Memorizables 1 Formulas
1/70
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Net Force
Fnet = ma
Fnet= net force
m=mass
a=acceleration
Gravitational Force on Earth
Fg=mg
Fg=gravitational force on earth
m=mass
g=gravitational acceleration
Gravitational Force in General
FG=Gm1m2/r2
FG=Gravitational Force
G=gravitational constant
m1,m2=masses
r=distance between centers of masses
Electric Force (charged object into electric field)
FE=qE
FE=Electrical Force
q=charge on object
E=electrical field
Electric Force (between two points of charge)
FE=kq1q2/r2
FE=Electric Force
k=electric force constant
q1,q2=charges on objects
r=distance between the centers of the objects
Electric Field Formula
E=kQ/r²
E=electric field
k=electric force constant
Q=charge
r=distance from charge
Spring Force Formula
F=kx
F=spring force
k=spring constant
x=amount stretched/compressed
(Max) Static Friction Formula
Fs,max=μsFN
Fs,max=max static friction force
μs=static friction coefficient
FN=Normal Force
Kinetic Friction Formula
Fk=μkFN
Fk=Force of Kinetic friction
μk=kinetic friction coefficient
FN=Normal Force
Buoyant Force Formula
Fb=ρVg
Fb=Buoyant Force
V=volume submerged
g=gravitational acceleration
Magnetic Force Formula
Fm=qvBsin(θ)
Fm=Magnetic Force
q=charge
v=velocity
B=strength of magnetic field
θ=angle between direction of velocity and direction of magnetic field
Torque Formula
T=rFsin(θ)
T=Torque (N*m)
r=distance from point that force is applied to pivot point of object rotating about
F=Force causing object to rotate
θ=angle between direction of the force and the line connecting the point the force is acting on to the pivot point of rotation
Net Force on Inclined Plane
Fnet=mgsin(θ)
Fnet= Net Force
m=mass
g=gravitational acceleration
θ=angle inclined plane makes with ground
Normal Force on Inclined Plane
FN=mgcos(θ)
FN=Normal Force
m=mass
g=gravitational acceleration
θ=angle inclined plane makes with ground
Acceleration Formula
a=Δv/t
a=acceleration
Δv=change in velocity
t=time
Simple Distance Formula
d=vt
Three General Motion/Projectile Formulas
vf=v0+at
vf2=v02+2ad
d=v0t+(1/2)at²
Gravitational Acceleration Formula (surface of planet)
g=GM/r²
g=gravitational acceleration (on surface of planet)
G=universal gravitational constant
M=mass of planet
r=radius of planet
Kinetic Energy Formula
KE=1/2mv²
KE - joules (J)
General Work Formula
W=Fdcos(θ)
W=Work
F=Force
d=distance force applied
θ=angle between direction of the force and the direction of the velocity of the object
Net Work Formula
Wnet=Fnetdcos(θ)
Wnet=Net Work
Fnet=Net Force
d=distance force applied
θ=angle between direction of the force and the direction of the velocity of the object
Gravitational Potential Energy (close to Earth’s surface)
UG=mgh
UG=Gravitational Potential Energy
m=mass
g=gravitational acceleration
h=height of mass
Spring Potential Energy
Uspr=1/2*kx²
Uspr=Spring Potential Energy
k=spring constant
x=amount spring stretched/compressed
Electrical Potential Energy Formula (1 point charge)
UE=qV
UE=electrical potential energy
q=charge
V=voltage
Change in Electrical Potential Energy Formula
ΔUE=qEd
ΔUE=change in electrical potential energy of object
q=charge
E=strength of constant electrical field
d=distance object “falls”
Change in Voltage formula
ΔV=Ed
ΔV=change in voltage
E=strength of electric field
d=distance the object moves through
Voltage Formula (single point charge)
V=kQ/r
V=voltage
k=electrical constant
Q=charge
r=distance from center of charge
Electrical Potential Energy Formula (2 point charges)
UE=kq1q2/r
UE=Electrical potential energy
k=electrical constant
q1,q2=charges
r=distance between centers
Energy of Photon Formula
Ep=hf
Ep=energy of photon
h=planck’s constant
f=frequency
Thermal Energy of Friction (kinetic) Formula
Ef= -Fkd
Ef=energy lost by object to heat of friction
Fk=force of kinetic friction
d=distance object travels
General Power Formula (w/o constant velocity)
P=ΔE/t
P=power
ΔE=energy transferred
t=time
General Power Formula 2 (constant velocity)
P=Fv
P=power
F=force
v=velocity
Wave Velocity Formula
vw=λf
vw=wave velocity
λ=wavelength
f=frequency
Period of Cycle Formula
T=1/f
T= time period required to complete one cycle
f=frequency
Intensity of Wave Formula 1 (simple)
I=P/A
I=intensity
P=power
A=area
Intensity of Wave Formula 2 (harder one, uses distance)
I1r1²=I2r2²
I1,I2=intensity at 1,2 location
r1,r2=distance from source at 1,2 location
*inverse square law
Decibels Formula
10log(I/I0)
I=intensity being studied
I0=reference intensity which is = to lowest intensity human hears can detect
Beat Frequency Formula
fbeat=f1-f2
fbeat= beat frequency
f1=frequency of first wave
f2=frequency of second wave
*beat frequency produced when two similar frequencies interfere producing 3rd frequency
*cant be negative
General Angular Frequency Formula
ω=2πf
ω=angular frequency
f=regular frequency
Doppler Effect Formula for frequency
fd=fs(vw±vd)/(vw±vs)
fd=frequency detected
fs=frequency emitted from source
vw=velocity of wave
vd=velocity of detector
Oscillating Spring Angular Frequency Formula
ω=sqrt(k/m)
ω=angular frequency
k=spring constant
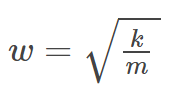
Pendulum Angular Frequency Formula
ω=sqrt(g/L)
ω=angular frequency
g=gravitational acceleration
L=length of pendulum
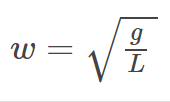
3 General Pressure Formulas
P=F/A
Ptot=Patm+Pgauge
Ptot=Patm+ρgh
P=Pressure
F=force
A=area
Pguage=pressure of fluid exerting, pressure on top of atmospheric pressure
ρ=density of liquid
g=gravitational acceleration
h-=height of liquid above point in question (depth)
Specific Gravity of Substance Formula
Specific Gravity = ρsubstance/ρwater
ρsubstance=density of substance
ρwater=density of water
Fraction of Object Submerged Formula
Fraction Submerged = ρobject/ρfluid
Volume Flow Rate Formula
Q=Av
Q=volume flow rate
A=cross sectional area of pipe
v=velocity of fluid
Bernouilli’s Equation
P+1/2ρv²+ρgh = constant
P=pressure
v=velocity
g=gravitational acceleration
h=height
ρ=density of fluid
Surface Tension Formula
T=F/d
T=surface tension
F=force
d=length over which the force is applied
Electrical Current Formula
I=q/t
I=current
q=charge
t=time charge flows
Voltage Drop Formula (ez)
V=IR
Resistance of Resistor Formula
R=ρ(L/A)
R=resistance
ρ=resistivity
L=length of resistor/wire
A=cross sectional area of resistor/wire
Conductivity Formula
σ=1/ρ
σ=conductivity
ρ=resistivity
Equivalent Resistance (In series)
Req=R1+R2+…
Equivalent Resistance (In parallel)
1/Req=1/R1+1/R2+…
Charged Stored on Capacitor Formula
Q=CV
Q=charge
C=capacitance (not conductivity)
V=voltage drop across capacitor
Capacitance of parallel plane formula
C=(kE0A)/d
C=capacitance
k=dielectric constant
E0=universal electricity constant
A=area of one of capacitor plates
d=distance between plates
Capacitance Circuit (in parallel)
Ceq=C1+C2+…
Capacitance Circuit (in series)
1/Ceq=1/C1+1/C2+…
Three formulas for Electrical Power
PE=IV
PE=I²R
PE=V²/R
PE=Electrical Power
Three formulas for Electrical Energy
UE=1/2 * Q²/C
UE=1/2 * CV²
UE=1/2 * QV
UE=electrical energy
Q=charge
C=capacitance
V=voltage drop
Average Current formula (AC circuit only)
Irms=Imax/sqrt2
Irms=average current
Imax= max current
Light passing through medium formula
n=c/v
nmedium=index of refraction of medium
c=speed of light in vacuum (3.0×10^8)
v=speed of light in medium
Two Snell’s Law Formula for Light Passing through Mediums
nsinθ=constant
n1sinθ1=n2sinθ2
n=respective index of refraction
θ=respective angle the light ray makes with normal line drawn to surface it passes through
Focal Length of spherical mirror formula
f=r/2
f=focal length
r=radius
Focal Length System Formula
1/f=1/do+1/di
f=focal length
do=distance from object to center of lens/mirror
di=distance from image to center of lens/mirror
Magnification Formula
m = -di/do
m=magnification (ratio of image height to object height)
di=distance from image to lens/mirror
do=distance from object to lens/mirror
*ex: if m=2. image is twice as tall as object
Power of optical system formula
P=1/f
P=power
f=focal length
Thermodynamics: Internal Energy Formula
ΔU=Q+W
ΔU= change in internal energy of substance
Q=heat transferred to gas
W=work performed on gas
Power of Radiation Formula
Prad=kAT4
Prad=power of radiation
k=radiating object constant
T=temperature of radiating object (K)
A=area of object radiating energy
Total Radiation Formula
Qrad=kAT4t
Qrad=total radiation
k=radiating object constant
T=temperature of radiating object (K)
A=area of object radiating energy
t=time
Internal Kinetic Energy of Monatomic Gas Formula
U=3/2*nRT
U=internal kinetic energy
n=number of molecules (moles)
R=gas constant (8.31)
T=temperature (K)