BIO181 MOD3- DNA/RNA Structure, DNA Replication, and Central Dogma (gene expression)
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Cytosine (C)
Pyrimidine
Thymine (in DNA) (T)
Pyrimidine
Uracil (in RNA) (U)
Pyrimidine
Adenine (A)
Purine
Guanine (G)
Purine
What is a bacteriophage?
a virus that infects bacteria
The experiments by Hershey and Chase helped confirm that DNA was the hereditary material on the basis of the finding that:
radioactive phosphorus was found in the cell
DNA double helix does NOT have which of the following?
uracil
Which scientist reported the first demonstration of bacterial transformation—a process in which external DNA is taken up by a bacterial cell?
Frederick Griffith
Which of the following is NOT a component of a DNA nucleotide?
amino acid
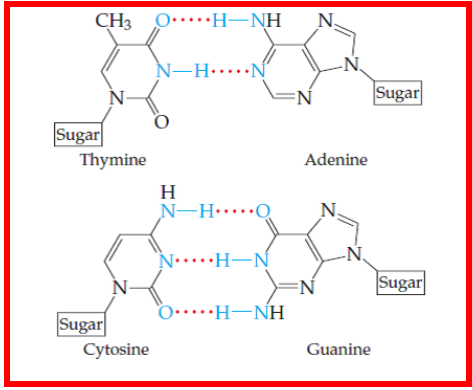
What type of bond links nitrogenous bases?
hydrogen bond
what bond links nucleotides?
phosphodiester bond
Phosphate of one group + sugar of another group=
phosphodiester bond
5’ end of DNA strand
Closest to phosphate group
required to add another nucleotide
free OH group
DNA replication model
semi-conservative
DNA polymerase function
adds complementary nucleotides to primer
Where does DNA unwind?
origin of replication
Helicase function
“unzips” DNA forming replication forks; breaks hydrogen bonds between bases
Single-stranded binding proteins
prevent strands of separated DNA from coming back together
Topoisomerase
binds ahead of replication fork to prevent supercoiling
RNA primase
synthesize RNA segment complementary to template strand
DNA polymerase II
adds nucleotides to the 3’ OH end of the primer
Which way does DNA polymerase synthesize?
5’-3’
Which way does DNA polymerase read?
3’-5’
Which way is the leading strand oriented?
5’-3’
Which way is the lagging strand oriented?
3’-5’
Prokaryotes have…
single origin of replication
Eukaryotes have…
multiple origins of replication
Ligase
joins DNA fragments by forming a phosphodiester bond between 3’ hydroxyl group and 5’ phosphate end
If the sequence of the 5'-3' strand is AATGCTAC, then the complementary sequence has the following sequence:
3'‘-TTACGATG-5’
How did Meselson and Stahl support Watson and Crick’s double-helix model?
They demonstrated that each strand serves as a template for synthesizing a new strand of DNA.
Which of the following components is not involved during the formation of the replication fork?
ligase
Which of the following does the enzyme primase synthesize?
RNA primer
In which direction does DNA replication take place?
5’-3’
The ends of the linear chromosomes are maintained by
telomerase
Which of the following is NOT a true statement comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication?
DNA replication always occurs in the nucleus.
What type of macromolecule is DNA helicase?
protein
What is the name of the region where the DNA double helix partially unwinds in preparation for transcription?
transcription bubble
Which DNA strand does RNA polymerase bind to for the process of transcription?
template strand
Which subunit of the E. coli polymerase confers specificity to transcription, helping polymerase begin from an appropriate initiation site?
σ
In which direction does RNA polymerase read the DNA strand?
3’-5’
The -10 and -35 regions of prokaryotic promoters are called consensus sequences because ________.
they are similar in all bacterial species
In which direction does RNA polymerase build the growing mRNA?
5’-3’
Which pre-mRNA processing step is important for initiating translation?
5’ cap (7-methylguanosine cap)
What processing step enhances the stability of pre-tRNAs and pre-rRNAs?
methylation

A scientist identifies a pre-mRNA with the following structure. What is the predicted size of the corresponding mature mRNA in base pairs (bp), excluding the 5’ cap and 3’ poly-A tail?
295bp
σ
involved in identifying the initiation site
α (x2)
assemble the polymerase on the DNA
β
binds to the RNA nucleotide about to be added to the mRNA
β’
binds to the DNA template strand
The sequence of a DNA fragment is shown in blue. The top strand is used as a template for RNA polymerase. What would be the sequence of the RNA transcript?
5’ - CTAATGC - 3’
3’ - GATTACG - 5’
3’-GAUUACG-5’
A mutation to which subunit of RNA polymerase would likely result in the enzyme adding the wrong RNA nucleotide to the growing mRNA chain?
β
Use the following mRNA to determine which strand below is the template strand.
mRNA strand: 5’ AUCCGUCGAAU 3’
Strand A: 3’ A T G C T A A G C T G C C T A G G G T 5’
Strand B: 5’ T A C G A T T C G A C G G A T C C C A 3’
strand B
The AUC and AUA codons in mRNA both specify isoleucine. What feature of the genetic code explains this?
degeneracy
How many nucleotides are in 12 mRNA codons?
36
In eukaryotes, the RNA components of ribosomes are synthesized in the ________.
nucleolus
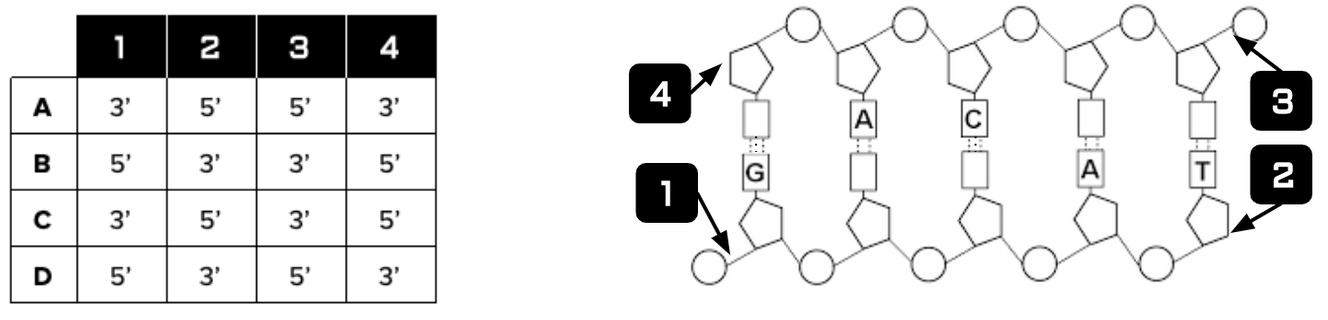
Which of the following combinations (A-D) accurately describes the directionality of the double stranded DNA fragment below? Select only ONE answer choice.
D
Of the following four 15 base-pair, double-stranded DNA sequences, which will be most stable at higher temperatures? In other words, which will most likely remain in a double-stranded form? Select only ONE answer choice.
CCCGCATCGCCATCG
Imagine that the value of a nucleotide is calculated as the percent of DNA it accounts for. For example, 30% of DNA may be A. If this were the case, the value of (A + C)/(G + T)... Select only ONE answer choice.
is equal to one if the DNA is double-stranded.

Consider the following sequence of bases in DNA that are part of the TEMPLATE STRAND of a gene that codes for a particular mRNA strand. The introns and exons have been indicated in the image below. Nucleotides that are bolded are part of exons; nucleotides that are not bolded are part of introns.
Assuming transcription occurs, the sequence of the mRNA transcript ultimately found in the cytoplasm for this sequence of bases would be: Select only ONE answer choice.
5’ – UGC CAG UCC GUU – 3’
True or False: Genes code for chromosomes and chromosomes are responsible for the individual traits we observe.
false
The backbone of this polymer is shown in box ______. The functional group denoted with ______ is necessary for the addition of the next monomer. Select only ONE answer choice.
W, X
Given the coding strand of DNA below, choose the correct RNA transcript.
5’ – ATGGCATTAGGGCGTTGA – 3’
5’ – AUGGCAUUAGGGCGUUGA – 3’
Which protein is responsible for holding the two parental DNA strands separated for DNA replication to proceed?
single strand binding protein