First Half of Soc
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
What is sociology?
The study of society or people “doing things together”
What are sociologists interested in?
All aspects of society; groups of people who shape their lives in pattern ways that make them distinguishable from other groups.
Institutions
Structures in our society, like education, economics, and politics-that help us better understand social relationships
Sociological perspective
A way of looking at the world through a sociological lens
Beginner’s Mind
Clearing one’s mind of stereotypes, expectations, and opinions so that we can be more receptive to our experiences.
Culture shock
Sense of disorientation that you experience on entering a new environment.
Can be where behaviors typical to one society or culture are strange in another.
Sociological Imagination
Quality of mind that allows us to understand the relationship between our particular situation in life and what is happening at a social level.
Microsociology
Level of analysis that examines small-group interactions to see how they impact larger institutions in society
Macrosociology
Level of analysis that examines large-scale social structures to determine how they impact groups and individuals
What makes up the macro-micro continuum?
Society, culture, social institutions, social inequality, groups, roles, socialization, interaction, and self.

Theories
Abstract propositions that explain the social world and make predictions about future events.
What are theories also known as?
Approaches , schools of thought, perspectives, or paradigms
Paradigms
Sets of assumptions, theories, and perspectives that make up way of understanding social reality.
The way things work, essentially.
Structural functionalism
A school of thought.
Views society as an ordered system of interrelated parts, or structures, which are the social institutions that make it up (family, education, politics, the economy).
Each meet the needs of society by performing specific functions for the whole system(society)
Conflict Theory
Sees social conflict as the basis of society and social change.
Power and inequality central to this theory.
What are the three main focuses of conflict theory?
A materialist view on society
Critical stance towards existing social arrangements
Dynamic model of historical change
Symbolic Interactionism
Sees interactions and meaning as central to society.
Assumes meanings are not inherent but more so created through interaction.
The way in which we use status differences to categorize ourselves and others
Our clothing, speech, gestures, possessions, friends, activities, and so on provide information about our socioeconomic status.
What are the basic tenets of Symbolic Interactionism?
We act towards things based on their meanings
Meanings are not inherent instead, negotiated.
Meanings can change
Social Facts
Ways of thinking, feeling, and acting that are external to individuals.
Coercive; apparent but not obvious.
“Subject matter” of sociology
What is an example of a Social Fact?
Think of social norms, laws, beliefs… so language, marriage, and religion
How do we think sociologically?
We use our sociological imagination which allows us to uncover social facts of society.
Paradigm shift
Change in the way we think about some aspect of life
Spurious correlation
Relationship that seems to exist between 2 variables but is caused by some external/intervening variable.
Ethnography
Studying people in their own environments in order to understand the meanings they give to their activities.
Provides a thick description of the setting observed.
Participant observation
Researcher both observes and becomes a member in a social setting
What are the 2 steps of Ethnography?
Researcher participates in & observes a setting
Makes written account (field notes) of what goes on there
Deductive approach
Forming a hypothesis first and then testing to see whether it is accurate
Inductive Approach
Beginning with specific observations and then forming broad generalizations from them
Interviews
Direct, fact-to-face contact with respondents.
Generate large amts of qualitative data.
A target population of interest is identified and then a sample of people are typically chosen to be contacted from that population.
Surveys
Questionnaires administered to sample of respondents selected from target population
Looks at large-scale social patterns and employs statistics and other mathematical means of analysis
Probability Sampling
Helps obtain a sample that reflects characteristics of members of the target population
Unobtrusive measure
Does not disturb the setting or subjects under study.
Example is existing sources (data produced for another reason but can be used for social research)
Comparative Historical Research
Analysis of different regions and time periods.
Cultural artifacts like literature, paintings, newspapers, and photographs are analyzed
Content Analysis
Identify and study specific variables or themes that appear in text, images, or media
Code of Ethics
Developed by American Sociological Association
Helps researchers avoid bias and adhere to professional standards.
Protects respondents from harm
Culture
Entire way of life of a group of people.
Includes language, standards of beauty, hand gestures, styles of dress, food, and music.
Learned by generations through communication
It may be hard to see our own culture. What does that do?
Makes it difficult to recognize the extent to which it shapes and defines who we are.
Ethnocentrism
When people use their own culture as standard to evaluate another group/individual, leading to the view that cultures other than their own are abnormal.
Cultural Relativism
Process of understanding other cultures on own terms rather then through judgement.
See others more objectively
What are the two categories of culture?
Material and Symbolic culture
Material culture
Objects associated with a cultural group, such as tools, machines, utensils, buildings, and artwork
Symbolic Culture
Ways of thinking (beliefs, values, and assumptions)
Ways of behaving (norms, interactions, and communications)
Allows communication through signs, gestures, and language
Language
Communication system through vocal sounds, gestures, & written symbols
Significant component of culture because it is primary means of communication
Sapir-Whorf hypothesis
Structure of language determines a native speaker’s perception and categorization of experience. (How we see things)
Values
Shared beliefs about what a group considers worthwhile or desirable; they guide the creation of norms
Norms
Rules regarding what kinds of behavior are acceptable and appropriate within a specific culture, time period, or situation.
Can be formal (laws or rules) and unwritten/unspoken
Folkway
Loosely enforced norm that involves common customs, practices, or procedures that ensure smooth social interaction and acceptance
More
Norm that carries moral significance, is closely related to the core values of a group, and often involves severe repercussions for violators
Taboo
Norm engrained so deeply that even thinking about violating that for most people, it evokes strong feelings of disgust, horror, or revulsion
Sanctions
Positive or negative reactions to ways that people follow/disobey norms, including rewards for conformity and punishments for norm violators
Social Control
Made up of the formal and informal mechanisms used to increase conformity to values and norms and thus increase social cohesion
Multiculturalism
Values diverse racial, ethnic, national, and linguistic backgrounds and thus encourages the retention of cultural differences within society, rather than assimilation.
Socialization
Process of learning and internalizing the values, beliefs, and norms of our social group.
Begins in infancy and lasts throughout the lifetime.
Language facilitates it
Self
Our experience of a personal identity that is separate and different from all other people.
Believed to be created and modified through interaction with others over the course of one’s life.
Charles Cooley
Believed that sense of self depends on seeing oneself reflected in interactions with others
Looking-glass self
Notion that the self develops through our perception of others’ evaluations and appraisals of us
George Herbert Mead
Expanded on Cooley’s ideas
Believed self created through social interactions & process starts in childhood as children acquire language skills
According to George Herbert Mead, what are the three stages of development of self?
Preparatory Stage
Play Stage (taking role of particular other)
Game Stage (In which children learn to take the perspectives of the generalized other)
Thomas Theorem
We encounter ambiguous situations every day, many meanings are possible.
The way we define each situation, becomes its reality
Erving Goffman
Believed meaning is constructed through interaction
Dramaturgy
Compares social interaction to the theater, where individuals take on roles and act them out for an audience
Impression management
A process, much like a “game”, where we work to control the impressions others have of us.
Agents of Socialization
Social groups, institutions, and individuals that provide structured situations where socialization occurs.
Major agents: Family, schools, peers, the media
How is family an agent of socialization?
Single most significant agent of socialization in all societies and teaches us the basic values and norms that shape our identity.
How is school an agent of socialization?
Provides education and socializes us through hidden curriculum that teaches us many of the behaviors deemed important later in life
Hidden Curriculum
Values and behaviors, such as punctuality, neatness, discipline, hard work, competition, and obedience, that students learn indirectly over the course of their schooling.
How are peers agents of socialization?
Provide very different social skills and often become more immediately significant than the family, especially as children move through adolescence.
How is the media an agent of socialization?
Has become important because it often overrides the family and other institutions in instilling values and norms.
Resocialization
Process of replacing previously learned norms and values with new ones as a part of a transition in life.
Total institution
An institution (such as a prison, cult, or mental hospital) that cuts individuals off from the rest of society so that their lives can be controlled and regulated.
Dramatic form of resocialization takes place here
Status
Position in society that comes with a set of expectations.
Ascribed Status
One we are born with that is unlikely to change
Embodied Status
One that is located in our physical selves
Achieved Status
One we have earned through our individual effort or that is imposed by others.
Roles
Set of behaviors expected from a particular status.
Role Conflict
Occurs when the roles associated with one status clash with the roles associated with a different status
Role Strain
Occurs when roles associated with a single status clash
Role Exit
Where a person disengages from a social role that was central to them. Caused by role strain or role conflict.
Emotion work
Process of evoking, suppressing, or managing feelings to create a public display of emotion
Saturated self
Idea that self is now developed by multiple influences chosen from a wide range of media sources
Deviance
Behavior, trait, or belief that departs from a norm and generates a negative reaction in a particular group.
What function does Deviance serve in society?
A positive social function by clarifying moral boundaries and promoting social cohesion.
Social Control Theory
Theory developed by Travis Hirschi to explain crime
Increase Conformity
Decrease Deviance
Structural Strain Theory
By Robert Merton
Goals in our society that people want to achieve but cannot always reach, which creates stress (or strain)
Merton’s Typology of Deviance
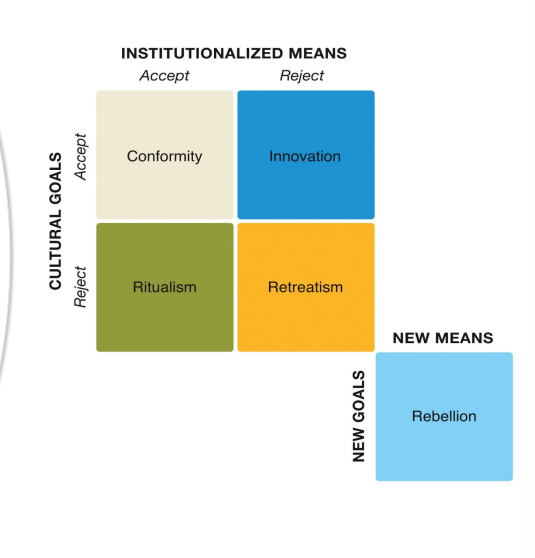
Theories of Deviance and Interactions
Interpersonal relationships and everyday interactions influence meanings and understandings of deviance.
Differential Association theory
A symbolic interactionist perspective developed by Edwin Sutherland
States that we learn deviance from interacting with deviant peers
Labeling Theory
Deviance caused by external judgements (labels) that change person’s self-concept and the way in which others respond to that person
“Labeling” can lead to self-fulfilling prophecy
Stereotype Threat
Self-fulfilling prophecy in which the fear of performing poorly and thereby confirming stereotypes about one’s social group causes people to perform poorly
Stereotype Promise
Self-fulfilling prophecy in which positive stereotypes lead to positive performance outcomes
Crime
Violation of a norm that has been codified into law
Deterrence
Preventing crime with the threat of harsh penalties
Retribution
Retaliating or taking revenge for a crime that has been committed
Incapacitation
Removing criminals from society by imprisoning them
Rehabilitation
Reforming criminals so that they may reenter society
Positive Deviance
An act that is outside the norm but may actually be heroic rather than negative.
Ex: taking a stand against an unjust law or unfair practice.
Social Institutions
Systems and structures that shape the activities of groups and individuals in society.
Can’t “visit” it. It’s a structure, not a place.
Ex. Politics, education, and religion are examples of institutions
Who rules America?
Pluralism. Power Elite. Interest Groups
Pluralism
A system of political power in which a wide variety of individuals and groups have equal access to resources and power
Power Elite
Coined by C. Wright Mills
A relatively small number of people who control the economic, political, and military institutions of society