Finals set (missing 1/2 endocrine, fluid balance)
1/1199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1200 Terms
nervous system overview
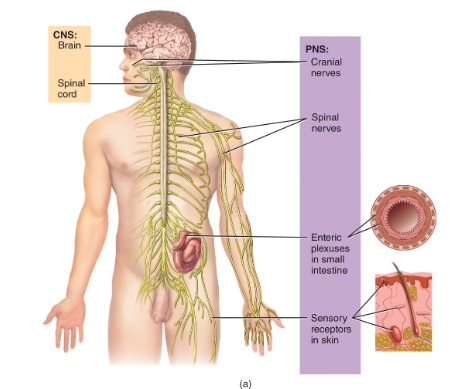
CNS VS PNS diagram
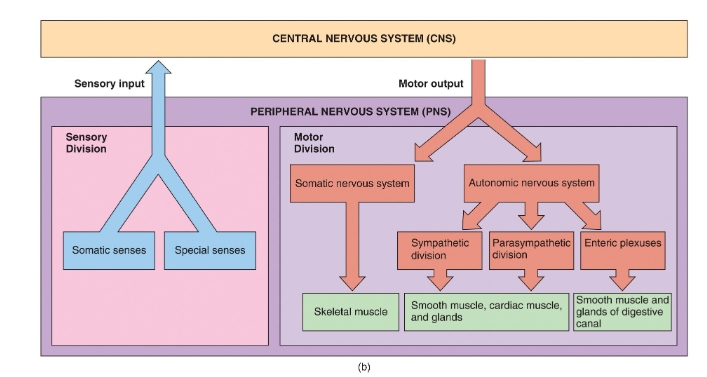
Overview of the nervous system diagram
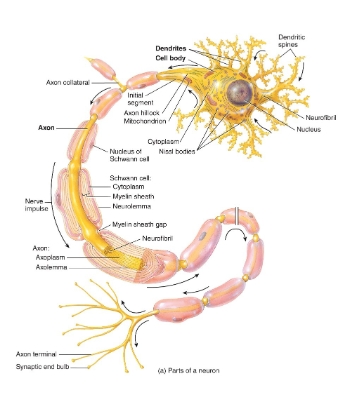
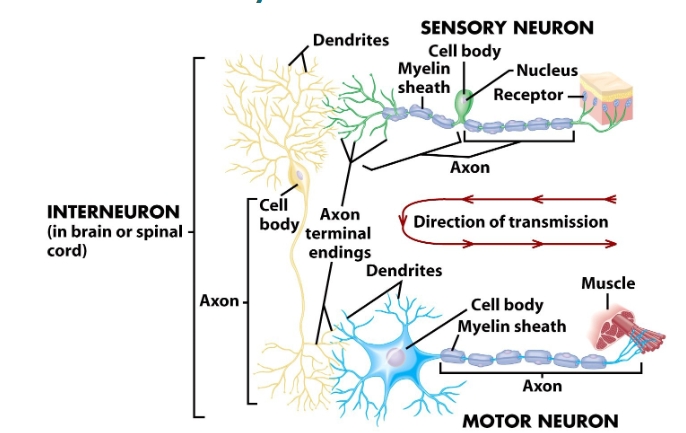
neuron diagram
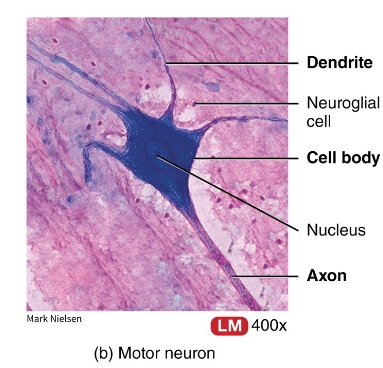
neuron under a microscope
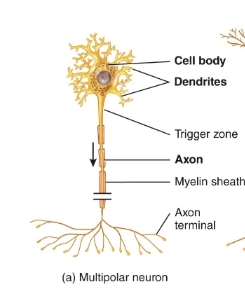
multipolar neuron diagram
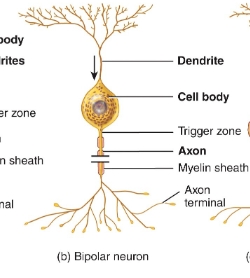
Bipolar neuron diagram
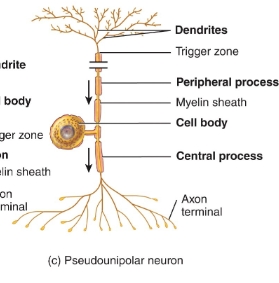
pseudopolar/unipolar neuron diagram
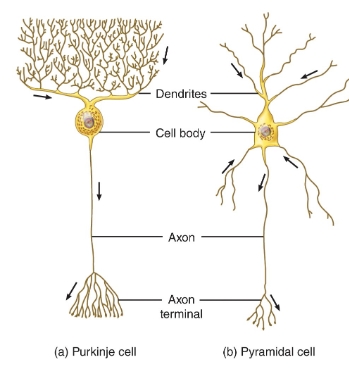
purkinje/pyramidal cell diagram
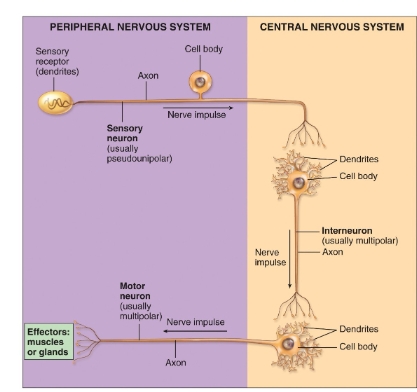
CNS vs PNS diagram of the neurons
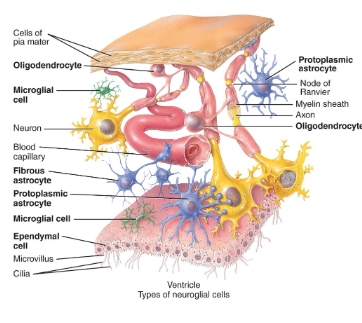
neuroglia diagram
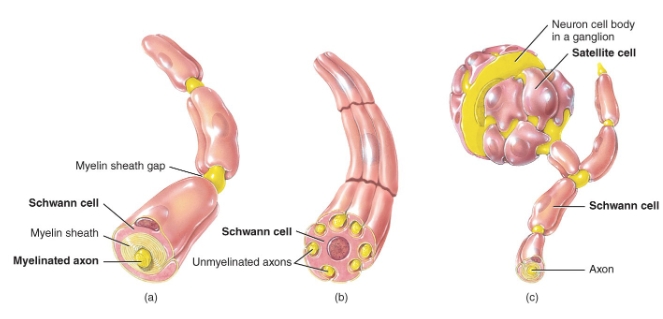
neuroglia of the PNS
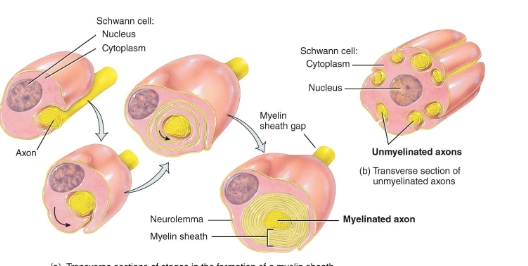
Schwann cell formation
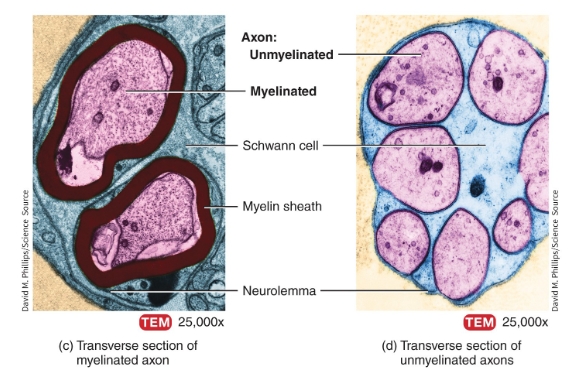
myelinated vs unmyelinated axons under a microscope
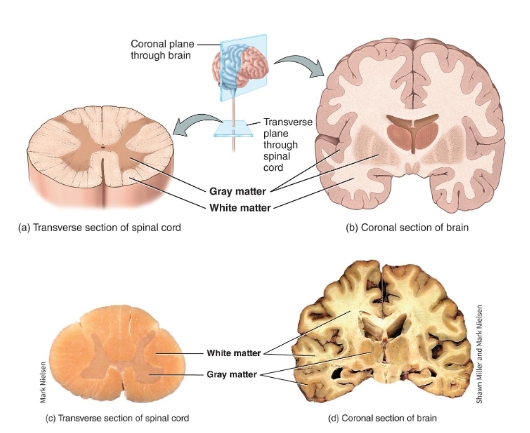
White matter vs gray matter diagram
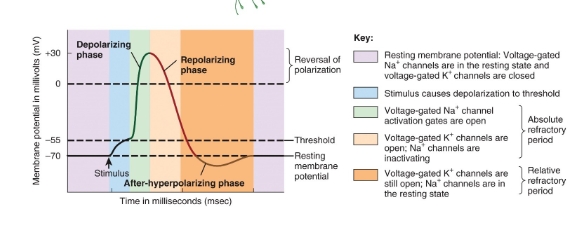
events during an action potential image
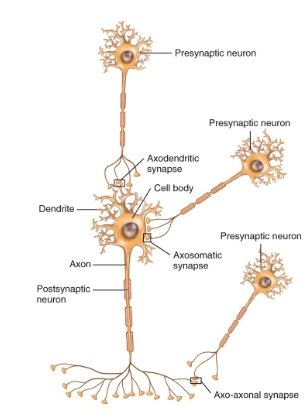
Types of synapses between neurons diagram
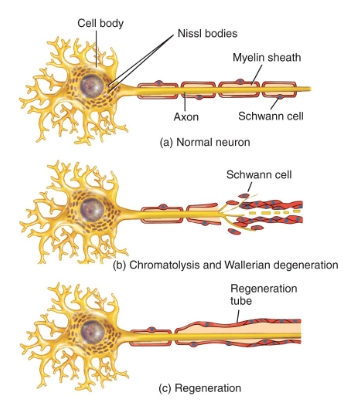
neuron repair diagram
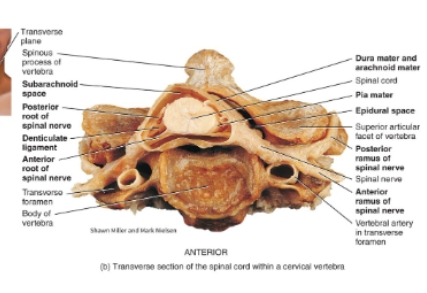
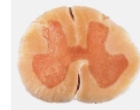
Spinal cord real diagram
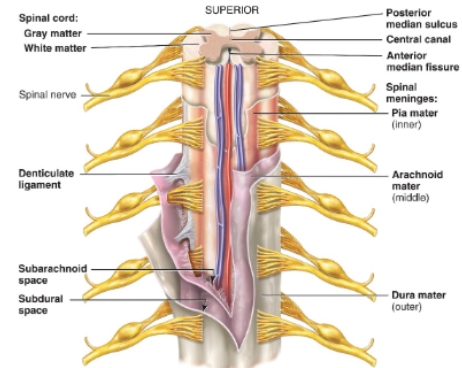
Meninges of the spinal cord diagram
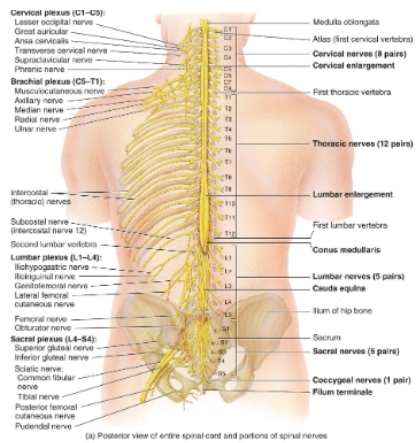
spinal cord diagram
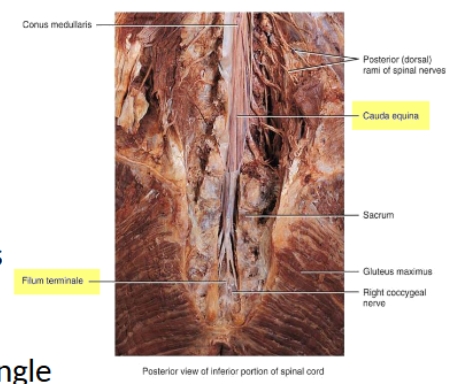
Spinal cord real diagram
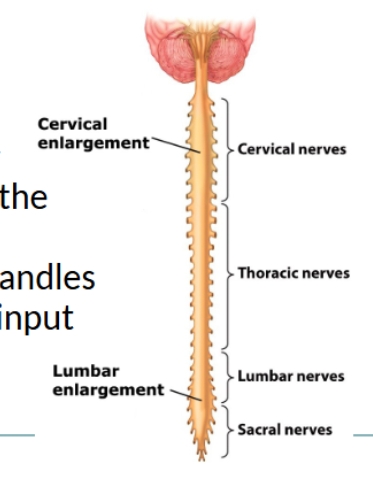
enlargement of spinal cord and spinal cord sections diagram
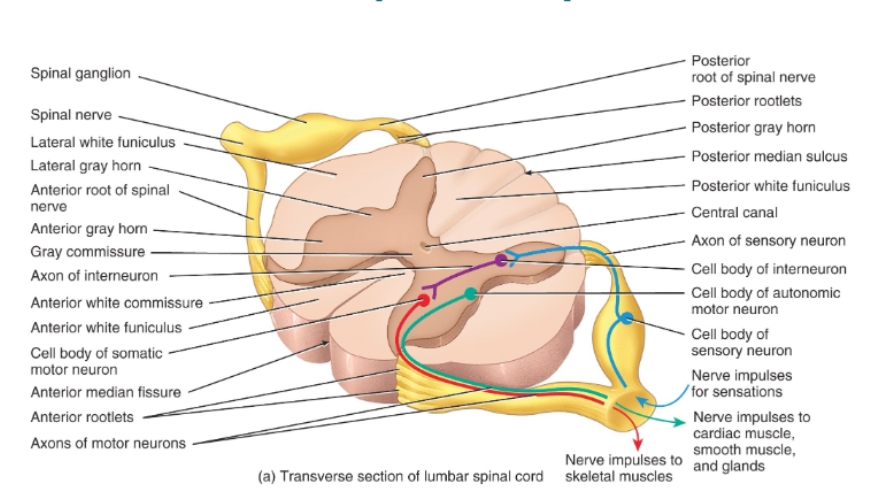
Transverse section of lumbar vertebrae diagram
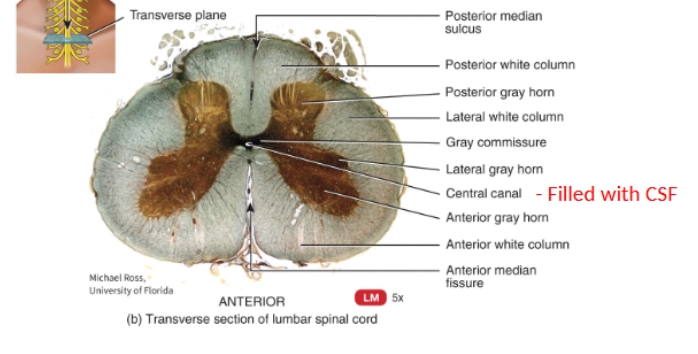
real transverse section of lumbar vertebrae diagram
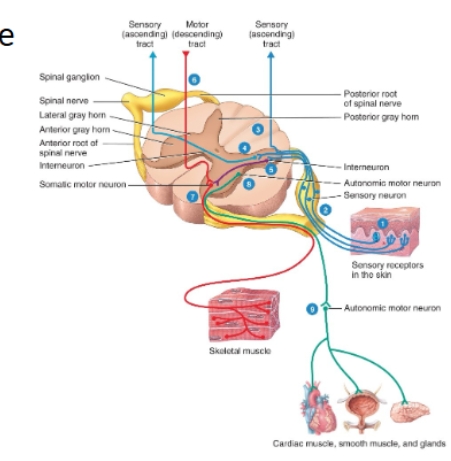
Sensory and motor processing diagram

cervical spinal cord image

Thoracic spinal cord real
lumbar spinal cord real
sacral spinal cord real
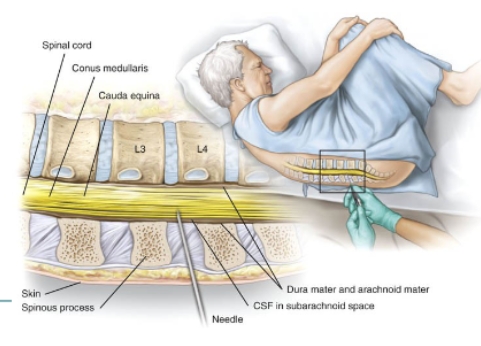
lumbar puncture diagram
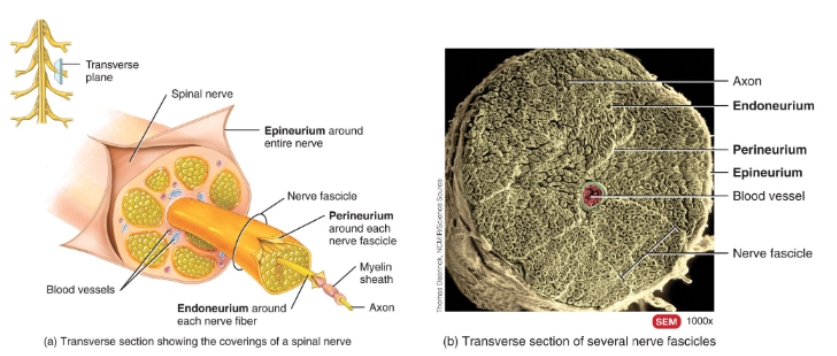
Connective tissue covering of spinal nerves diagram and picture
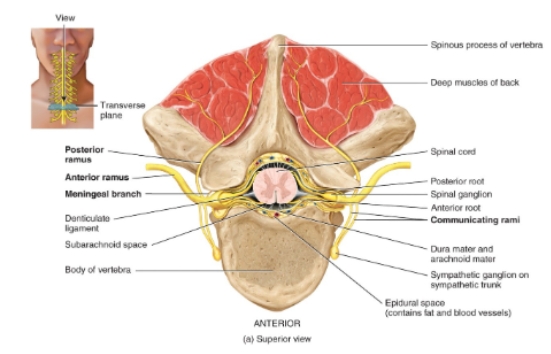
Spinal nerve and spinal cord diagram
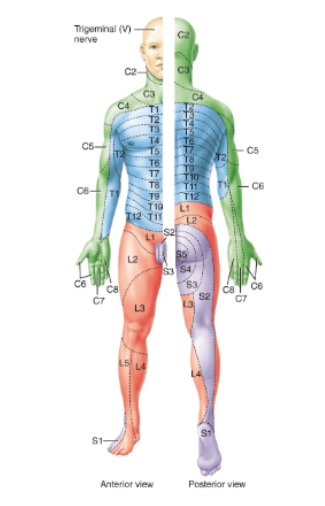
dermatomes diagram
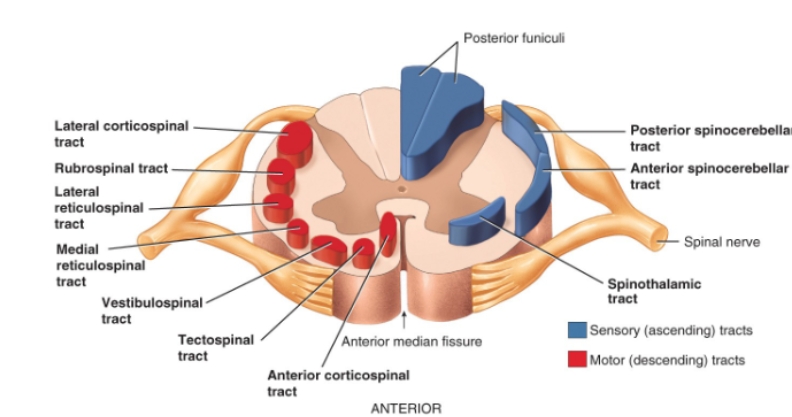
sensory and motor tracts diagram
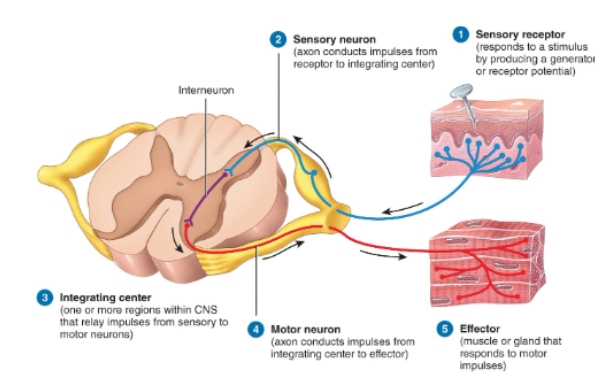
reflex arc diagram
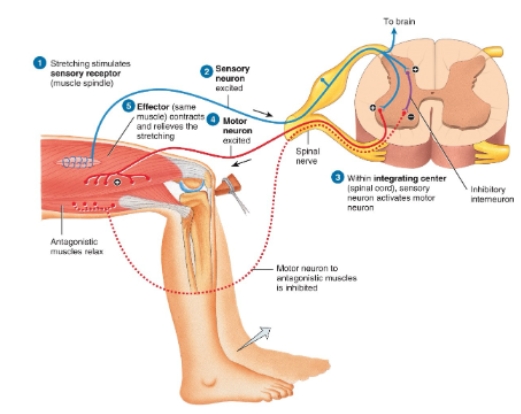
Stretch reflex diagram
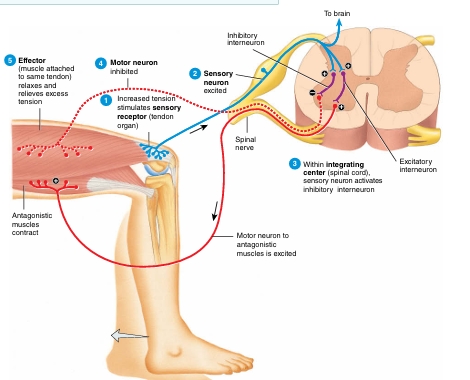
Tendon reflex diagram
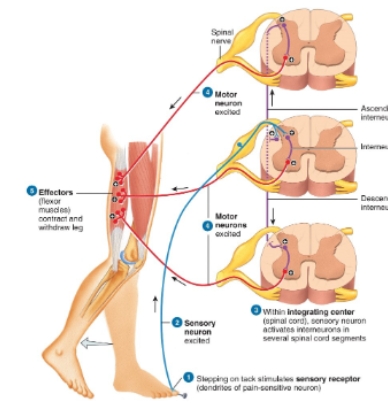
Flexor (withdrawl) reflex diagram
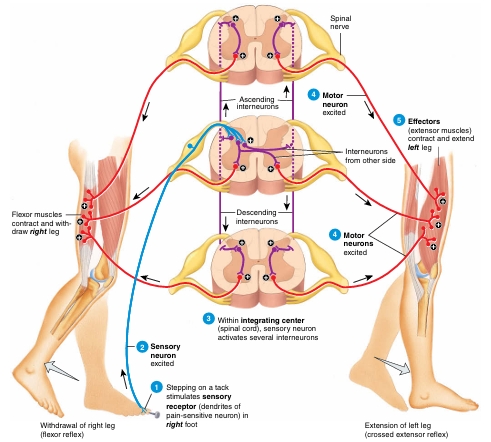
Crossed extensor reflex diagram
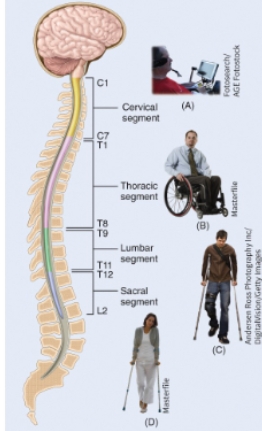
Injury to the spinal cord chart
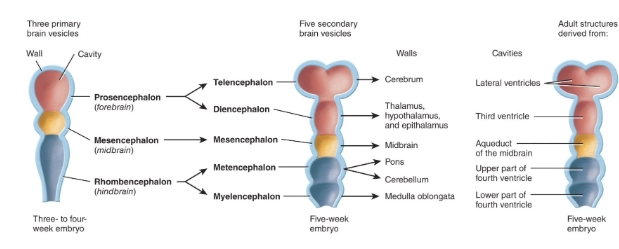
development of the brain diagram
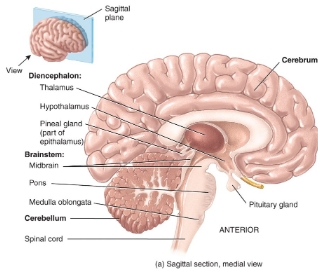
diagram of the brain
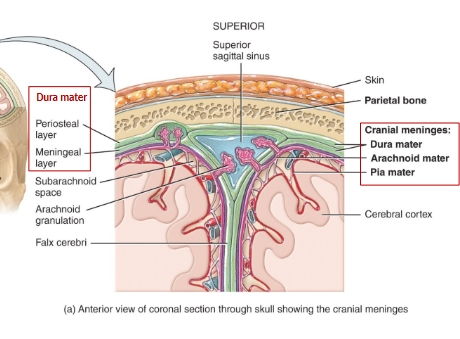
cranial meninges diagram
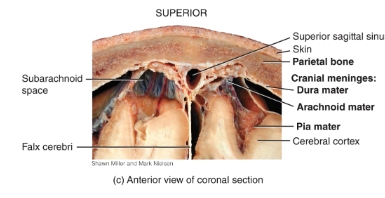
Cranial meninges and dura mater extensions picture
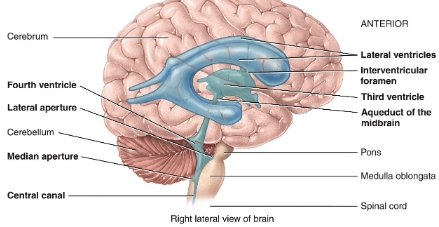
ventricles of the brain diagram
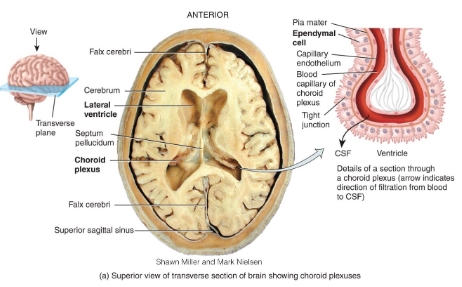
ventricles and choroid plexus diagram
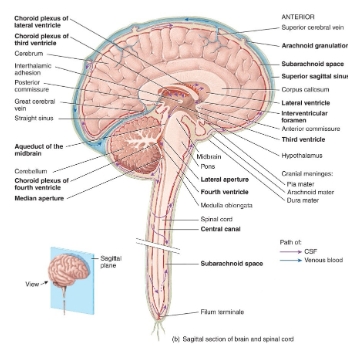
Flow of CSF diagram
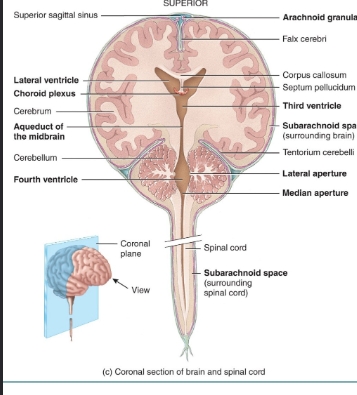
Frontal section of the brain and spinal cord diagram
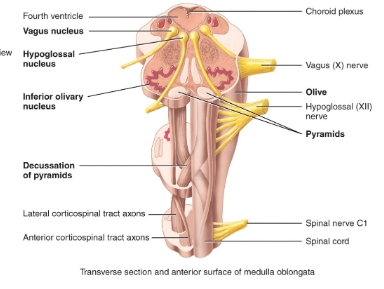
medulla oblongata diagram
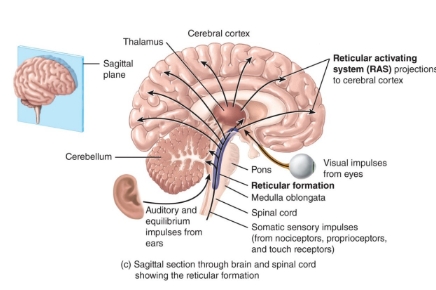
pons and reticular formation diagram
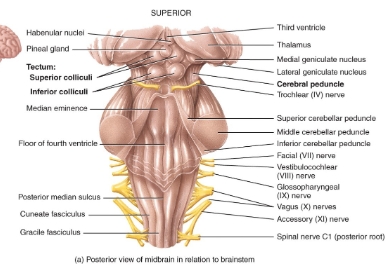
Midbrain diagram
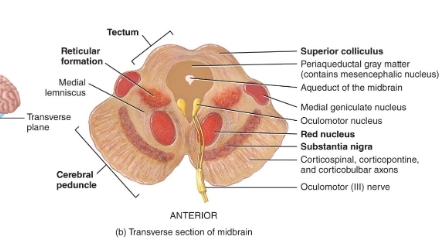
Transverse section of midbrain diagram
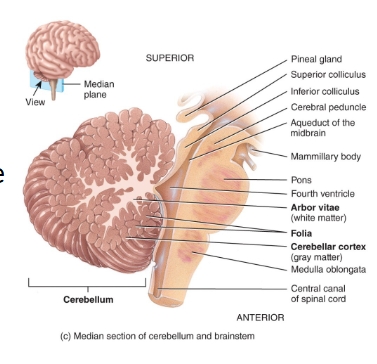
cerebellum diagram
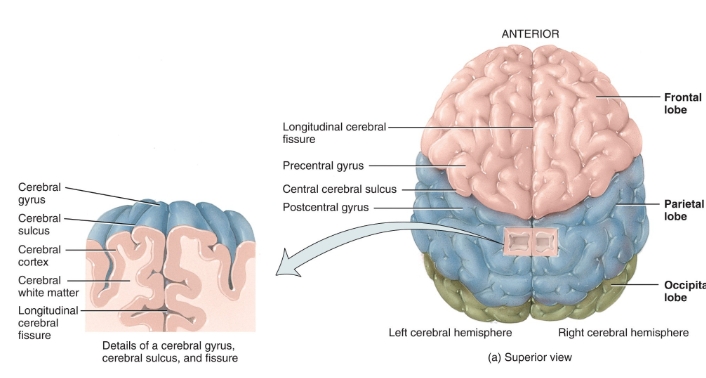
fissures and lobes of the cerebral cortex diagram
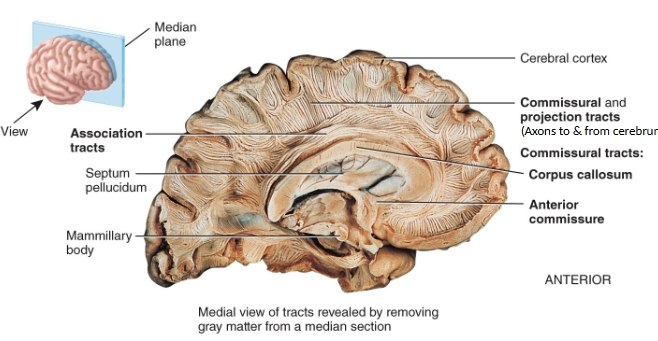
white matter tracts of the cerebrum
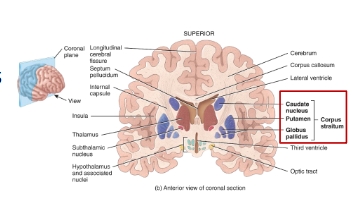
Basal nuceli (corpus striatum) of the cerebrum diagram
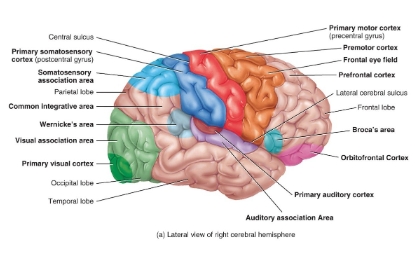
Functional areas of the cerebrum diagram
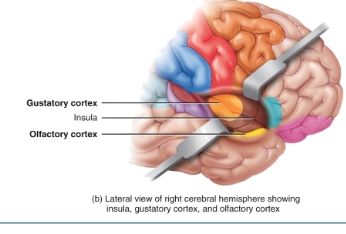
Gustatory and olfactory cortex location diagram
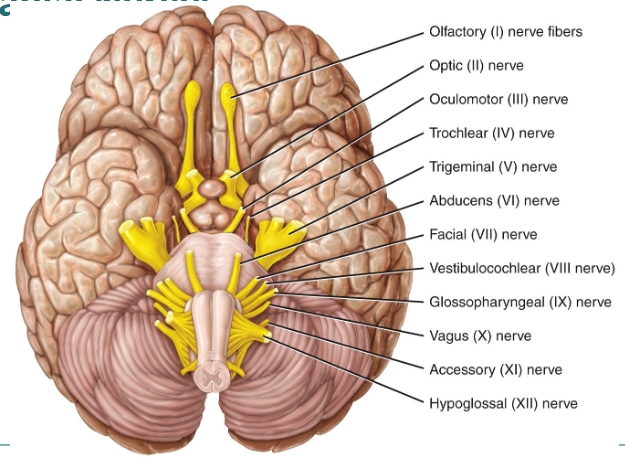
cranial nerves diagram
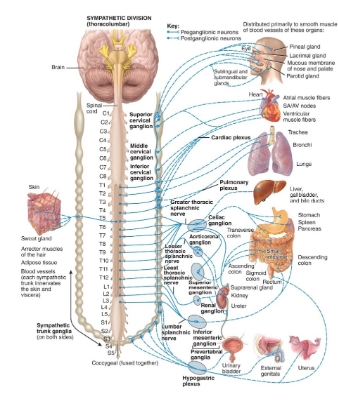
Thoracolumbar (sympathetic) diagram
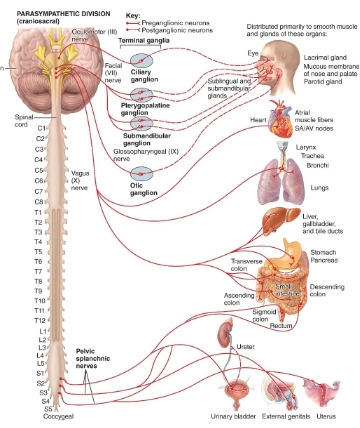
craniosacral (parasympathetic) diagram
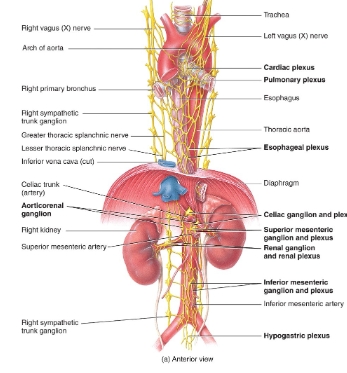
Nerve plexuses autonomic nervous system diagram
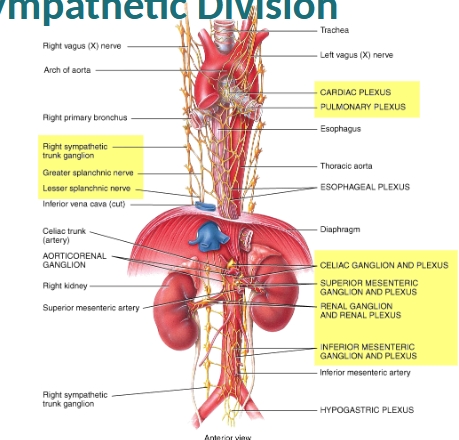
Sympathetic plexuses/ganglion diagram
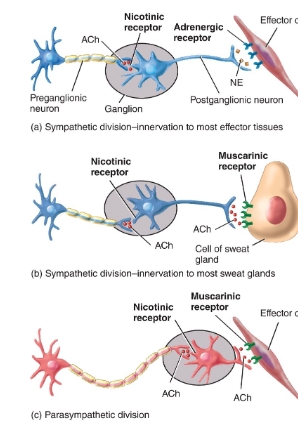
Neurotransmitters and receptors diagram
What does the urinary system consist of?
The kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
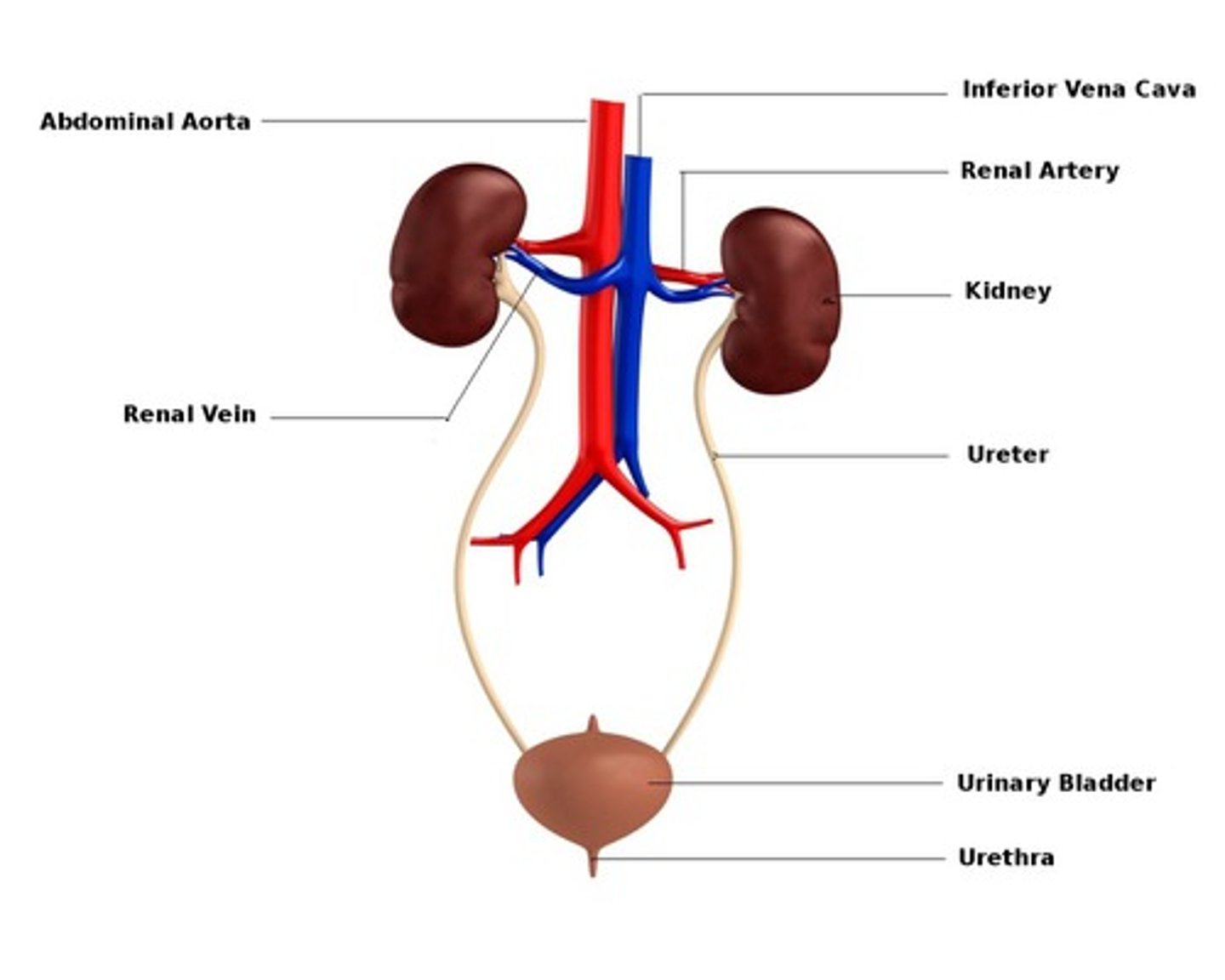
What is the function of the urinary system?
To maintain homeostasis by managing the volume and composition of fluid reservoirs, primarily blood
What are the functions of the kidneys?
1. Excretion of wastes
2. Regulates blood ionic composition
-Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, phosphate
-adjusts the amounts of ions excreted in urine
3.Regulates blood pH
-excrete variable amount of H+ and conserves bicarbonate ions
4. Regulate blood volume
-conserve/eliminate water in the urine
5. Regulate blood pressure
-renin activates angiotensin-aldosterone pathway
6. Maintains blood osmolarity
-regulate loss of water and solutes in urine
7. hormone production
8. regulate blood glucose level
The position of the kidneys are described as being _______
retroperitoneal, are located behind to the peritoneum of the abdominal cavity and are partly protected by the lower ribs
What is the indented area of the kidney called?
the renal hilum, the entrance for the renal artery + vein, ureter, nerves, lymphatics
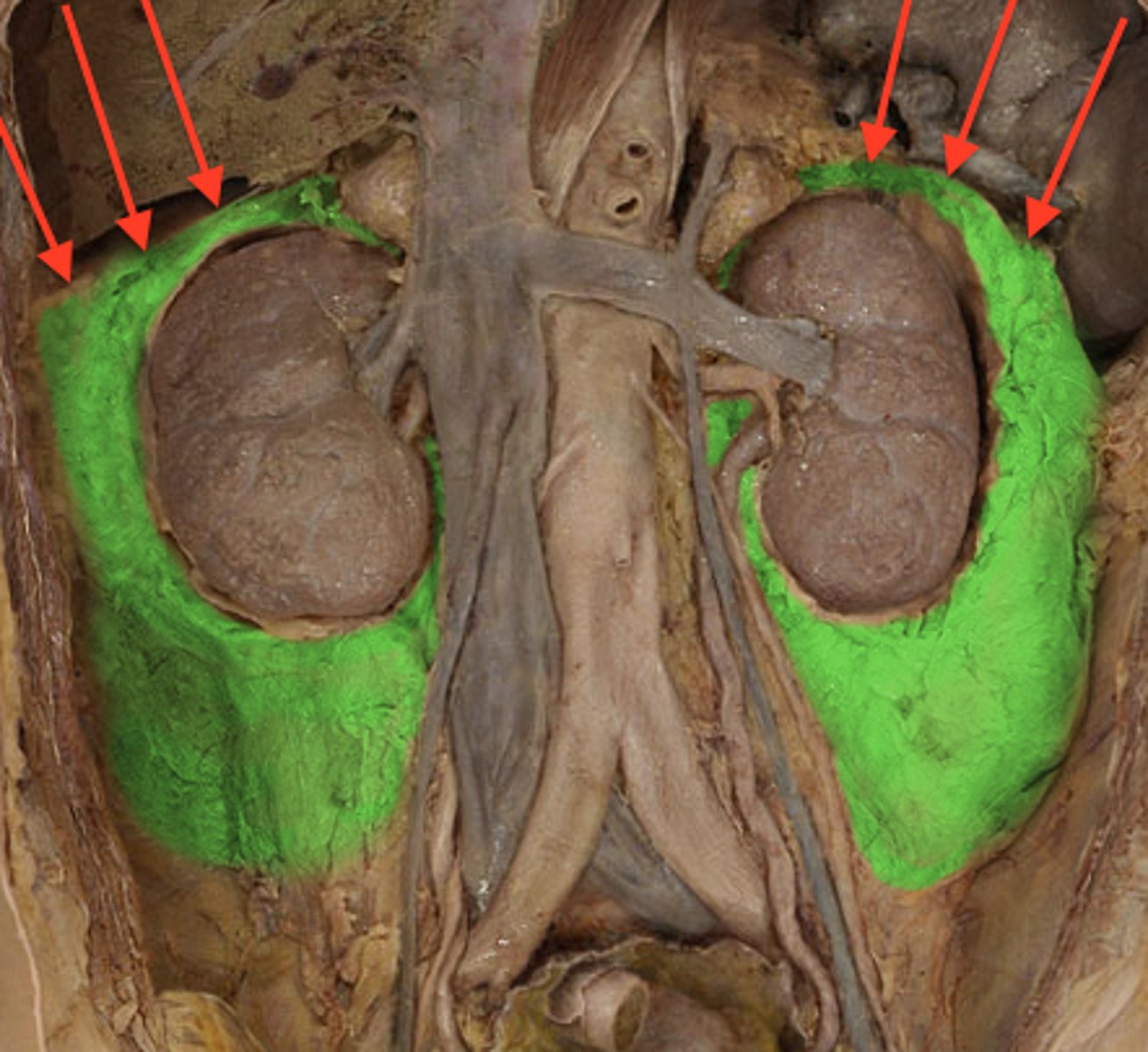
What are the external connective tissue layers of the kidney?
(superficial to deep)
1. renal fascia - anchors to other structures
2. adipose capsule - protects and anchors
3. renal capsule - continuous with ureter
The right kidney is ______ than the left
lower, due to the liver on the right side that pushes the kidney down.
What is the renal capsule?
connective tissue layer covering the kidneys. Smooth sheet of dense IR CT that is continuous with the outer coat of the ureter
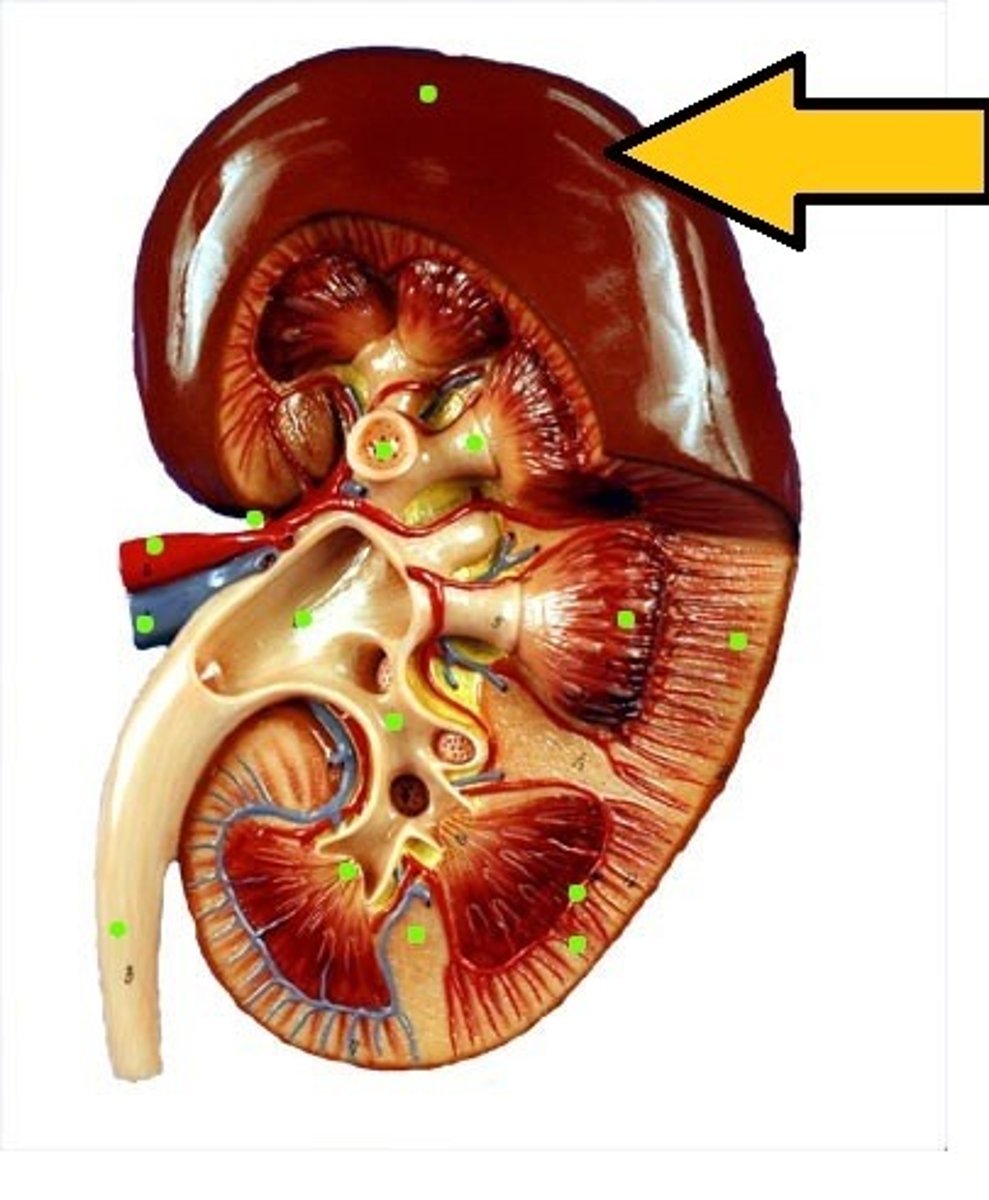
What is the adipose capsule of the kidney?
The middle layer of the kidney. A fatty mass of tissue that surrounds the renal capsule.
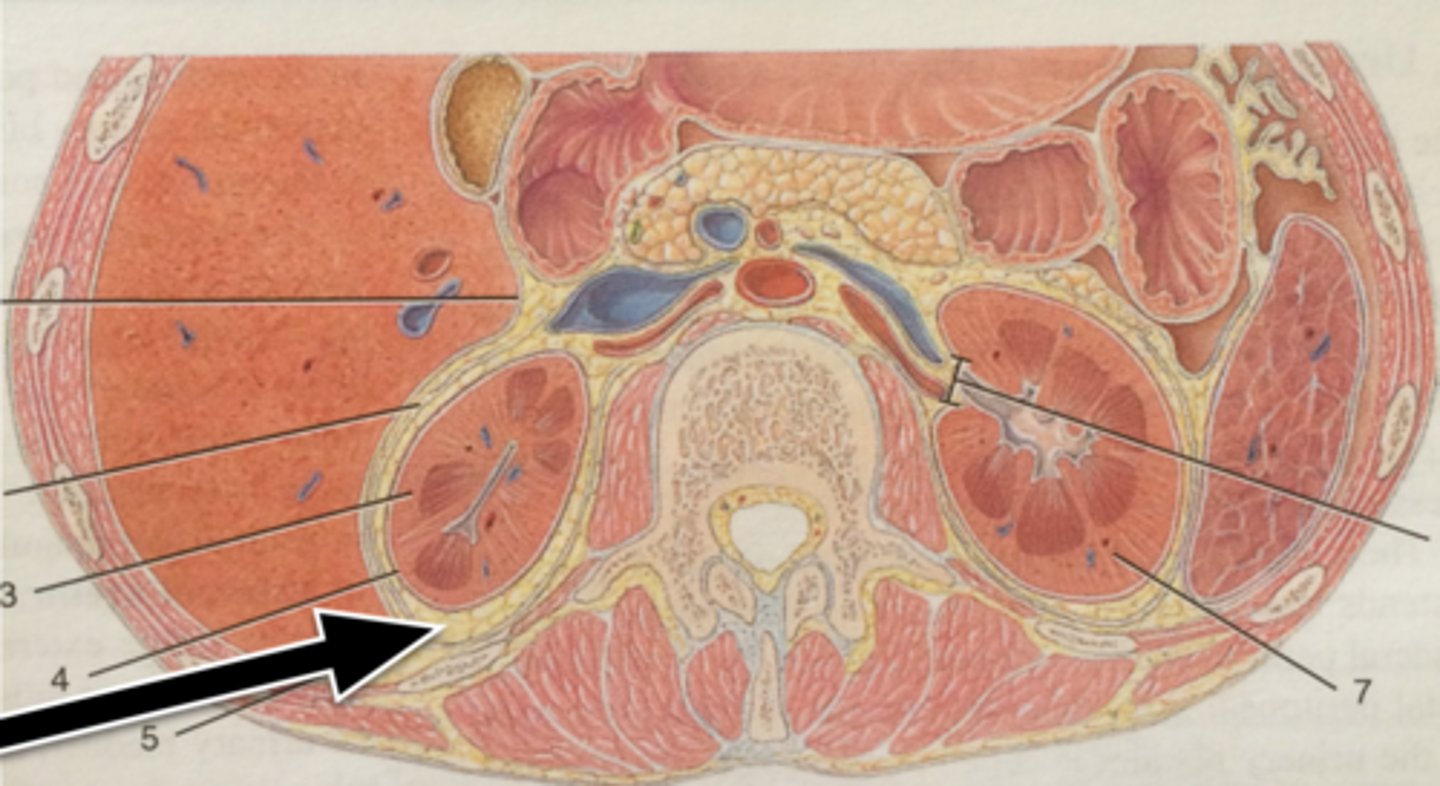
What is the renal fascia?
The superficial layer, thin dense IR CT anchors the kidney to surrounding structures to the abdominal wall.
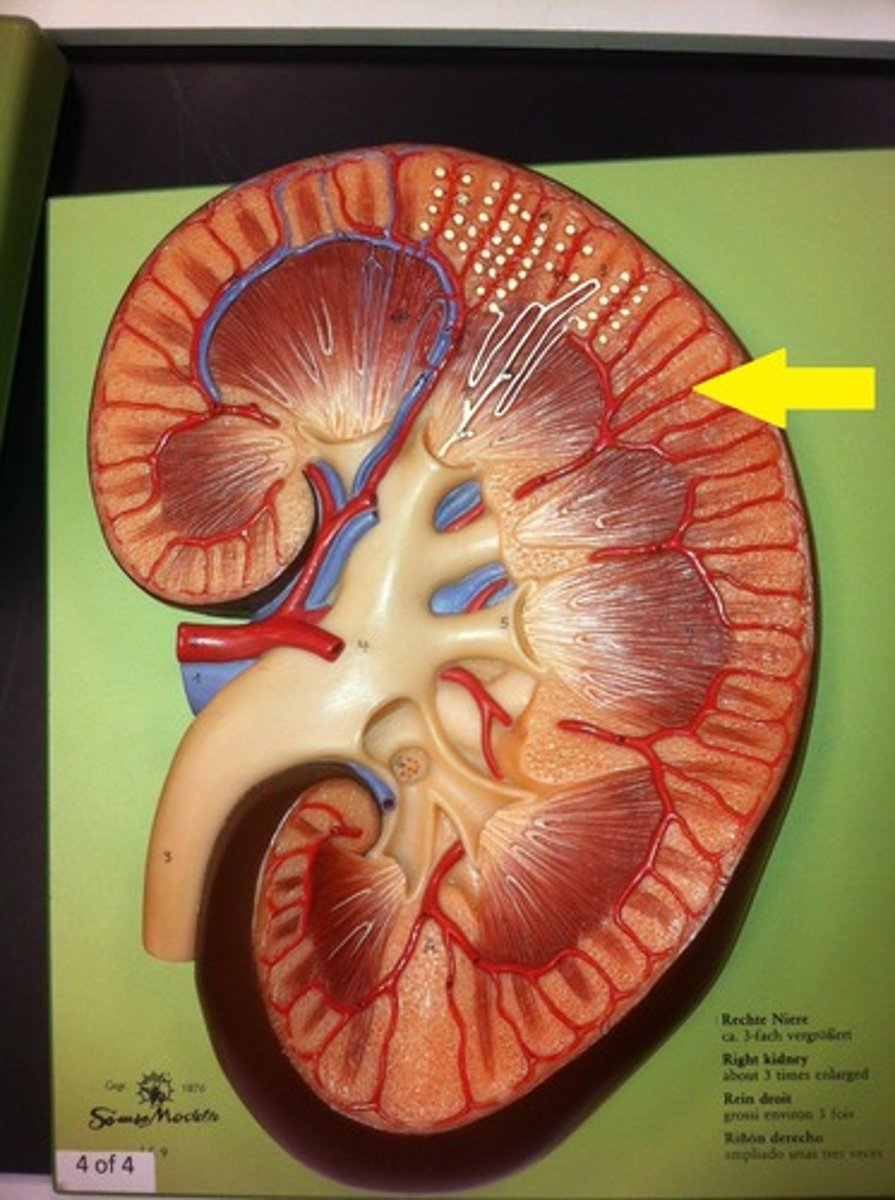
What is the renal cortex?
Outer portion of the kidney. Superficial, light and red region.
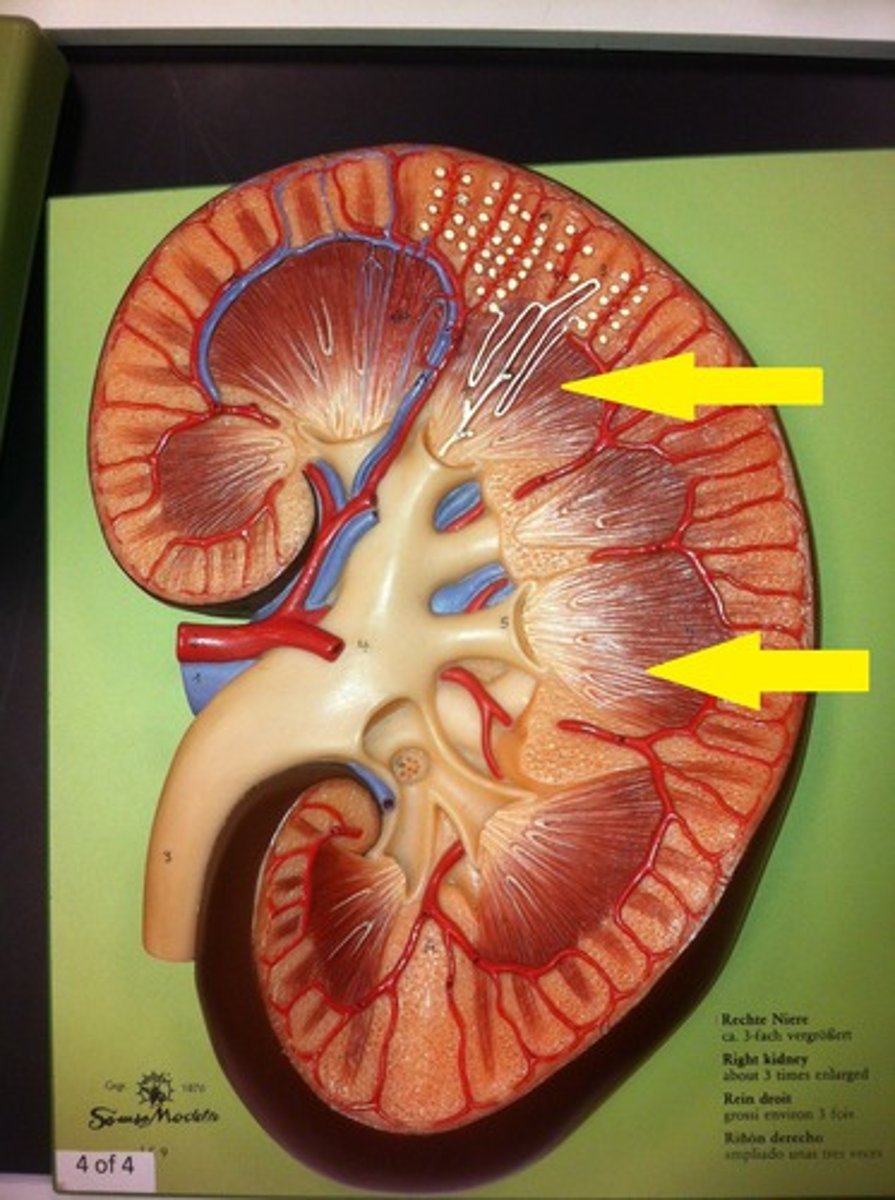
What is the renal medulla?
The inner portion of the kidney. A deep, darker reddish-brown inner region. Consists of renal pyramids.
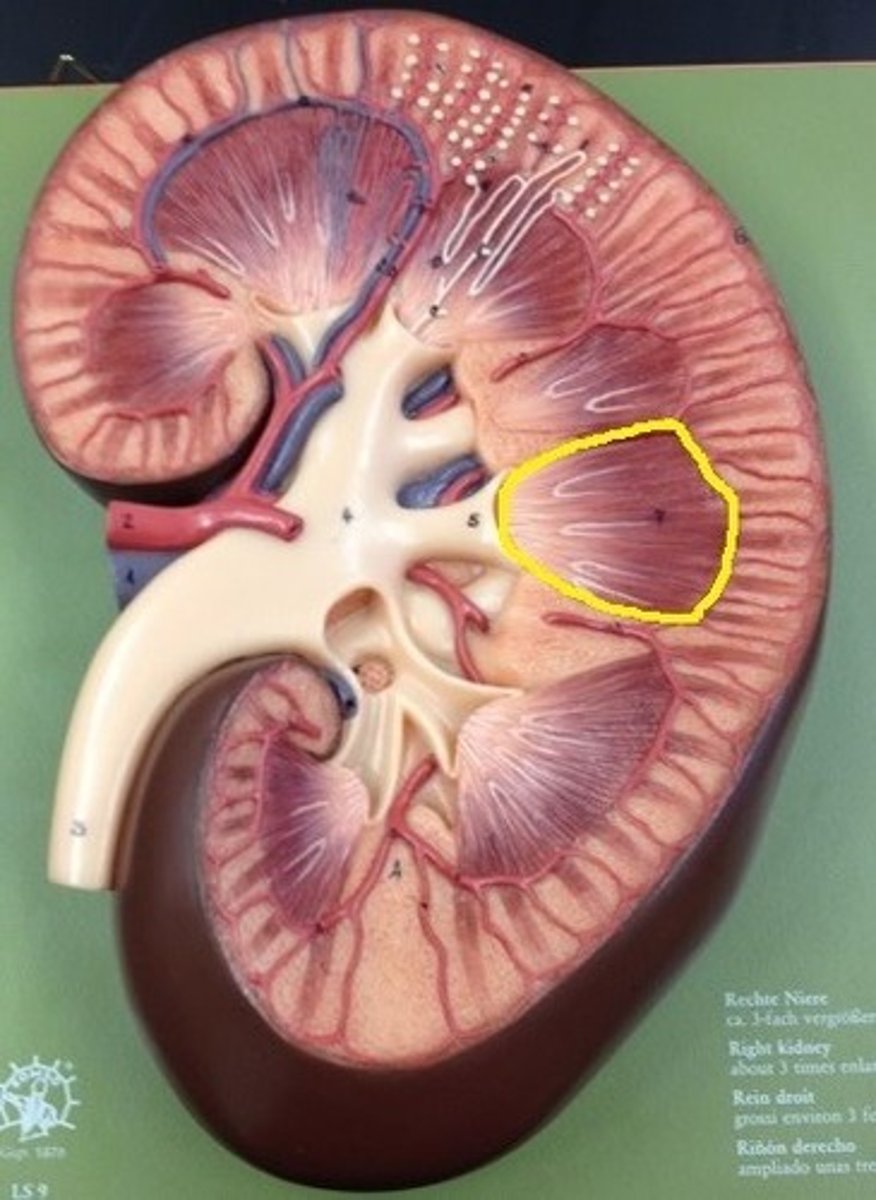
What are renal pyramids?
triangular divisions of medulla. The base of each faces the renal cortex, and the apex (the renal papilla) points toward the renal hilum.
Contains secreting apparatus and tubules
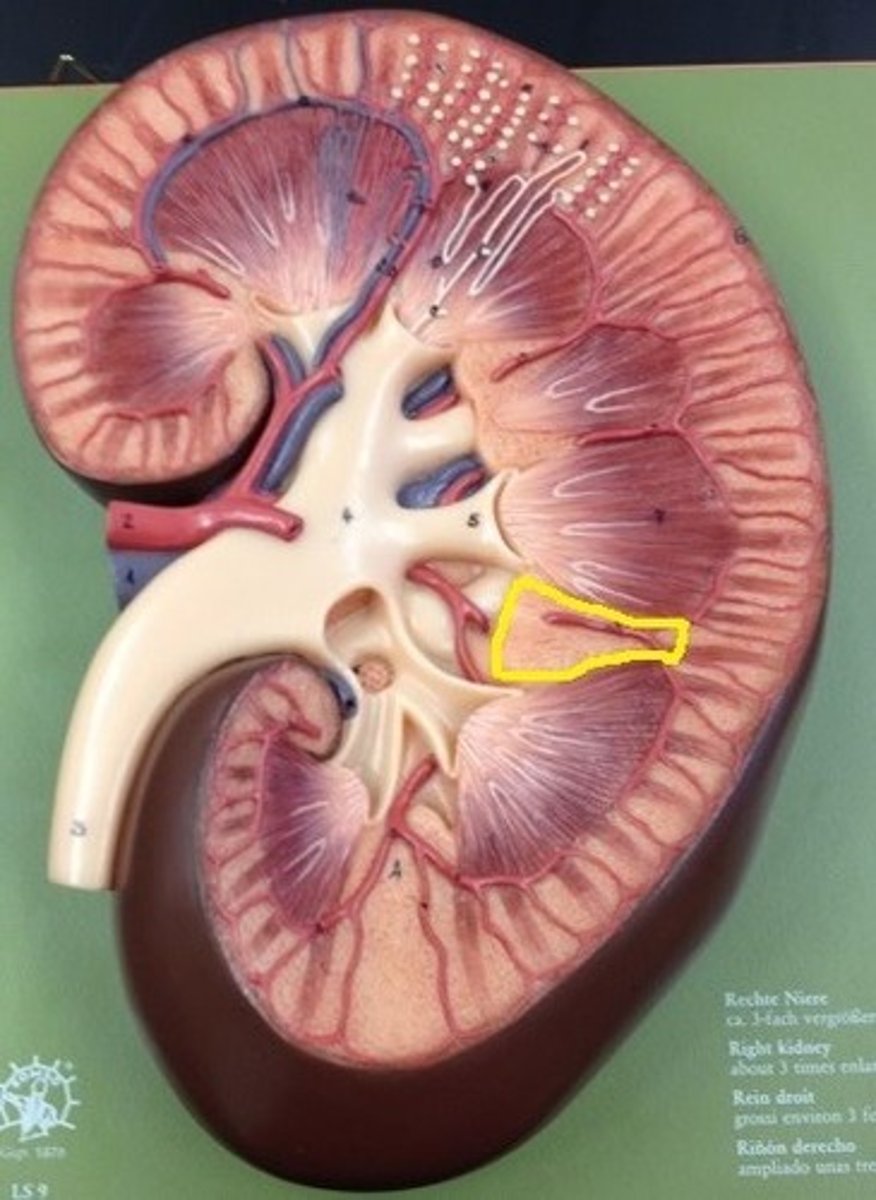
What is found at the narrow end of the renal pyramid?
The renal papilla
What are the renal columns?
Portions of the renal cortex that extend between renal pyramids. Anchors the cortex.
What is the normal pH level of the blood?
7.35-7.45
What is osmolarity?
How many particles are in a solution.
Higher osmolarity = higher pressure.
-detected by osmoreceptors
What are the functional unit of the kidneys?
Nephrons, contained within the renal pyramids and cortex.
Each kidney has ~1 million
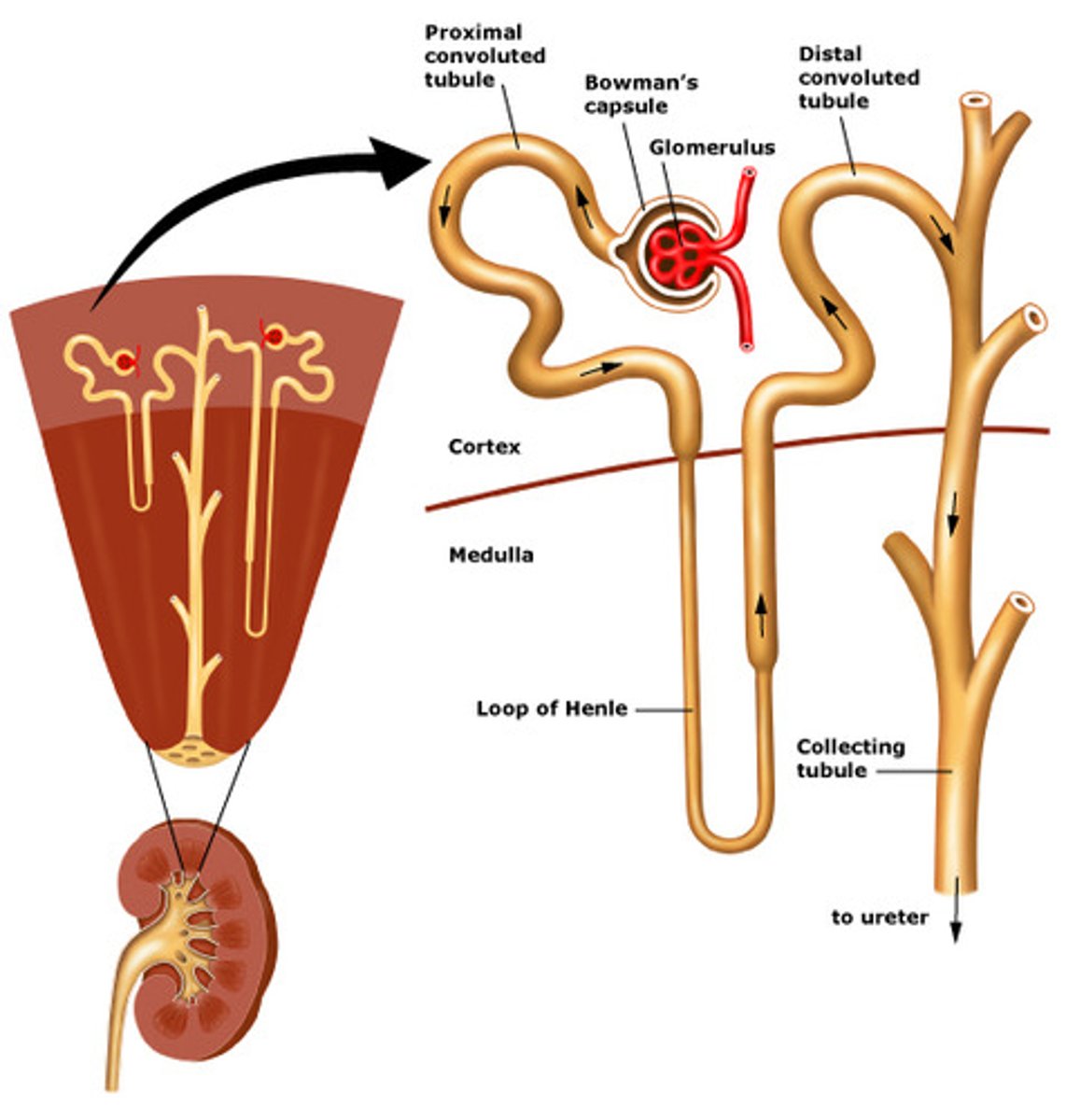
Where does filtrate formed by nephrons drain into?
Papillary ducts, called minor and major calyces.
Filtrate will then drain into the renal pelvis, out through ureter to urinary bladder
What are nitrogenous wastes?
Contain nitrogen, Ammonia, urea, creatine, uric acid
What is glucose in urine indicative of?
Exceeded capacity of the kidneys to reabsorb sugar. Kidneys should reabsorb all sugar, there should not be glucose in urine = diabetes
How much of the body's resting cardiac output is delivered to the kidneys?
20-25% via the right and left arteries, as kidneys remove waste and regulate volume and ionic composition of blood
What makes up the nerve supply to the kidneys?
-renal nerves carry primarily sympathetic outflow
--> to regulate blood flow through the kidneys
What are the two parts of the nephron?
1. renal corpuscle: where blood plasma is filtered
2. renal tubule:
where filtered fluid passes
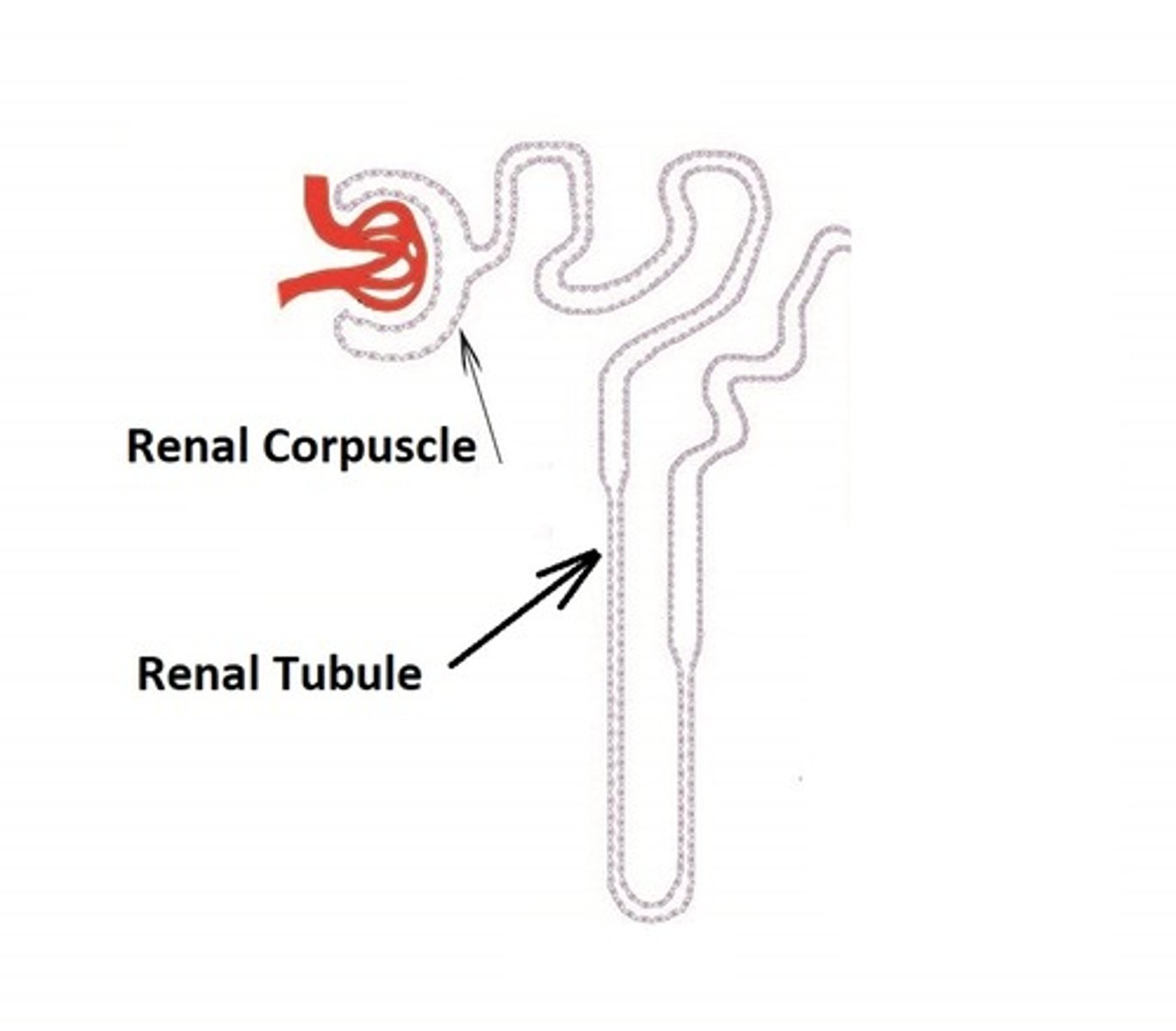
What are the two components of the renal corpuscle?
1. glomerulus - capillary network
2. glomerular capsule - double-walled epithelial cup that surrounds glomerular capillaries. Blood plasma is filtered in the capsule and the filtered fluid passes into the renal tubule.
What are the basic functions 3 of the nephron?
1. to filter
2. to absorb
3. to secrete
What are the three main sections of the renal tubule?
1. Proximal convoluted tubule
2. nephron loop (loop of henle)
3. Distal convoluted tubule
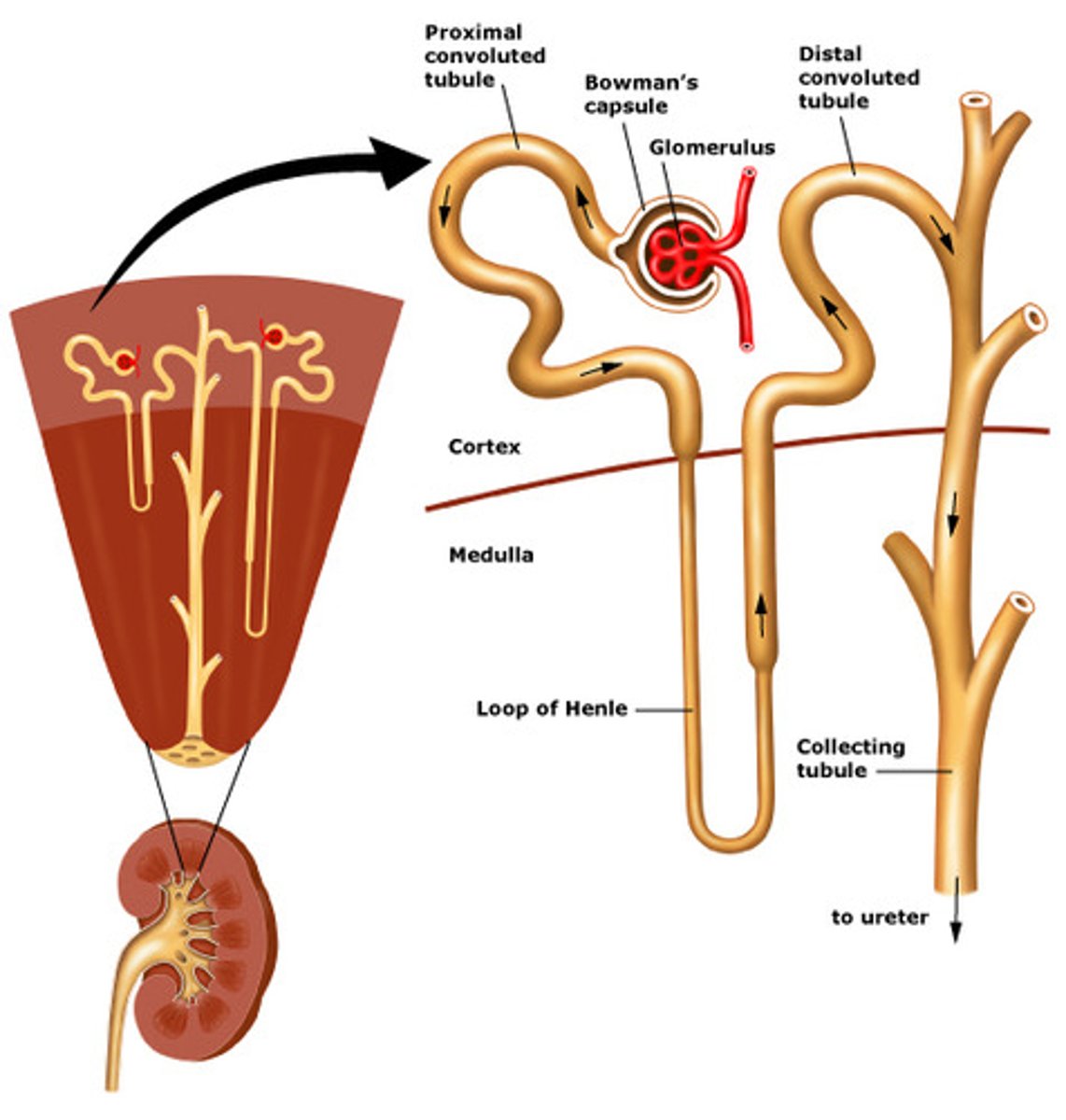
Where does the distal convoluted tubule empty into?
A single collecting duct. Which converge and unite into large papillary ducts.
what are peritubular capillaries?
the efferent arterioles divide into _____ ____, which surround tubular parts of the nephron in the renal cortex
What is the efferent arteriole?
Where glomerular capillaries reunite to form an ______ arteriole, to carry blood out of the glomerulus
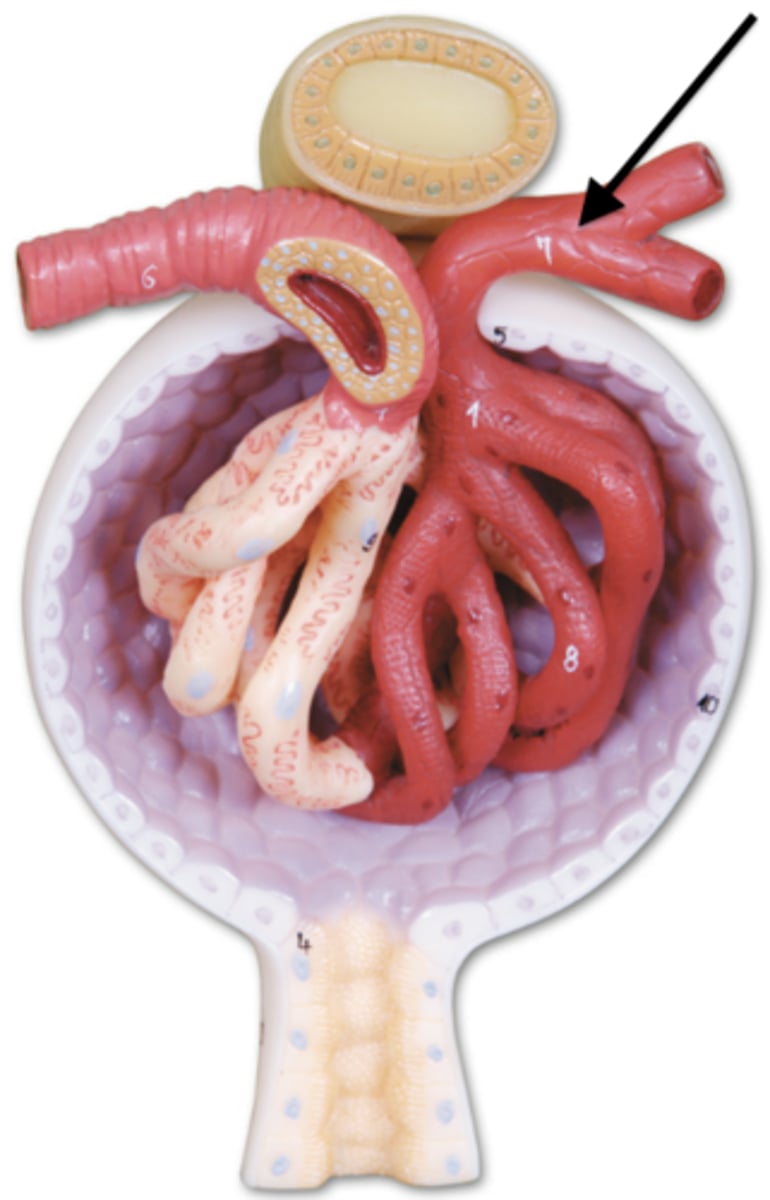
What are cortical nephrons?
85% of nephrons. -Renal corpuscles lie in outer portion of cortex
Have short nephron loops that receive blood supply from peritubular capillaries that arise from efferent arterioles
-create urine with osmolarity similar to blood
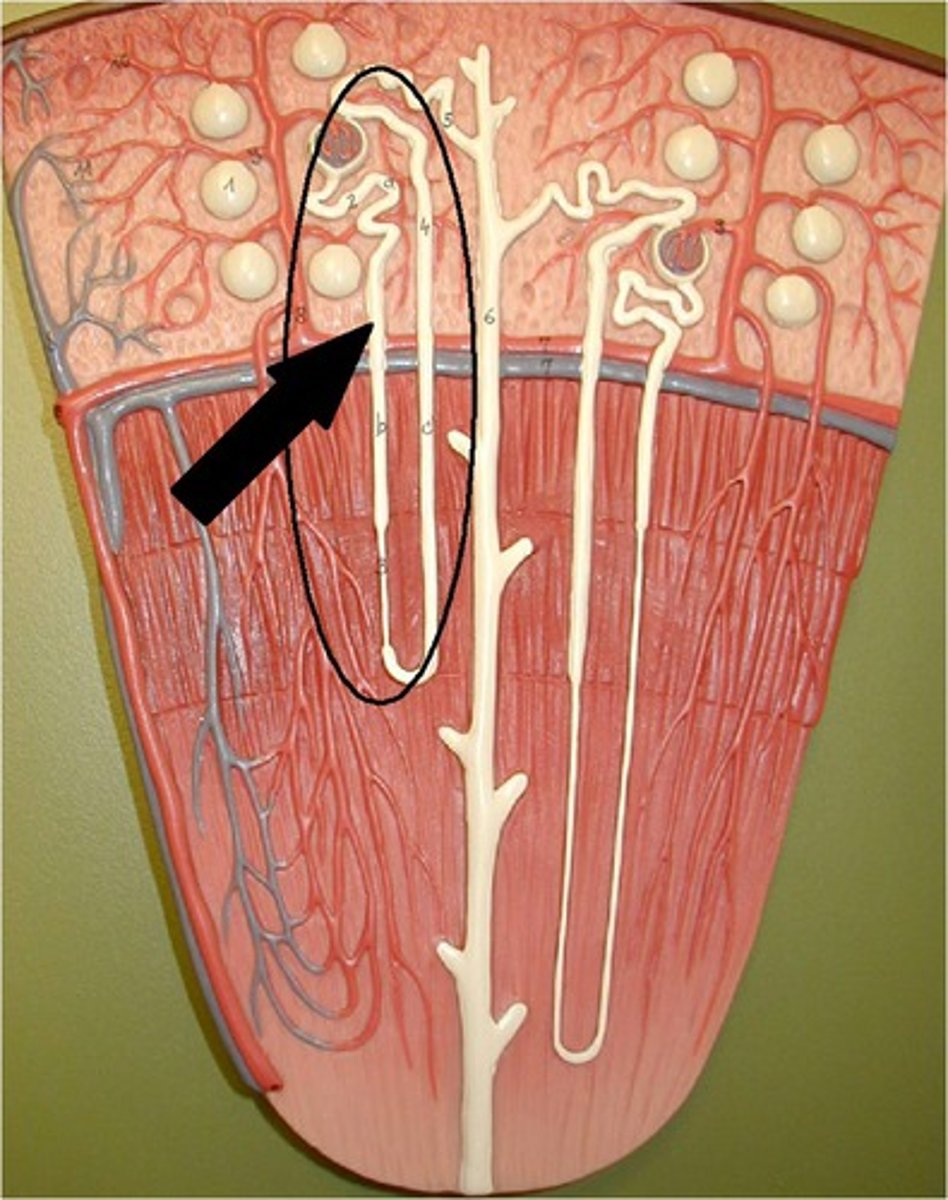
What are juxtamedullary nephrons?
15-20% of nephrons.
-renal corpuscles lie deep in the cortex, close to medulla
-have a long nephron loop that extends into the deepest region of the medulla
-receive blood supply from peritubular capillaries and form the vasa recta arising from efferent arterioles
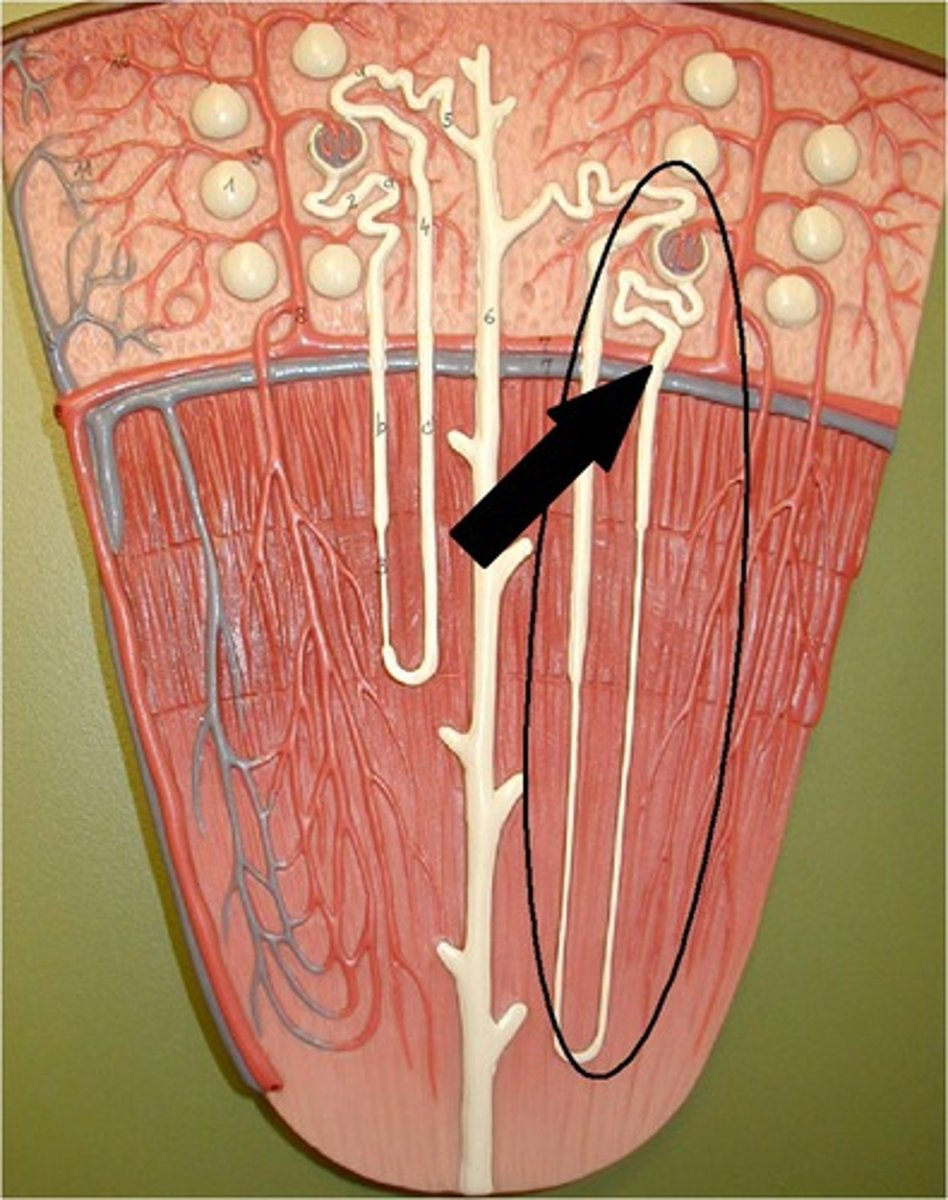
The glomerular capsule consists of what two layers?
Visceral and parietal layers.
-visceral: podocytes that wrap around endothelial cells of the glomerular capillaries, form the inner wall of the capsule
-parietal:
simple squamous epi. forms the outer capsule wall
Fluid filtered from the glomerular capillaries enter the _____ _____
capsular space, between two layers (visceral, parietal) of the glomerular capsule.
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
In the nephron, the final part of ascending limb of nephron loop makes contact with the afferent arterole of the renal corpuscle. -Two cell types here: macula densa, juxtaglomerular cells