BIO 106 - Final Exam
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
actin
thin filaments
function: muscle contraction, cell mobility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell signaling, and establishment and maintenance of cell junctions and cell shape
action potential spread in a normal heartbeat
action potentials spread rapidly through the heart’s electrical conduction system, causing a coordinated wave of muscle contractions
initiation —> spread —> contraction
resting heart rate of 60-100 bpm
amphibians
caecilians, frogs and toads (anurans), salamanders
an early split in the tetrapods led to the 2 main vertebrate groups (amphibians and amniotes)
most live in moist environments - the lose water easily through the skin, and eggs dry out if exposed to air
some adults live on land but must return to water to reproduce
arthropods
huge and diverse group
muscles attached to inside of rigid exoskeleton
segmentation - each segment has muscles that operate that segment and its appendages
jointed appendages allow complex movement and specialization
rigid exoskeleton provides support in water or on land, protection from predators, and prevents drying out
arthropod relatives with segmented bodies and fleshy unjointed legs: velvet worms(onychophorans), tardigrades (water bears),chelicerates
the remaining arthropod groups are the mandibulates: myriapods (centipedes/millipedes), crustaceans, hexapods, pterygote
avian air sacs
expand and contract, acting like bellows to push air past gas exchange surfaces in the lungs
air sacs don’t participate in gas exchange
inhalation: fresh air goes to the posterior air sacs, then flows through parabronchi to anterior air sacs
exhalation: fresh air in posterior air sacs is driven into parabronchi, while the stale air is exiting the parabronchi at the anterior end and anterior air sacs
bulk flow
flow of matter form one place to another
O2 and CO2 are transported by diffusion and bulk flow (no active transport)
diffusion is effective for moving gases over very short distances - all cells depend on diffusion for O2 to pass
calcium ions (Ca2+)
convert electrical energy into mechanical energy
role: activates myosin by shackling to troponin on the cytoskeleton; plays an important role in excitation-contraction coupling
cardiac output
volume of blood pumped per minute
chemical synapse
very narrow space between cells (synaptic cleft) that an action potential cannot cross
circulatory system
consists of muscular pump (heart), fluid (blood), series of conduits (blood vessels)
closed system - blood always remains within blood vessels
open system - blood exits vessels as it flows through the body (no distinction between blood and interstitial fluid)
cleavage
rapid series of cell divisions, but no cell growth (I, II, III)
cells increase in # but get smaller and smaller
cells end up with different cytoplasmic determinants
these cells are called blastomeres (group - blastula)
plane of cleavage determined by the orientation of the mitotic spindle
cocurrent gas exchange
the 2 fluid streams flow in the same direction
water has a much higher O2 partial pressure than blood and O2 diffuses rapidly into the blood
common ancestors of animals
phylogenetic analyses of gene sequences has shown that all animals have a common ancestor (monophyletic)
animal common ancestor was probably very different from any living animals; large multicellular animals appear to have evolved several times in different lineages
complete cleavage
cytoplasm is completely divided by each cell division
countercurrent gas exchange
the 2 fluid streams flow in opposite directions
as blood flows along the gas exchange membrane and its O2 partial pressure rises, it encounters fresher water with higher and higher O2 partial pressure
O2 partial pressure of water is always higher than that of blood
more efficient than cocurrent
cross-bridges
formed when myosin and actin interact when the globular heads of myosin bind to actin
determination
cell fate is established
differentiation
cells become different from one another
electrical synapse
cells are joined by gap junctions where the cytoplasm is continuous; signals cross with essentially no delay
embryonic development
a fertilized egg is transformed into an embryo
excitation
when a nerve impulse arrives at the neuromuscular junction, an action potential is initiated in the muscle fiber membrane
excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs)
graded membrane depolarizations shift membrane potential towards threshold
function of grey crescent
helps establish polarity and is crucial for embryo development
turns into Spemann’s organizer, a signaling center that “talks” with other tissues to direct development
acts as organizer in the embryo
gas exchange membranes
thin layers of tissue where respiratory gases move between the environment and the internal tissues
gastrulation
involved movement of cells: the 3 germ layers are formed and the embryo becomes a gastrula
general characteristics of animals
multicellularity
heterotrophic metabolism
internal digestion
movement and nervous system
growth
increase in size by increasing cell number, cell size, production of extracellular material, or a combination
hyperosmotic
solution with higher osmotic pressure
hyposmotic
solution with lower osmotic pressure
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs)
shift membrane potential away from threshold; produce graded membrane hyperpolarizations
isosmotic
2 solutions have the same osmotic pressure
mammalian breathing system
inhalation: contraction of diaphragm expands the thoracic cavity, which pulls on the lungs and expands them; air is sucked in
exhalation: the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, allowing elastic recoil of the lungs and thoracic cavity to push air out
conducting airways - conduct flowing air in and out of the lungs during inhalation and exhalation (trachea, bronchi)
gas exchange occurs in the respiratory airways (bronchioles, alveolar sacs)
tidal volume - amount of air that moves in and out of lungs per breath
respiratory minute volume - total volume of air inhaled and exhaled per minute
morphogenesis
process leading to the final form of the animal
muscle contraction
Z line: the Z discs move closer together
H zone: shortens
sarcomere: shortens, the primary structural and functions unit responsible for muscle contraction
A band: doesn’t change i length, but A bands from different sarcomeres move closer together and eventually disappear
actin and myosin pull towards the center of the sarcomere, increasing the zone of overlap
I band: shortens
M line: moves closer
muscle contraction steps
discharge of motor neuron at endplate
release of the neurotransmitter ACh at endplate
binding of ACh to its receptors
increased Na+ and K+ conductance in endplate membrane
generation of action potential at endplate
generation of action potential along muscle fibers
spread of potential along muscle fibers
release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum and diffusion to actin and myosin
binding of Ca2+ to troponin and thereby uncovering myosin binding sites on actin
formation of cross-bridges between actin and myosin and sliding of actin and myosin, producing muscle shortening
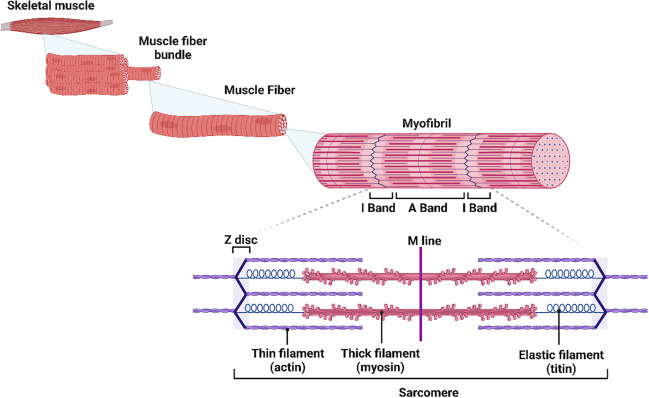
myofibrils
bundles of actin and myosin filaments arranged in repeating units called sarcomeres
each sarcomere starts and ends with a z-line, which actin attaches to
myosin filaments extend out from the M band in the center
H zone and I band have no overlap of actin and myosin
myosin
thick filaments
function: converts chemical energy in the form of ATP to mechanical energy, generating force and movement
neuromuscular junction
chemical synapses between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells
signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with muscle fibers to cause them to contract:
presynaptic terminal depolarization and ACh (acetylcholine) release
ACh binding and ion channel opening
postsynaptic membrane depolarization and muscle action potential generation
neurotransmitter
chemical messengers
function: to carry chemical signals from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell (nerve cell, muscle cell, or gland)
movement, sensation, heart rate, information processing, brain development
osmosis
the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
osmoregulation
the process by which an organism regulated the water balance in its body to maintain homeostasis
freshwater fish: hyperosmotic to fresh water because water passes in across gills and other membranes by osmosis
Na+ and Cl- are more concentrated in blood plasma than in fresh water, and thus pass out by diffusion
osmotic pressure
measure of the total concentration of solutes; determines direction of water movement
water moves from regions where osmotic pressure is low (high water concentration) to regions where its high (low water concentration)
oxygen loading/offloading
loading: the process by which hemoglobin binds oxygen to form oxyhemoglobin, happens in lungs
offloading: the process of oxygen unbinding from hemoglobin in red blood cells as blood flows through metabolizing tissues, occurs in areas with lower oxygen concentration (respiring cells)
partial pressure
the portion of the total pressure exerted by a gas in a mixture of gases
a gas always diffuses from an area where its partial pressure is high to where its partial pressure is lower
postsynaptic cells
cells that receive signals from other neurons or cells through a synapse
processes signals into electrical and biochemical changes
presynaptic cells
neurons that send information to other neurons through a synapse
quickly releases chemical neurotransmitters in response to electrical impulses, or action potentials
the neurotransmitter is diffused across the space
primates
evolved from a lineage of small, arboreal, insectivorous eutherians
2 clades: wet-nosed primates (lemurs lorises, galagos) restricted to Africa, Madagascar, and tropical Asia; dry-nosed primates (tarsiers, Ole World monkeys, New World monkeys, apes)
Asian apes (gibbon, orangutan), African apes (gorilla, chimpanzee), and humans are modern descendants of Old World monkeys
became hominin clade
had bipedal locomotion
in the homo lineage, brain size increased while jaw muscles decreased in size
radial and spiral cleavage
seen in eggs with little yolk and complete cleavage
rotational cleavage
at the 2nd division, blastomeres divide in different planes
sarcoplasmic reticulum
surrounds every muscle fiber
role: stores calcium ions and releases them into the sarcoplasm for the generation of action potential during muscle contraction
sequence of blood flow (human circulatory system)
oxygen-poor blood enters heart through superior and inferior vena cava
blood moves to right atria, then right ventricle
blood is pumped into lungs through pulmonary artery
oxygen-rich blood returns to heart through pulmonary veins
blood moves to the left atria, then left ventricle
blood is pumped to body through aorta
skeletal muscle
the type attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides power for walking, flying, swimming, etc.
skeletal muscles appear striated due to the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle fibers (sarcomeres)
Spemann experiment
a series of graftings in which some cells were removed from the dorsal side of an amphibian embryo and then transplanted to the other side of a second embryo
the transplanted dorsal cells caused the embryo to develop a second set of complete body structures
stroke volume
volume of blood pumped per heartbeat
synaptic plasticity
synapses can undergo long-term changes in functional properties and physical shape during an individual’s lifetime
titin
the largest protein in the body, runs the full length of the sarcomere
each titin molecule runs between the M band and a Z line, directly through a myosin filament
tropomyosin
a protein twisted around each actin filament
role: prevents actin and myosin from interacting and causing the muscle to contract at the wrong time (blocks myosin binding sites)
troponin
molecules attached at intervals of tropomyosin
role: sarcomeric Ca2+ regulator and helps trigger muscle contraction
ventilation
bulk flow of air or water between the gas exchange membrane and the outside world
tidal - air moves in and out the same passageways
unidirectional - in animals with gills water moves in a one-way stream across gills
blood O2 partial pressure also controls ventilation, but is not as influential as CO2