L13 - cell migration + invasion
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
how does cytoskeletal organisation contribute to cell motility
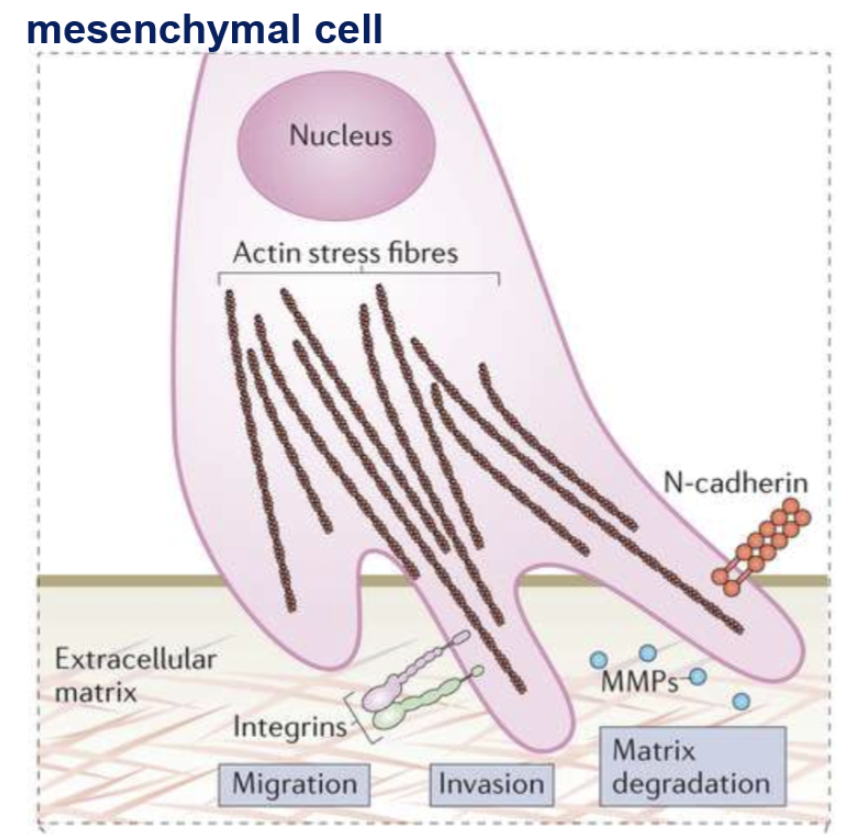
mesenchymal cell migration is promoted by remodelling of actin cytoskeleton
actin cytoskeleton
composed of actin filament (microfilaments) + accessory proteins (RhoGTPase, myosin) crucial for cell structure + cell migration
actin cytoskeleton remodelling
drives membrane protrusion
cell shape changes
maintaining cell-ECM linkages
cell contraction
cellular regulators of actin cytoskeleton
TGFb1 receptor
how does TBFb1 receptor activation contribute to changes in actin cytoskeleton
downstream pathways of TGF1b receptor drives alterations in Rho GTPase proteins (RhoA, cdc42, Rac1)
leads to disassembly of adherent junctions + remodelling of actin cytoskeleton
Rho GTPase cycle
binary molecular switch
inactive form: Rho bound to GDP
effector proteins drives activation (GTPase activating protein)
active form: Rho bound to GTP
conformational change allows interactions with downstream effectors
cdc42
actin polymerisation, filopodia formation
Rac
actin polymerisation, actin branching (lamellipodia formation)
Rho
drives actin polymerisation, stress fibre formation and contraction
focal adhesions
multi-protein complex that connect the extracellular matrix to the actin cytoskeleton in cells.
consists of actin-binding proteins, signalling proteins, structural proteins, integrin receptor (mediated interaction with ECM)
provides tensile strength, cell shape, facilitates membrane protrusions
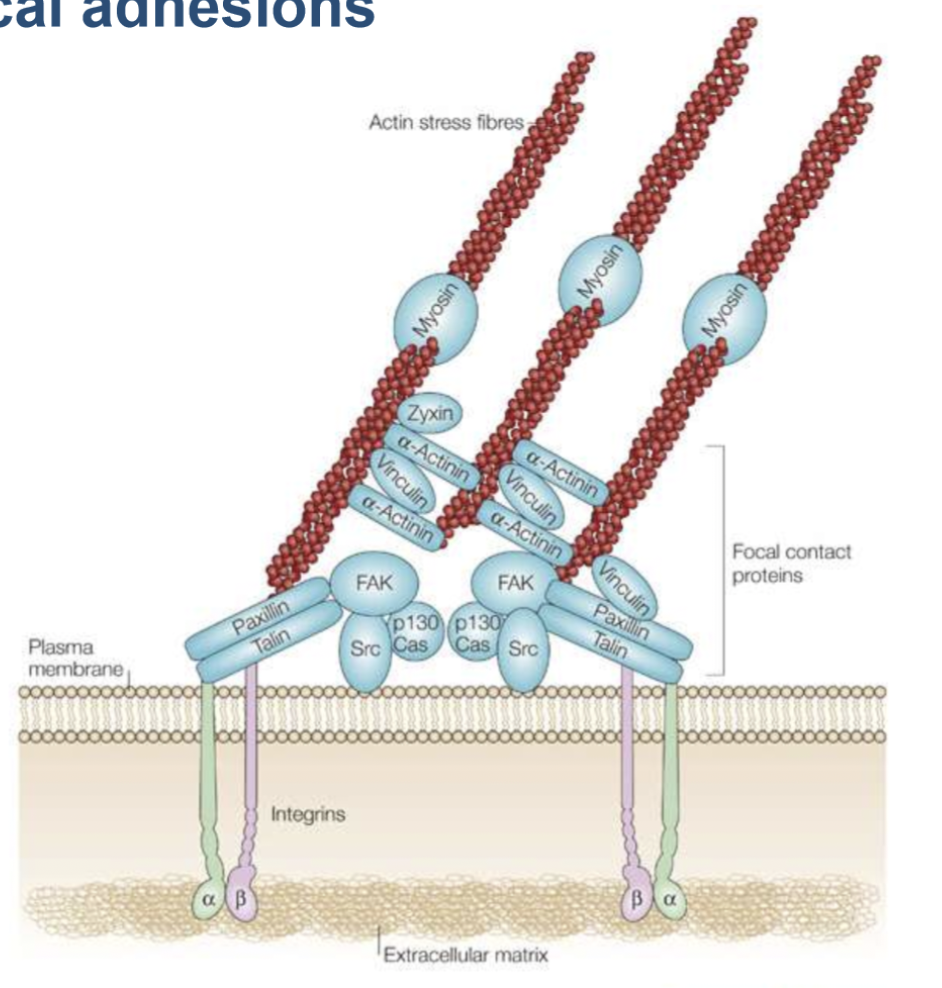
focal contact proteins
FAK - structural support
Src - signalling platform
vinculin and talin - actin binding proteins
paxillin - adaptor protein
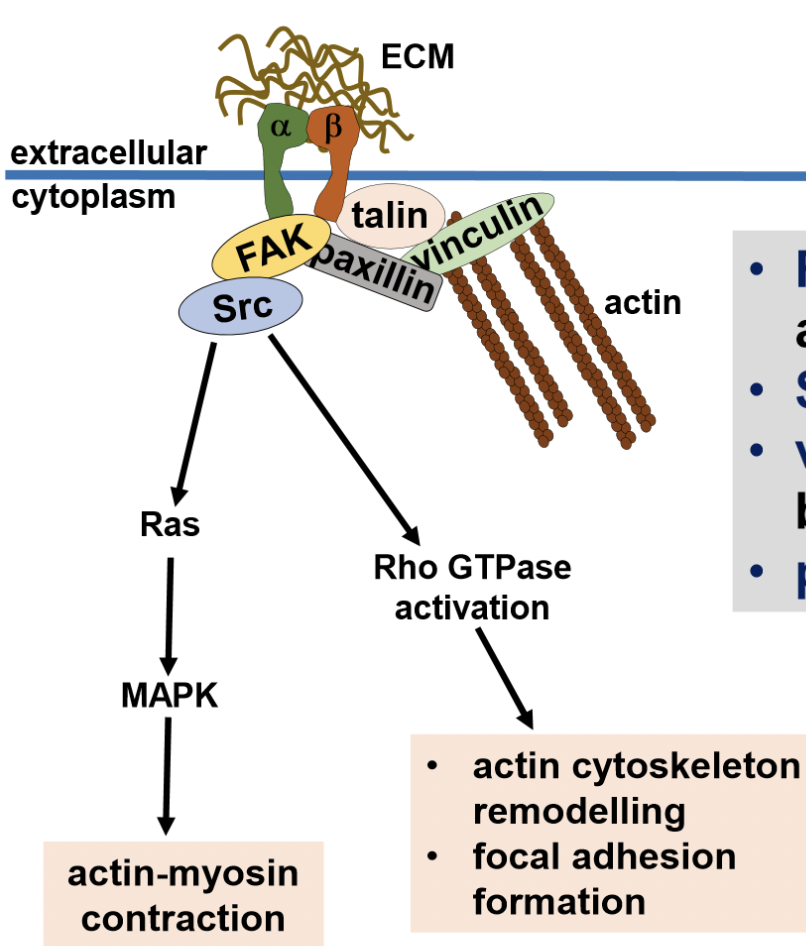
integrin receptors
heterodimeric transmembrane proteins that link internal actin cytoskeleton to ECM (alpha + beta chain)
how does coordinated cellular movement occur
extension - actin polymerisation (addition of G-actin monomers at + end of actin filament) and branching sends out filopodia extensions to local environment
adhesion - forms focal adhesions that anchor the cell, pull it forward
translocation - retraction is facilitated by increased tension/contraction of motor proteins (actin, myosin, sliding filament theory)
de-adhesion - breaking of focal adhesions at the rear of the cell, allowing for forward movement.
actin cytoskeleton organisation at leading edge of migrating cell
filopodia
bundles of parallel actin filaments that form thin, finger-like projections from the cell surface. facilitates membrane protrusions
two actin fibres linked together by actin cross-linking protein
lamellipodium
branched actin filaments that form ruffles facilitated by Arp2/3 complex. push celll membrane outward so it can make attachment sites.
actin cytoskeleton regulators
Arp2/3 - mediates actin branching + actin polymerisation - driven by Rac1 + Cdc42 effector proteins
Rho GTPase
leading edge of migration
presence of focal adhesions (cell-ECM attachments)
collective cell migration
group of cells linked by cell-cell junctions/adhesions migrating in a certain direction with leader cells that drive movement and pull the cell colony in one direction (facilitated by cell-ECM attachments)
types of cell migration
collective migration - cell-cell + cell-ECM interactions
mesenchymal cell migration (single cell)- cell-ECM interactions
amoeboid migration (single cell) - cytoskeletal + membrane protrusion/constriction (don’t interact well with ECM, weaves their way through gaps and holes)
scaffold cell-dependent migration - dependent on cell-cell interaction, migration along cells
difference between collective and single cell migration
collective: sheets, strands, clusters of cells
single: amoeboid or mesenchymal
mesenchymal vs collective cell migration
both path-generating
collective - retains cadherin cell-cell junctions, only exhibits focal cell-matrix adhesions + ECM degradation in leader cells
amoeboid vs mesenchymal cell migration
mesenchymal migration: path generating by degrading ECM, uses integral focal adhesions to anchor + interact with ECM
amoeboid migration: path finding by constricting their membrane to fit into gaps in ECM, relies on signalling events that shape their membrane. no cell-ECM interactions, less anchorage to ECM.
matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
zinc-dependent proteases secreted by cells into Extracellular space
secreted as inactive pro-form and activated in extracellular space
following activation, they cleave ECM proteins or activate latent TGFb1
regulate migration, invasion, proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis
the action of MT1-MMP (membrane type) in cancer cells
transmembrane MT1-MMP directly degrades ECM (basal lamina)→ allows cells to invade into underlying tissue layer
indirectly remodels through MMP-2 activation
can activate MMP-2 (soluble) within connective tissue layer (pro-MMP-2 → activated MMP-2) → facilitates ability to migrate and invade surrounding tissue
(TIMP)2
natural inhibitor of MMP activity. levels of TIMP2 regulate MMP2 activation
when TIMP2 levels are low - activation of MMP2
homodimerisation of MT1-MMP (one subunit acts as binding site, other acts as protease)
addition of TIMP-2 that recruits pro-MMP-2 to one MT1-MMP subunit
the free MT1-MMP subunit acts as protease, able to cleave and activate pro-MMP-2
release of active MMP-2
when TIMP2 levels are high - MMP2 inactive
TIMP2 binds on both monomers / subunits of MT1-MMP
TIMP2 inactivates protease
MT1-MMP unable to cleave and activate MMP2
invadopodia
actin-rich, filopodia-like structures that protrude from the plasma membrane, secretes MMPs and degrades ECM
invadopodia formation
initiation
cell senses local environment signals (TGFb)
integrins link to ECM by focal adhesions
assembly
Arp2/3 recruitment
drives actin polymerisation - helps membrane protrusion
maturation
secretion and activation of MMPs
MT1-MMP sent to tip to degrade ECM