AP WORLD
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
231 Terms
🟥 Abassid Caliphate
-Islamic empire with capital in Baghdad.
-Built around trade, used receipt and bill system.
-Ethnically Arab
-Rules by a Caliph, who was the head of the state (both political and religious leader)
🟥 House of Wisdom
-Located in Baghdad during Golden Age of Islam
-Library where scholars from all around the world came to study religion and science. Some scholars were responsible for preserving Greek works of philosophies by translating them into Arabic and making commentaries
🟥 Seljuk Empire
-Rise of Seljuks was caused by the decline of the Abassid Caliphate.
-Ethnically Turkic (major change)
🟥Jizya Tax
Made more people convert to Islam
🟥Sufi Missionaries
Mystic rituals. Appealed by adjusting to local culture.
🟥Crusades
Advocated by the Pope, Military campaign by European Christians to convert Muslims and non-Christians. Power shifted back to Church, it was a holy war to take land back (Jerusalem) and fighting in it would allow entrance to heaven
🟥Delhi Sultanate
Led to the spread of Islam in southEast Asia.
Rajput Kingdoms resisted Muslim intrusion, maintaining Hindu influence. Gave grants to Brahmans who spread religion
Vijayanagara Empire: Missionaries who betrayed sultans, converted back to Hindu and set up rival Hindu empire.
🟥Khmer Empire
Founded as a Hindu Empire. Built Angkor Wat which was a Hindu Empire with Buddhist influences (syncretism)
🟥Bhakti Movement
Emphasized devotion to one god within the polytheistic religion
🟥Maya Civilizations
-Built urban centers, writing systems (0), advanced mathematics
-State structure was a decentralized collection of city states frequently at war with one another
-Fought to create a vast network of tributary states among neighboring regions
-Emphasized human sacrifice
🟥Aztec Empire
- capital: Tenochtitlan. vast marketplaces were set up w/roads linking areas, thriving city. economy was commercialized.
-decentralized power w/tribute system and self-govern
-human sacrifice
🟥Inca Empire
-Centralized empire w massive bureaucracy
-Vast network of roads and bridges
Mit’a System- mandatory service on state projects.
CONTINUITY, later exploited by the Spanish circa 1450-1750 when they came to the Americas in search of gold and silver and forced the Incans to work as slaves in silver mines in Potosi.
🟥Mississippian Culture
-Mississippi river valley
-Cahokia: large mound. hosted religious ceremonies on tops of mounds
-Dominated by great chiefs (Great Sun)
🟥Swahili Civilization
-Organized by trading along the East African Coast (INDIAN OCEAN TRADE)
-Politically independent w/ common social hierarchy (merchant class on top
-Influenced by Muslim traders through emergence of Swahili language
🟥Great Zimbabwe
-Facilitated Indian Ocean Trade by controlling several ports on coast
-Centralized government
-Farming revolved around farming and cattle herding, but grew exceedingly wealthy and shifted to gold exports
-Never converted to Islam, maintained indigenous shamanistic religion . Spoke Bantu
-Known for great walls
🟥 Hausa Kingdoms
-Decentralized; politically independent collection of city states
-Organized by trading along TRANS-SAHARAN Trade network
-Converted to Islam which further facilitated trade with Muslim merchants
🟥Ethiopia
-Christian state & constructed massive churches
-known for SALT, INDIAN OCEAN TRADE
-Centralized power w/ hierarchy
🟥Feudalism (Dark Ages)
- Europe was fractured politically into small tribal kingdoms, constantly at battle for dominance
-System of mutual obligations between powerful lords, monarchs, knights
-King gave land to Vassals (lords) in exchange for service and tribute. Vassals employed knights for protection in exchange for money.
🟥Manoralism
Manors were pieces of land owned by a lord. Serfs were bound to this land and worked in exchange for food and protection
🟥Magna Carta
-Baron vs King John (England)
-Created bc of tensions w/feudal system. Limits the power of the monarchy and gave power back to nobles such as jury trial, right of all free citizens to own and inherit property
🟥 Neo-Confucianism
Continuity: Carried over from the Tang Dynasty. Hierarchy & Filial Piety. Change: Had the influence of Buddhist and Daoist philosopher ideas.
🟥Women in Song China
All legal rights restricted - patriarchal society. Foot Binding: status symbol for upper class women, if they couldnt walk they couldnt work
🟥Imperial Bureaucracy
Helped Song China maintain their rule. Ruler used Mandate of Heaven to justify their rule. Merit-Based officials (Civil Service Exam)
🟥Tribute System
Involved foreign states sending tribute to the Chinese emperor in exchange for recognition of their sovereignty and trade benefits. KOREA & VIETNAM maintained a tributary relationship with China and was also influenced by Confucianism and the Civil Service Exam.
🟥Buddhism in Song China
Tolerated. Mahayana Buddhism was from Vietnam and became very popular.
🟥Champa Rice
-Introduced through Vietnam Champa Kingdom
-Drought Resistant
-Harvestable twice a year
-Led to population Explosion
🟥Transportation Innovations
-Expanded Grand Canal (linked Yellow and Yang Se rivers)
-Magnetic compass & Navigation Charts
-Junk Ships w/ lots of cargo
🟥Metalworking
developed iron plows. produced enough iron and steel to create armor for war, coins for trade, and tools for agriculture
🟥Renaissance
Rebirth of ancient Greek and Roman culture, art, and lterature
Ideas of humanism stressing importance of individuality
🟥France
-Decentralized but expansion collided with English (Hundred Years War)
-France gained more power bc of Joan of Arc, fueled national identity and unified France
🟥Spainish Inquisition
-Enforce religious orthodoxy
-300,000 Jews and Muslims converted to Catholicism (Claim they had false religious beiefs)
🟧Silk Road
Vast network of roads and trails that facilitated trade and the spread of culture and ideas across Eurasia in and before the period 1200-1450.
Mostly luxury goods were exchanged, especially Chinese Silk
🟧Causes of Silk Road Expansion
-Money Economics (paper money)increased ease of travel and security of transactions
-Increasing use of credit (flying money)
-Rise of banks
-Caravanserai, provided safety for merchants and became centers of cultural exchange & diffusion
-Saddles, made riding easier for long distances
🟧Effects of Silk Road Expansion
-Rise of powerful trading cities such as Kashgar and Samarkand
-Increased demand for luxury goods (Proto-industrulization in China)
-Cultural diffusion
-Disease (bubonic plague, killing half of European, Chinese, Muslim population)
🟧The Mongol Empire
-Established largest land-based empire of all time.
- Organized his army into groups of 10,000, 1000, 100, and 10, making controlling the groups very efficient
-Choice of weapon was a stronger, deadlier bow and arrow and they could often outride their opponents on horseback
-Significantly allowed Silk Roads to fluorish because they provided safety and connectivity around them.
-Facilitated technological and cultural transfers, increased communication through Yam System, adoption of Uyghur script (written language)
🟧Yuan Dynasty
-Adopted the norms of people over which they ruled
-United warring factions in Chin, so Confucian elites believed he possessed the Mandate of Heaven to rule China.
🟧Indian Ocean Network
Network of sea routes that connected the various states throughout Afro-Eurasia through trade
Easier to travel so more common goods like textiles and spices
🟧Causes of Indian Ocean Network Expansion
Magnetic Compass (allowed merchants to know where they were going)
-Astrolabe (measured stars to reckon longitude and latitude)
-Knowledge of Monsoon ships to strategically power ships
-Lateen sail, dhows
-New Ship deisgns (Chinese Junks)
🟧Strait of Malacca
Controlled by Srivijaya Empire. Only passage between Southeast Asia and China/Japan. Placed taxes on ships that went through the strait in Indian Ocean Trade and became filthy rich.
🟧Diasporic Communities
A group of people from one place who establish a home in another place while retaining their cultural customs, new languages emerge
🟧Zheng He
Commissioned by Ming Dynasty to explore Indian Ocean and go through other states in China’s tributary system. His ships were equipped with the latest military technology like gunpowder canons, which was later adopted by places he visited. After his death, the Ming Dynasty began to shift their focus on internal affairs resulted in isolationist trade policies that shut down sea based trade in China.
🟧Trans-Saharan Trade Routes
Series of trade routes that connected North Africa and the rest of the Mediterranean world with the interior of West Africa and the rest of Sub-Saharan Africa.
Salt was high in demand, gold, kola nuts, horses
Introduction of Arabian camels facilitated trade
🟧Chan Buddhism
Syncretism between Buddhism and Chinese Daoism, became popular in lower classes
🟧Empire of Mali
Converted to Islam which made it easier to trade. During the Hajj of Mansa Musa, he gave much gold into the Egyptian economy. Became exceedingly wealthy through taxation of merchants.
🟧Ibn Battuta
-Muslim scholar from Morocco
-Travelled all over Dar-al Islam
-Took detailed notes about places, people,, rulers, and cultures
-First hand notes
🟧Marco Pollo
-Travelled from Italy to China and throughout the Indian Ocean
-Wrote about the court of Kublai Khan and China’s grandeur and wealth
🟨Ottoman Empire
-Founded after the fall of the Mongol Empire
-Grew rapidly: Controlled the Dardanelles (used to launch explosions), gunpowder weapons
-Mehmed II seized and took Constantinople from the Byzantine Empire and renamed it Istanbul. He also converted Hagia Sophia into a mosque.
-Suleiman the Magnificent took control of the Ottoman Empire during its golden age. He conquered more area around the mediterranean and attempted to push further into Europe past Hungary but was stopped.
-Tolerant towards monotheistic religions
🟨Devshirmine System
Ottomans took young enslaved Christian boys from Southern Europe and Balkans. Janissaries were sent to live with Turkish families to learn the language and Istanbul for a proper Islamic education. These boys went either into the military or became part of the Bureaucracy
🟨Tax Farming
Helped the Ottoman government by providing a steady source of income at the beginning of the year which came from bidding the right to tax
Whoever got the right to tax was authorized to collect taxes from a particular group of people and they enriched themselves by collecting more taxes than were legally required.
🟨Women in the Ottoman Empire
-Patriarchal Society
-Women did domestic work or supervised their servants.
-Restricted from leaving home, but could attend weddings, cemeteries, and public baths.
-Few women were literate.
-Women could earn a living, own industries, and practice medicine
-The Harem: private domain for sultan
🟨Ottoman Timars
Land grants made by Ottoman state to an aristocratic class in payment for service to the government. Timars grew exceedingly rich and powerful through taxation. Sultans began increasingly taking over these timars and converted them to tax farms which directed revenue to the state
🟨Safavid Empire
-Expanded rapidly under Shah Ismail through gunpowder weapons
-Shia state, opponent to neighboring Sunni Muslim empires, carried out w/ violence
🟨Muhgal Empire
-Babur founded the Mughal Empire using gunpowder weapons
-Akbar: religiously tolerant (bc of his desire to maintain peace, abolished jizya tax), masterful administrator, under his rule the Mughal empire was the most prosperous
-Established Din-i-llahi as a universal religion which had elements of Zoroastrisism
-Shah Jahan: patron of arts, built Taj Mahal, but less tolerant
🟨Zamindar System (Mughal)
-Employed local landowners, zamindars, to collect taxes throughout the empire on behalf of the emperor
-Extended imperial authority and consolidated imperial power
🟨Qing Dynasty
-were not ethically han like the majority of the Chinese population (from Ming dynasty)
-Hans Had to wear a quene braid (signifies submission). Emperor Kangxi displayed imperial portraits of himself w traditional confucian values, appealing to the Chinese population
-Continuity: Civil service exam, footbinding
-Restored wall of China
-Relied on agriculture
🟨Safavid Mughal Conflict
Series of wars fought in the 17th ceuntry between the two empires due to their desire to expand into the Persian gulf. Erupted more because of the religious rivarly.
🟨Rise of the Russian Empire
Ivan III stopped paying tribute to the Mongol Empire. Many peasants found themselves in debt. Established a strong central government ruled by a czar who ruled by divine right.
🟨Peter the Great
-Strict autocrat and firm believer in military power (ruling with an Iron First)
-Began the “westernization” movement in Russia. Unified Russian culture from boyars to merchants, standardizing society. Beard Tax (strong opposition; disregarded cultural and religious customs). Created tensions
-Developed “secret police” who prevented dissent and supervise bureaucracy
-Moved capital from Moscow to St.Petersburg, consolidating his power. Peasants were used as labor and thousands died due to harsh conditions.
🟨Russian Serfdom
-Bound to the land only. Not racially different from the rest of the population in Russia
-Serfs were chained, beaten, disgraced, seperatd from family, and overworked, many died young.
-Tsar Alexander II abolished serfdom
🟨Catherine The Great
-Westernization
-Restricted Jews to the “Settlement of Pale”
🟨Protestant Reformation
-Eastern Orthodox vs Roman Catholic Church
-Church became filthy rich and built St. Peter’s Basilica, began the sale of indulgences to pay off all structures
-Simony: put high church positions for sale.
-Martin Luther challenged this, didnt see anything in the Bible that said sins could be exchanged for money
-Wrote the 95 theses, used the printing press to spread his ideas throughout Europe
-Catholics gathered in the Council of Trent and tossed out corrupt practices, implemented reforms to attract some of new protestants back
🟨Sikhism
-Blended elements of Islam and Hinduism
-Continuity: belief in one god, cycle of death & reincarnation
-Change: Caste system and gender hierarchies were disregarded
🟨France
-Henry IV of France signed the Edict of Nantes, religious toleration and civil rights. Later revoked by Loui XIV
-Louis XIV called himself the “sun god”, auto
-built Palace of Versailles to show power
-Tried to expand France’s borders to the Rhine RIver and Aps, made France nealry bankrupt
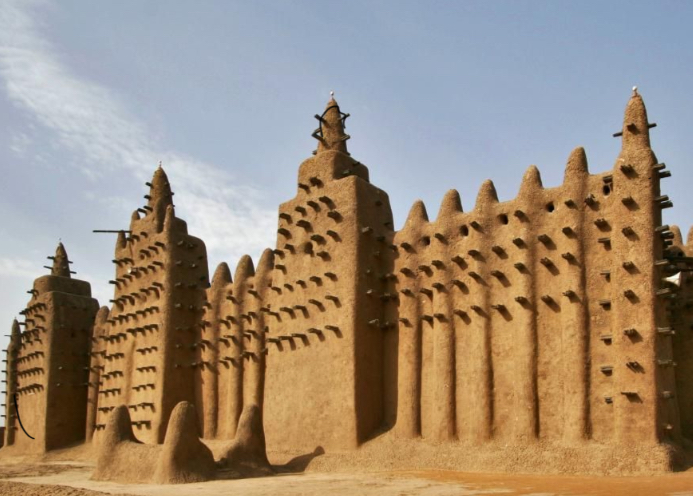

🟨The Songhay Empire
-Sunni Ali consolidated empire, expanded former Mali empire by conquering
-Timbuktu: city of learning (Mosques, schools, Islamic university)
-Jenne: major trading city
-Trans-Saharan trade brought salt, textiles, and metal in exchange for gold and slaves.
-Largest empire in African history, but defeated by the Moroccans
🟩Technology in Sea-Based Empires
-Magnetic Compass (used to reckon direction)
-Astrolabe (determines longitude and latitude)
-Lateen Sail (takes wind on either side)
-Astronomical Charts
Europeans adopted these technologies due to the Pax Mongolica
🟩Ship-Building Innovations
-Caravel (Portugal): smaller ship but more mobile on water and navigable (square and Lateen Sails). equipped w/ cannons so good fighting ships
-Carracks (Portugal): bigger version of the caravel, could carry more cargo and guns
-Fluyt (Dutch): exclusively for trade, cheap, massive cargo ships
🟩Mercantilism
increased power and wealth of state by maximizing exports and minimizing imports. promoted a government regulation of the economy to achieve a favorable balance of trade
-establish colonies
-regulate trade through tariffs
-encourage the accumulation of gold and silver
🟩British East India Company
-East Indies, East Asia
-Trade; particularly spices, textiles, tea,
-Controlled vast territories and played a significant role in the British empire. Eventually led to its takeover by the British crown
🟩Dutch West India Company
-Americas, West Africa, Caribbean
-Trade; colonization / participation in the Atlantic Slave Trade
-Dominated Atlantic slave trade, dutch colonization of the Americas, established trading posts
-Less successful; Faced challenges Dutch-Portuguese War
🟩Motives for Imperalism
Gold, God, Glory
🟩Portugal
Prince Henry sponsored Vasco de Gama to set up trading posts all around Africa to Southeast Asia. Grew rich by controlling trade. Established dominance through their loaded caravels/carracks with huge firepower. Trading posts established in cooperation w/ African leaders; traded gunpowder for enslaved people, plantations produced sugarcane. Gave them gold, ivory, slave trade. BRAZIL was a major territory for Portugal.
🟩Spain
Queen Isaballa and King Ferdinand agreed to pay for Christopher Columbus’ voyage. Discovered two new continents, eventually leading to more expeditions. Used tribute system, taxation, coerced labor. Ferdinand Magellan was also a key explorer, colonized the Philippines, set up full blown colonies.
🟩British
Established Virginia colony in North America. Set up a few trading posts along the coast of India. By the end of the 18th century, transformed trading posts into full blown colonial rule.
🟩France
-Established French colonies in North America, Quebec
-Fur & timber trade, Trading posts
🟩 Dutch
-Emerged as the wealthiest state in all of Europe using Fluys after competing for trading posts across Africa and dethroned the Portuguese.
-Established Dutch colony of new Amsterdam
-Transformed trading posts in Indonesia into full blown colonies by the end of the 18th ceuntry.
🟩Columbian Exchange
Transfer of new diseases, food, plants, and animals between the Eastern and Western hemispheres
Diseases
Since the indigenous had never experienced these diseases before, ended up devastating the population. Made European takeover much easier
Malaria
Measles
Smallpox
Plants & Food
Diversified diets, healthier diets, significant population growth
European settlers brought wheat, grapes, olives
Americans had potatoes, manioc, maize
Animals
Domesticated animals (pigs, sheep, cattle), horse fundamentally changed the society of several indigenous peoples in North America by allowing them to more effectively hunt herds of buffalo
Gave Europeans muscle power
🟩Treaty of Tordesillas
Rivalry between Spain and Portugal, both wanted to have control over America. This treaty split America into a meridian (vertical line). Portugal had everything east (Brazil)
🟩Atlantic Slave Trade
Imported enslaved laborers from Kongo Kingdom, however despite the large amounts of slaves being exported, African population saw an overall growth from the amount of new foods being introduced. Led to overharvest, deforestation, depletion of soil, strained water supply, introduced pollution
🟩Tokuguawa Japan
Japan was united under a shogun after a period of civil war. First was open to trading w/ Europeans but they realized they were a threat - Europeans wanted to convert them to Christianity. The Shogun expelled Christian missionaries and suppressed the faith with violence. The Dutch/China allowed for translations of Western books on physics, chemistry, math, geography, navigation, and military tactics. Economy grew despite the Closed Country Edict. Still had Haiku poetry, Kabuki theater, landscaped gardens, woodblock art.
🟩Japanese Feudal System
China during the Han/Tang Dynasty had this same social structure. Shogun (military ruler) —> Daimyos (lords/land owning nobles) —> Samurai (Knights, was imposed w the Code of Bushido - they would die if they failed to defend the social structure). —> Farmers & Fishermen (produced food) —> Merchants (selling what others produced.
🟩Women during Tokugawa Period
-Patriarchal society; wives had to obey their husband or face a death penalty
-Women received less education than men
-Women were encouraged to pursue artistic and cultural activities. Some women gamed status as geishas who were talent musicians and artists.
🟩Asante Emperor
Key trading emperor with the Portuguese and later the British. Provided highly desirable goods such as gold, ivory, enslaved laborers. Grew wealthy, allowed them to expand their military and political power.
🟩Kingdom of Kongo
Strong diplomatic ties with the Portuguese, King Alffonso I and nobles converted to Christianity. Syncretism occured: Cross in Kongo (Crucifix), Ancestors holding Jesus down (Idea brought by Animism), different representations of Jesus to make him more relatable. Provided gold, copper, enslaved peoples.
🟩Letter from King Alfonso to King Jao of Portugal (1526)
-Slave trade has damaged the kingdom, population declining, bringing in more ideas, questioning Alfonso’s authority
-As Alfonso knew the Portuguese was a higher power, he sought to end the slave trade in a respectful way. The Portuguese only cared about money
-Wanted a more mutually beneficial relationship with the Portuguese
🟩Chattel Slavery
-People are owned as property
-Race based; slavery became hereditary
-Gender imbalance, changing family structures, creole languages (European + Africa/indigneous)
🟩Indenturd Servitude
-Laborer could sign a contract to work for a set amount of time (7 years)
-Many poor Europeans used this to pay for their passage to the colonies
-Once the contract was up, they could go free and live their lives
🟩Encomienda System
-Invented by Spanish; used to force indigenous people into working for colonial authorities
-Indigenous people provided labor in exchange for food and protection. Spanish landowner had to Christianize and protect the natives.
🟩Las Casas
-Empathetic towards the natives because he was a missionary and a churchmen. He believed all people of the world are men and enslavement goes against his Christian beliefs.
-He has a bond with the natives and can be biased - perceived the Spaniards in an awful way and exaggerating the number of Indians killed
-His reports allowed the New Laws of 1542 to get passed, making enslavement forbidden and freeing all enslaved Indians
🟩Theodore De Bry
-Illustrated Las Casas accounts of the Indians
-His POV is based on Las Casas POV, De Bry was also abused by the Spanish so he can be biased.
🟩Hacienda System
-Indigenous laborers forced to work fields of large plantations known as Haciendas
-The crops were exported and sold on a global market (focused on the economics of food export)
🟩Spanish Casta System
Organized colonial society based on race and ancestry, made Spanish elite favored.
Penninsularies: born on Iberian penninsula
Creoles: Europeans born in Americas
Mestizos: mixed native and European ancestry
Mulattoes: mixed African and European ancestry
Zambos: mixed African and native ancestry
Indigenous people
African people
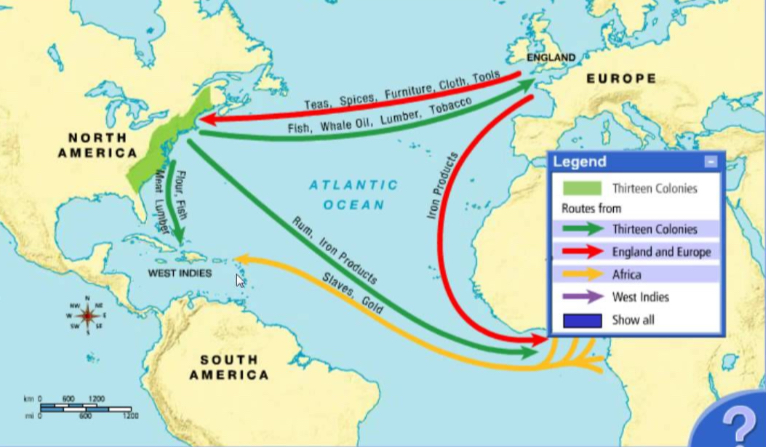
🟩Atlantic Slave Trade
-Forced migration of millions of Africans to the New World
-Triangular Trade (European firearms to Africa, traded for slaves, slaves brought to Americas, American products back to Europe)
-Middle Passage: Packed into ships made specifically to hold slaves across the Atlantic. So tightly packed that most slaves died from disease or suffocation before even arriving.
🟩Fronde
Louis XIV wanted more wars for expansions, but wars of expansion dont pay for themselves. As a result of absolutism, new edicts increased taxation. The French nobility led peasants in spontaneous rebellions known as the Fronde. monarchy increased in power
🟩Queen Ana Nzinga’s Resistance
Was growing concerned over the encroachment of Portuguese merchants in West Africa. Allied to the Dutch and the Kingdom of Kongo in order to fight back, which she successfully did.
🟩Pueblo Revolt
Indigenous warriors resisting to forced labor, cultural suppression, and religious persecution. Drove Spanish out of present day New Mexico for over a decade and killed many missionaries and leaders
🟩Maroon Societies
Free blacks/runaway slaves in Caribbean and Brazil. Their resistance was successful due to the violent fight backs of Queen Namy, recognizing their freedom.
🟩Pugachev Rebellion
Cossacks rebelled against Catherine the Great, mainly due to serfdom, suppressed by government and increased oppression.
🟩Expulsion
Spanish issued a decree expelling all Jews from their kingdom, Christians were superior. Mehmed II tolerated the Jews in the Ottoman Empire but still had too pay the Jizya.
🟦Galileo
Proved the Heliocentric Theory, sun is the center of the universe. The Catholic Church supported the Geocentric Theory, Earth was the center of the universe. He later faced significant conflicts with the church. Questioning and re-examination of the role of religion in public life, significant shift of authority.
🟦John Locke
Identifies certain rights that the government needs to protect (life, liberty, and property)
Influenced the Declaration of Independence