What Molecule is That?
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Carbohydrates are made of…
C, H, and O (CH2O)n and sometimes contain nitrogen!
What kind of structure do carbohydrates have?
It varies, though in most examples they usually are arranged in rings or have long carbon backbones. Some polysaccharides also like to “hold hands“ (hydroxyl (O-H) bonds) or have double bonds (carbonyl (C=O) groups).
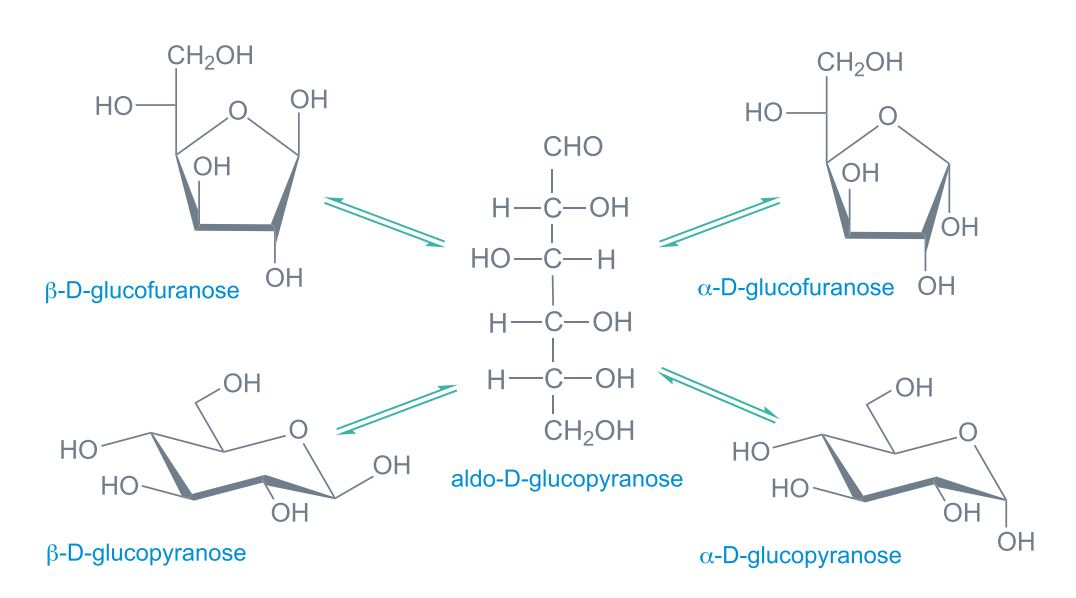
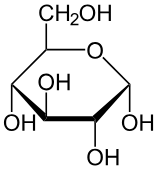
What is this molecule?
Glucose, a carbohydrate (simple sugar/monosaccharide).
Lipids are made of…
C and H
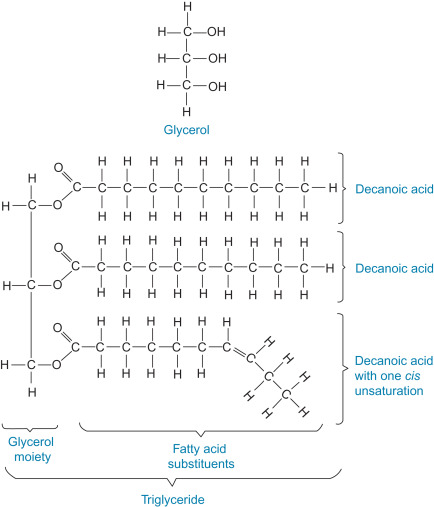
What kind of structure do fats (a type of lipid) have?
A fatty acid (a hydrocarbon chain + a carboxyl group) and glycerol. Usually they tend to arrange themselves in long chains and are sometimes bent in the presence of double bonded carbons.
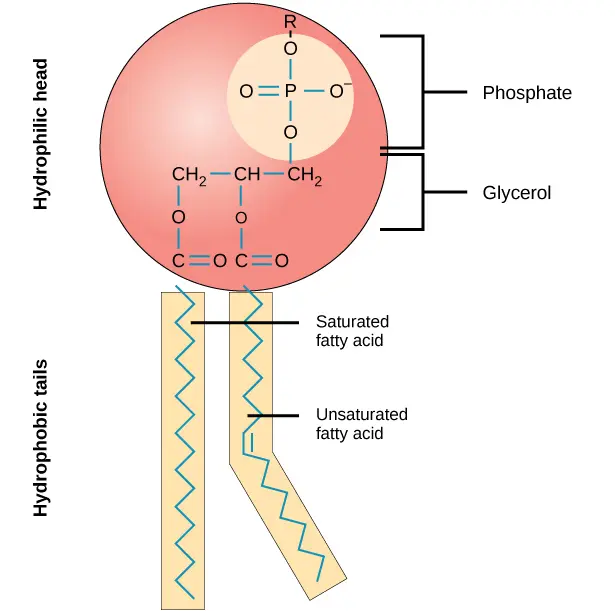
What kind of structure do phospholipids (a type of lipid) have?
A phosphate group and glycerol which make up the hydrophobic head and 2 fatty acids which make up the hydrophobic tails. It might not always be obvious though so try and pay attention for a phosphorus with four oxygen atoms surrounding it.
What kind of structure do steroids (a type of lipid) have?
A four carbon ring structure + functional group; some have tails. These are typically the easiest lipid to identify.
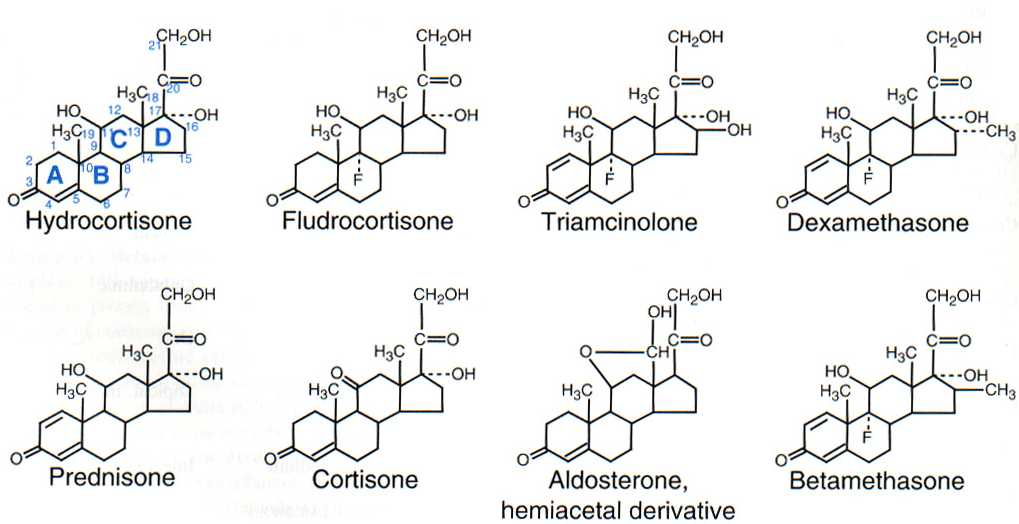
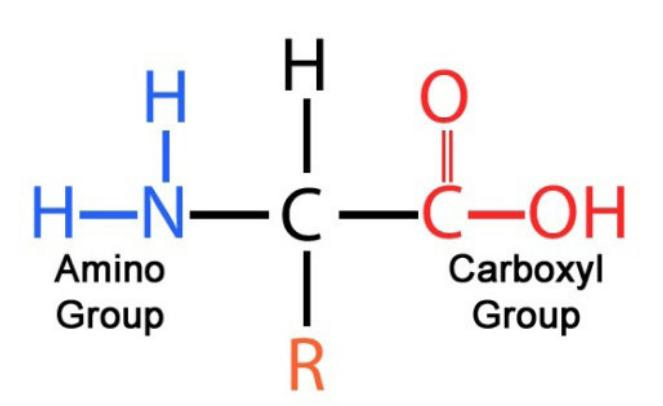
Proteins are made of…
Mostly C, H, N, O, and S
What kind of structure do proteins have?
An amino group + a side chain (R-group) + a carboxyl group. If you’re lucky, these are the easiest to identify in their abstract form because they look like a bunch of twisted up ribbons. Otherwise, try to pay attention to finding their N-C-C backbone.
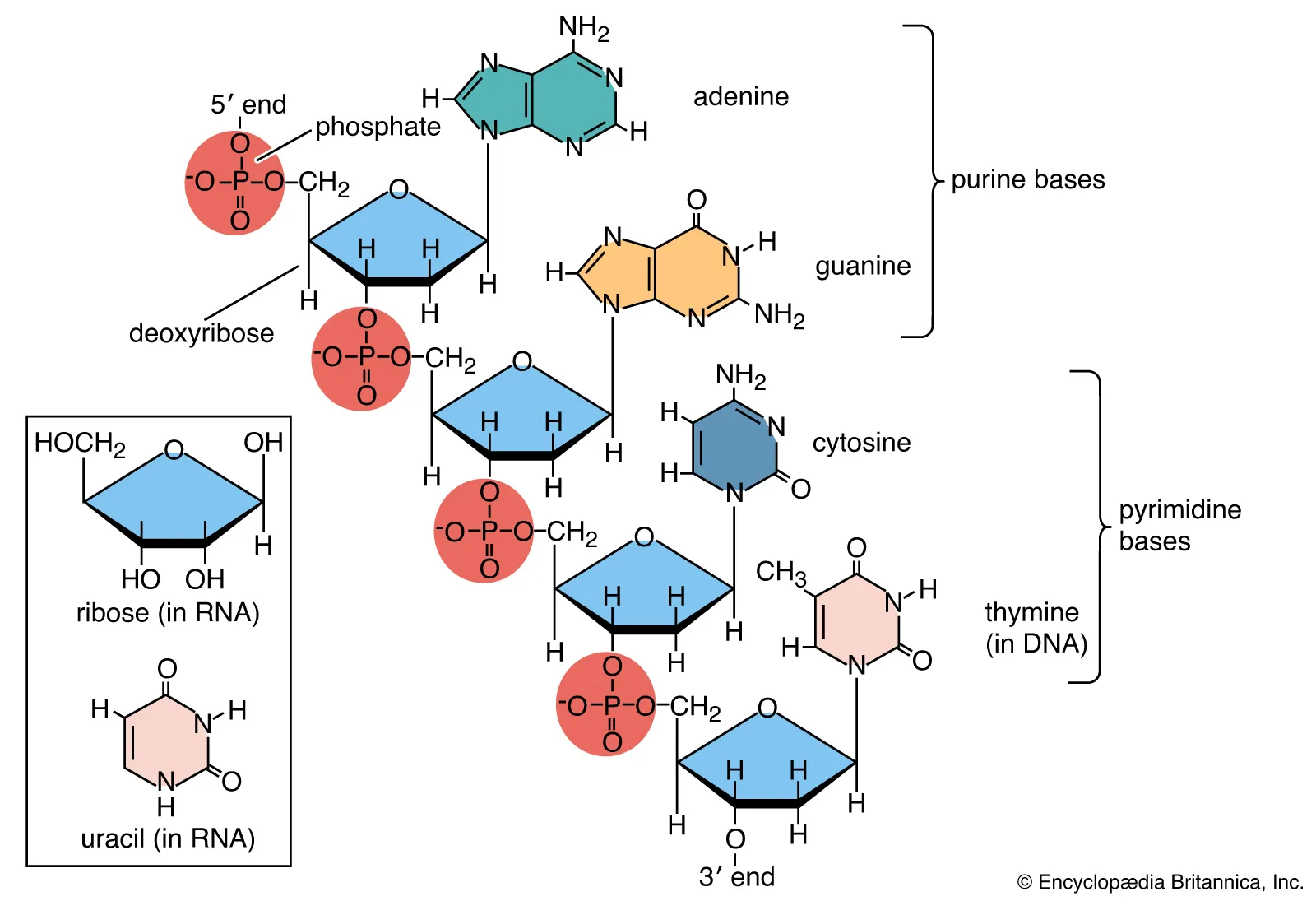
Nucleic acids are made of…
Mostly C, H, N, O, and P
What kind of structure do nucleic acids have?
A phosphate group + a pentose (five-carbon sugar) + a nitrogenous base (variable). These are the most likely to be confused with carbohydrates since they literally contain sugars but try and look for the phosphate group (P and four O) since the only other molecules with phosphorus will be lipids.
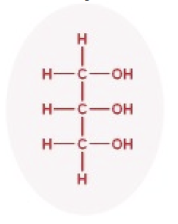
How to tell the difference between a carbon and a lipid?
Literally count the atoms if you need to. Carbohydrates will be in the form (CH2O)n and lipids… won’t lol.
Carbon or lipid?
Lipid
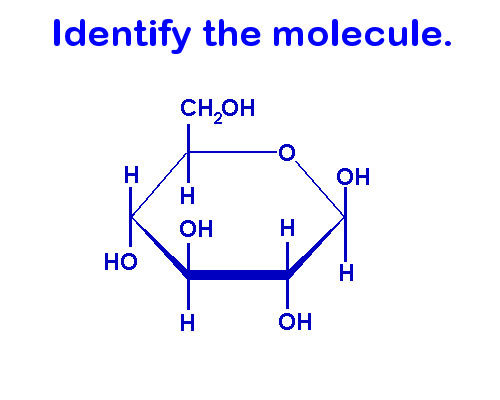
Carbohydrate (glucose)
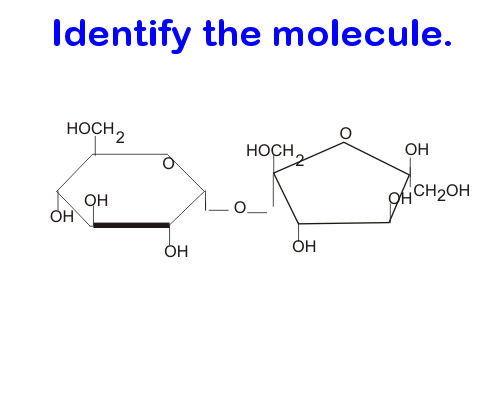
Carbohydrate (disaccharide)
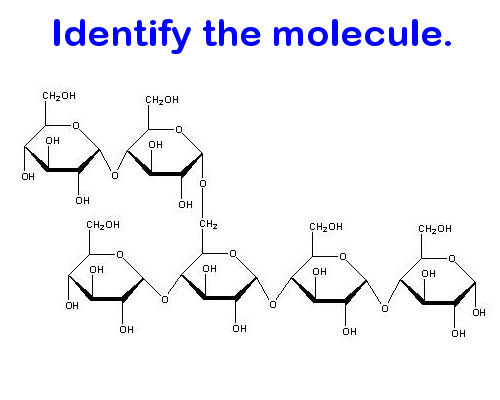
Carbohydrate (polysaccharide)
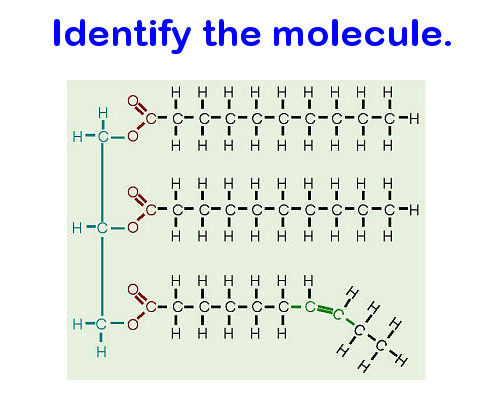
Lipid (unsaturated triglyceride)
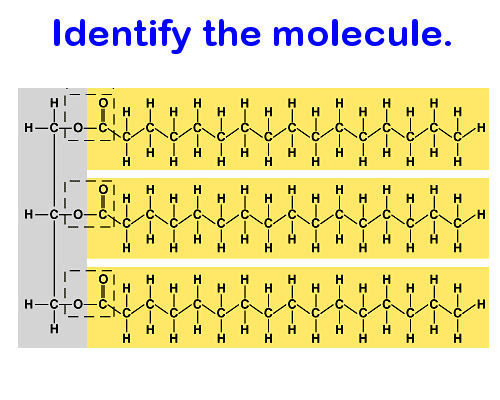
Lipid (saturated triglyceride)
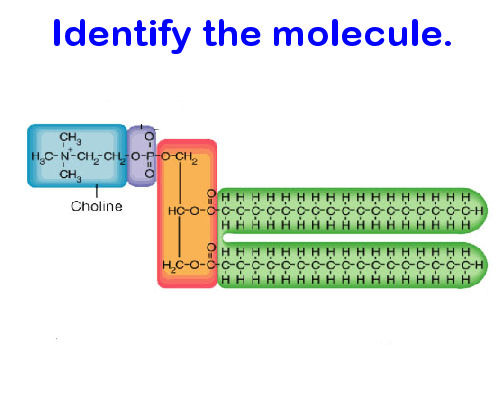
Lipid
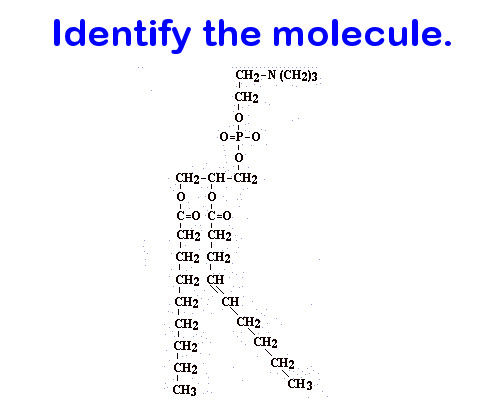
Lipid
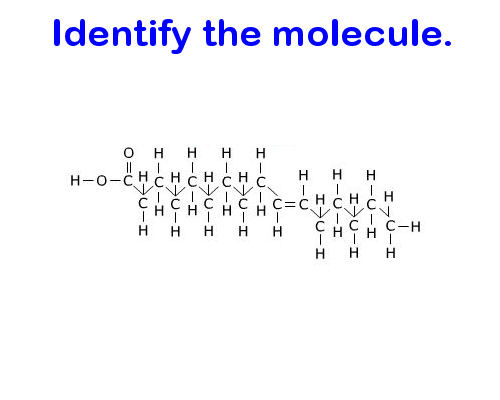
Lipid
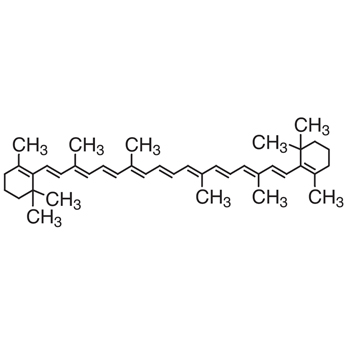
Lipid
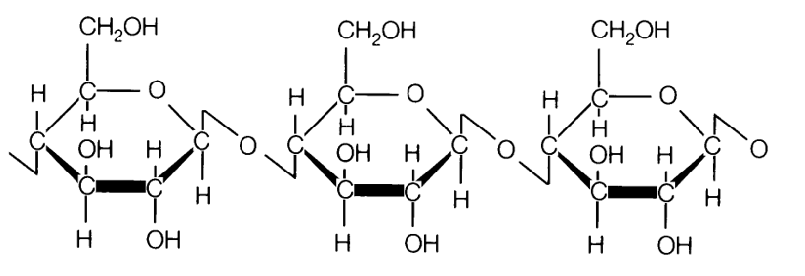
Carbohydrate (cellulose: the main component of cell walls in plants providing structural support)
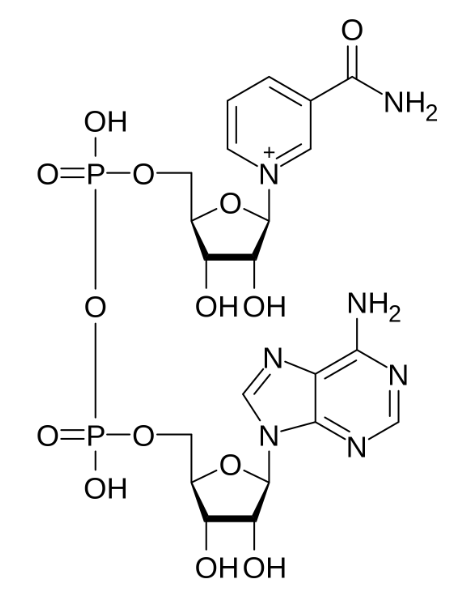
Nucleic acid (2 nucleotides that make NAD+)
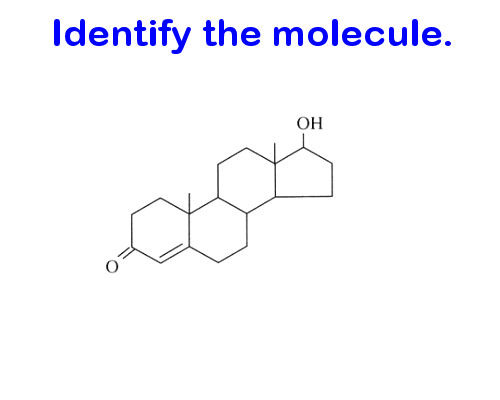
Lipid
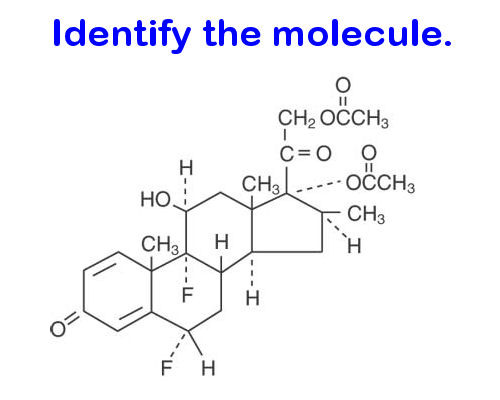
Lipid

Lipid
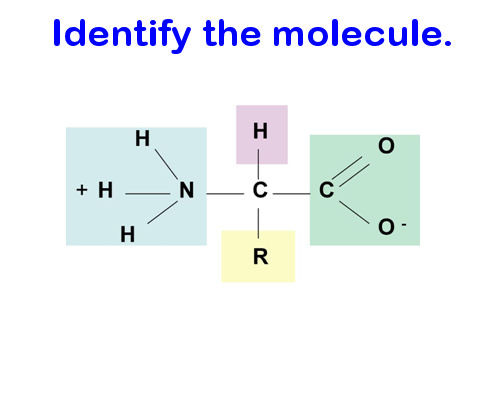
Protein monomer (amino acid)
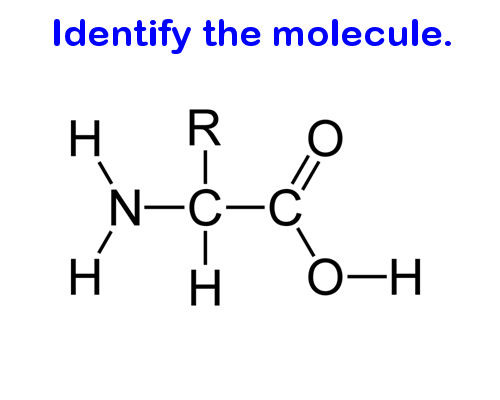
Protein monomer (amino acid)
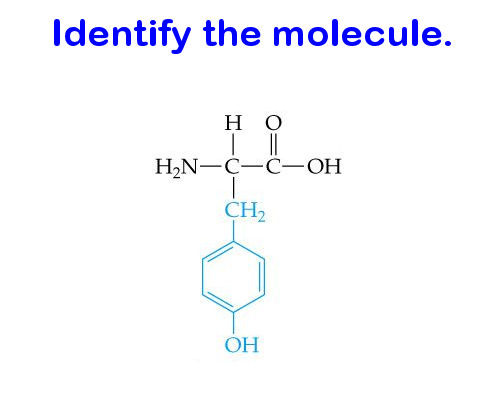
Protein monomer (amino acid)
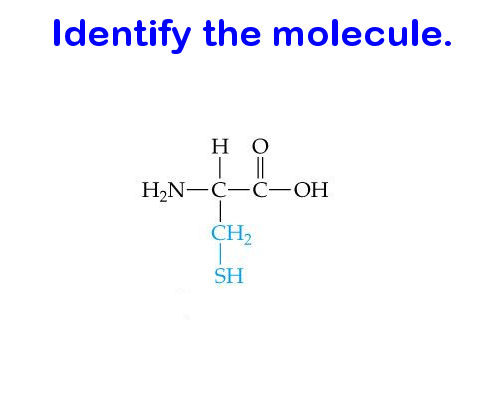
Protein monomer (amino acid)
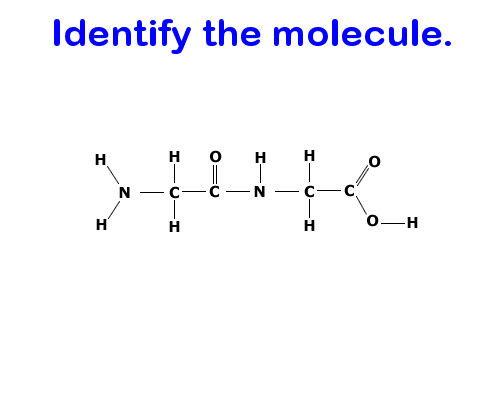
Protein (dipeptide)
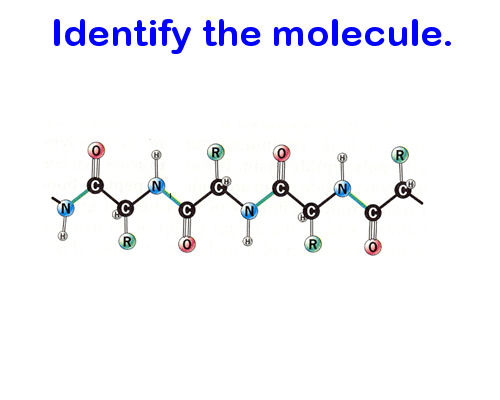
Protein (polypeptide)
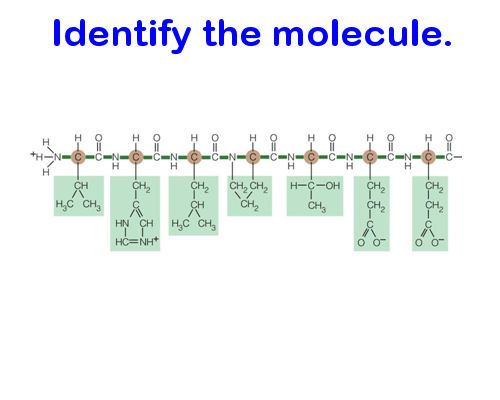
Protein
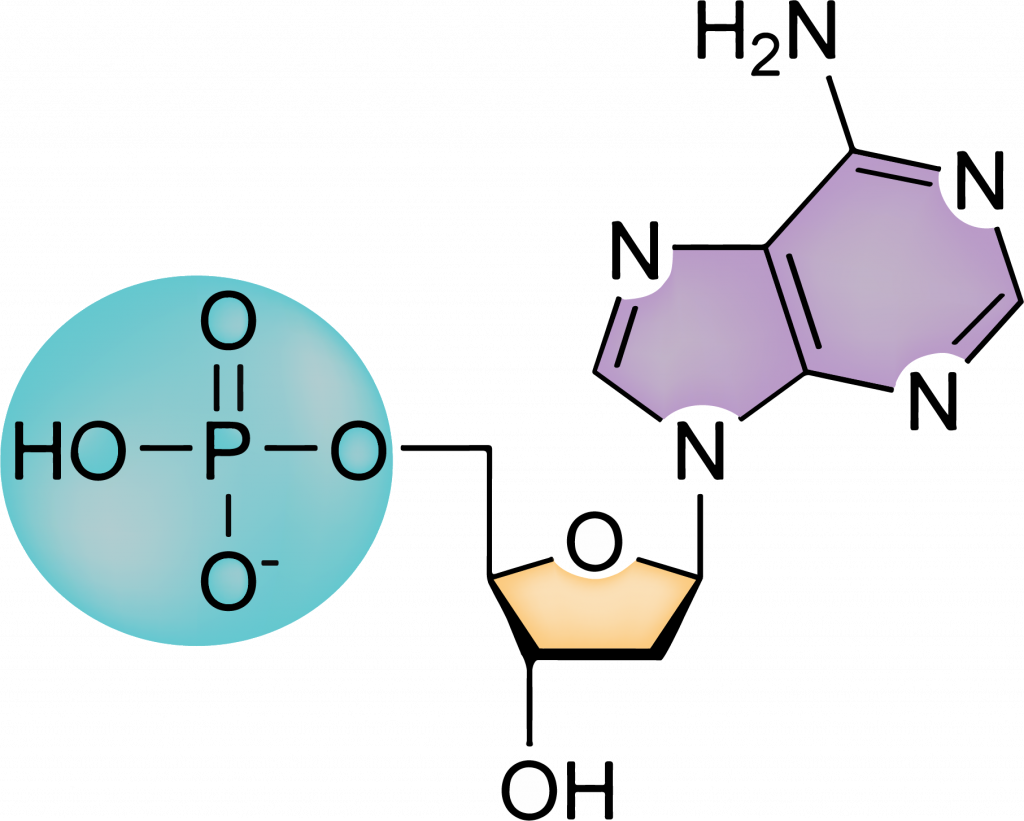
Nucleic Acid
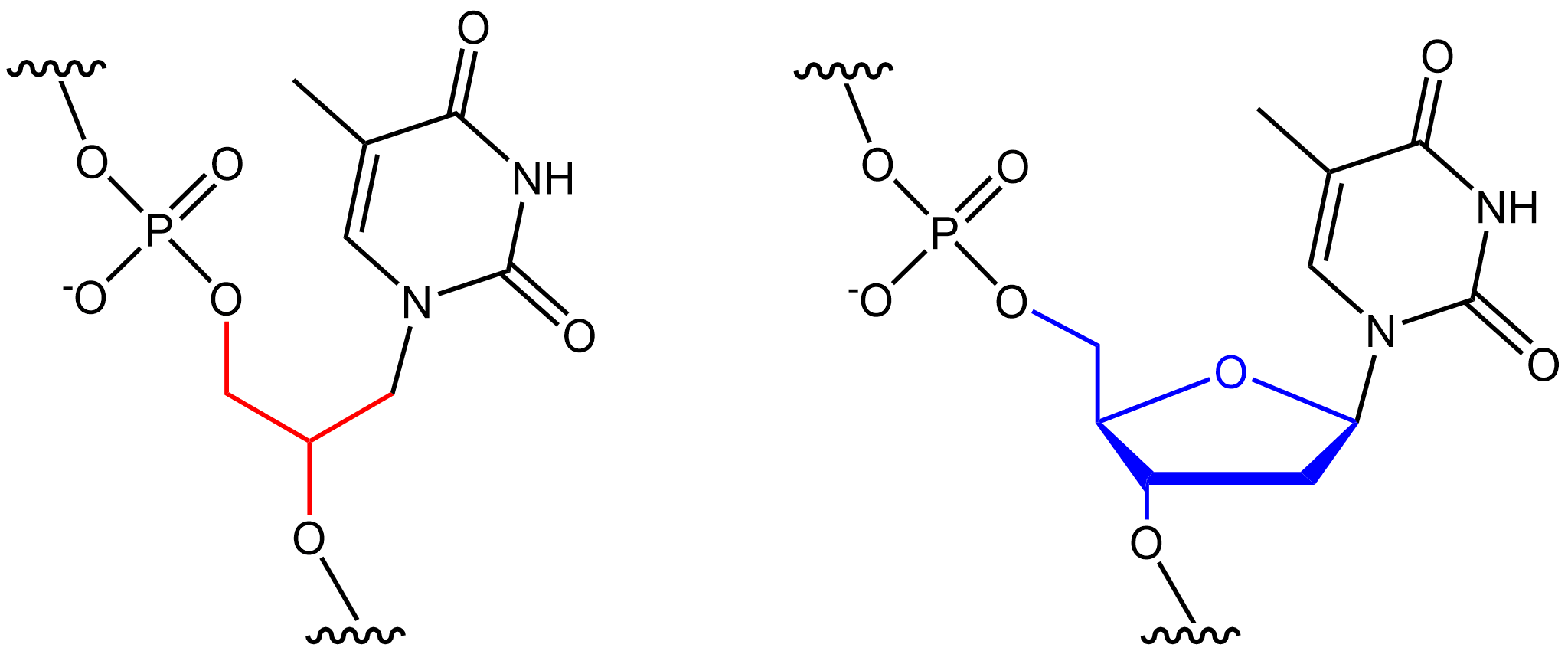
Nucleic Acid