Social 20: Chapter 7/8 Study Guide
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Foreign Policy
the set of policies which influence decisions a country makes internationally.
course of action that a sovereign nation takes in its conduct with other nation-states or international organizations
(goals that outline how a country interacts with another.)
National Interest
cultural, economic, political, religious, or military goal of a nation
Nationalist
believes nation should spend its money on its citizens first, and citizens of other nations after
Internationalist
nation should care for both its own citizens and greater group of world citizens
Causes of WWI
Forces of:
Nationalism
Imperialism
Militarism
Formation of Alliances
Nationalism (a feeling)
The collective, shared sense of belonging of people who identify themselves as a nation
Imperialism
extending a country’s power and influence through military force or diplomacy.
resulted in clashes between nations for control over undeveloped countries that had raw materials or were situated in strategic locations.
Militarism
the belief that a country should have a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote its interests.
led nations to increase military spending and build up armaments.
took on a more important role in gov’t, especially in Germany.
Formation of Alliances
Europe was divided into two armed camps:
Triple Alliance
Triple Entente
“If other nations attack us, we will have other nation-states as backup”
“We must go to war because ___ is going to war”
“If we form an alliance, there will be more of us, therefore would make for a tougher battle. They cannot take on ALL of us”.
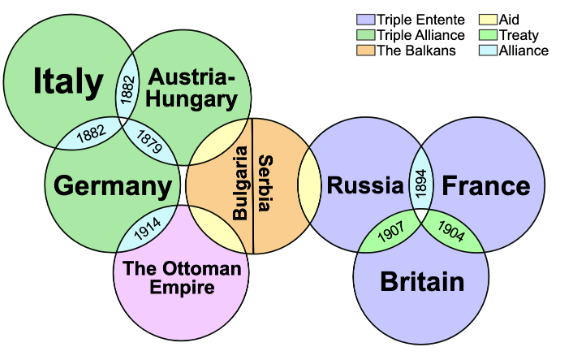
Triple Alliance (Central Powers)
Germany
Austria-Hungary
Italy
Triple Entente (Allied Powers)
Britain
France
Russia
WW1 Timeline
Bosnian Serb (Gavrilo Princip) assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne (Archduke Franz Ferdinand)
Austria Hungary → declared war on Serbia
Russia → defended Serbia (wanted influence in Balkan Region)
Germany → defended Austria-Hungary
Germany → declares war on Russia
Germany knows it might have to fight a two-front war.
Prepared with the Schlieffen Plan:
Phase 1: take out France quickly to take them out of the war.
Phase 2: turn against Russia
Britain → declares war on Germany
Germany moved troops through Belgium, a neutral area. Violating Treaty of Neutrality.
Britain → defends Belgium neutrality
Aids France on declaring war on Germany and its allies (Triple Alliance)
British Empire was now at war.
Triple Entente + Serb VS. Triple Alliance + Turkey.
Italy switches sides and joins the Triple Entente.
Declares war on Austria Hungary and severing ties with Germany.
Switches side because was offered land. (Treaty of London)
America joined Triple Entente.
Results of WWI
Trench Warfare
Millions Dead
War of Attrition
military strategy → to repeatedly wear out the other side.
Paris Peace Conference (1919)
Treaty of Versailles was negotiated.
Treaty of Versailles
Woodrow Wilson outlined a blueprint for peace in Europe
Known as the Fourteen Points → a foreign policy that was applied for all Allies.
The Big Four
Clemenceau (France)
Woodrow Wilson (USA)
Lloyd George (Britain)
Orlando (Italy)
What did the Big Four want with the Treaty?
Clemenceau (France):
wanted to cripple Germany so that they would never wage war again.
Woodrow Wilson (USA)
did not feel harsh punishment was the way.
wanted to create a humane treaty with Germany.
Lloyd George (Britain)
promised British that Germany would pay for the damages of the war.
wanted Britain to maintain access to colonies without Germany threating access.
Orland (Italy)
wanted land if they switched up.
Rhineland
a region on both sides of the Rhine River in western Germany-Industrial key location.
was to be demilitarized
Reparation Payments
War Reparation Commission determined:
Germany had to pay $33 billion in reparations.
for death and damages incurred by the victorious nations.
Expansionism (example of foreign policy)
a policy advocating for territorial or economic expansion.
often pursued aggressively.
initiated the WW2.
Reasons for Expansionism and how?
During Interwar period and Great Depression, leaders of Germany, Italy, Japan → needed more land to accomplish their goals!
racial, economic factors and empire building were used to justify the foreign policy.
Japan’s Expansionism
Was behind in all aspects due to isolationist policies.
Swiftly changed from feudal, agricultural society → modern, industrialized.
Believed it was their right to colonize in the Pacific → saw it as a “obligation” to liberate other Asian Nations from EU and NA domination.
Wanted to emulate the foreign policies of US and EU nations.
Japan also needed more resources from other Asian countries to support its large population.
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
Japan expansionism/domination of East Asia
Manchuria (China)
Japan’s population increased greatly → country was no longer self-sufficient in food production.
completely depended on international trade in Manchuria (China)
Japan built railroads and invested large sums of money in Manchuria Economy.
was bombed later on, many believed it was staged by Japan itself.
Italy’s Expansionism
Fascist Leader Mussolini came into power → wanted to create a new “Roman Empire”.
Took over a financially strained society that felt wronged by Treaty of Versailles.
Wanted to bring back wealth and prosperity to the nation which also guided Italian foreign policy.
Abyssinia (Ethiopia)
Mussolini planned to unify the two Italian colonies in Africa by trying to conquer Abyssinia, which contained farm, coal, iron, copper and gold.
Two Italian armies invade Abyssinia
international community, struggling with the effects of the Depression → did little to stop the aggression.
Lack of resolve and aid from outside nations → served as a green light to Hitler, confirming his belief in the weakness of his enemies.
Germany’s Expansionism
Financially devastated due to the measures of the Treaty of Versailles
Loss of Territory
Extreme decrease in military might
All points of Treaty of Versailles damaged German people financially, politically, and socially. → this environment that Hitler capitalized on in order to gain power.
Anschluss (“connection, joining”)
An event that formed a union between Germany and Austria.
Breaking one of the conditions in the Treaty of Versailles (Union with Austria is forbidden)
Broke these conditions in an attempt to rebuild their nation’s capacity for war.
Appeasement
the policy of settling international conflicts by satisfying grievances through rational negotiation and compromise.
avoiding armed conflict → can be expensive and harmful
Ultranationalism
an extreme form of nationalism which promotes hostility and the interests and identity of one nation over and at the expense of others.
Propaganda
Information and ideas that are spread to achieve a specific goal.
often used to persuade people to think and behave in a certain way.
Techniques of Propaganda
Bandwagon
Card Stacking
Glittering Generalities
Name Calling
Plain Folks
Testimonial
Transfer
Military Service Act
attempted to recruit 100,000 more men into WW1
would be arrested if they didn’t enlist.
forced register or else treason
Self Determination
the process by which a group of people form their own state and choose their own government
War Measures Act 1914
Temporary removal of rights and freedoms in times of conflict
Rise of Hitler and Nazi Party
Hitler blamed Germany’s economic , political and social problems on:
Jews
Physically and Mentally Disabled
Homosexuals
Communists'
Feminist Groups
Democratic Socialists
Enabling Acts 1993
Helped Adolf Hitler get closer to his goal of achieving full control over the German Parliament
It granted Hitler the right to enact laws without consulting the German Parliament
Formed the legal and constitutional basis for the Third Reich because it allowed Hitler’s plans to deviate from the existing constitution
Hitler → The Dictator
Created his own form of Fascism - NAZISM
his ideology believed that there was one superior race → ARYANS
Used:
Propaganda
Youth movements
Elimination of his opposition force and terror
Scapegoats (Jewish , Communists , Liberals)
Hitler’s Pursuit of National Interest
Took advantage over the economic distress that overcame Europe following the Great Depression.
Manchuria, Abyssinia
1936 - Hitler had an army of almost 1 million strong, ordered Rhineland to be remilitarized
“Forbidden Union” with Austria is complete
Nazi Propaganda
Posters, movies, books to pursue the belief of the Aryan race and Hitler's domination
Mussolini
An Italian dictator that coined the term of “Fascism”.
individually weak, but collectively strong
Fascism
characterized by the exercise of control over virtually all aspects of the nation and its people by its rulers.
referring to the roman symbol for “power through unity”
Fascism Vs. Communism
Fascism (Mussolini and Hitler):
full control of social classes
prosperity of the nation matters more than individual rights and happiness
Communism:
full control for equality
Conscription
compulsory enlistment in military