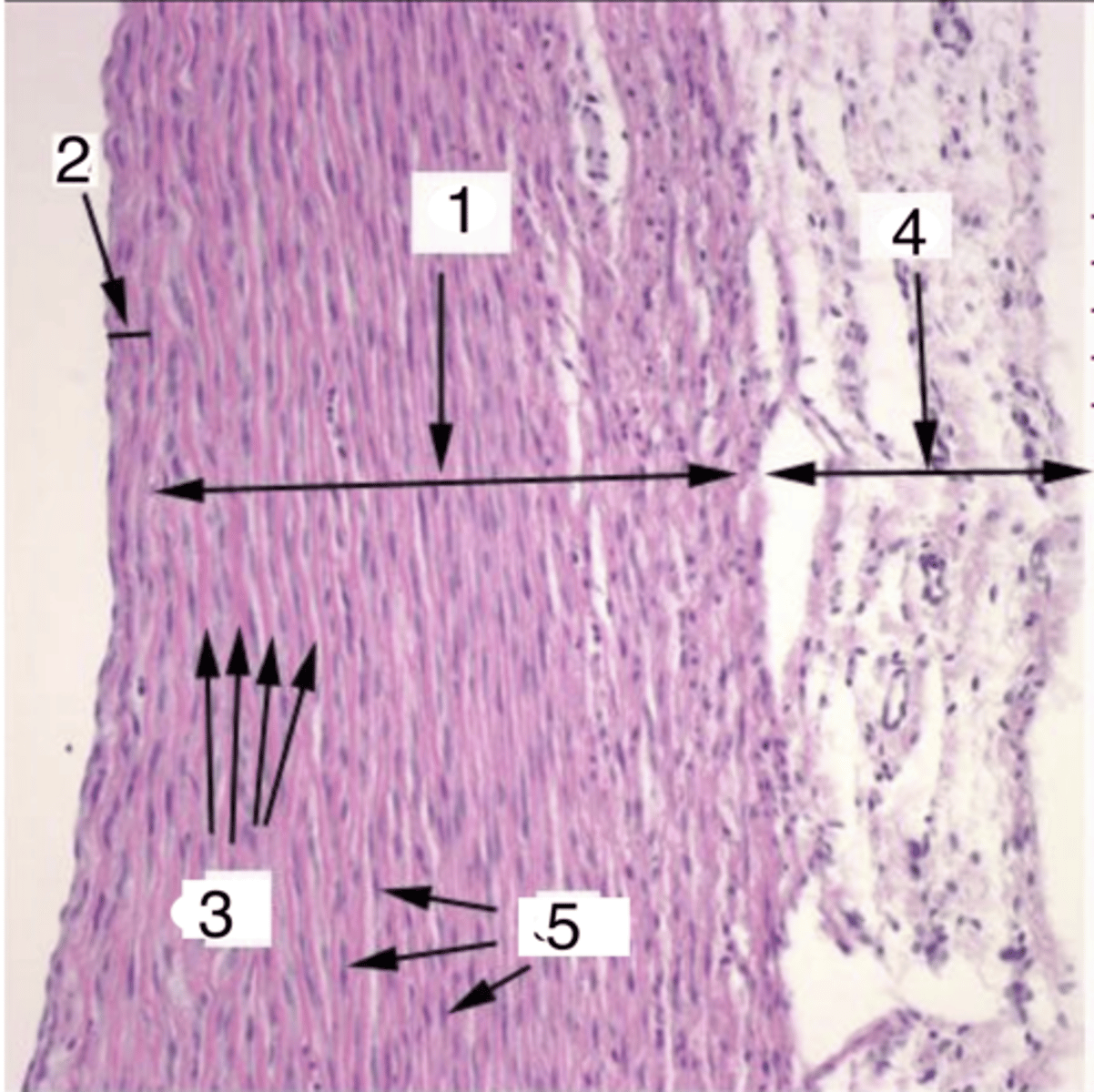
4
where is the tunica adventitia?
elastic
what type of artery is this- elastic, muscular, or arteriole?
muscular
which type of artery is the main limb artery- elastic, muscular, or arteriole?
thin, fenestrated internal elastic lamina (very thin)
describe the tunica intima in muscular arteries
no
does the tunica media of the muscular arteries have elastic?
smooth muscle
the tunica media of the muscular arteries is mainly composed of....
left
no fenestrated elastic fibers in tunica media
which is a muscular artery? why?
muscular
very thin tunica intima
no elastic fibers in tunica media
what type of artery is this?
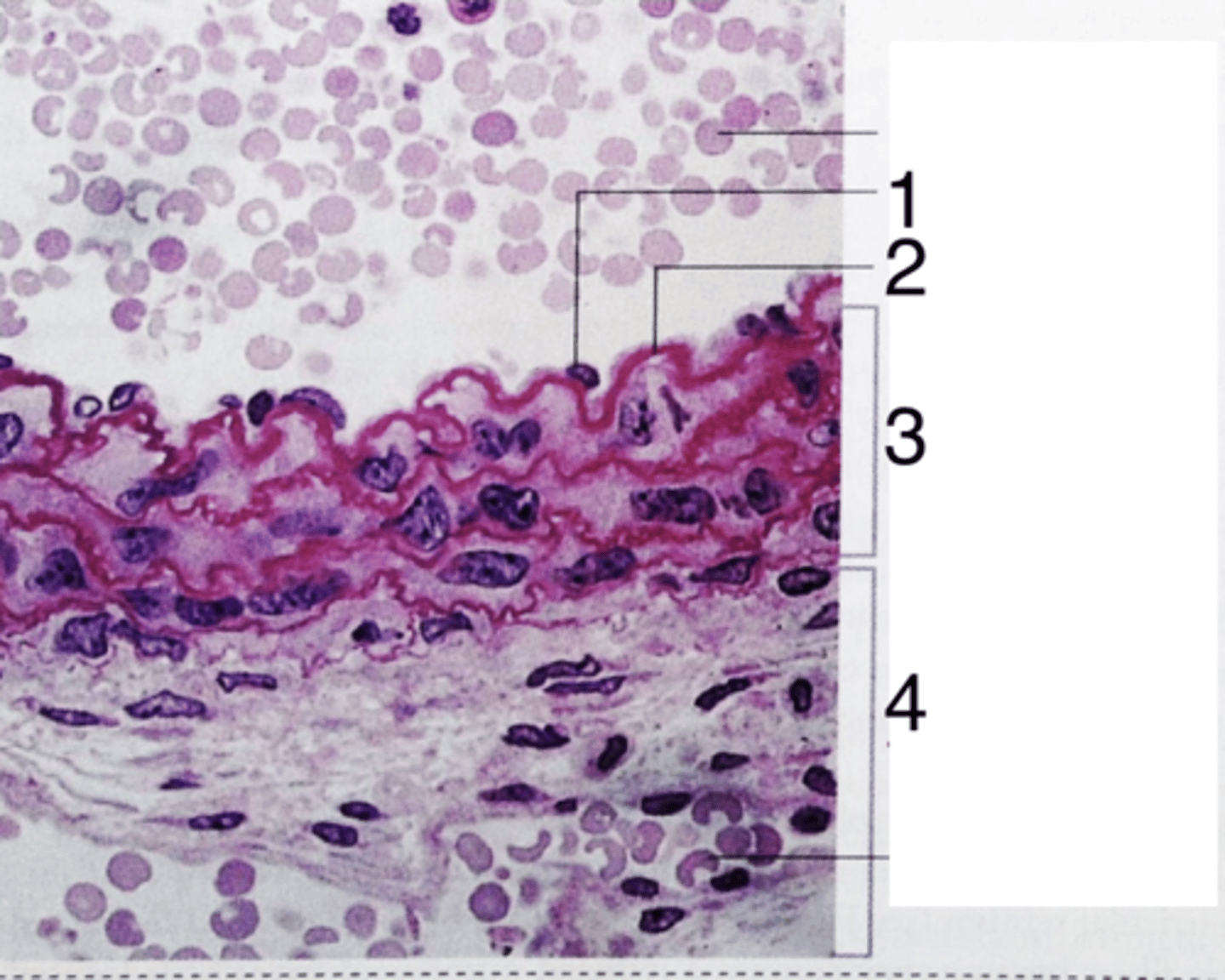
endothelium
what does 1 point to?
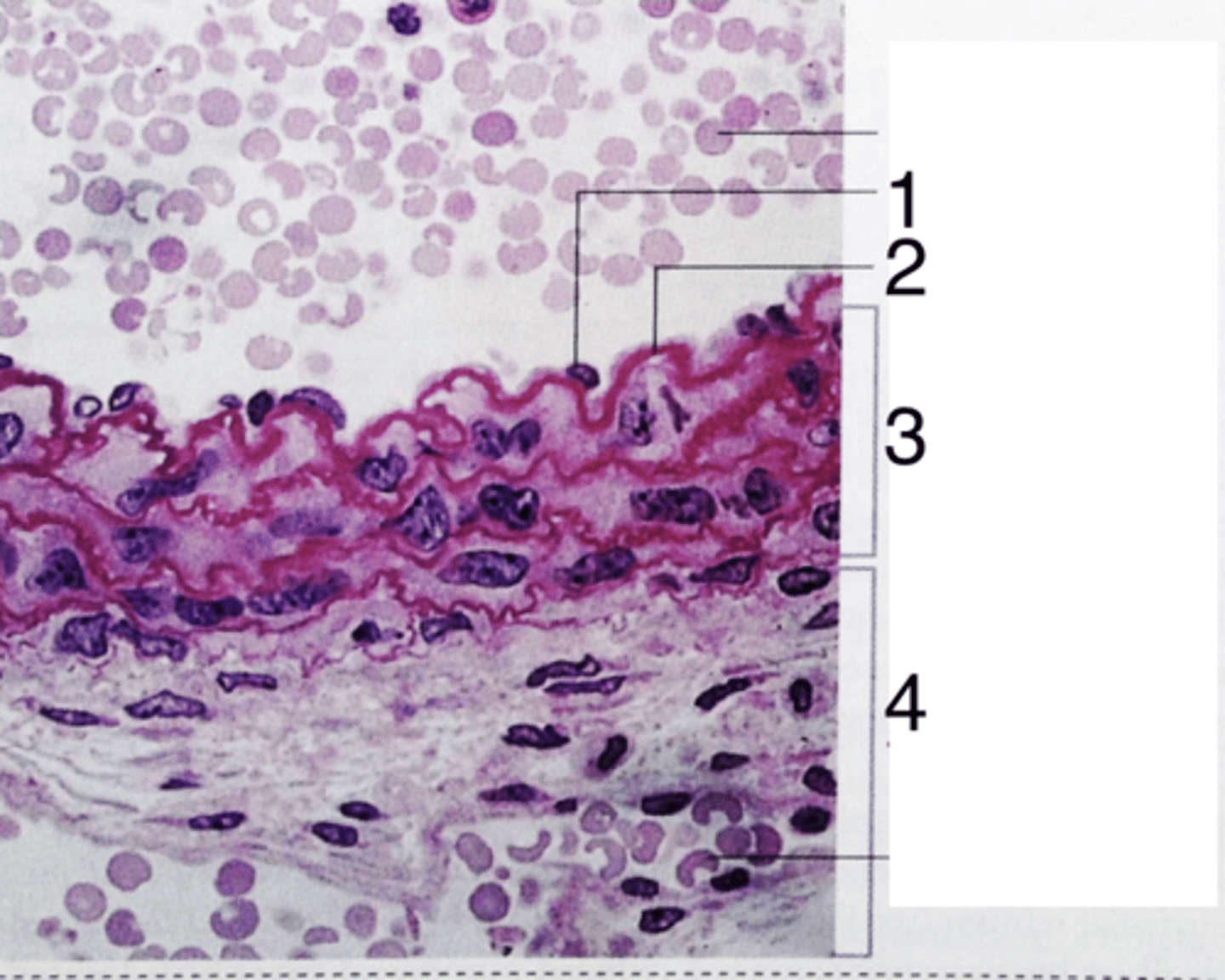
3
where is the tunica media?
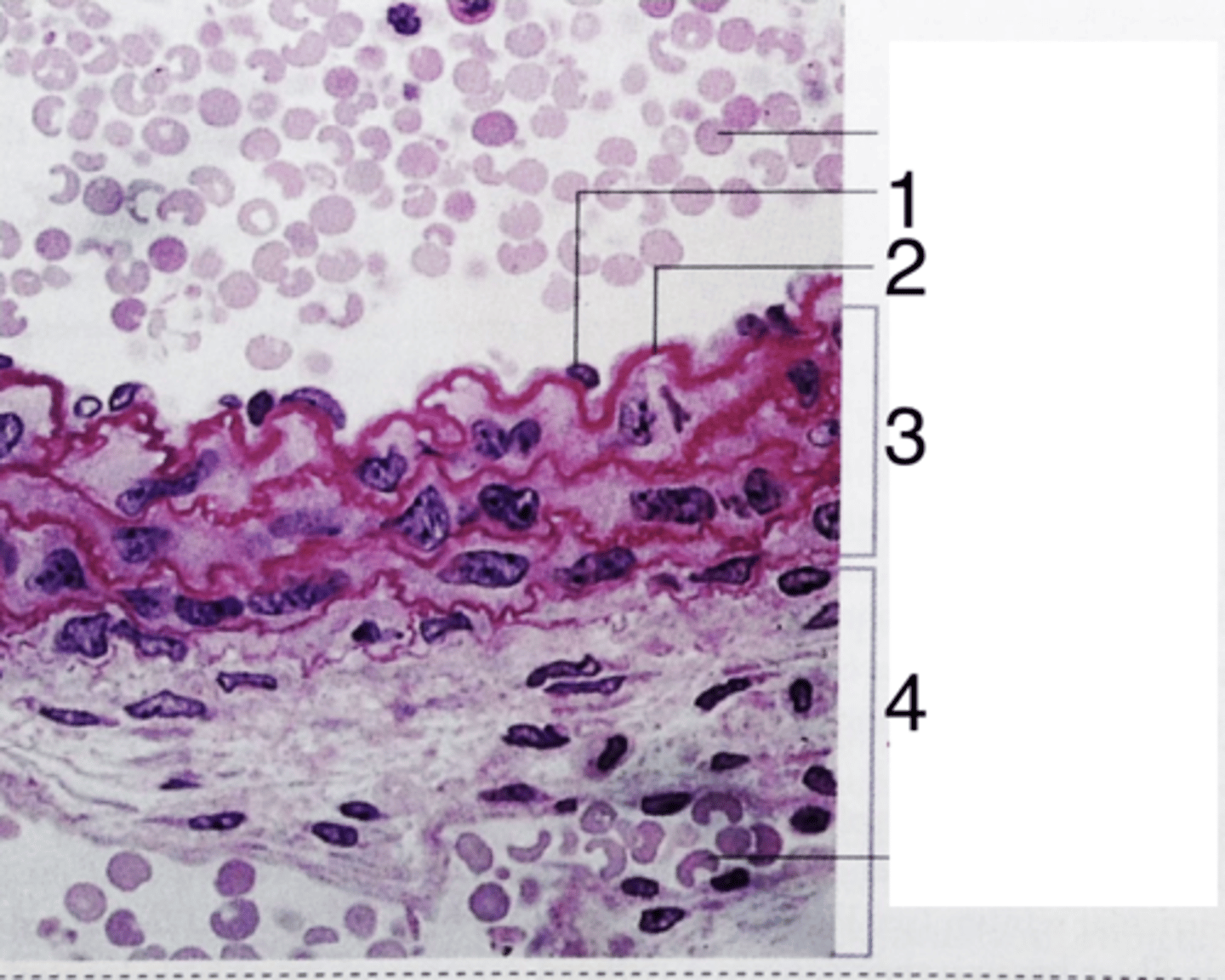
internal elastic lamina
what is 2?
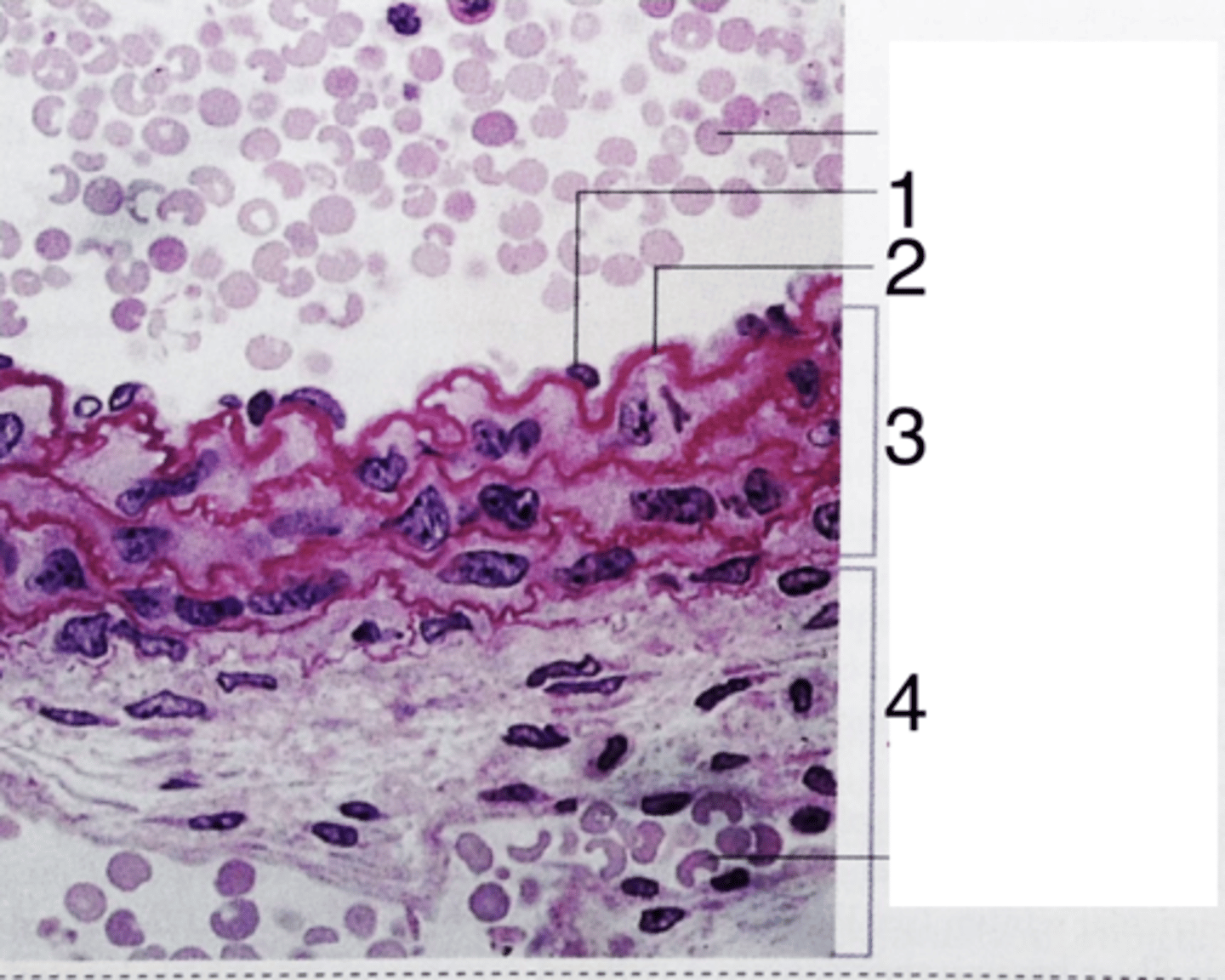
tunica adventitia
what is 4?

muscular
what type of artery?
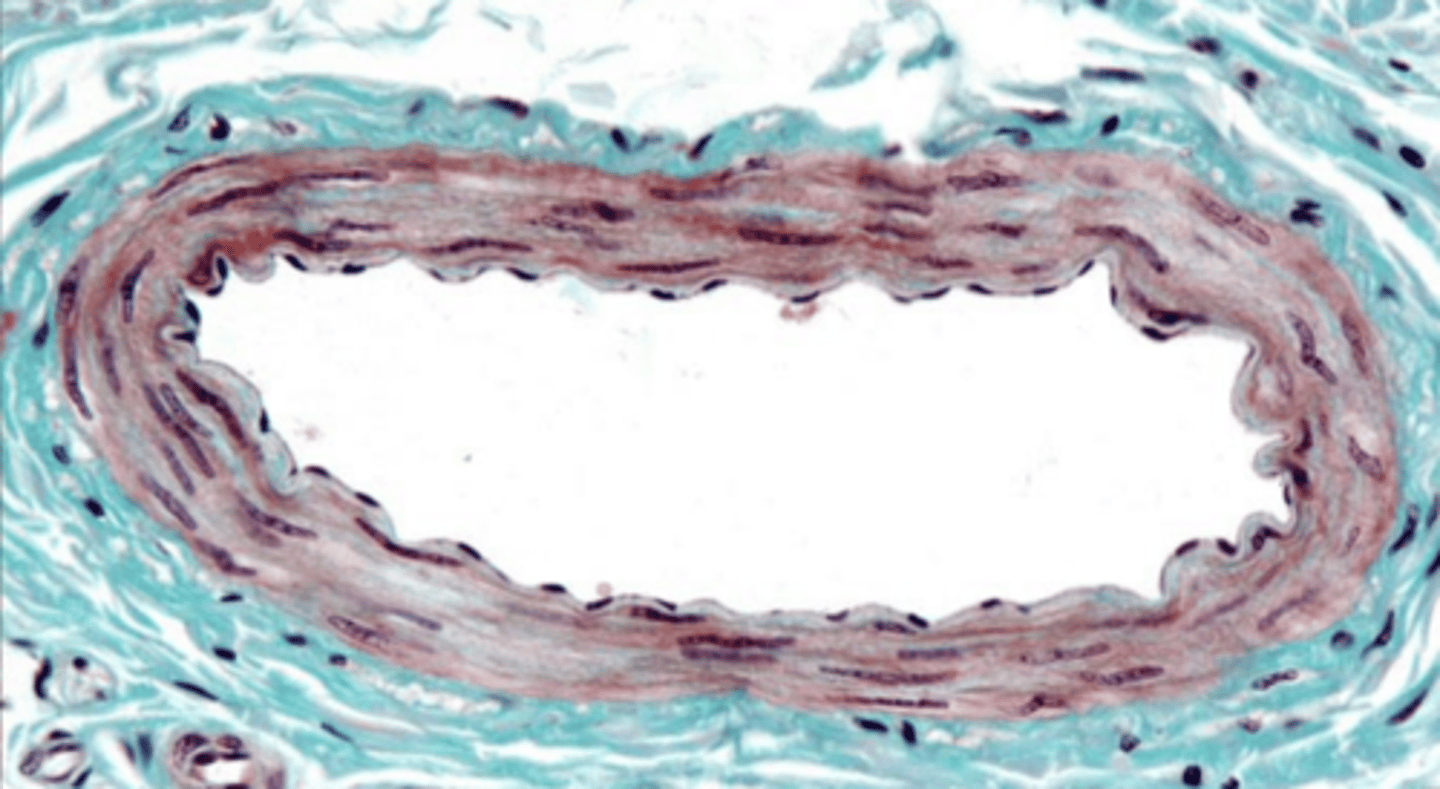
muscular
which has a thinner tunica intima- elastic or muscular artery?
muscular
which has a tunica media made only of smooth muscle- elastic or muscular artery?
arteriole
which is the smaller type of artery?
arteriole
which type of artery has the thinnest layers?
only endothelium
describe the tunica intima of an arteriole
composed of only 2-5 muscle layers
the tunica media of an arteriole is_____
no
does an arteriole have internal or external elastic laminas?
is not differentiated from surrounding connective tissue
describe the tunica adventitia of an arteriole
arteriole
what type of artery is this?
arteriole
thin layers
only endothelium in tunica intima
only a few layers of smooth muscle
what type of artery is this? why?
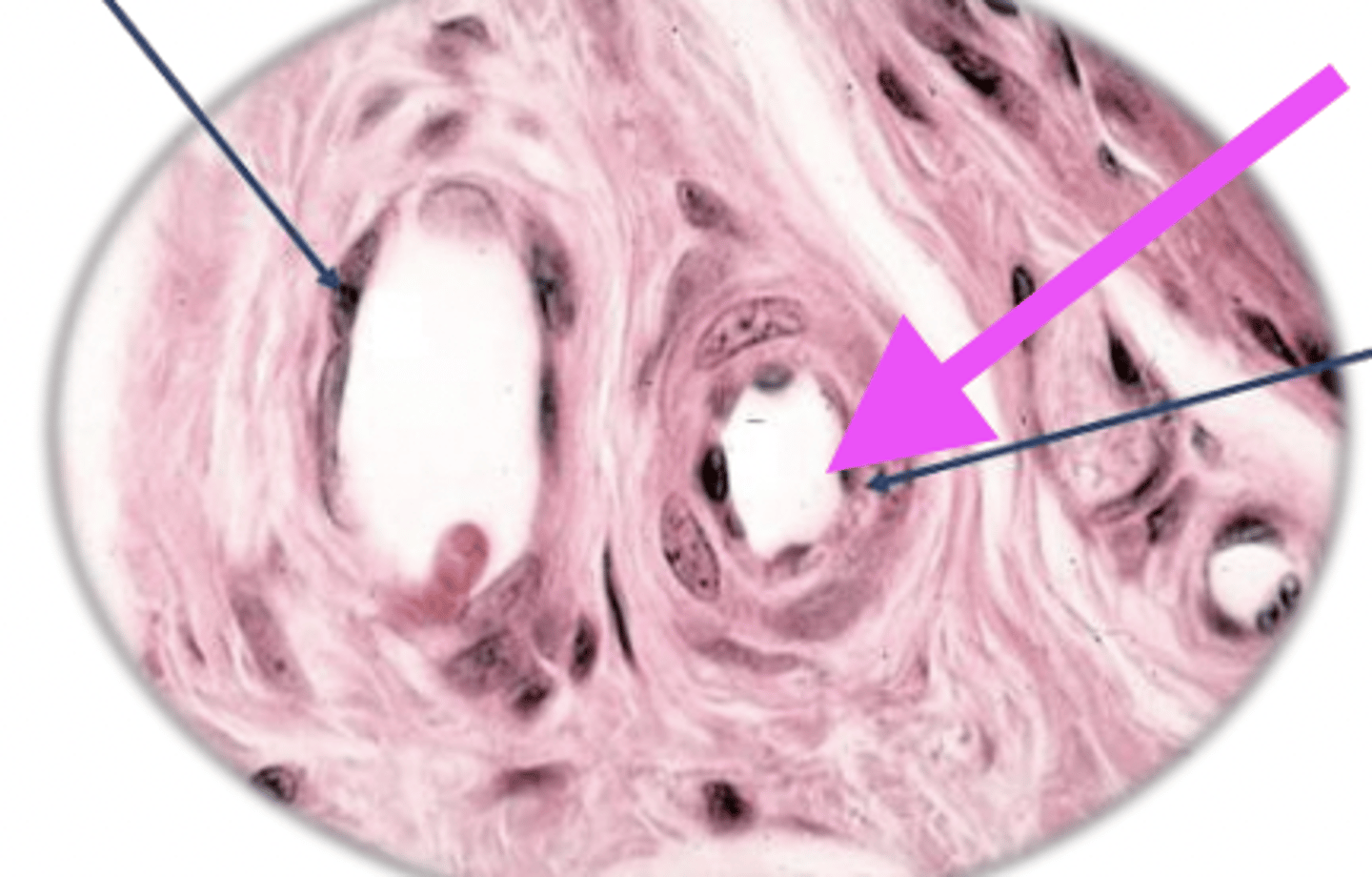
endothelium
what is 1?
tunica media
what is 2?
thin
are the capillaries thick or thin?
no
do capillaries have muscle?
pericytes (cells that compress the vessel, making small contractions)
what do capillaries have instead of muscle?
communicate arterial and venous circulation
what is the function of capillaries?
ONLY tunica intima
describe the layers of a capillary
only 1-4 very flat cells (squamous)
what is the endothelium of a capillary like?
capillary
only a few flat endothelium cells
no tunica media or adventitia
what is this vessel? why?
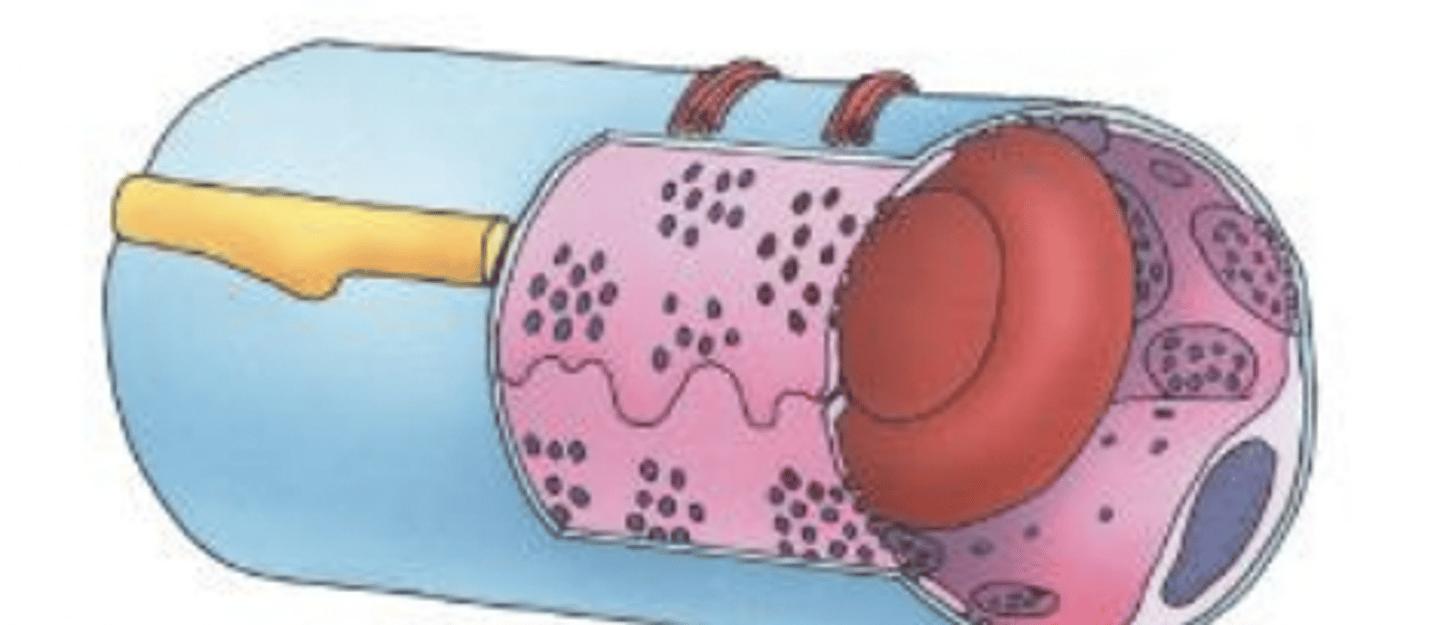
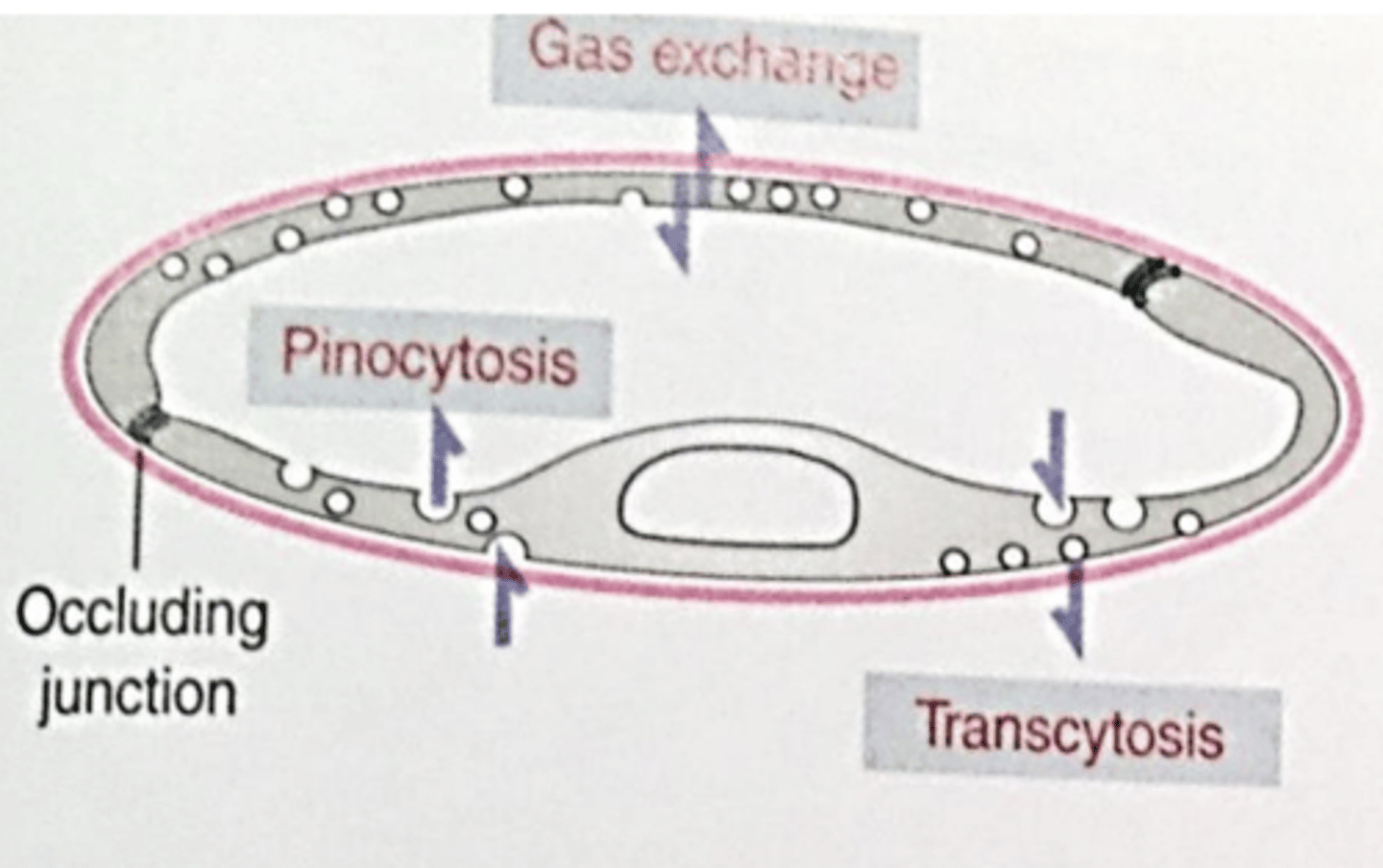
continuous
fenestrated
sinusoidal
what are the 3 types of capillaries?
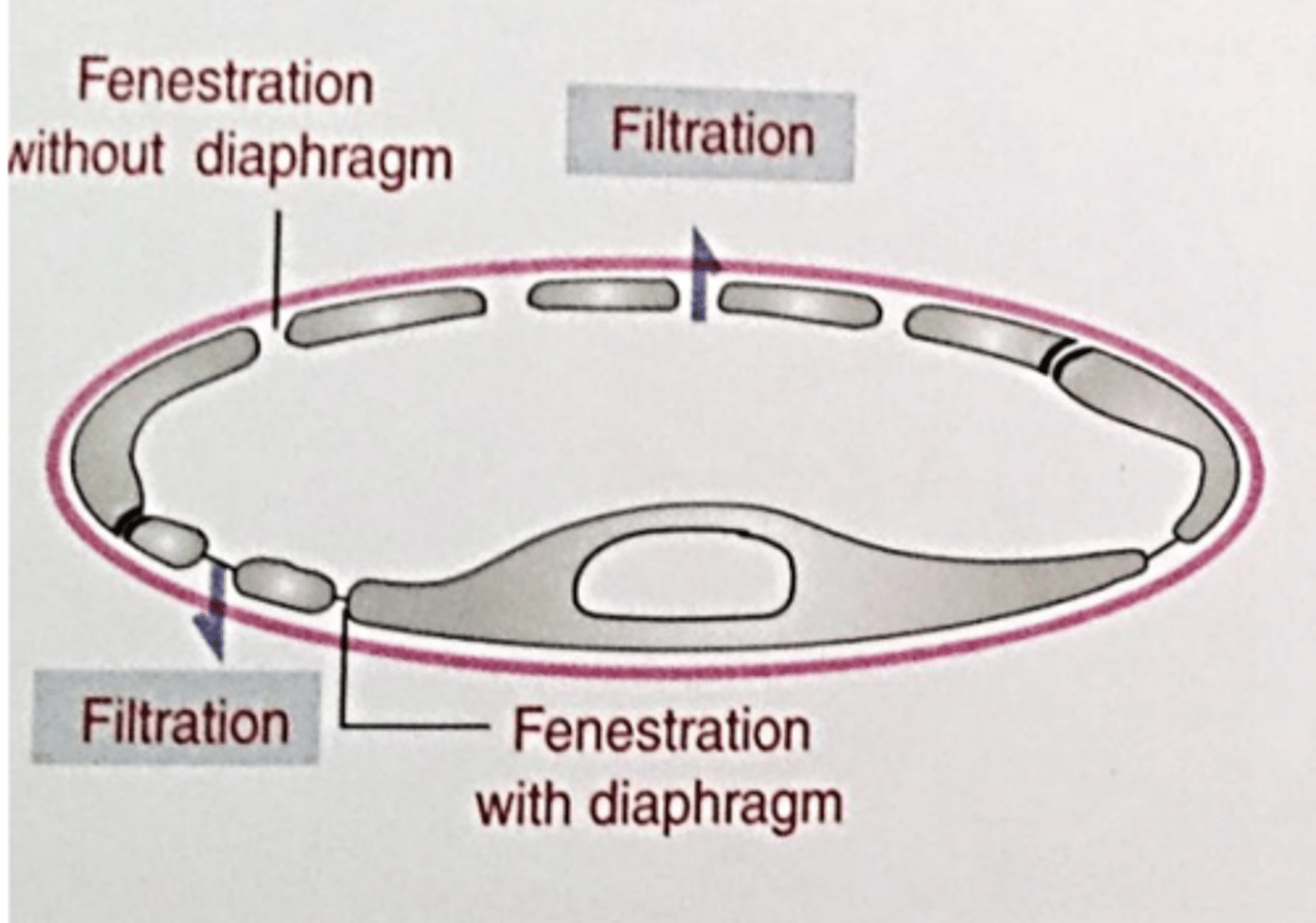
fenestrated
what type of capillary is this?
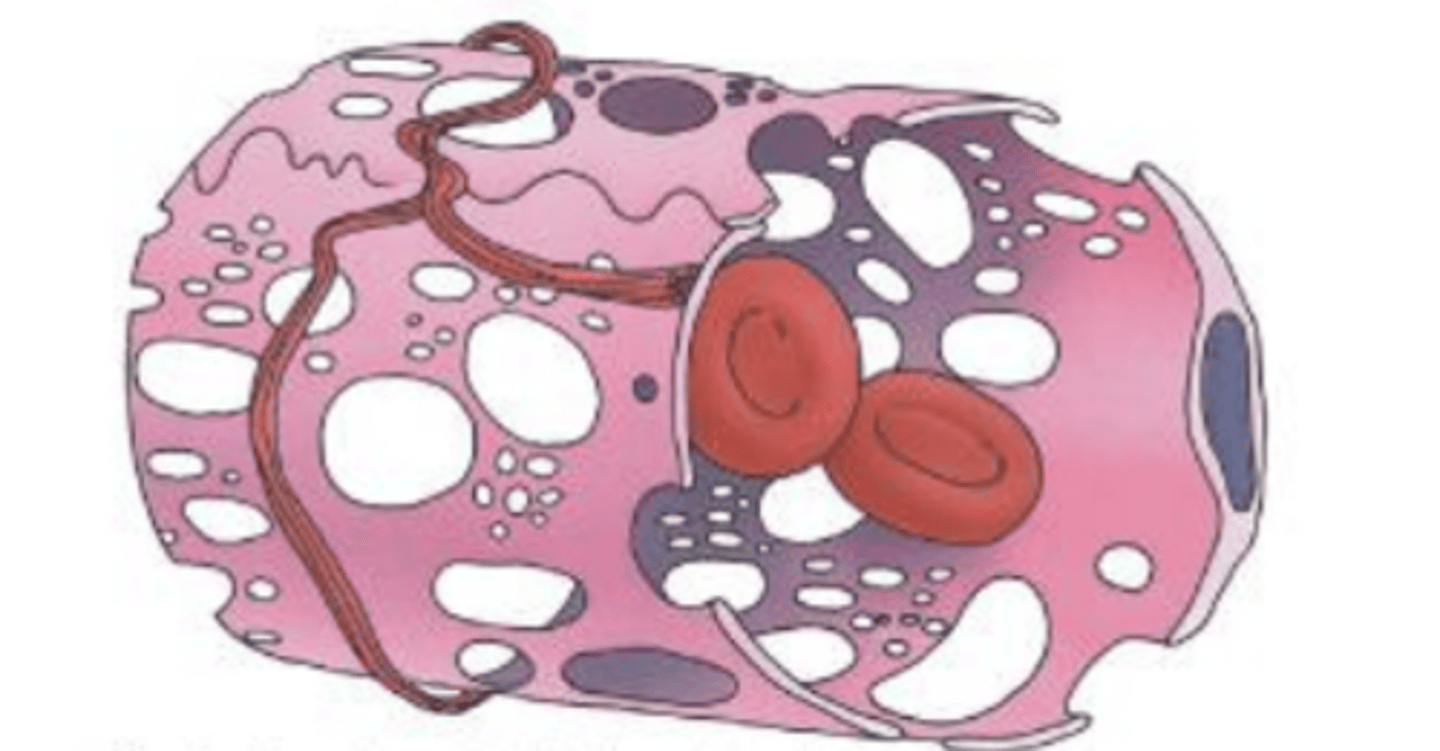
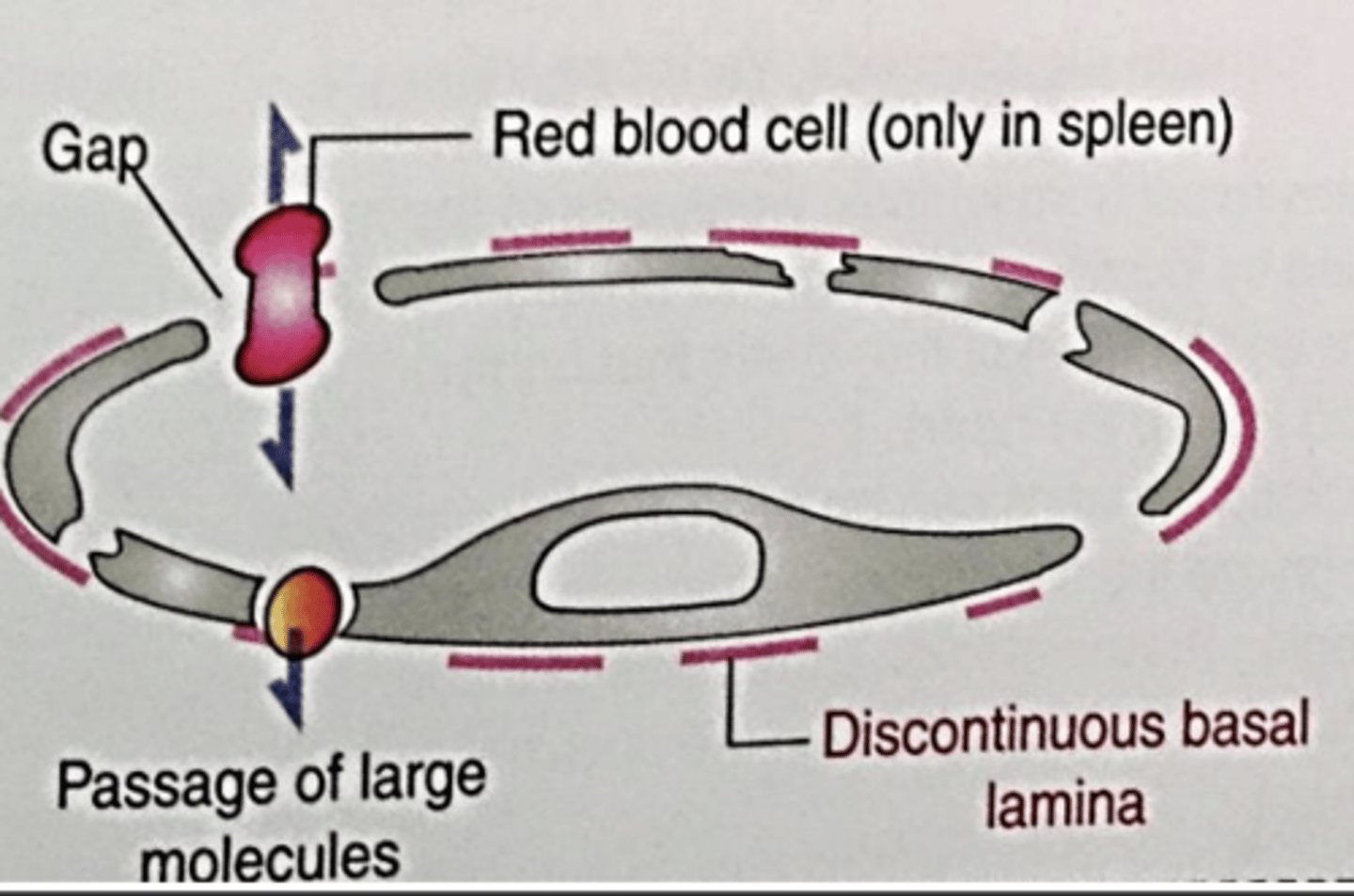
sinusoidal
what type of capillary?
continuous
what type of capillary?
to not let many substances through the walls
what is the function of a continuous capillary?
brain, muscle, skin, thymus, lungs, etc
where can you find continuous capillaries?
complete endothelium
describe the appearance of a continuous capillary
with pores/fenestrae
continuous basal lamina
what is a fenestrated capillary like?
pancreas, endocrine glands, intestines, kidney, glomerulus
where can you find fenestrated capillaries?
allows permeability of small substances
why does the endothelium of fenestrated capillaries have pores?
sinusoidal capillaries
which capillary has endothelium with very large gaps?
passage of cells
what are sinusoidal capillaries for?
discontinuous
what is the basal lamina of a sinusoidal capillary like?
liver, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes
where do we find sinusoidal capillaries?
continuous
what type of capillary?
continuous
is the basal lamina in a continuous capillary continuous or discontinuous?
fenestrated
what type of capillary?
sinusoidal
what type of capillary?
sinusoidal
cells can pass easily through the walls of which type of capillary?
venules
what type of venous vessel is similar to capillaries?
post capillary venules
what is the name for the venules right after capillaries?
muscular venules
as they widen, venules become ______
in post capillary venules
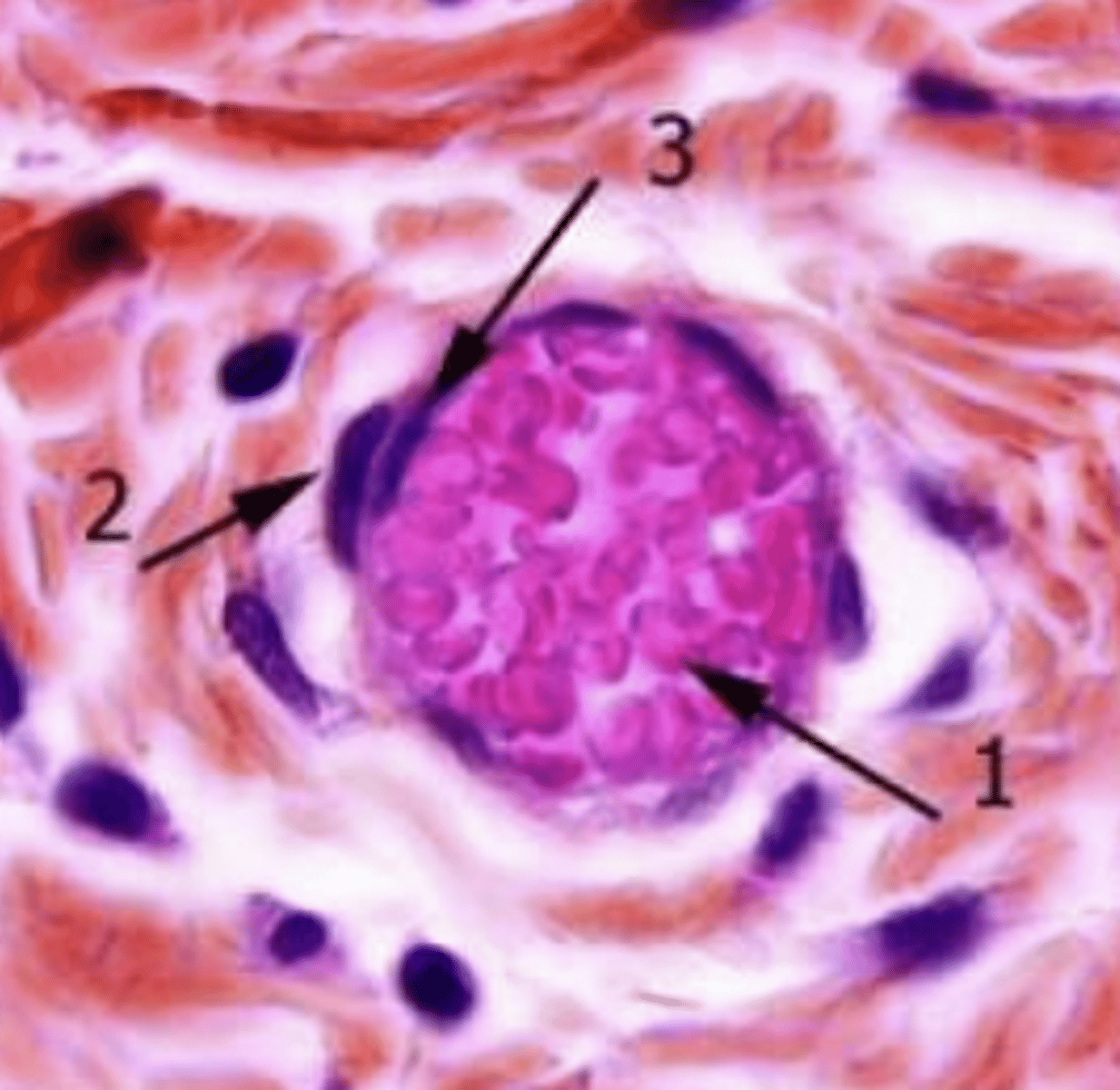
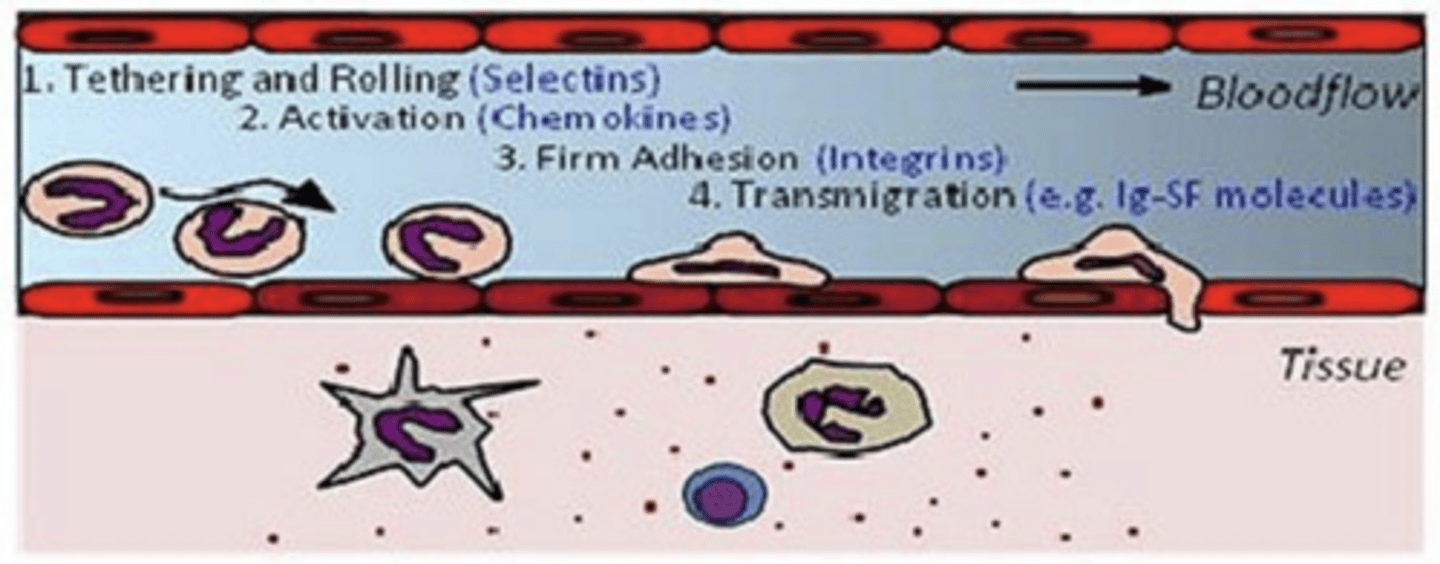
where does diapedesis occur?
the migration of blood cells into tissues
what is diapedesis?
diapedesis, in the post-capillary venules
what is this process called? where does it occur?
veins
which, arteries or veins, have valves?
because veins have low pressure blood, which increases the possibility of backflow- valves are necessary to prevent this. arteries do not need valves because the blood is very high pressure, so has a lower risk of flowing backwards
why do veins have valves and not arteries?
collagen and muscle (not much)
what does the tunica media consist of in veins?
veins
which is thinner, arteries or veins?
veins
which has a wider lumen, arteries or veins?
veins
which, arteries or veins, has an irregular shape?
artery-left
vein- right
which is an artery? which is a vein?
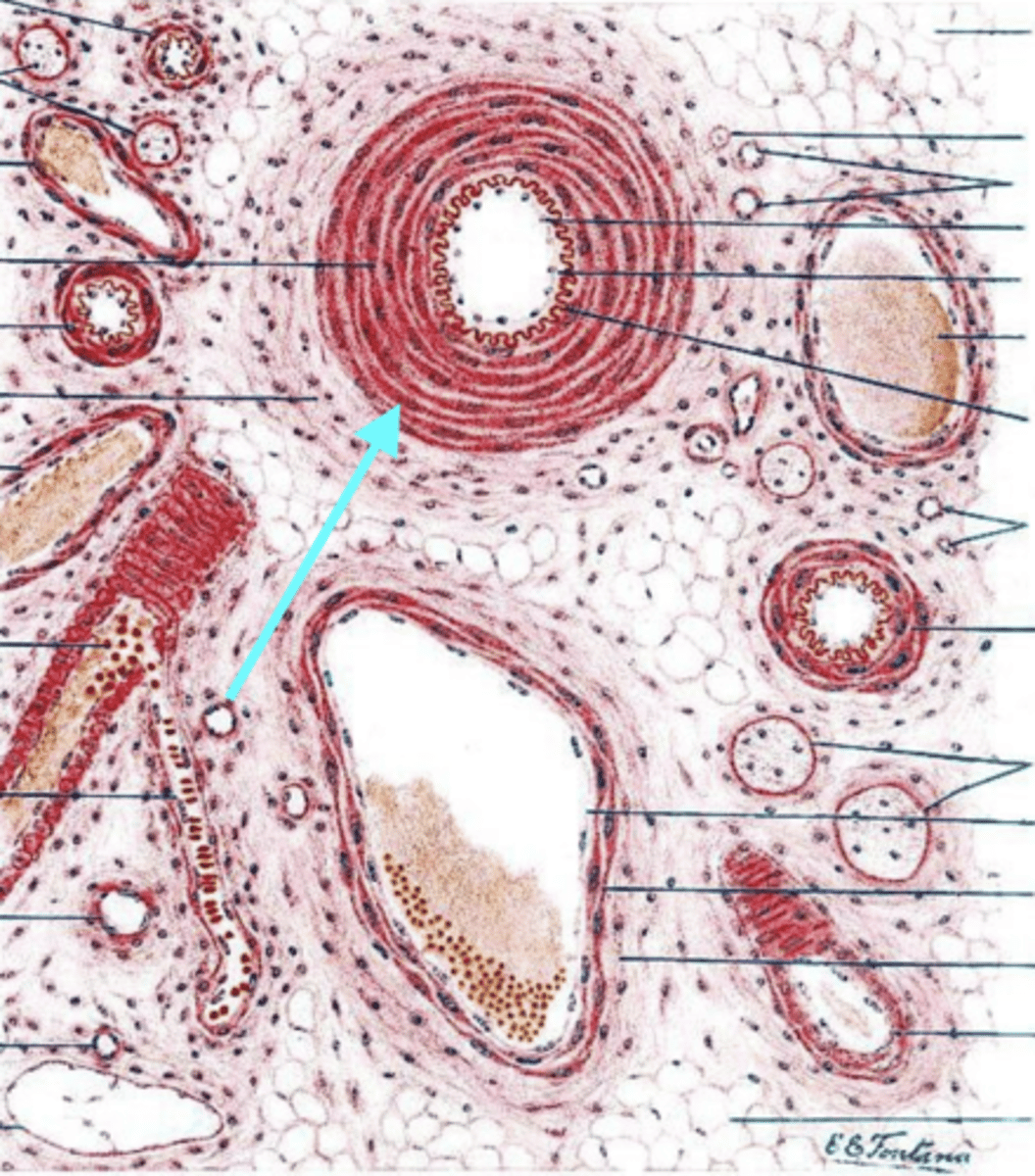
artery
what is this vessel?
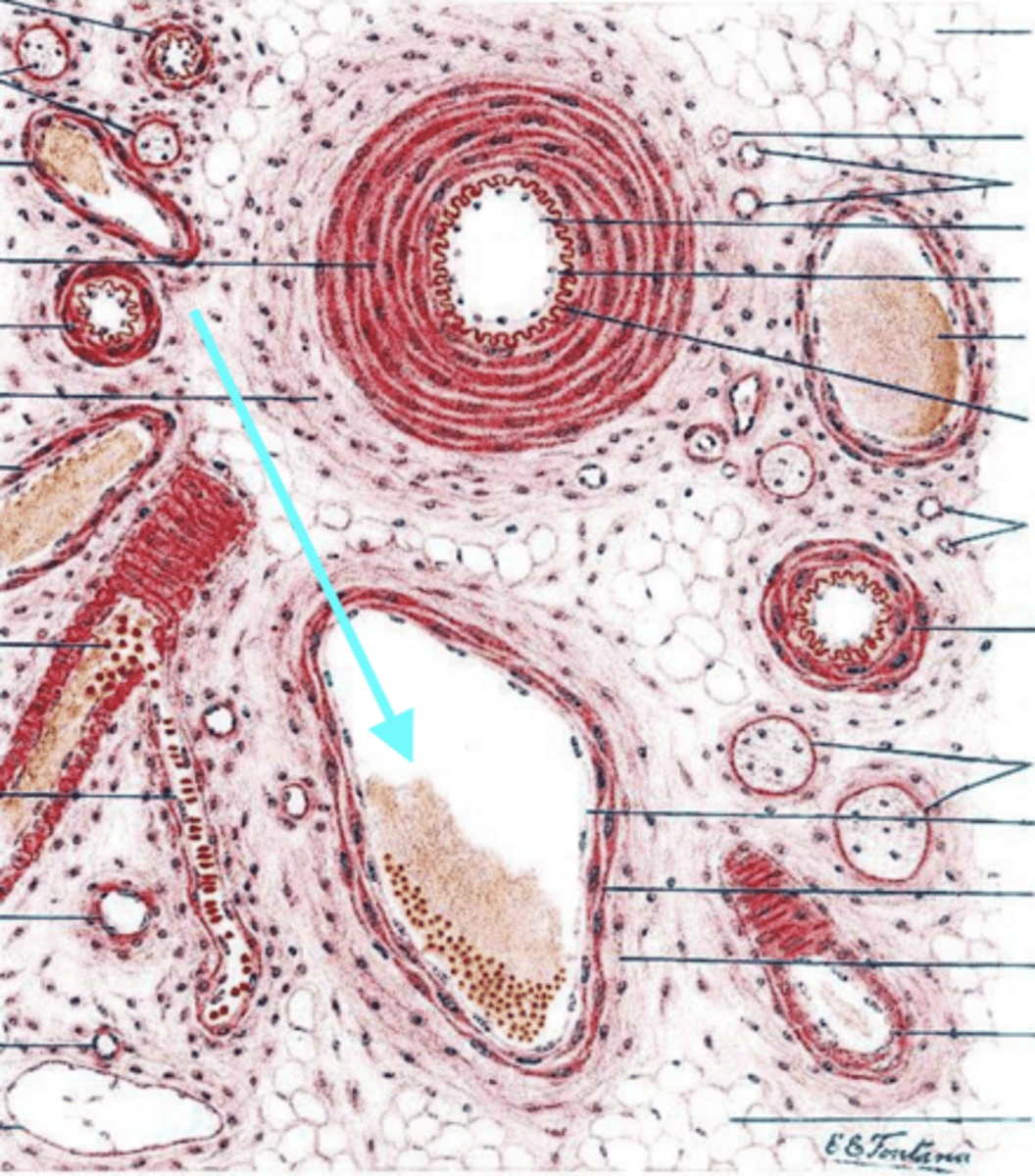
vein
what is this vessel?
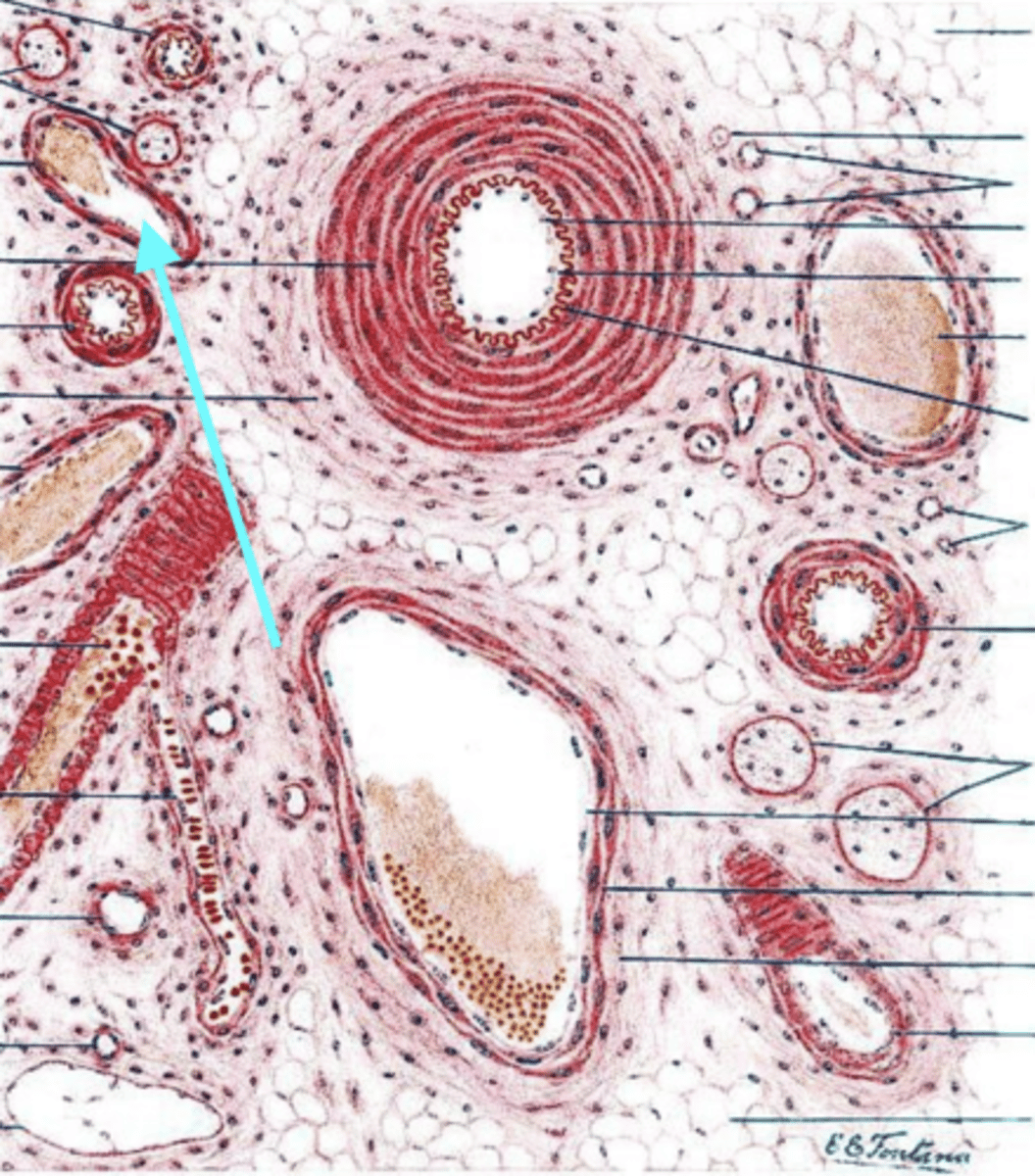
arteriole
what is this vessel?
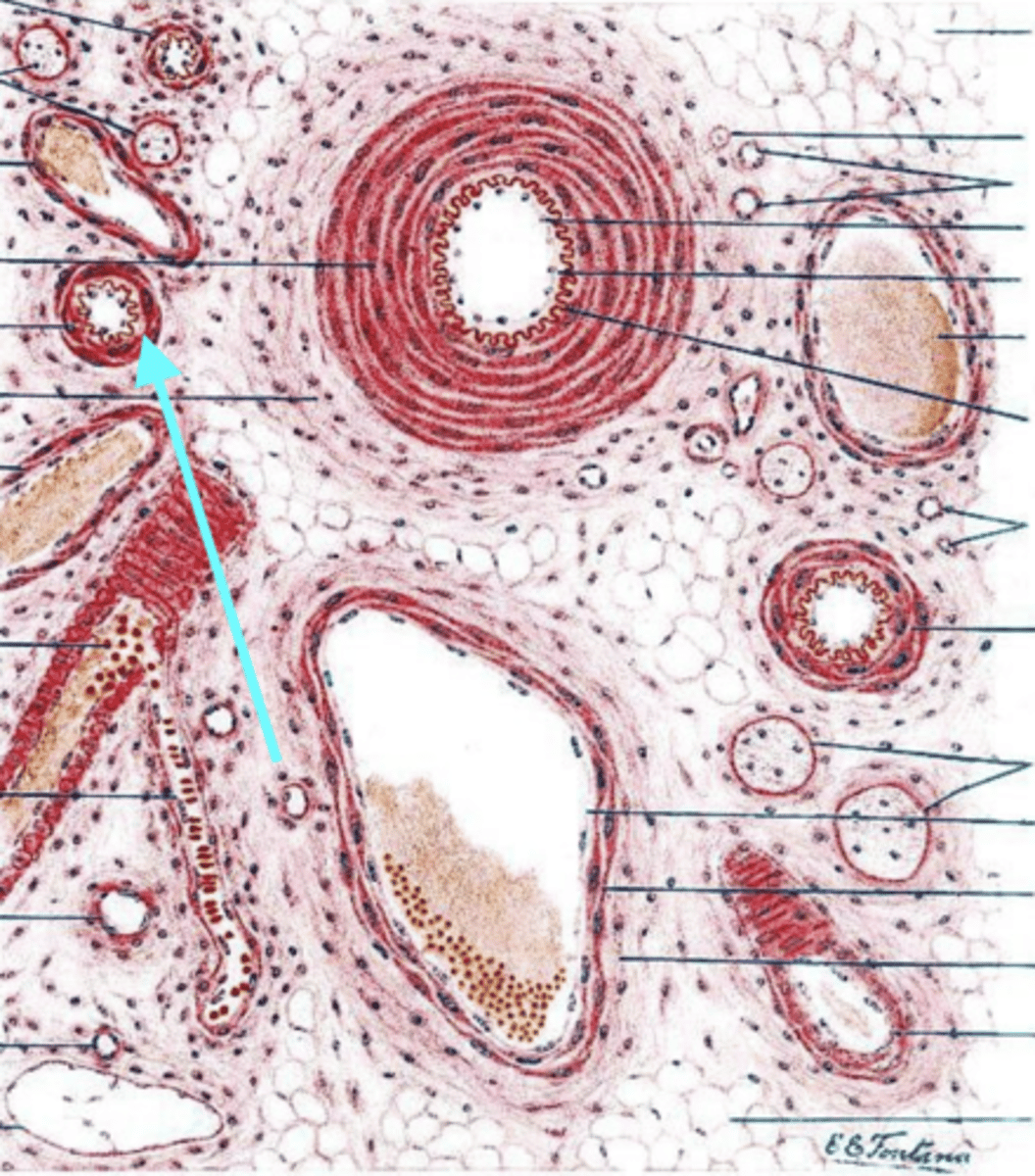
venule
what is this vessel?
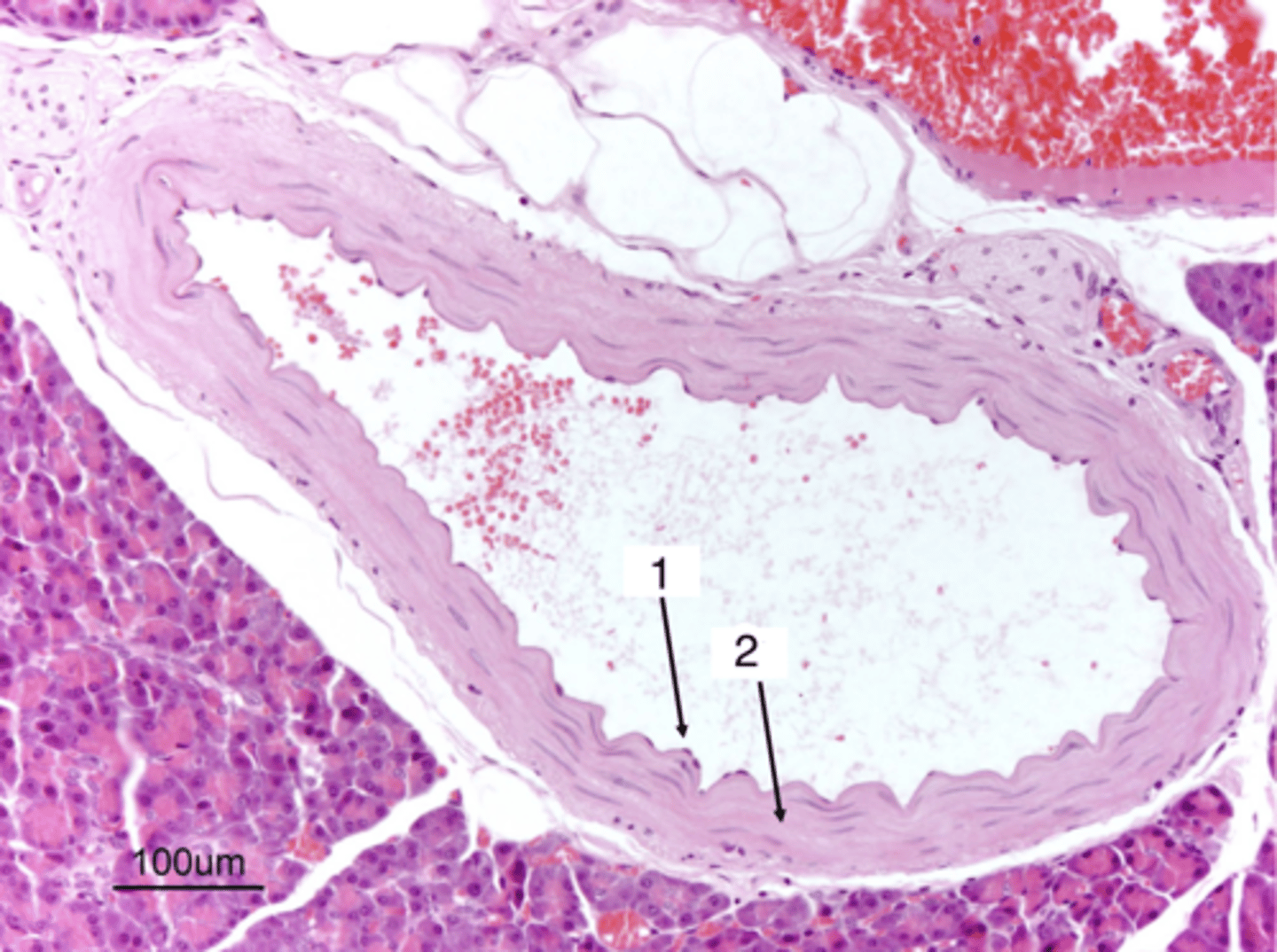
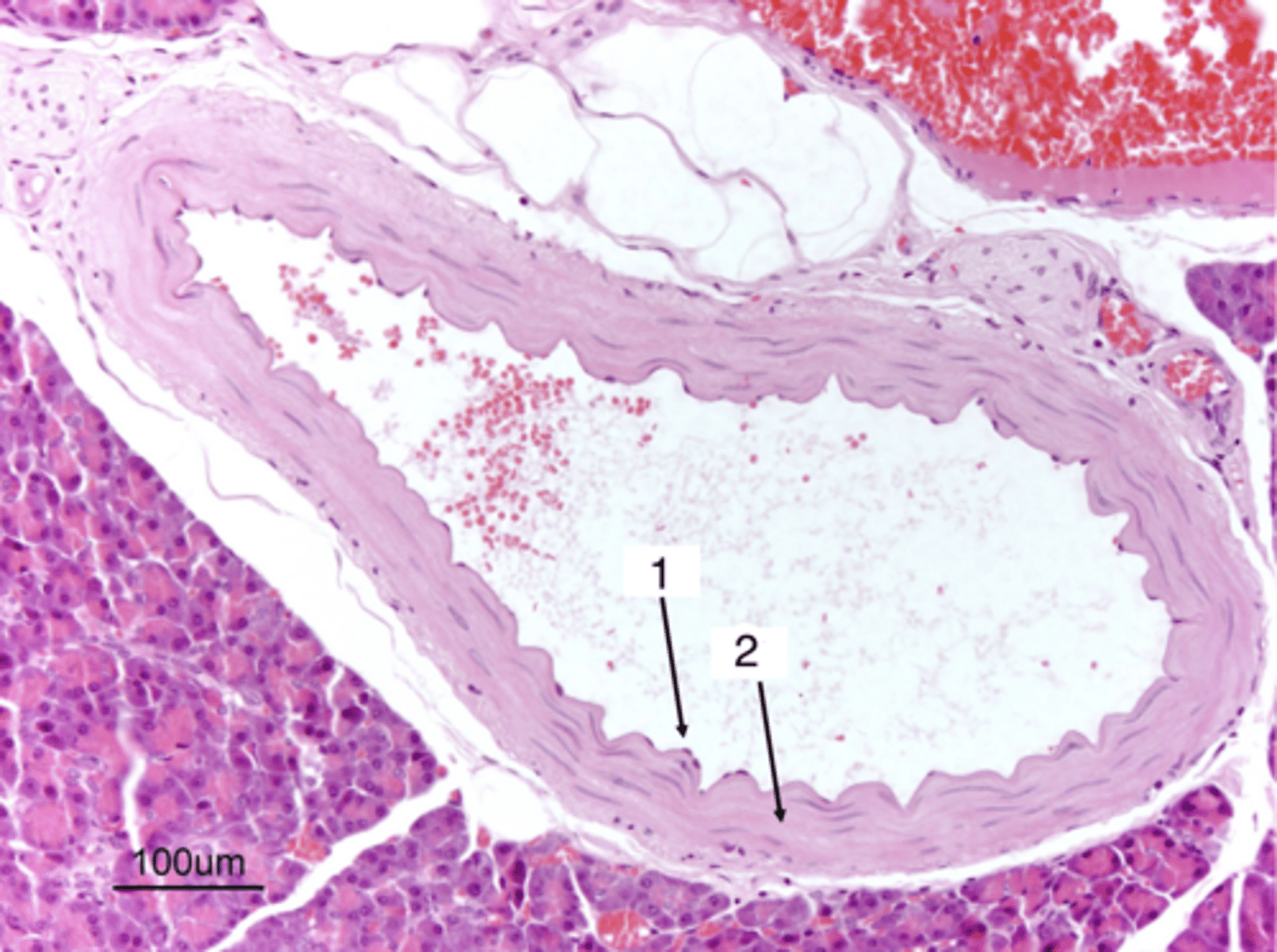
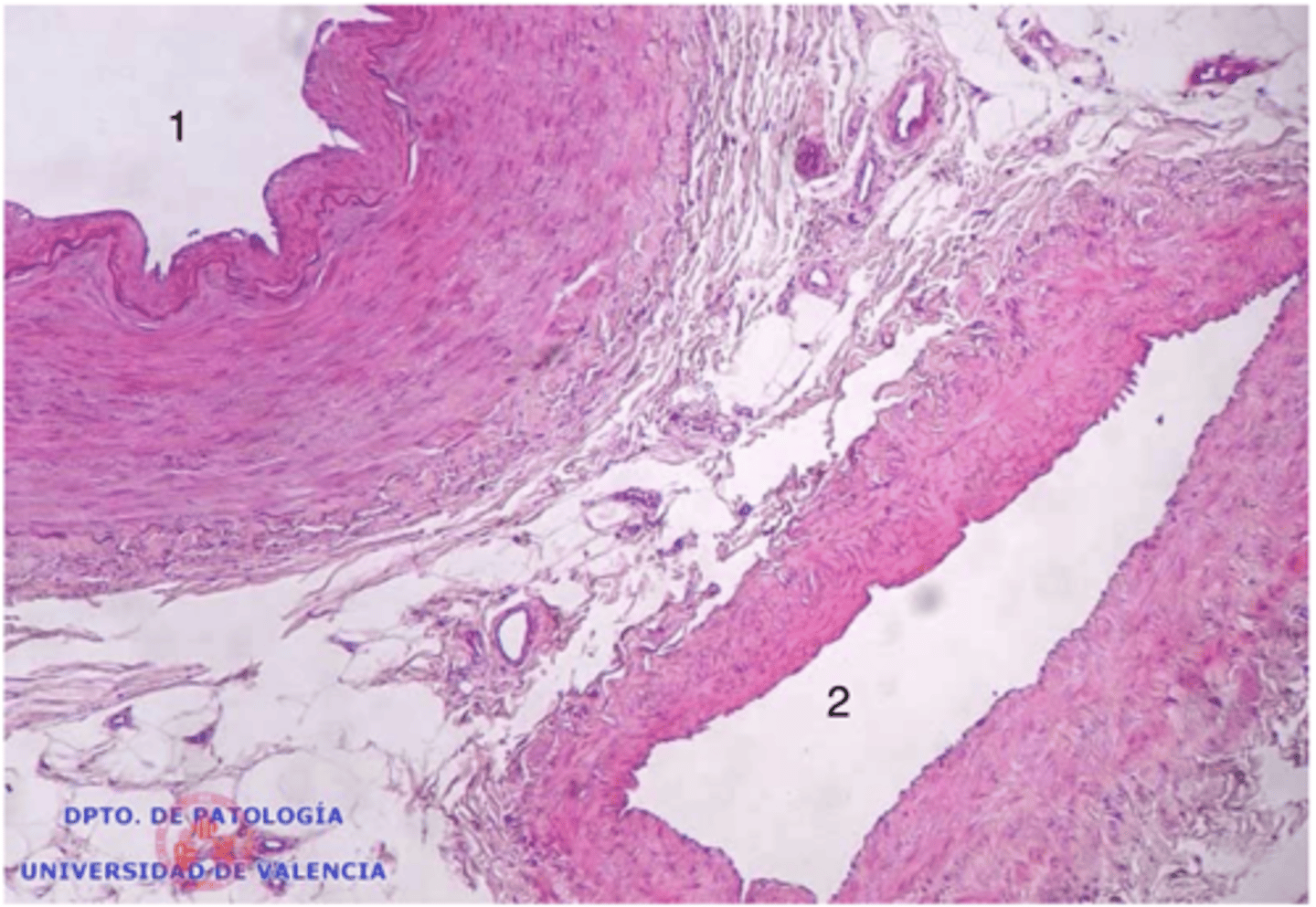
1- artery
2- vein
which is an artery and which is a vein?
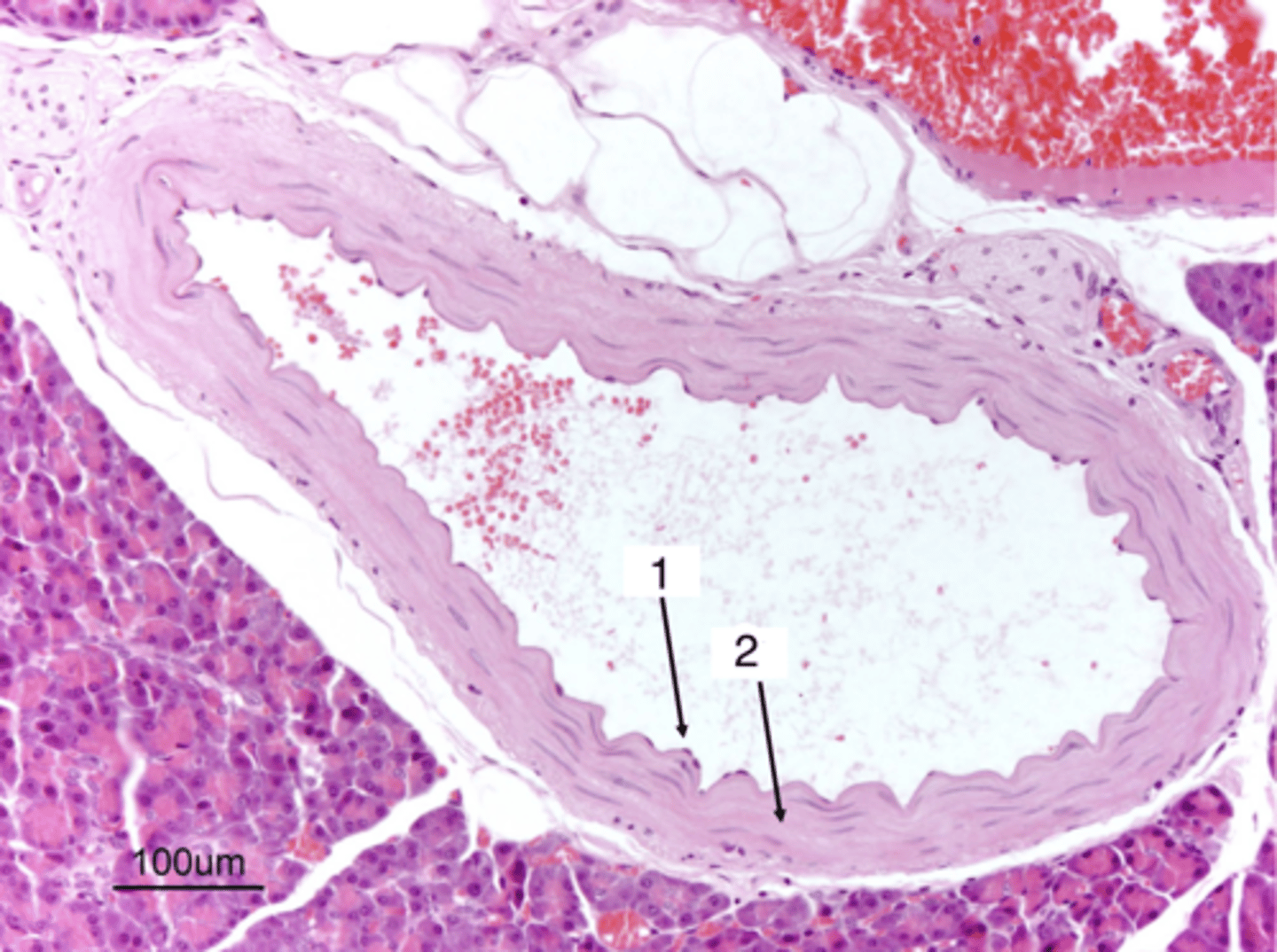
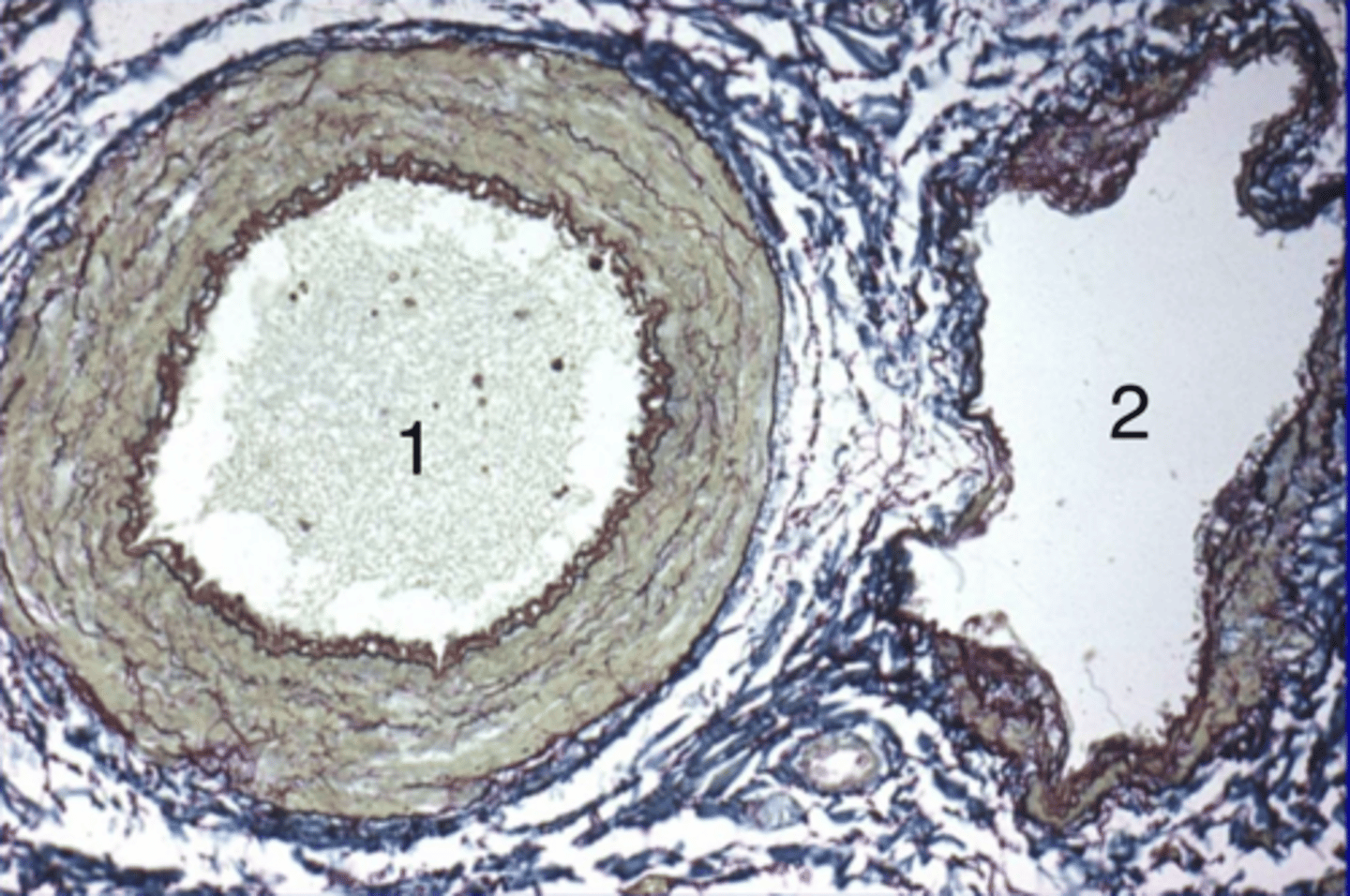
1- artery
2- vein
which is an artery and which is a vein?
3
how many muscular layers does the heart have?
endocardium
myocardium
epicardium (and pericardium)
what are the 3 layers of the heart?
endocardium
which heart layer is most internal?