L23: Microanatomy of the Kidneys
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
filtration of blood
removal of metabolic waste
reabsorption
preserving necessary metabolites and nutrient and the required amount of water
what is the endocrine function of the kidneys?
production of renin
what is the functional unit of the kidneys?
the nephron
what is the kidney surrounded by?
dense connective tissue capsule
what is the parenchyma of the kidney divided into?
outer cortex and inner medulla
what are the general functions of the kidneys?
filtration
reabsorption
secretion
countercurrents
what is the flow of the urogenital tract?
kidneys
ureters
urinary bladder
urethra
penile urethra or vestibule and vulva
why does the outer cortex appear granular?
presence of renal corpuscles
what is important to understand about the lobes of the bovine kidney?
each lobe acts as an independent functional unit
where is the only place you will see lobation in a porcine kidney?
will only see internally
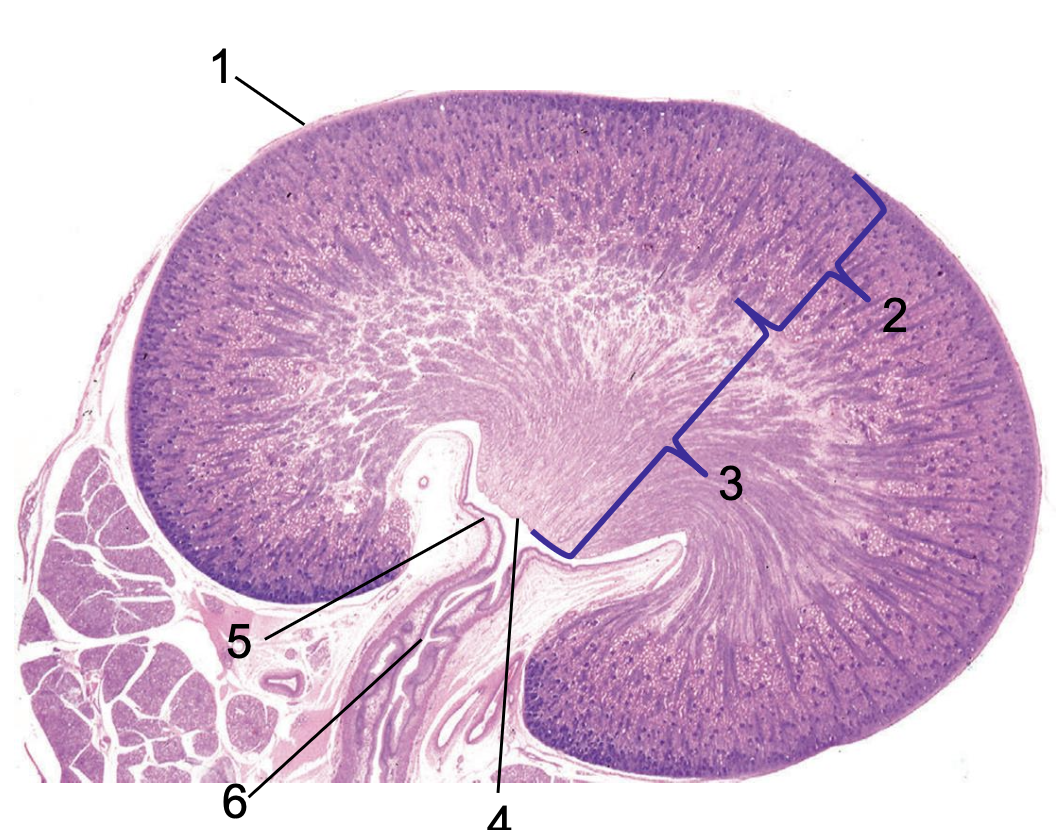
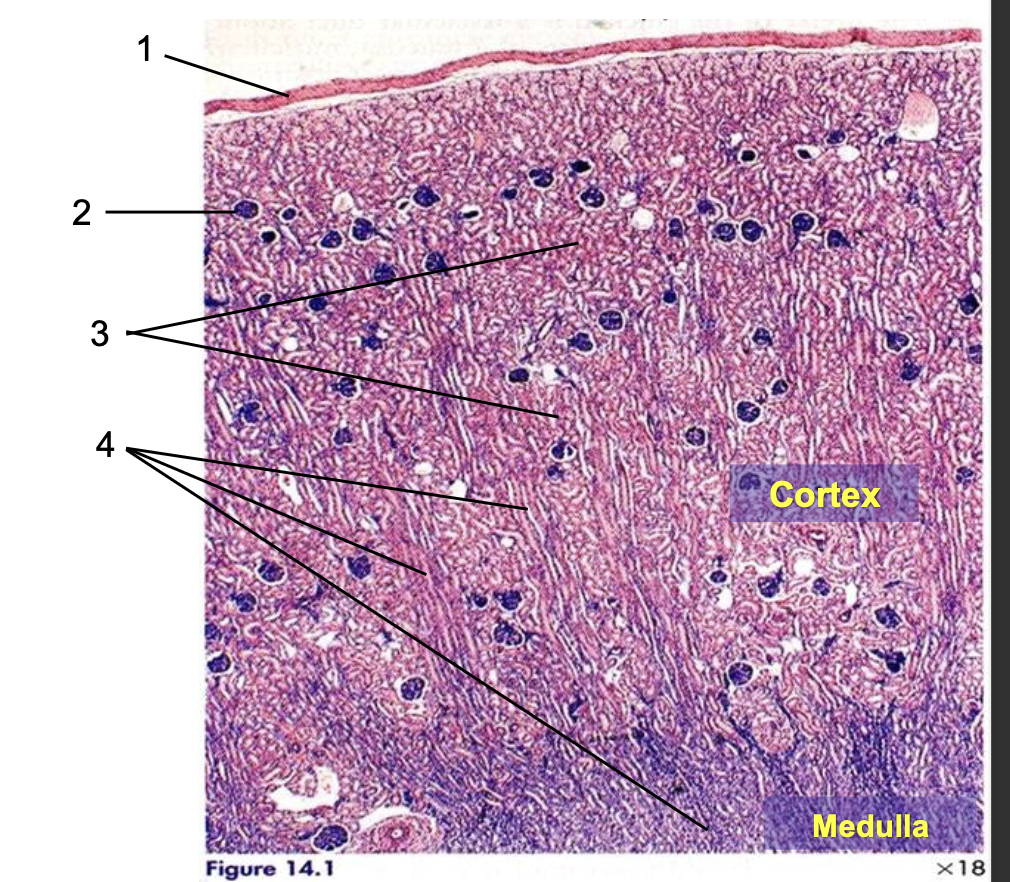
what is 1?
capsule
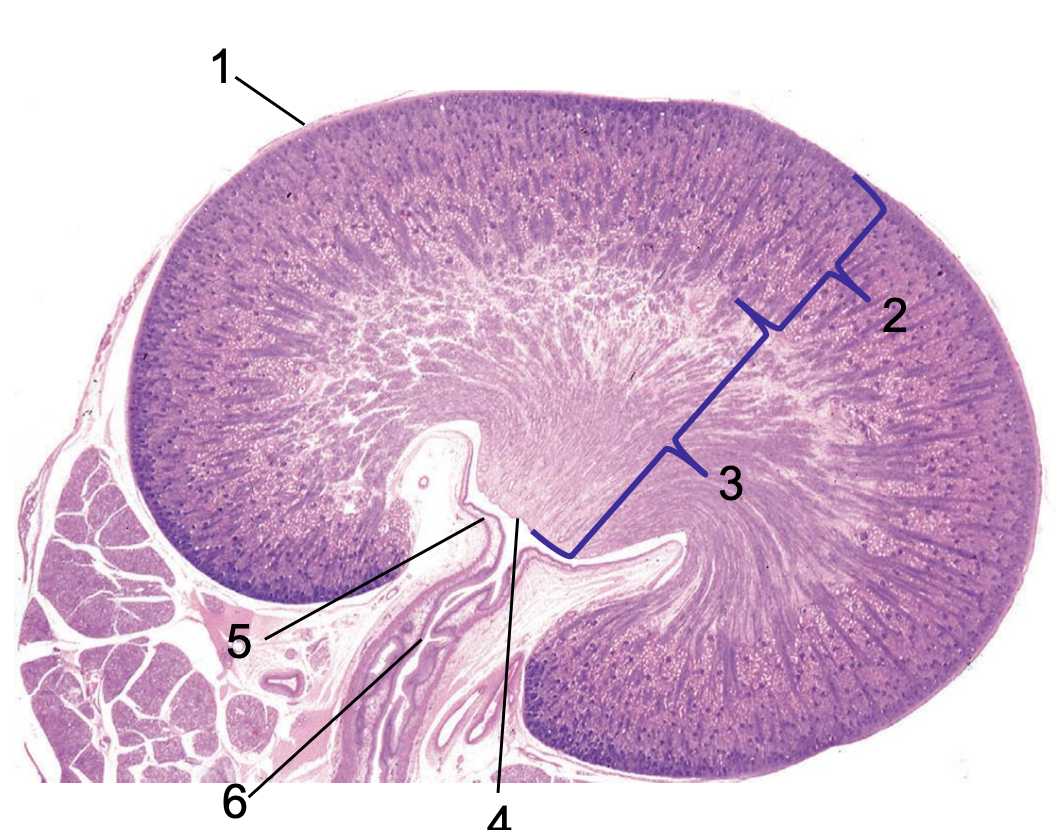
what is 2?
cortex
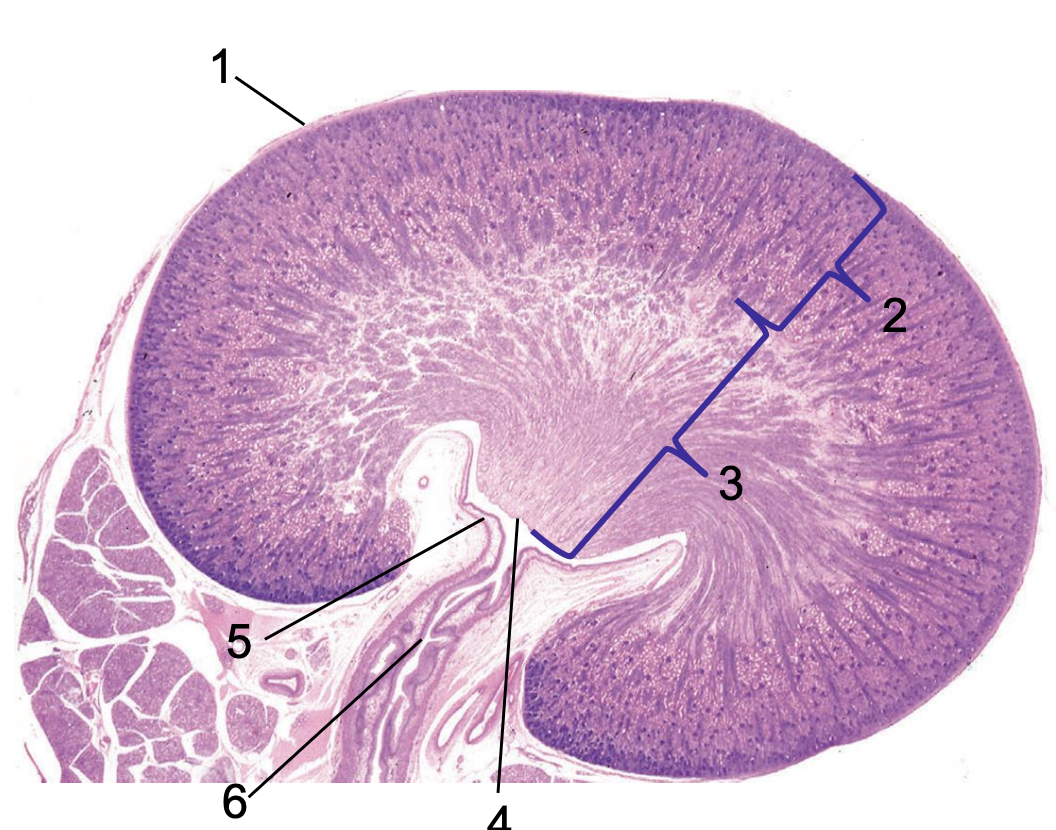
what is 3?
medulla
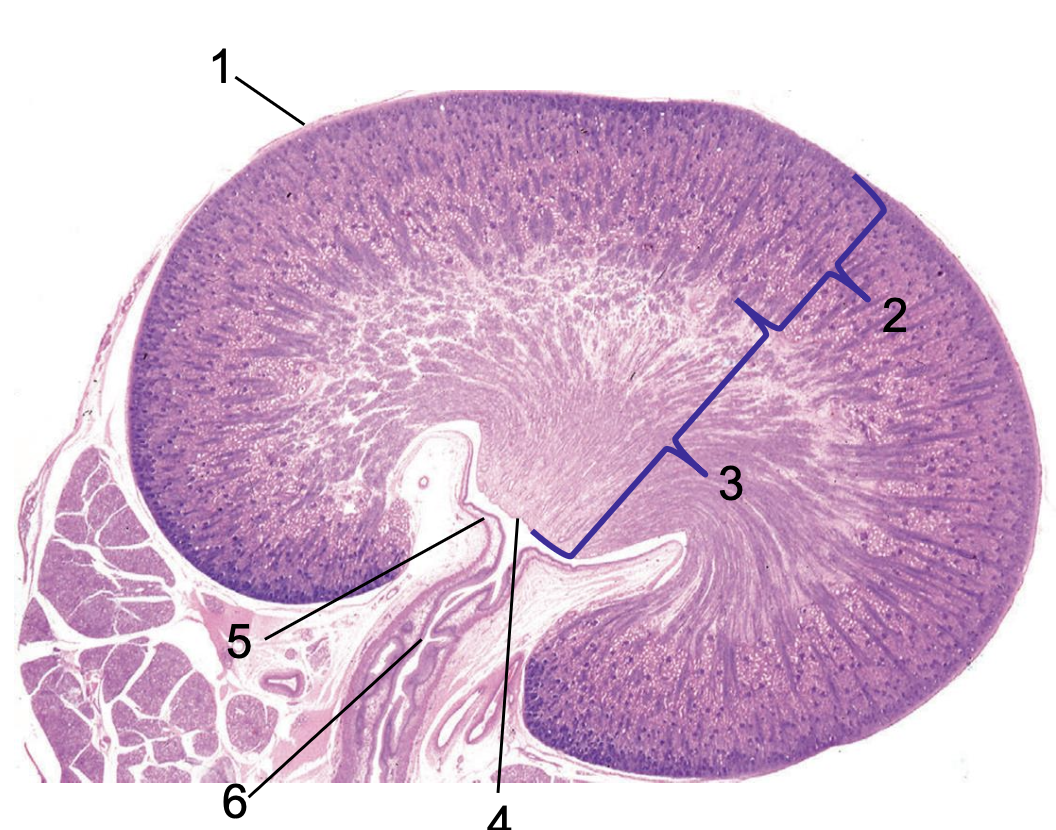
what is 4?
crest
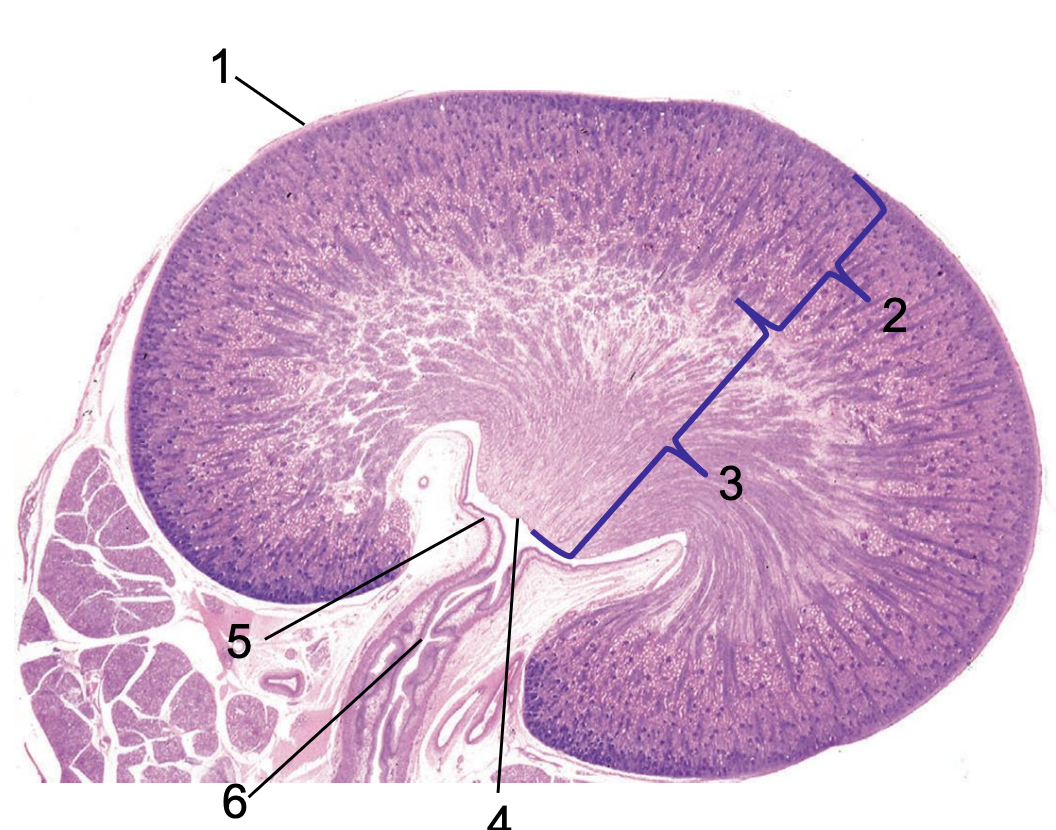
what is 5?
renal pelvis
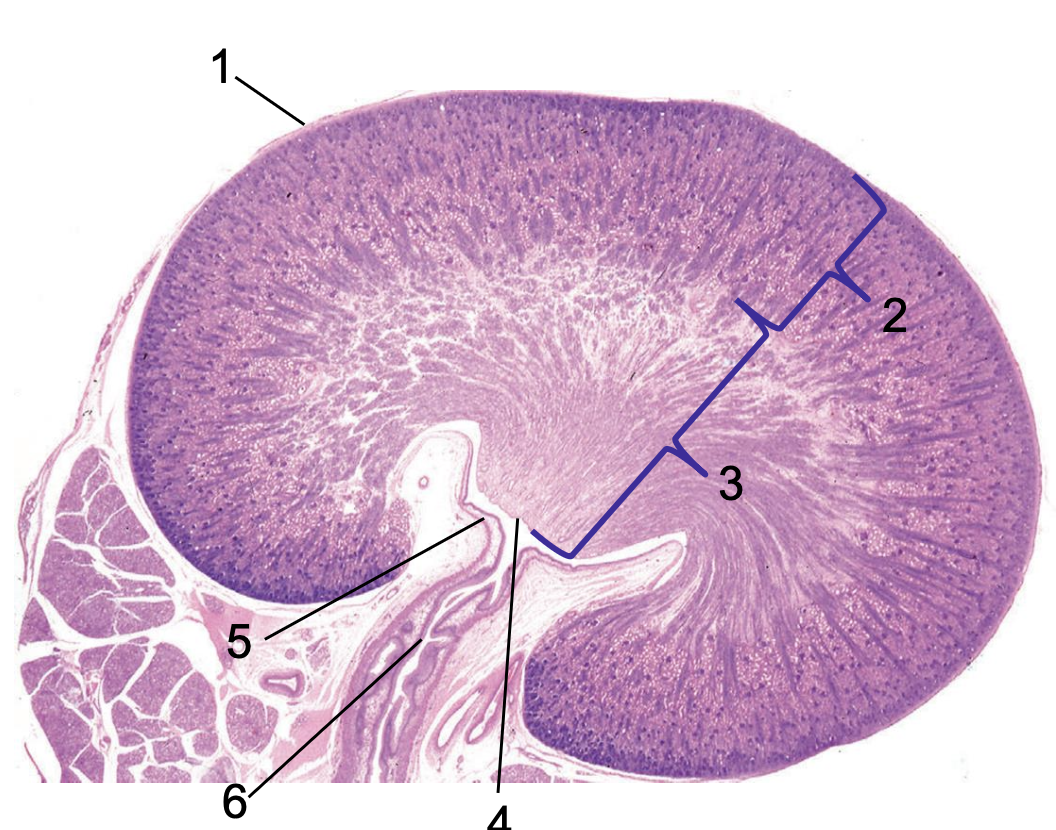
what is 6?
ureter
what components are part of the outer cortex?
renal corpuscles
pars convoluta
pars radiata
blood vessels
pars convoluta
proximal and distal convoluted tubules
pars radiata
collecting ducts that are partly in cortex and partly in medulla
what structure in the kidney is the renal corpuscles associated with?
glomerulus
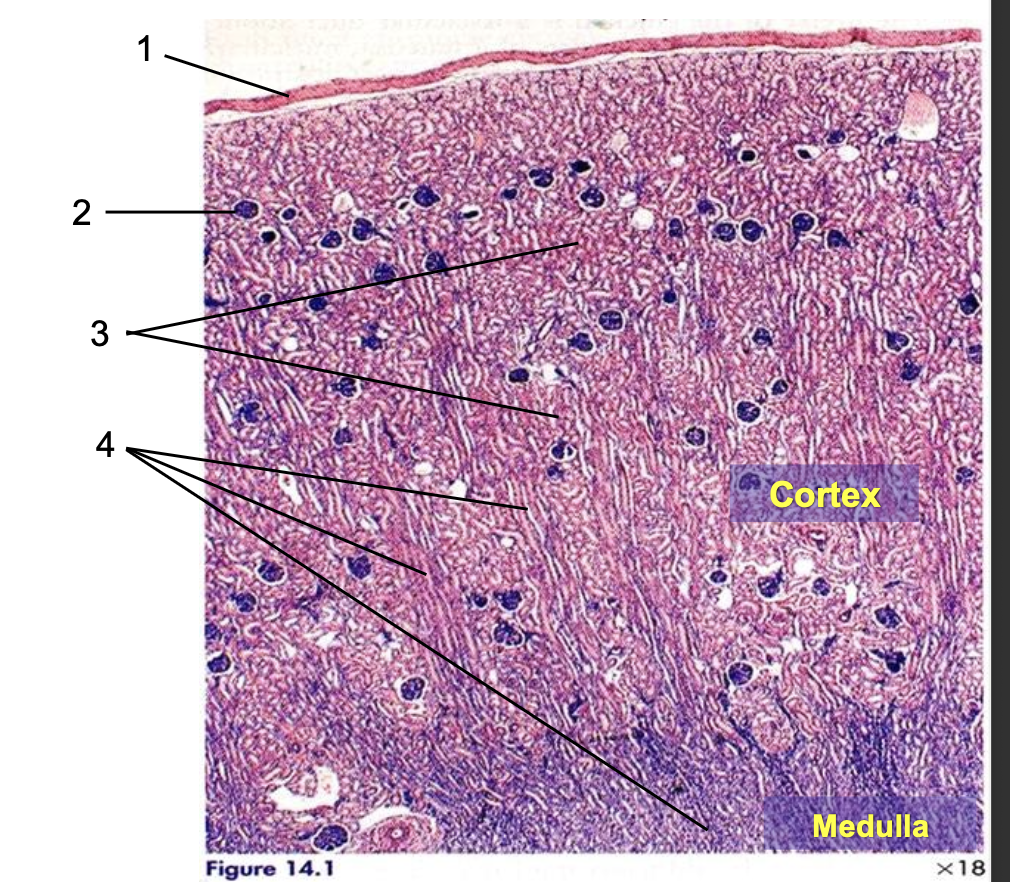
what is 1?
capsule
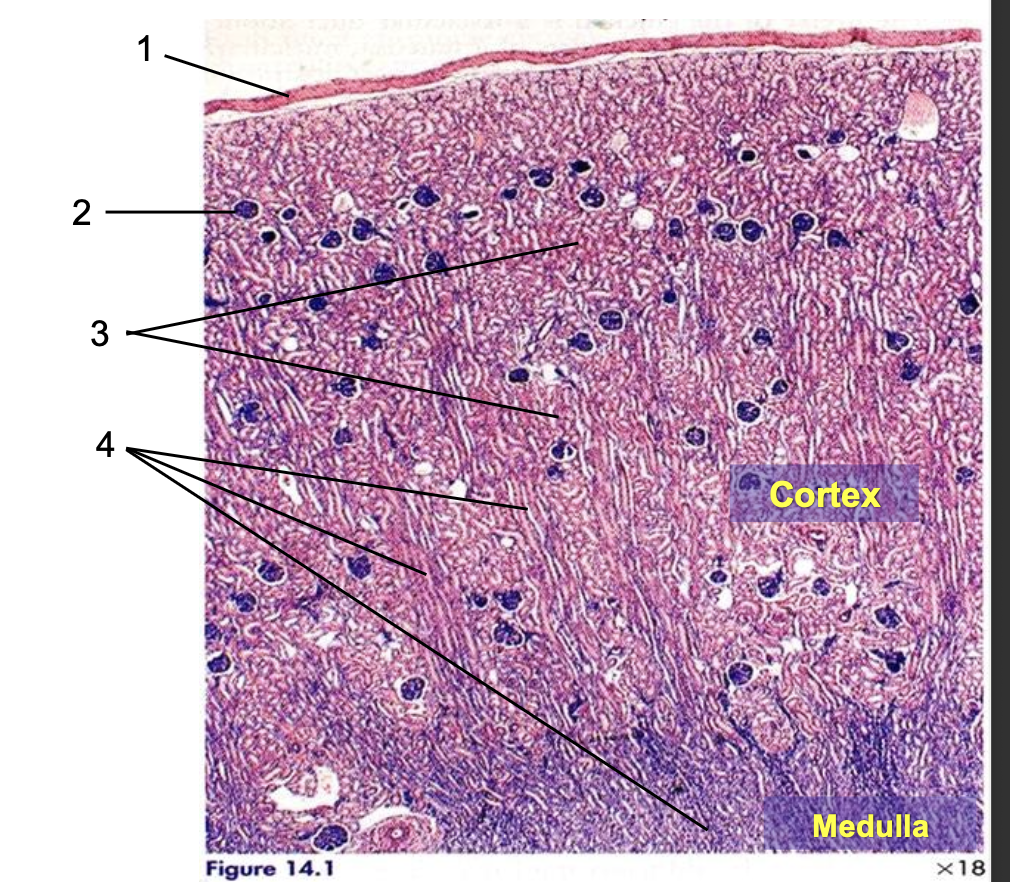
what is 2?
renal corpuscle
what is 3?
pars convoluta
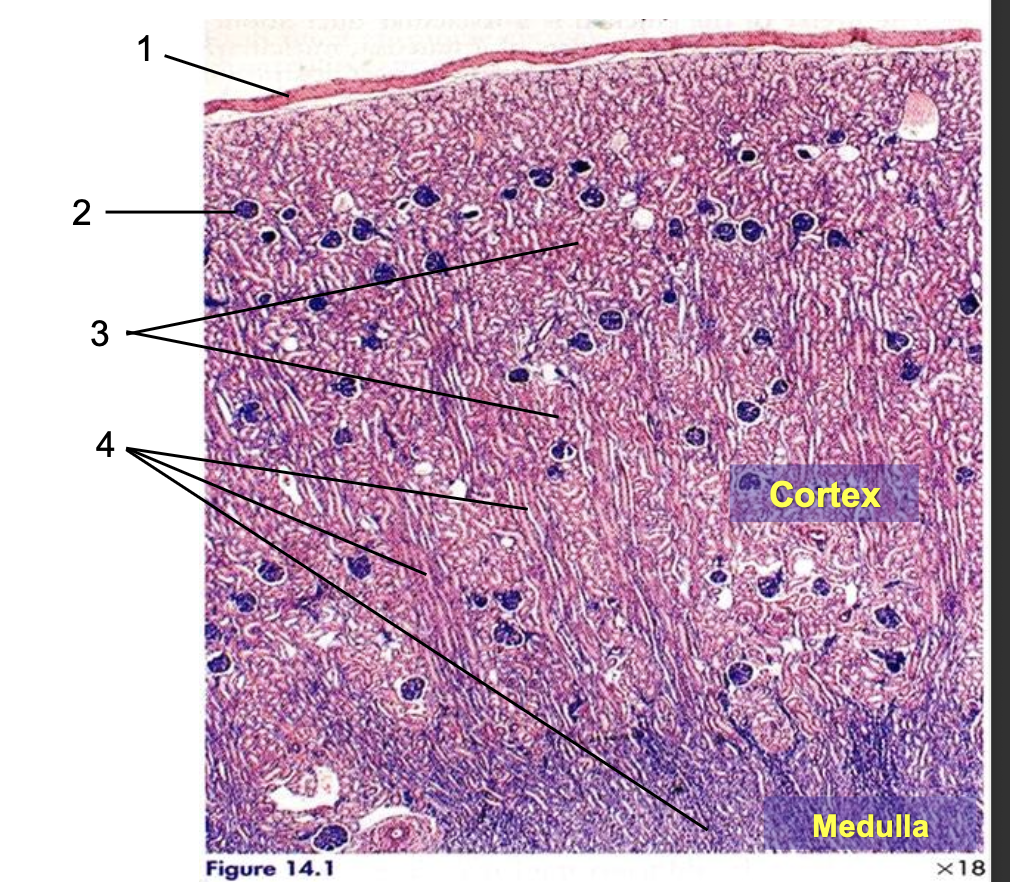
what is 4?
pars radiata
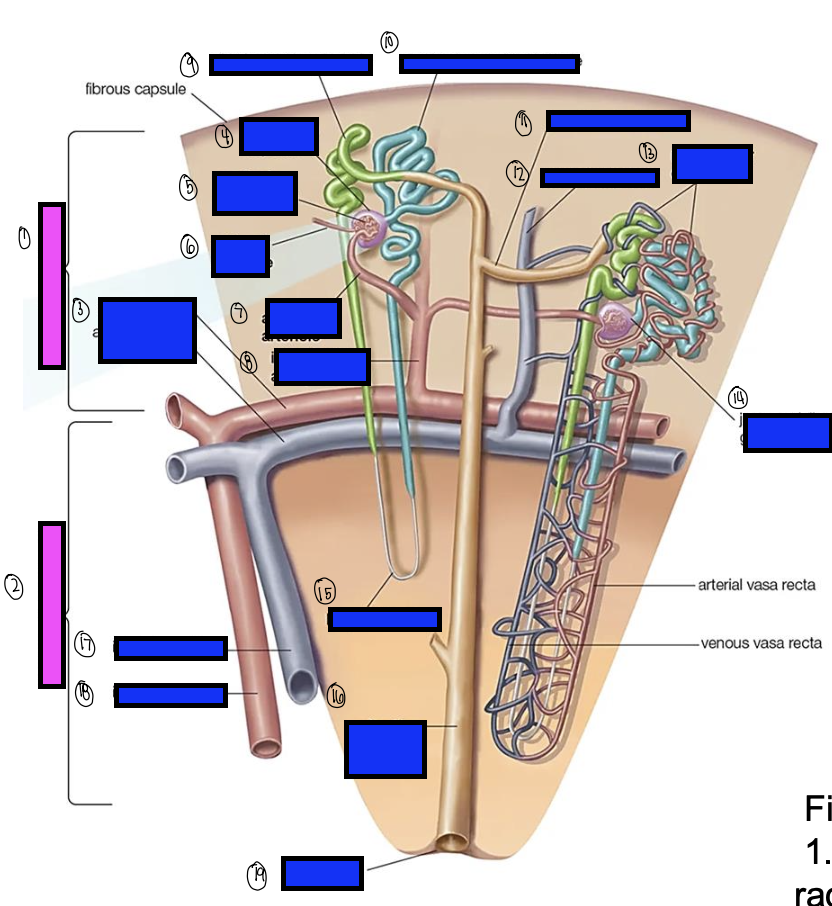
what is 1?
renal cortex
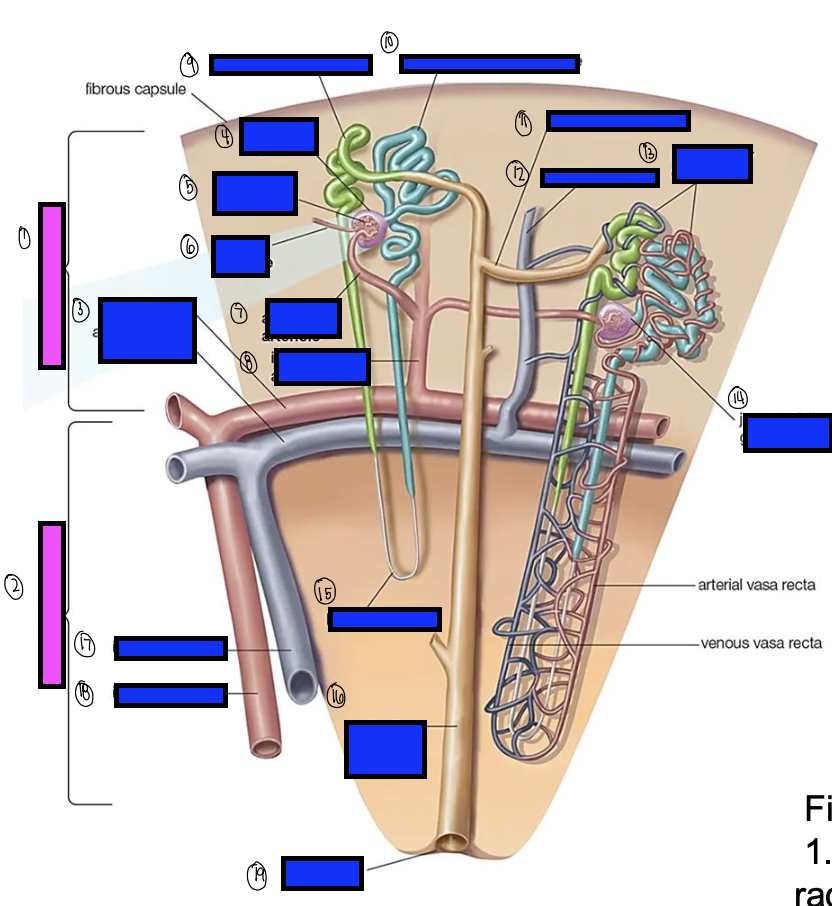
what is 2?
renal medulla
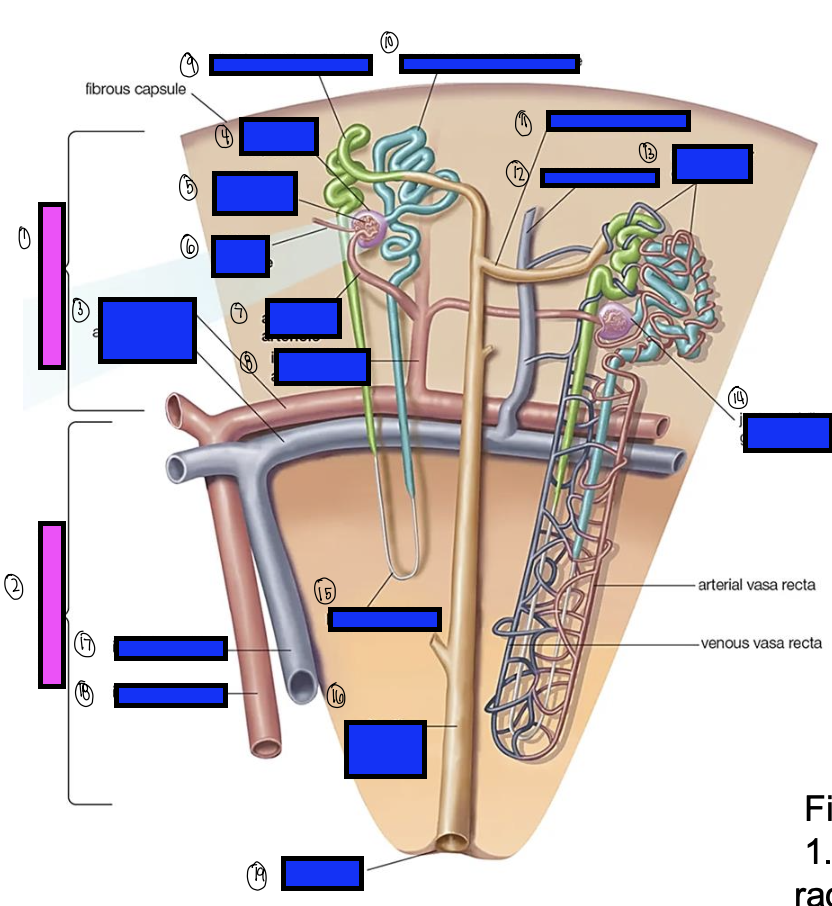
what is 3?
arcuate artery
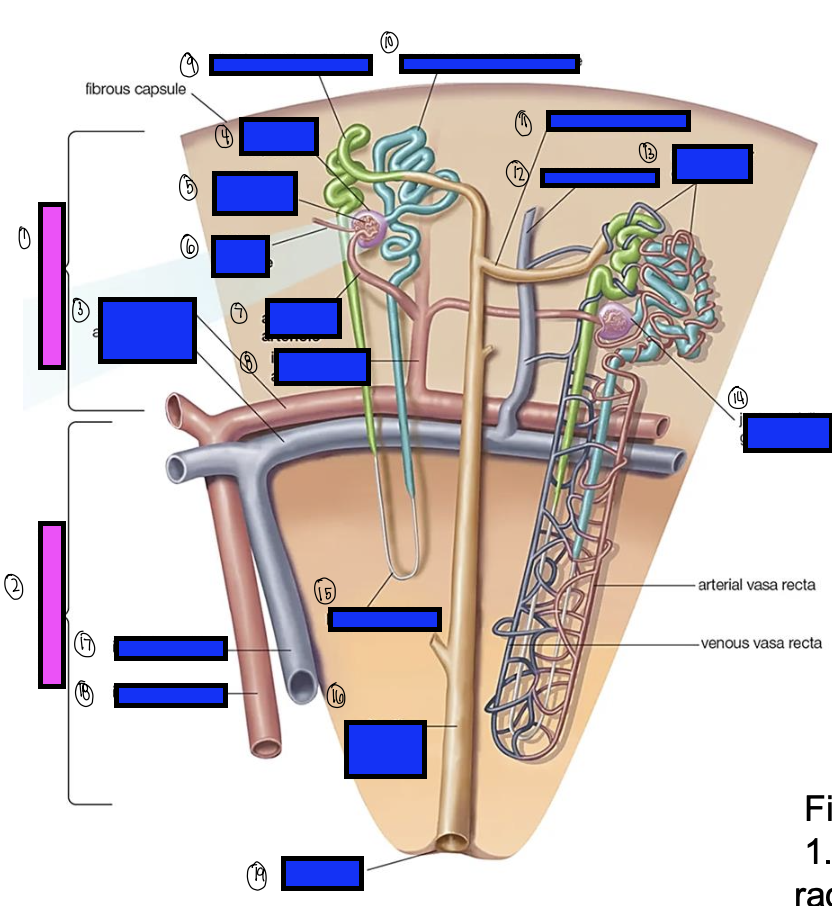
what is 4?
bowman’s capsule
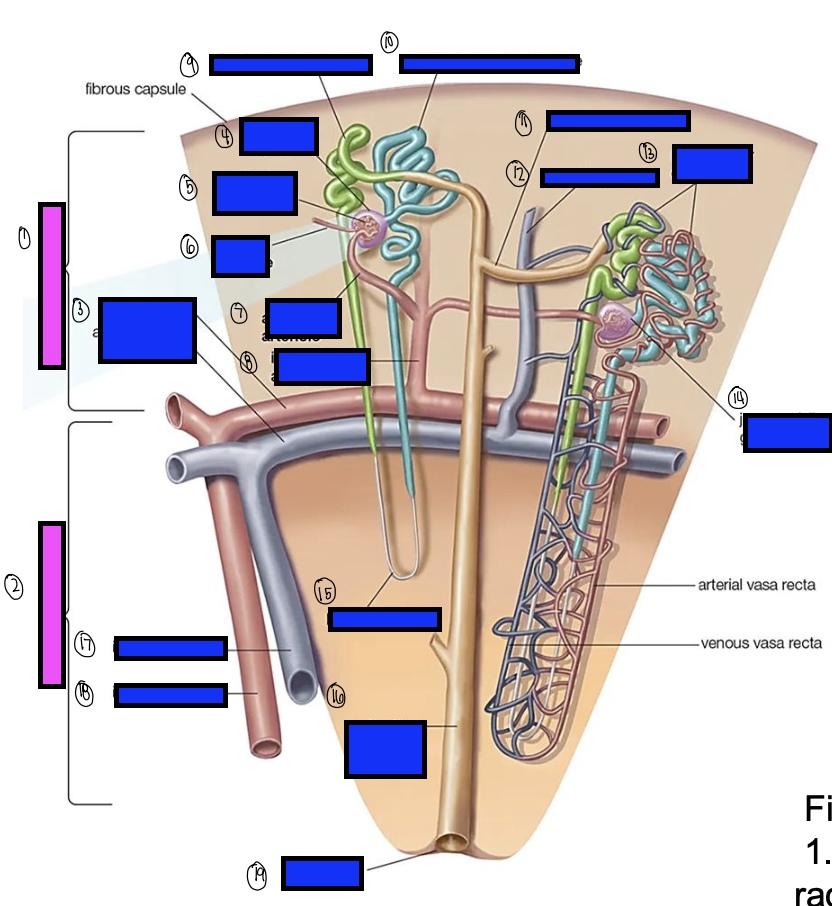
what is 5?
cortical glomerulus
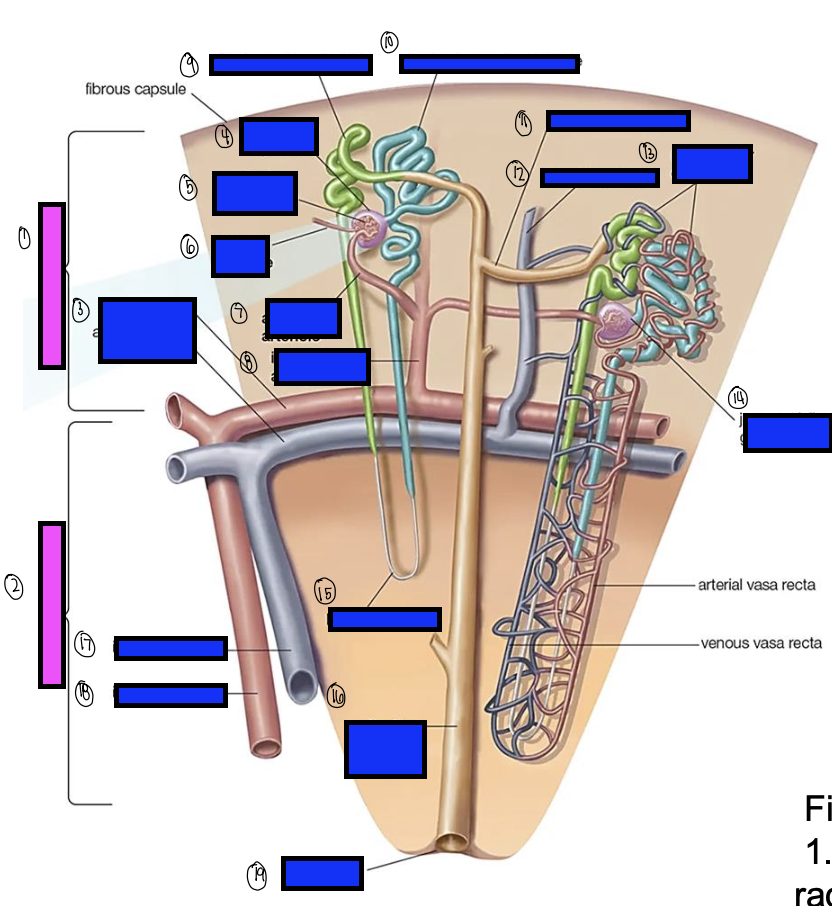
what is 6?
efferent arteriole
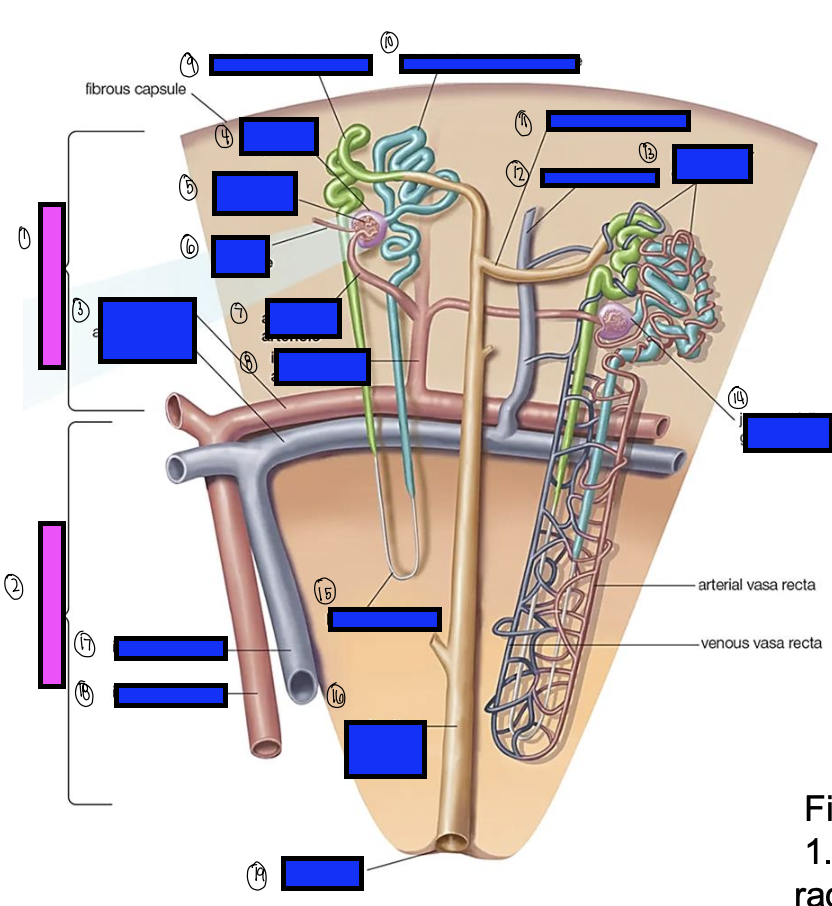
what is 7?
afferent arterioles
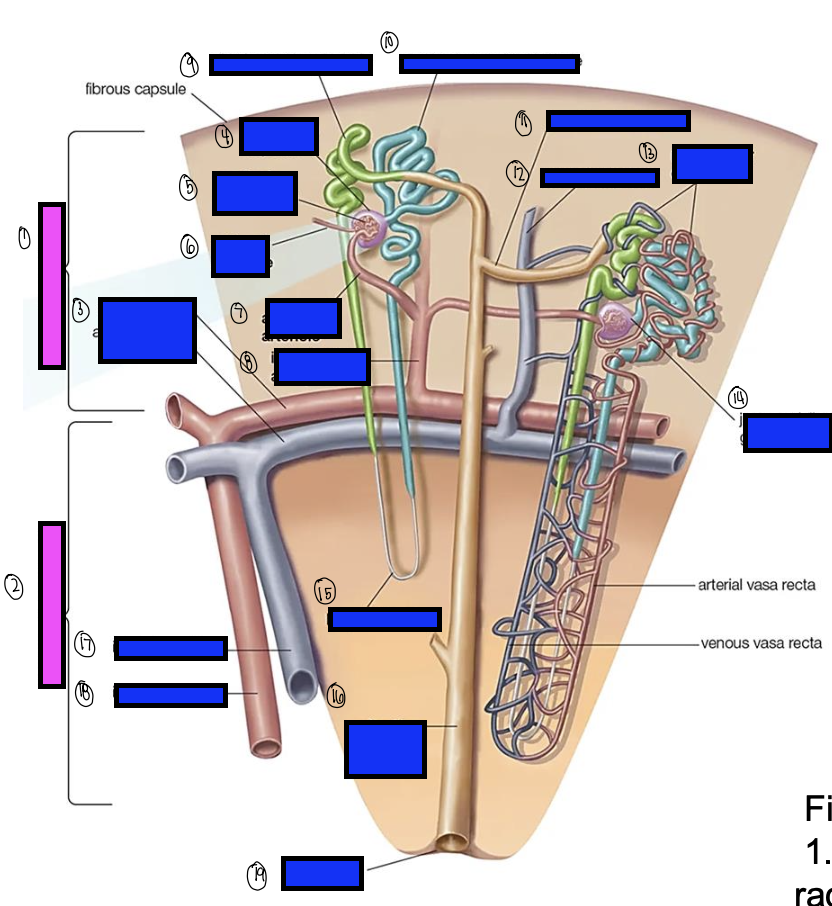
what is 8?
interlobular artery
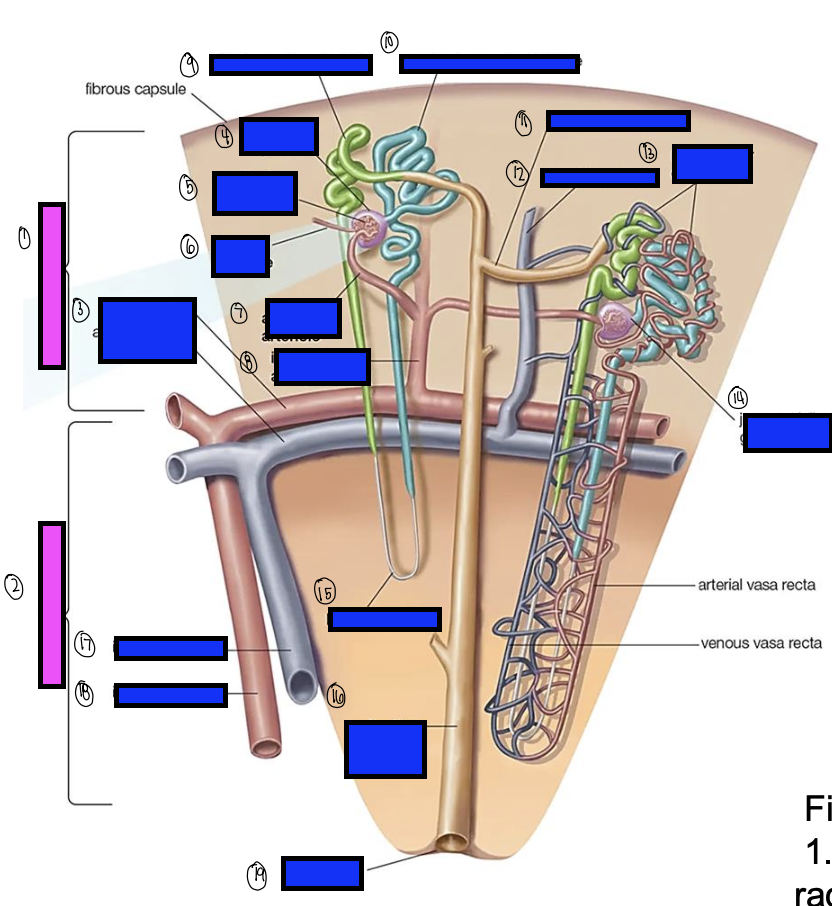
what is 9?
distal convoluted tubule
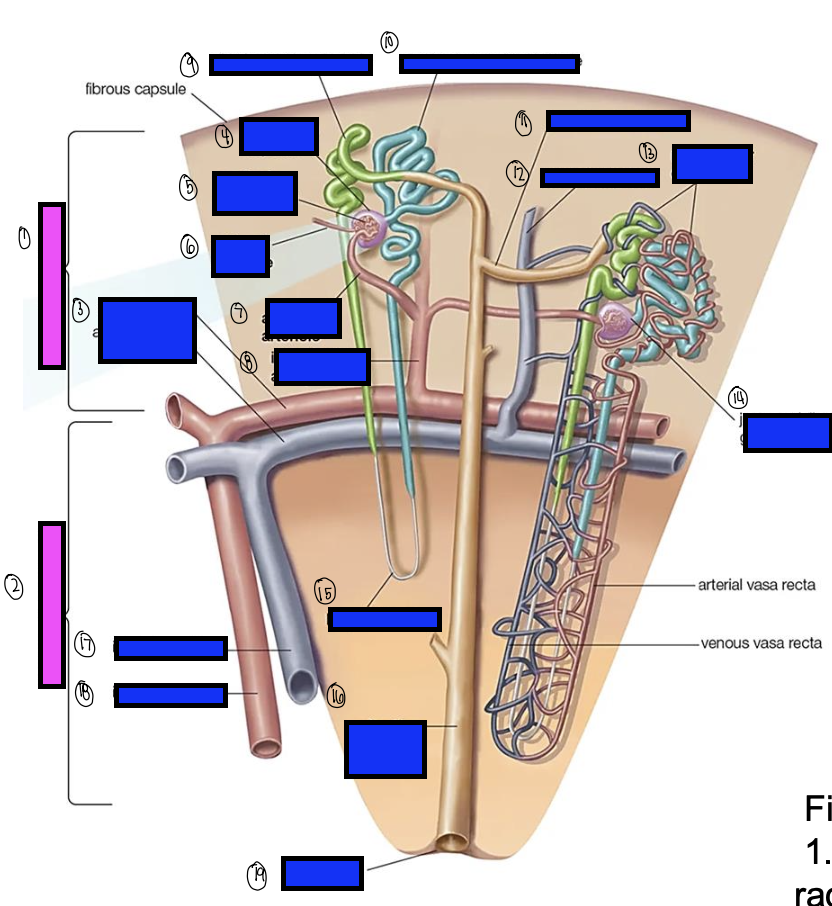
what is 10?
proximal convoluted tubule
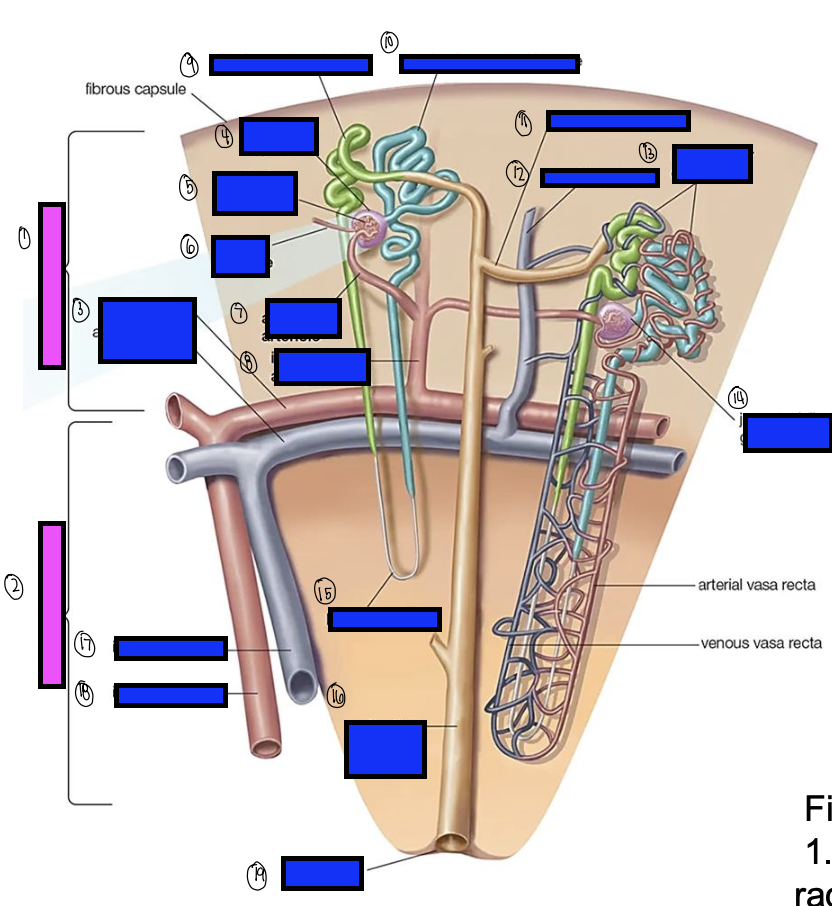
what is 11?
junctional tubule
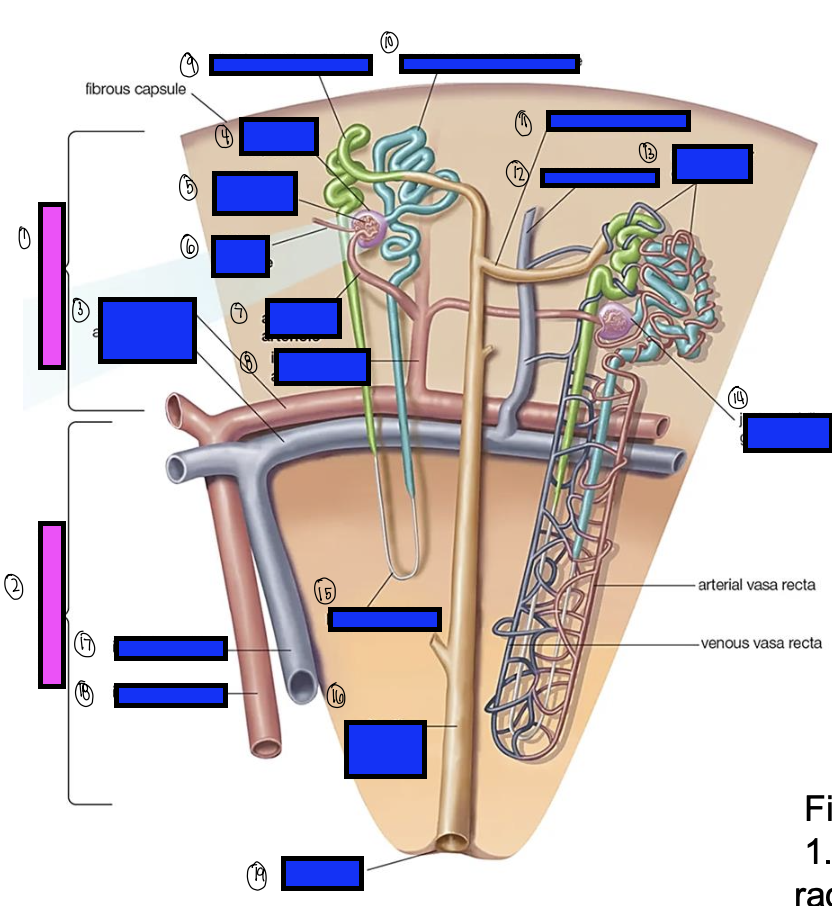
what is 12?
interlobular vein
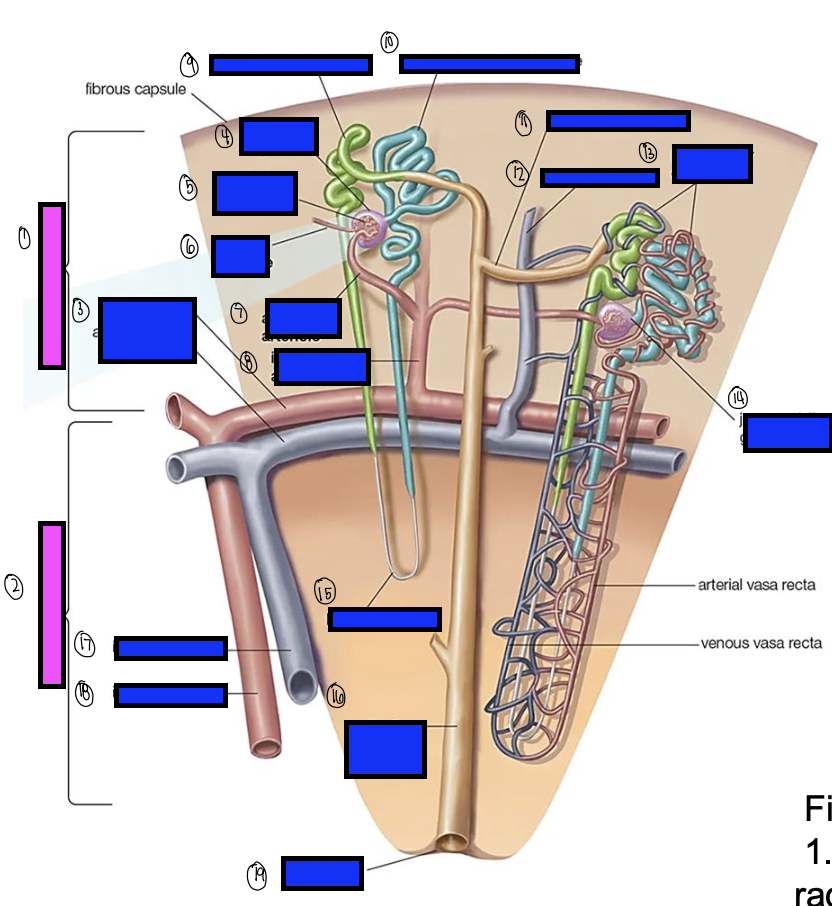
what is 13?
intertubular capillaries
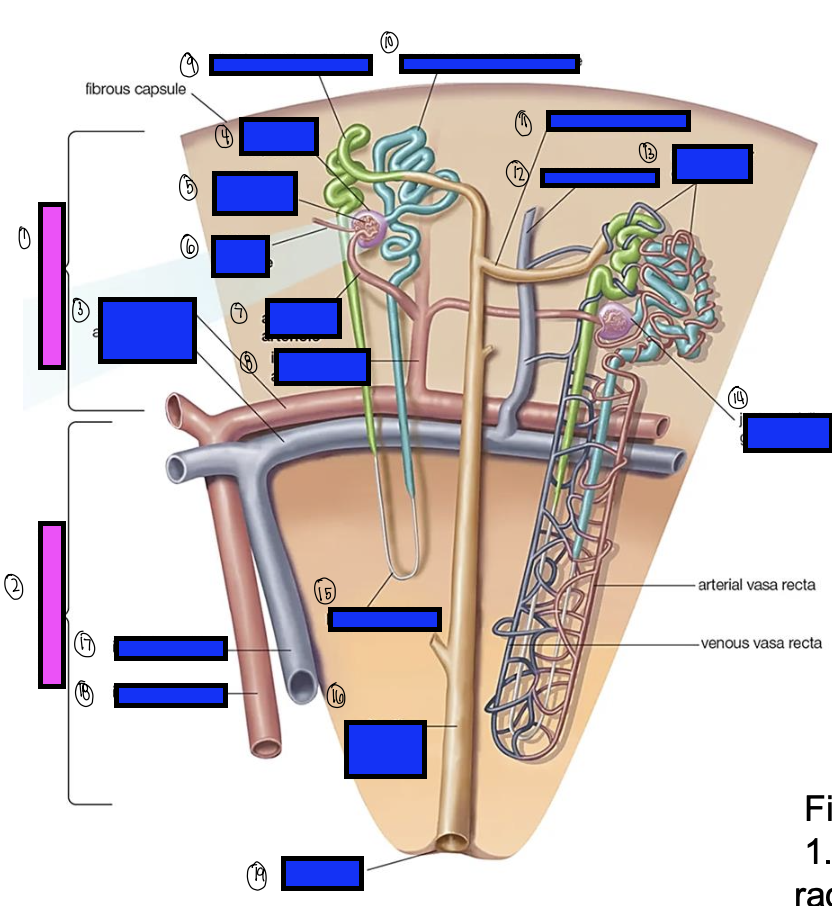
what is 14?
juxtamedullary glomerulus
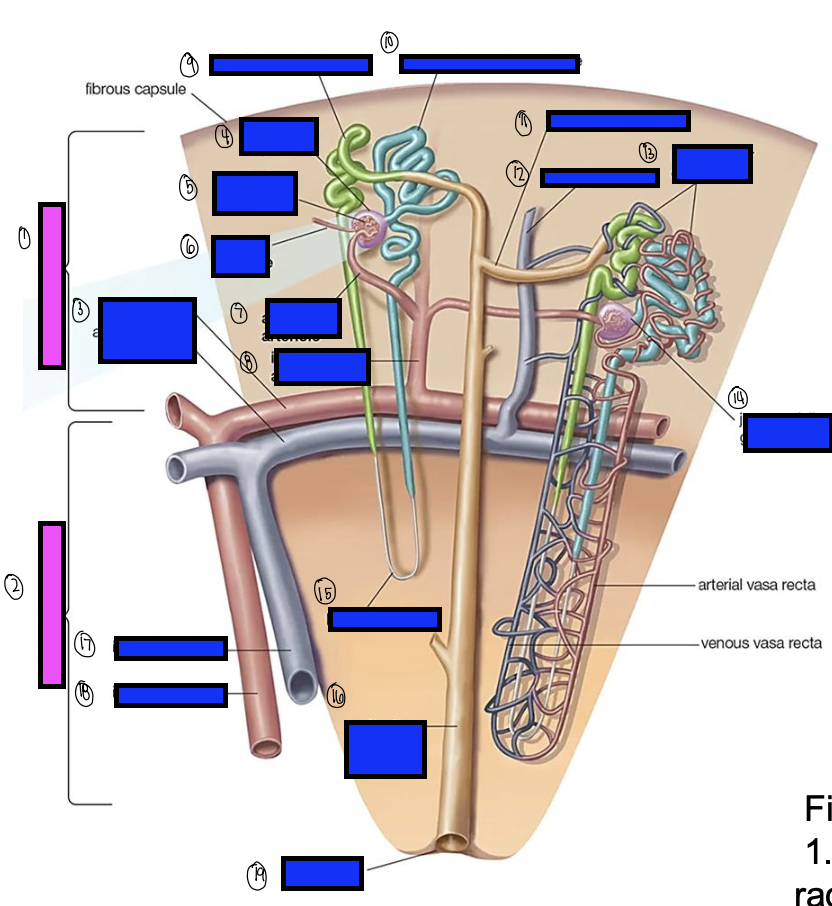
what is 15?
loop of henle
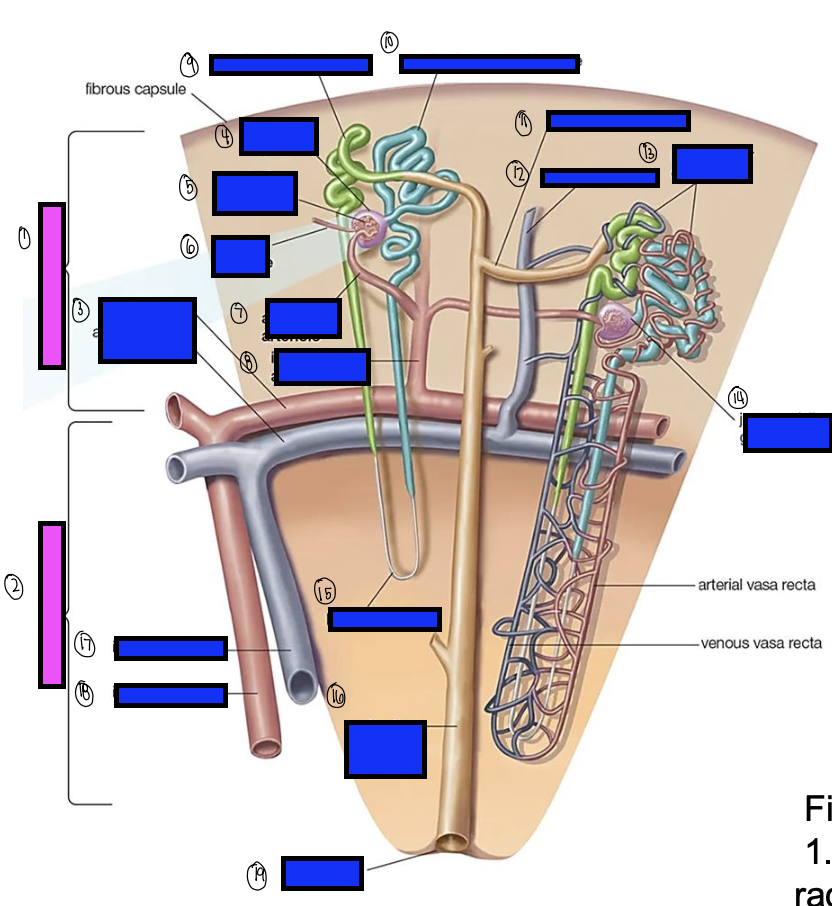
what is 16?
collecting ducts
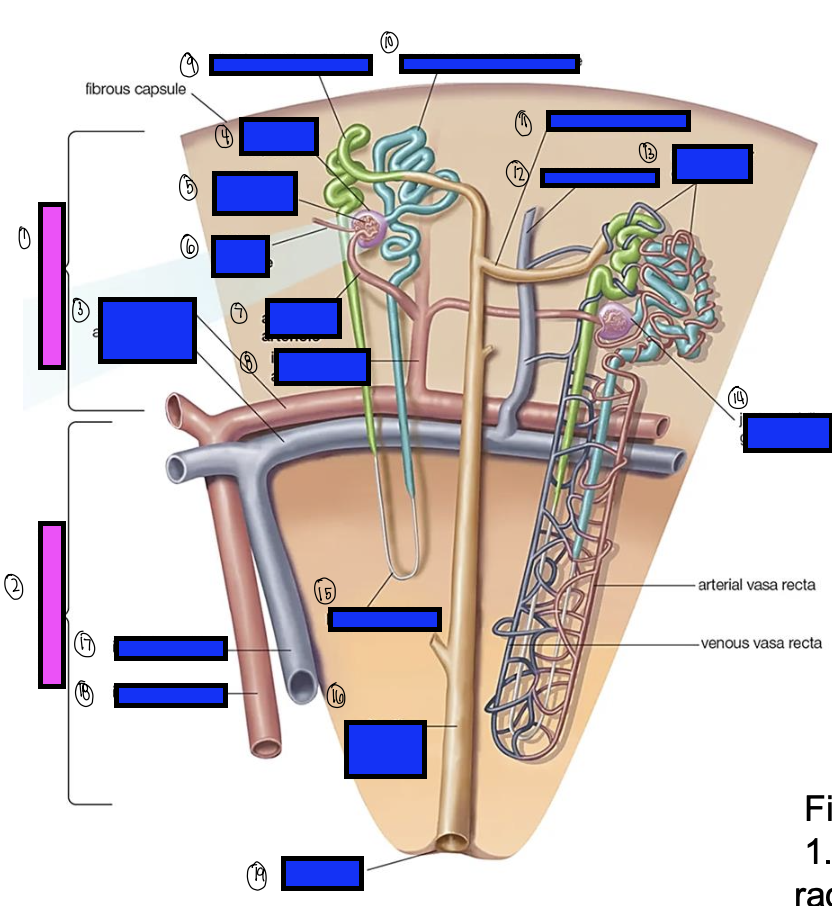
what is 17?
interlobar vein
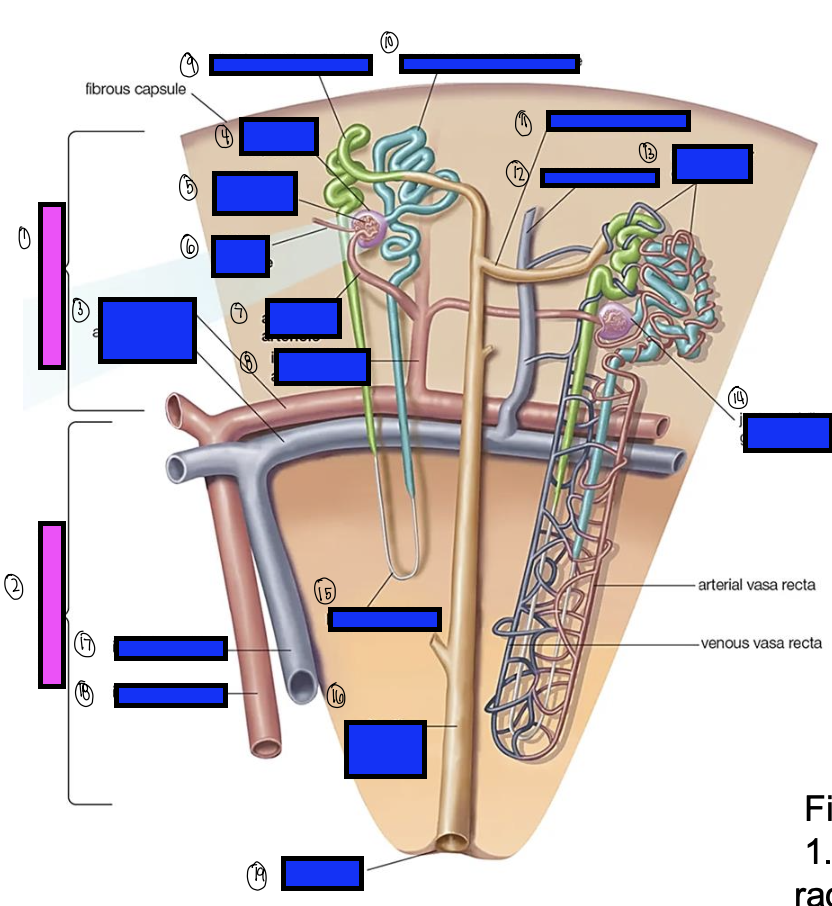
what is 18?
interlobar artery
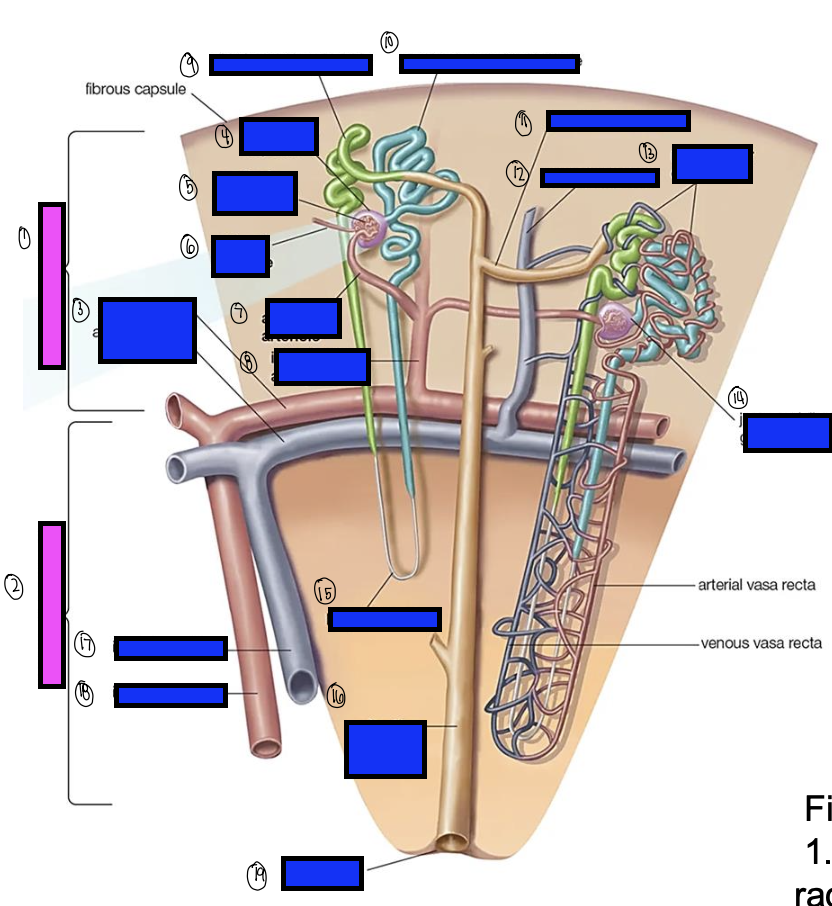
what is 19?
renal papilla
how is the proximal convoluted tubule different than the distal convoluted tubule on histology slide?
lumen not as clear because proximal has more microvilli to increase surface area for absorption
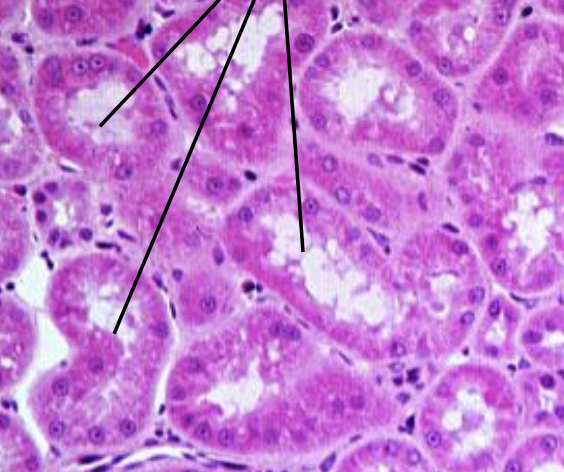
what is this histology representing?
proximal convoluted tubule
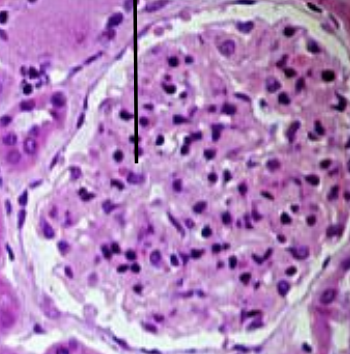
what is the black line on the histology representing?
renal corpuscle
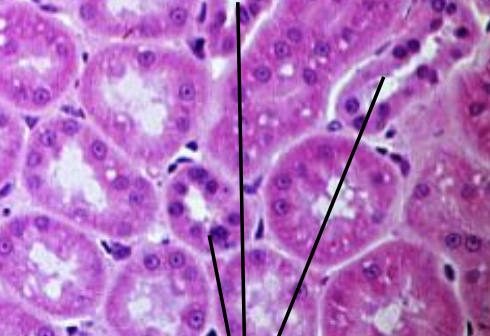
what is the histology showing?
distal convoluted tubule
what structures are located in the inner medulla?
collecting ducts
descending and ascending thin segments of loop of henle
ascending thick segmenets of loop of henle
vasa recti
peritubular capillaries
MCQ: Considering the structure of the nephron, which structure will appear only in the section through the medulla of the kidney?
thin and thick limb of the Henle’s loop
what are the components in order of the nephron?
renal corpuscle
proximal convoluted tubule
proximal straight tubue
the loop of Henle/ hairpin loop
distal convoluted tubule
collecting tubule
renal tubule
what structure is within the renal corpuscle?
glomerulus
what structures are within the loop of Henle?
thin descending limb
thin ascending limb
thick ascending limb
what is another name for the proximal straight tubule?
thick descending tubule
what is another name for the thick ascending limb?
distal straight tubule
renal tubule
nephron and collecting duct system
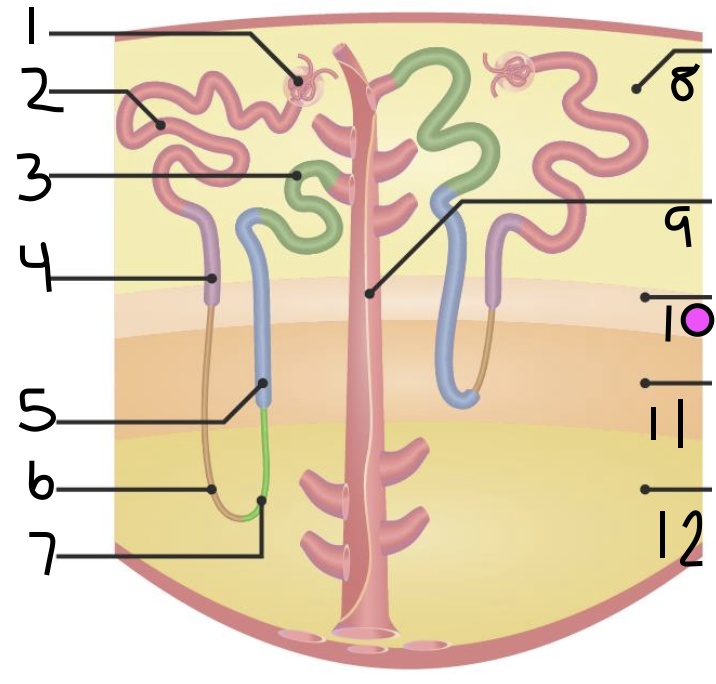
what is 1?
Bowman’s Capsule
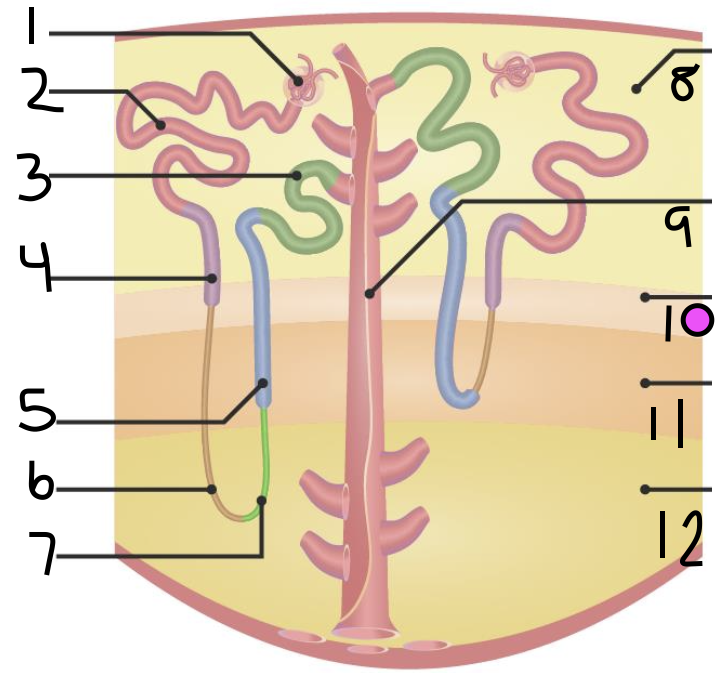
what is 2?
proximal convoluted tubule
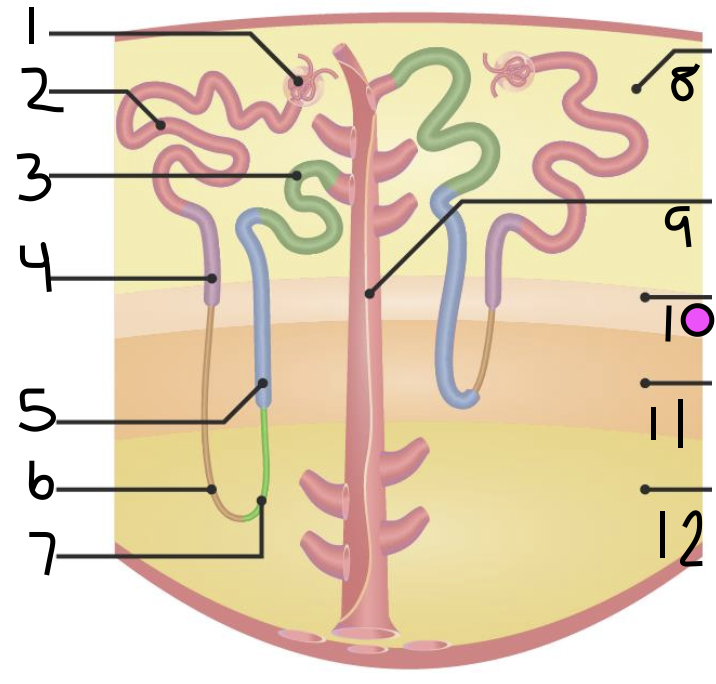
what is 3?
distal convoluted tubule
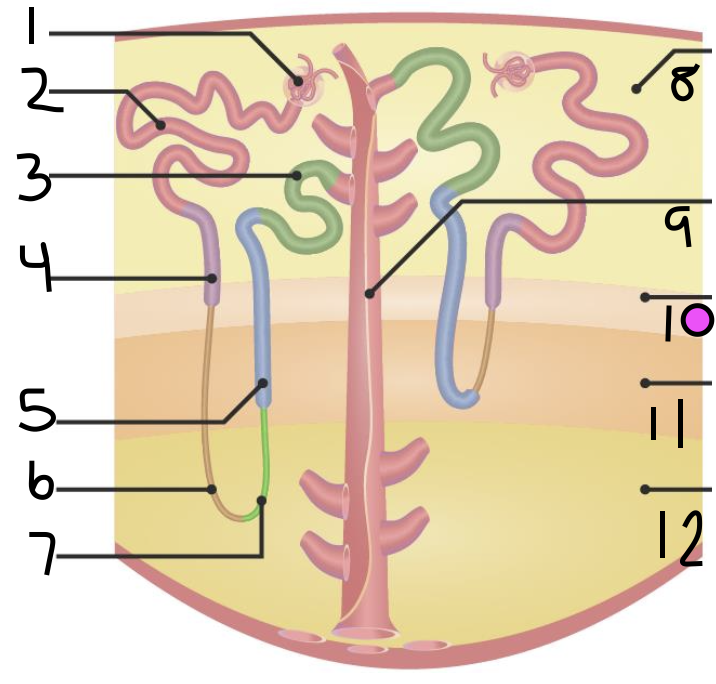
what is 4?
proximal straight tubule
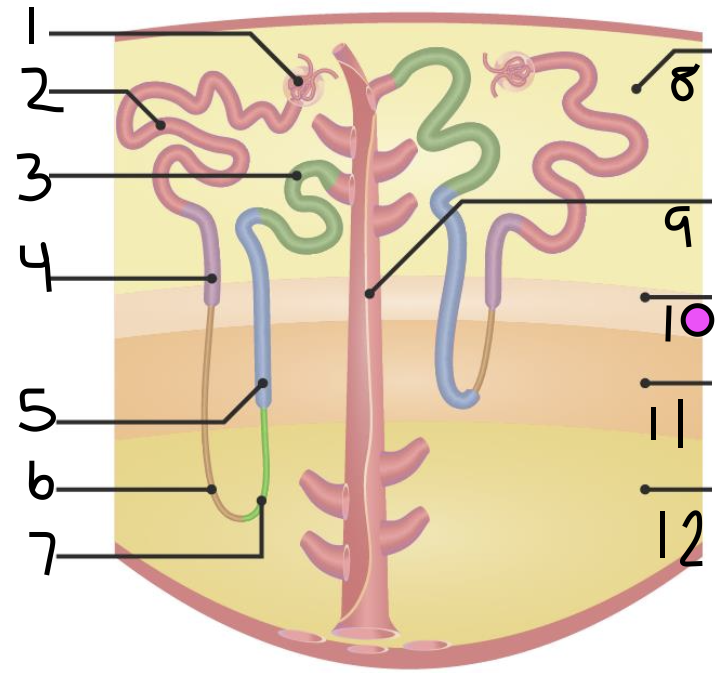
what is 5?
thick ascending limb
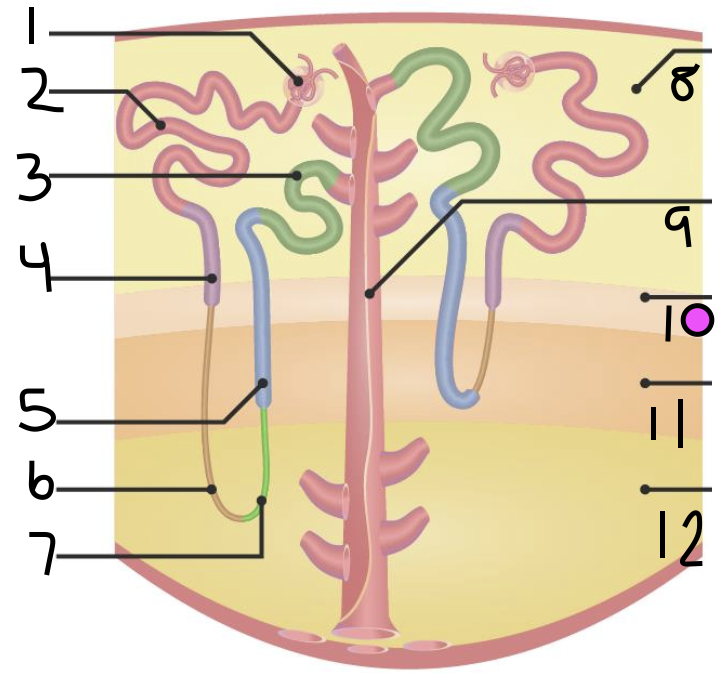
what is 6?
thin descending limb
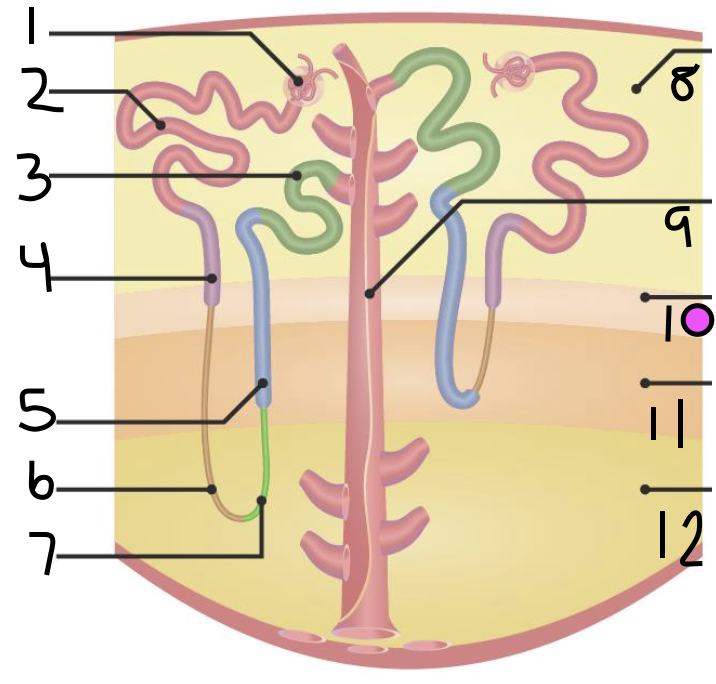
what is 7?
thin ascending limb
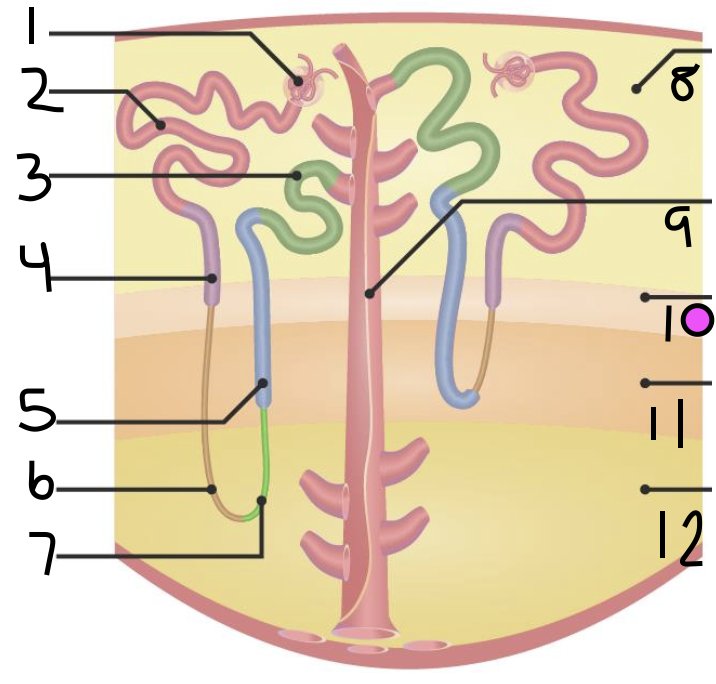
what is 8?
cortex
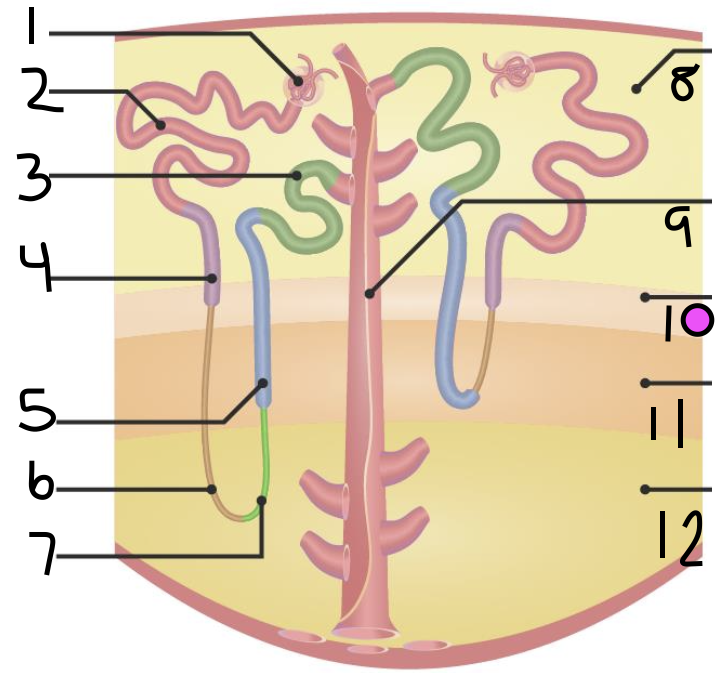
what is 11?
inner medulla
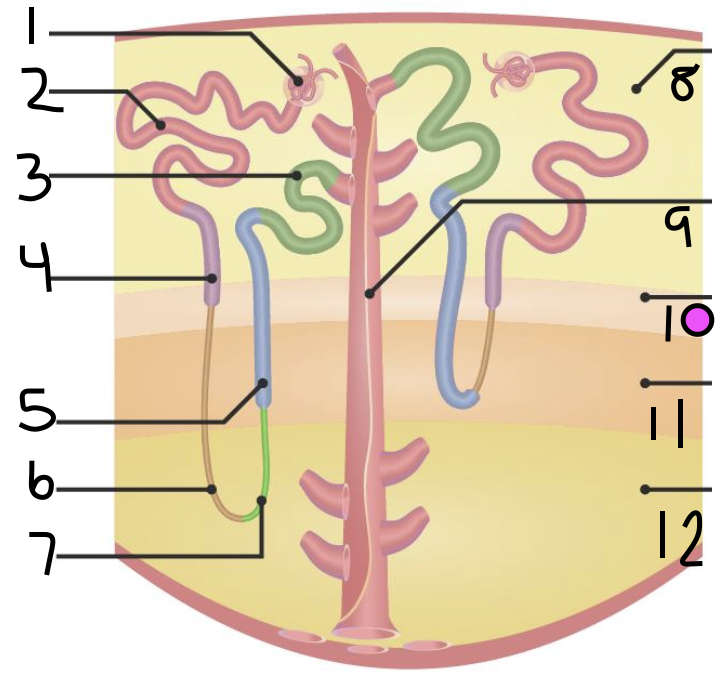
what do 9 and 10 make up?
outer medulla
what does the vasa recta capillary surround?
loop of henle
efferent arterioles
branch away from the glomerulus to form secondary circulation component surrounding the nephron
afferent arterioles
only enter renal corpsucles to form glomerulus
in order list the microcirculation of the kidney.
interlobar arteries and veins
arcuate arteries
interlobar arteries
afferent arterioles
glomerulus
efferent arteriole
peritubular capillairies
vasa recti
venules
interlobar / arcuate veins
the efferent arteriole only supplies what part of the kidney?
only supplies to medulla from peritubular network
MCQ: what structure makes up the peritubular capillary network?
efferent arteriole
glomerulus
the tuft of the capillaries responsible for filtration of blood
bowman’s space
space between the visceral and parietal layers of Bowman’s capsule
what makes up the parietal layer of bowman’s capsule?
simple squamous epithelium
what makes up the visceral layer of bowman’s capsule?
podocytes
what is another name for bowman’s capsule
urinary space
where is pre-urine filtrate collected?
bowman’s space
what structures make up the renal corpuscles of the kidney?
glomerulus
bowman’s capsule
where does the urinary pole of bowman’s capsule continue to?
proximal convoluted tubule of nephron
what poles are in bowman’s capsule?
vascular pole
urinary poles
what is the function of the glomerulus?
filtration of the blood
what does it mean when we say “the glomerulus will have 20% filtrate of blood”?
approximately 20% of the plasma that flows into the glomerular capillaries via the afferent arteriole is filtered into Bowman’s space
how many liters of blood is circulated to produce 1 liter of urine?
100
what is in filtrate?
water
glucose
nutrients
bicarbonates
urea
creatine
small proteins
amino acids
what lines the renal calices and pelvis?
transitional epithelium and loose connective tissue
what is present under the epithelium of calices and pelvis in horses and what does this do to the urine of the horse?
mucus glands
have cloudy urine (mucus)
what are smaller collecting ducts lined by?
simple cubodial and lateral borders are clear
what is the larger collecting duct lined by?
simple columnar
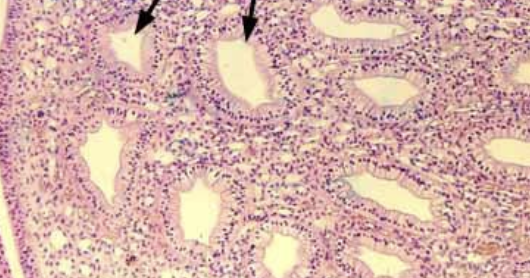
what are the large white spots in the histology?
collecting ducts
what lines the papillary duct?
2 layered epithelium
later becomes transitional
what are macula densa sensitive to?
chloride ions
what is the function of the macula densa?
regulate the filtration rate
juxtaglomerular apparatus
formed by the contact of the distal tubule and afferent tubule
where are macula densa located?
in distal tubules of juxtaglomerular apparatus
what cells are present in macula densa?
modified cubodial to columnar cells
where are juxtaglomerular cells located?
afferent arteriole of juxtaglomerular apparatus
what cells are present in juxtaglomerular cells?
modified smooth muscles
what cells make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
macula densa
juxtaglomerular cells
extraglomerular mesangial cells
what is the function of juxtaglomerular cells?
produce renin