SOLO 3 -- dematiaceous fungi, subcutaneous/cutaneous mycoses, dermatophytes
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
dematiaceous fungi list:
aureobasidium pullulans
Cladosporium spp.
Helminthosporium
bipolaris
cuvularia
Exserohilum
Alternaria
Ulocladium
stemphylium
Epicoccum
Nigrospora
Chaetomium (perithecia w/ ascospores)
Phoma (pycnidia)
dematiaceous fungi overview:
dark colonies — melanin pigment in cell walls
diseases are classified according to presentation and appearance of organism in tissue:
chromoblastomycosis
phaeohyphomycosis
mycetoma
chromoblastomycosis
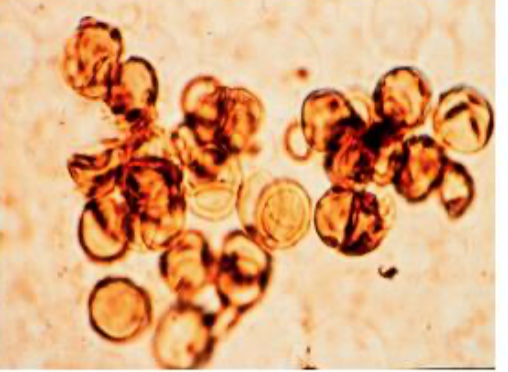
fungi in tissues are seen as sclortic bodies or “copper pennies.”
chronic infection, which causes warty nodules, tumor-like masses, or cauliflower-like lesions containing sclerotic bodies
the lesions usually develop in subcutaneous tissue of the lower extremeities but are sometimes on other exposed areas, such as hands, head, or trunk
phaeohypomycosis
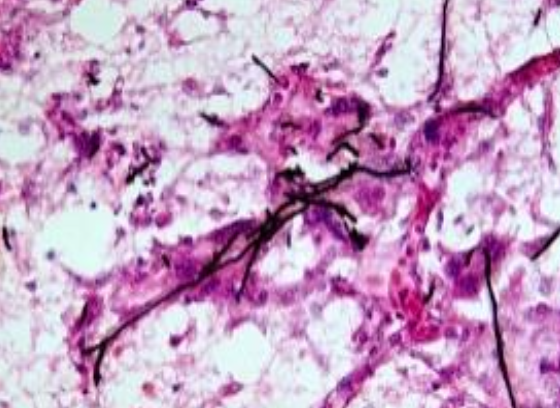
fungi appear as dark, yeast-like cells, pseudohypha-like elements, variously shaped hyphae, or any combination of these forms
can be cutaneous, subcutaneous, or systemic
mycetoma
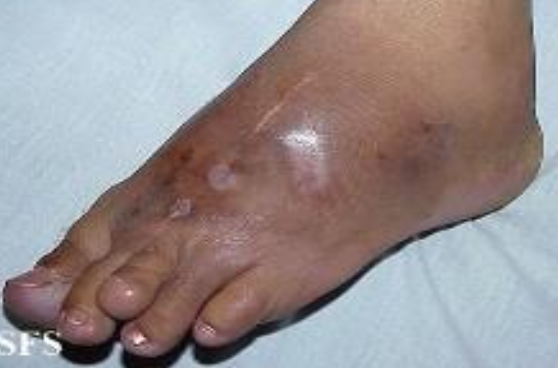
characterized by swollen, tumor-like lesions containing granular pus through draining sinuses
very few of the meatiaceous fungi are etiologic agents of this disease
usually in hands or feet
Aureobasidium pullulans basic info
Common contaminant; rare agent of phaeohypomycosis
moderately rapid growth
white at first, matures to black, shiny, and leathery; black reverse
Aureobasidium pullulans microscopic morphology
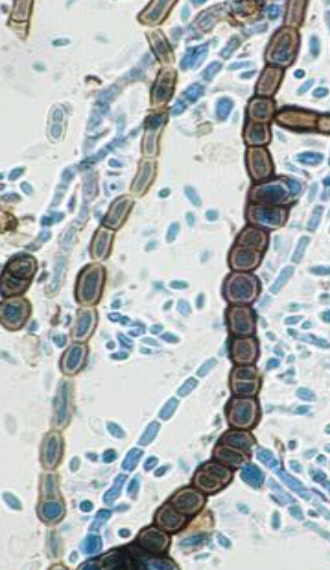
young colonies are typically yeast-like
two types of hyphae:
hyaline, delicate: thin walled, producing conidia directly from the walls at certain fertile points
thick walled, dark, closely seprated: with some cells forming short tubes which produce hyaline and oval onidia
What can Aureobasidium pullulans be confused with?
Exophilia (wangiella) dermatitidis
Hortaea (phaeoannellomyces) werneckii
***review rate of growth and microscopic morphology for each***
Cladosporium basic info
common contaminant; must be differentiated from cladophialophora spp.
Cladophialophora carrionii causes chromoblastomycosis (Australia, Venezuela, South Africa)
Cladophialophora bantiana causes cerebral phaeohyphomycosis
moderately rapid growth
greenish brown to black colonies, becoming heaped or folded; black reverse
Cladosporium microscopic morphology
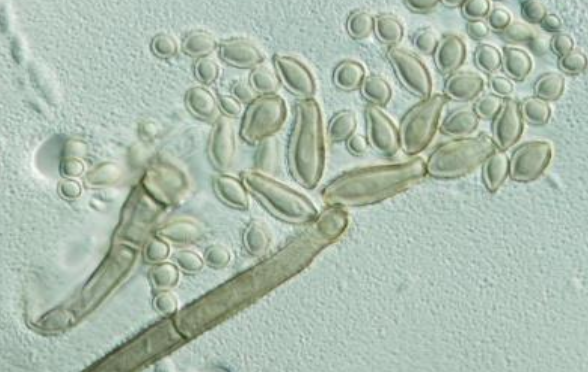
dark septate hyphae
branched conidiophores, which may produce two or more conidial chains
conidia are oval and form branching tree-like chains, which are easily dislodged, revealing dark spots (hila -scars of attachment)
“shield cells” are also present
Helminthosporium spp. basic info
common contaminant
rapid growth
dark gray to black colonies, black reverse
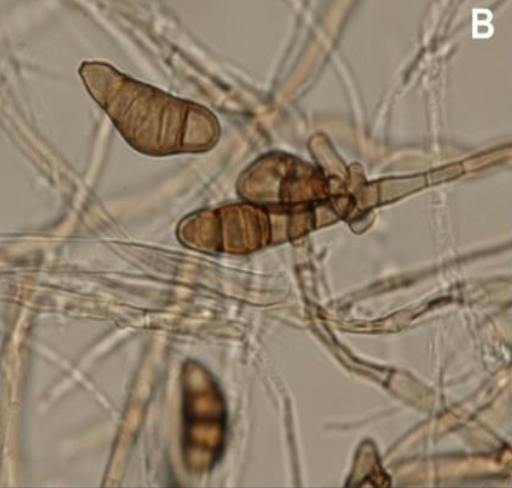
Helminthosporium spp. microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
conidiophores are brown and determinate (do not elongate at the point of conidium formation)
condidia characteristics
form along sides of conidiophores
frequently in whorls
large
club-shaped w/ broader end toward the conidiophore
usually contains six or more cells
Bipolaris spp. basic info
common contaminant, but occasionally can infect the eye, bones, aorta, sinuses, lung, brain, and skin
rapid growth
graish brown colonies at first, becomes black w/ matted center and raised gray periphery; black reverse
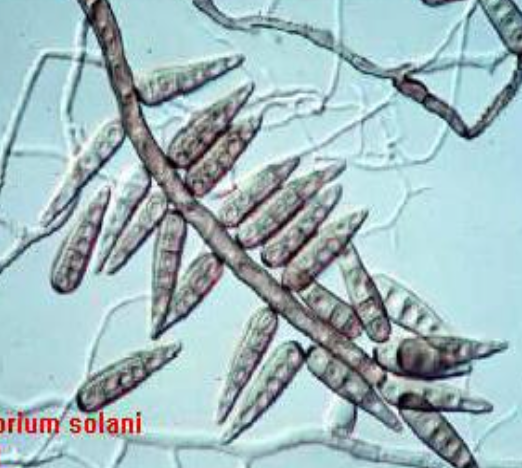
Bipolaris spp. microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
conidiophores elongate and bend at the point where each conidioum is formed (sympodial geniculate growth)
conidia are thick-walled, oblong, or cylindrical, have 3-5 septations, and a slightly protruding hilum
Bipolaris spp. confirmation
germ tube test must be performed
differentiates Bipolaris spp. from Drechslera spp.
bipolaris spp. germinate at the ends (poles) of the conidia
Drechslera spp. germinate on the sides of conidia (perpendicular to axis)
Curvularia spp. basic info
contaminant and opportunistic pathogen; can cause phaeohyphomycosis
rapid growth
colony surface is dark olive green to brown or black w/ pinkish gray surface; dark reverse
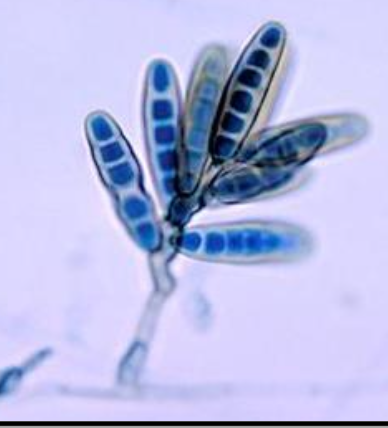
Curvularia spp. microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
simple or branched conidiophores that are geniculate
large conidia, which usually contain four cells, appear curved due to the swelling of the central cell
The central cell also tends to be darker than the end cells
Exserohilum spp. basic info
causes phaeohyphomycosis
rapid growth
surface is dark gray or black and cottony; black reverse
Exserohilum spp. microscopic morphology
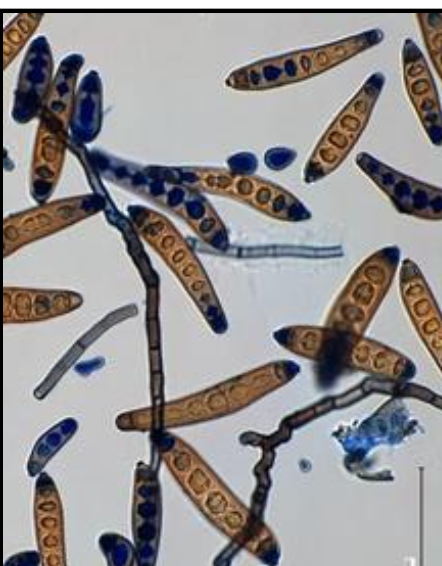
septate hyphae
elongated, geniculate conidiophores
conidia are long, fusiform, and usually has 7-11 septa
hilum is dark, conspicuous, and usually square
germ tubes are produced along the axis of the conidium
distinctive dark septum at each end of cell (basal and distal septa)
Alternaria spp. basic info
common contaminant but sometimes assoc w/ phaeohyphomycosis
rapid growth
surface is graish white and wooly, becoming greenish black or brown; reverse is black
Alternaria spp. microscopic morphology
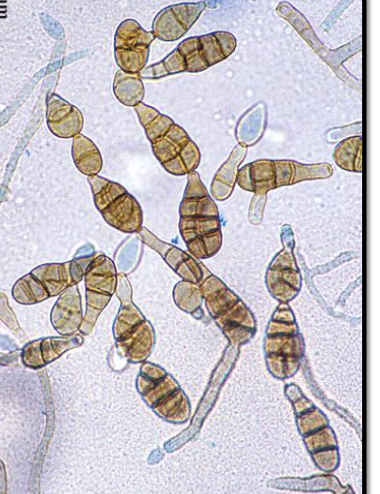
septate hyphae
septate conidiophores w/ zig-zag appearance
large conidia w/ transverse longitudinal septations (muriform)
conidia form singly or in chains, and take club-like shape
Ulocladium spp. basic info
common contaminant; rarely causes phaeohyphomycosis
rapid growth
surface is cottony, dark brown to black; black reverse
Ulocladium spp. microscopic morphology
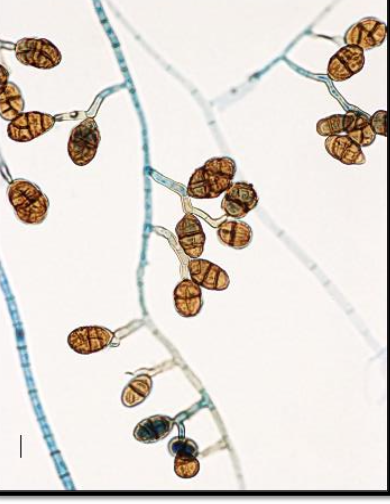
septate hyphae
simple or branched conidiophores that are bent at the point of conidial produciton
conidia can be smooth/rough, round to oval, w/ transverse and logitudinal septations (muriform)
Pithomyces spp. basic info
common contaminant
rapid growth
surface is cottony, brown to black ;dark reverse
Pithymyces spp. microscopic morphology
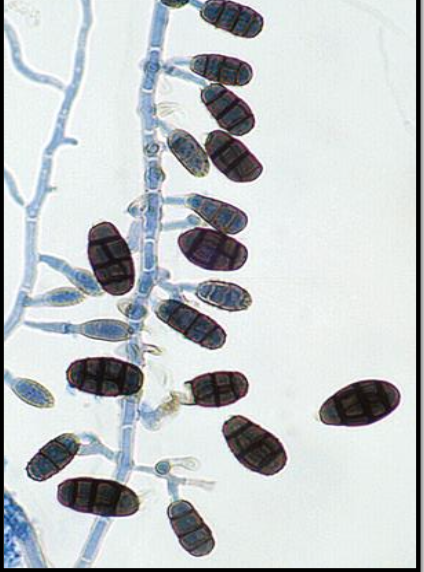
septate hyphae
peglik conidiophores (much shorter and simpler than Ulocladium)
conidia are oval, yellow to brown, and rough w/ transverse and longitudinal septations
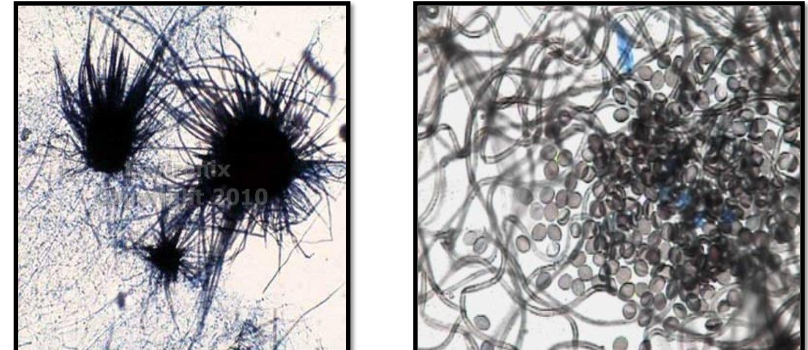
Stemphylium spp. basic info
common contaminant
rapid growth
surface is browth to balck and cottony; black reverse
Stemphylium spp. microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
simple or branched conidiophores w/ swollen terminus bearing individual conidia
The condia are smooth/rough, round or oval, and have transverse and longitudinal septations, sometimes marked w/constriction at the central septum
Epicoccum spp. basic info
common contaminant
moderatley rapid growth
cottony, yellow to orange becoming dark w/ age colonies; reverse is sometimes red w/ diffusible pigment that may turn the agar yellow, orange, red, or brown
Epicoccum spp. microscopic morphology
conidiophores form in clusters on hyphae by repeated branching to form a dense mass from which conidia arise
Young conidia are smooth/round or pear-shaped; mature conidia are round w/ transverse and longitudinal septations and are often rough/warty
characteristically, all stages of condia will present simultaneously in clusters
Nigrospora spp. basic info
common contaminant
rapid growth
wooly, surface is white turning gray with age; black areas of conidiation apepar as it ages; reverse is black
Nigrospora spp. microscopic appearance
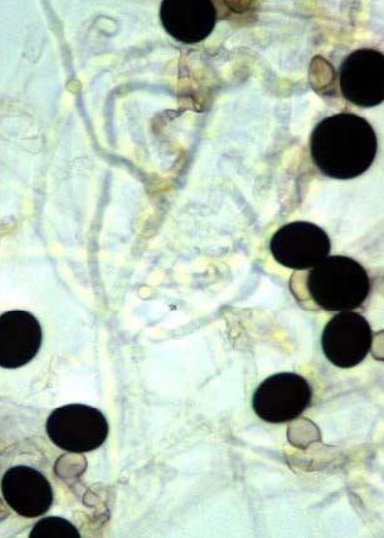
septate hyphae
short, swollen conidiophores which taper at the poitn of conidia formation
conidia are large and densely black, almost round, and slightly flattened
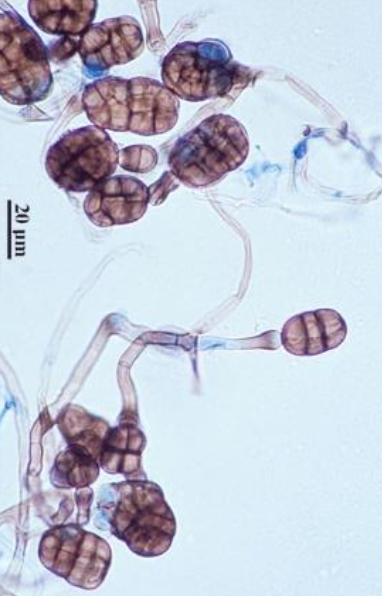
Chaetomium spp. basic info
common contaminant; occassionally causes phaeohyphomycosis
rapid growth
surface is cottony, usually white but comes gray to grayish olive w/ age; reverse is usually orange-tan tinted w/ red but may be dark
Chaetomium spp. microscopic appearance
septate hyphae
large, round, oval, or flask-shaped perithecia that have wavy and/or straight filamentous appendages (setae)
asci contain four to egith oval or lemon shaped ascospores, and usually dissolves after release from the ostiole of the perithecium
Phoma spp. basic info
common contaminant that can cause phaeohyphomycosis
rapid growth
surface is powdery or velvety
graish-brown; reverse is black; some spp. have a reddish or brown diffusible pigment
Phoma spp. microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
large pycnidia (asexual fruiting bodies), which are dark and round or flask-shaped and have ostioles
conidia (formed on conidiophores inside the pynicida) are oval, single-celled, and hyaline
list of subcutaneous mycosis — A. fungi associated w/ mycetomas
Scedosporium spp. complex
Graphium spp.
Exophiala jeanselmei complex
list of subcutaneous mycosis — B. fungi associated w/ Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis
fonsecaea pedrosoi
fonsecaea compacta
phialophora verrucosa
cladophialophora (cladosporium) carrionii
cladophialophora (xylohypha) bantiana
Exophiala (wangiella) dermatitidis
list of cutaneous mycosis — dematiaceous fungi
hortae (phaeoannellomyces (exophiala)) werneckii
piedraia hortae
Scedosporium spp. complex nomenclature
was considered an anamorph (asexual stage) of Pseudoallescheria spp., the telemorph (sexual) state
newer guidelines stipulate each fungus has only one name
Scedosporium is now the preferred name for the entire holomorph (sexual and asexual states) of the organism
four spp. of Scedosporium complex that are clinically encountered:
Scedosporium apiospermum — MOST common clinically; cleistothecia (indicative of sexual Pseudoallescheria apiospurmum) rarely develop in clinical cultures
Scedosporium boydii — more likely to form cleistothecia; its telemorph is Pseudoallescheria boydii
Scedosporium aurantiacum
Scedosporium dehoogii
pathogenicity of Scedosporium spp. complex
common cause of… mycetoma and phaeohyphomycosis
can cause fungus ball in CF pt… may disseminate
most often infects upper or lower extremities — may occur on any exposed parts of the body
Scedosporium spp. are the most common cause of eumycetoma in north america… can infect subcutaneous tissue, muscle, bones, lungs, sinuses, eyes, and CNS; also the most common cause of fatal lung/CNS infections complicating near-drowning accidents in immunocompromised pts
Scedosporium spp. complex basic colony info
moderately rapid growth (<7 days)
spreading, white cottony aerial mycelium which turns gray/brown
reverse begins white then turns gray/black
spp. of the complex can be separated by reverse colony color, growth at 40C and 45C, and growth in cyclohexamide…
S. apiospermumi/boydii have variable yellow diffusible pigment, grow and 40C and grow in cycloheximide
S. aurantiacum cylindrical or slightly flask-shaped condidiogenous cells, reverse orangish colony, diffusible yellow pigment, growth at 40C AND 45C, and growth in cycloheximide
S. dehoogii has cylindrical or slightly flask-shaped condidiogenous cells, no pigment, does not grow at 40C OR 45C, but does growth in cyclohexamide
Scedosporium spp. complex microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
short OR long conidiophores bearing unicellular, oval truncate (cut off at the base) conidia singly or in small groups
in the sexual state, large, brown cleistothecia can be formed, which release elliptical ascospores when ruptured
Graphium spp. pathogenicity and basic info
common contaminant, can be another asexual synapomorph of Scedosporium spp.
moderately rapid rate of growth
colony morphology: gray, cottony surface, dark reverse
Graphium spp. microscopic morphology
Septate hyphae
Long conidiophores that are cemented together, forming synemata
The apex of each synnema holds a cluster of oval, single-celled conidia
Exophiala jeanselmei complex basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity: causes mycetoma (black grain) as well as phaeohyphomycosis
slow grower — <14 days at RT; may or may not grow at 37C
colony morphology — the surface is first dark and ‘skin like’ becoming velvety and gray; black reverse
Exophiala jeanselmei complex microscopic morphology
young cultures have many yeast-like budding cells
older cultures will have septate hyphae w/ conidiophores bearing slender, tubular, sometimes branched annelids, which are characteristically tapered to a narrow, elongated tip
conidia are oval and clustered
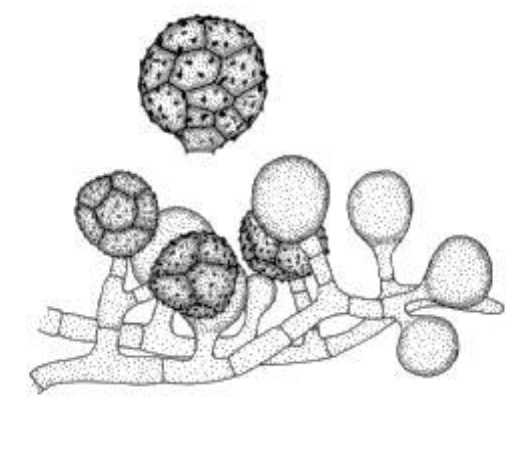
Fonsecaea pedrosoi basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity: MOST COMMON cause of chromoblastomycosis worldwide
slow grower — <14 days
colony morphology — surface is dark and velvety, usually flat but soon develops a convex cone-shaped protrusion in the center; black reverse
Fonsecaea pedrosoi microscopic morphology
septate hyphae, usually branched
four types of conidial formation can be seen
fonsecaea type
cladosporium type
rhinocladiella type
phialophora type
characteristically, multiple types of conidiation (but not necessarily all) are seen in a single organism/colony
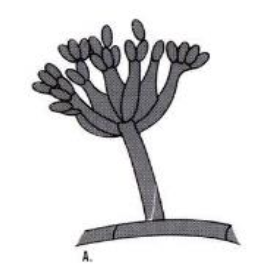
Fonsecaea pedrosoi: conidial formation — fonsecaea type
septate, erect, and compactly sympodial conidiophores; swollen denticles bear single-celled oval primary conidia; denticles on the primary conidia support secondary single-celled conidia that may produce tertiary conidia, but long chains are not formed; conidia can form at fertile sites along the conidiophore, forming an asterisk-like appearance
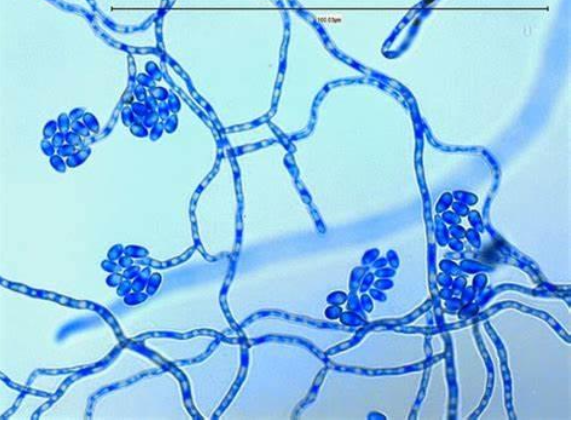
Fonsecaea pedrosoi: conidial formation — cladosporium type
erect conidiophores which produce shield-shaped conidia which in turn, produce chains of oval conidia having small dark hila
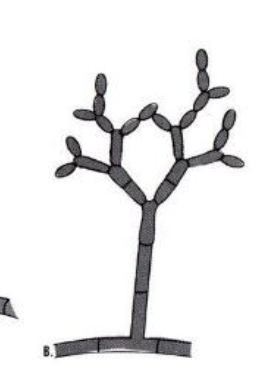
Fonsecaea pedrosoi: conidial formation — rhindocladiella type
septate, erect, and sympodial conidiophores; swollen denticles bear oval conidia at the tip and sides of the conidiophores; chains of conidia are rare
Fonsecaea pedrosoi: conidial formation — phialophora type
vase-shaped phialides w/ terminal cup-like collarettes; conidia accumulate at the apex of the phialides; this type of conidiation is very RARE
Fonsecaea compacta basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity — causes chromoblastomycosis
very rarely encountered and considered as a mutant form of F. pedrosi
very slow grower <28 days
colony morphology — dark surface which is heaped and brittle; black reverse
fonsecaea compacta microscopic morphology
septate and branched hyphae bearing predominantly fonsecaea type conidiophores, which produce short chains and masses of conidia in a compact arrangement
conidia have cask-like shape
other three types of conidiation may also be seen w/ this spp.
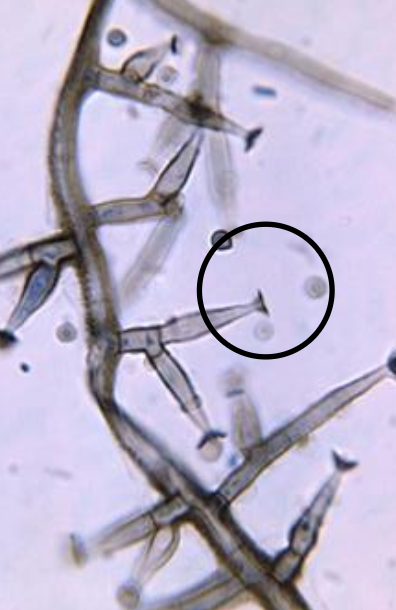
Pleurostomophora (phialophora) richardsiae basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity — UNcommon agent of cystic subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis
moderate rate of growth <10 day
colony morhpology — dark surface, brown diffusible pigment may develop w/ age; dark reverse
Pleurostomophora (phialophora) richardsiae microscopic morphology
septate hyphae; similar to phialophora verrucosa
phialides are slightly flask-shaped w/ a characteristic flared, saucer-shaped collarette
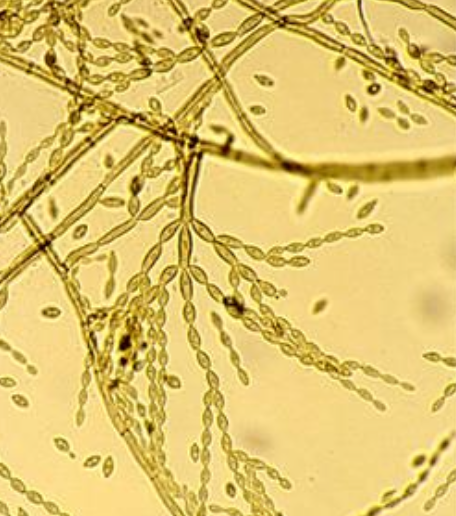
Cladophialophora (cladosporium) carrionii basic info and pathogenicity
causes chromoblastomycosis
slow grower <18 days
colony morphology — dark surface; black reverse
Cladophialophora (cladosporium) carrionii microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
conidiophores produce long, branching chains of smooth, oval conidia w/ pale scars of attachment that are easily dispersed
in contrast to Cladosporium, ‘shield cells’ are usually NOT seen, does NOT grow in 15% NaCl, and is MDG assimilation positive
Cladophialophora (Xylohypha) bantiana basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity — usually assoc. w/ disease of the CNS (cerebral phaeohyphomycosis); use extreme caution when handling
slow grower <15 days
colony morphology — dark surface; black reverse
Cladophialophora (Xylohypha) bantiana microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
conidiophores resemble the hyphae
long, sparsely branched, wavy chains of smooth oval conidia which lack hila
no ‘shield cells’ seen, does not grow in 15% NaCl, and is MDG assimilation positive, max growth temp is 42-43C, whereas carrionii is 35-37
temperature studies for: Cladosporium spp, Cladophialophora carrionii, and Cladophialophora bantiana
Cladosporium spp — growth at <37 C
Cladophialophora carrionii — growth up to 37 C
Cladophialophora bantiana — growth up to 42 C
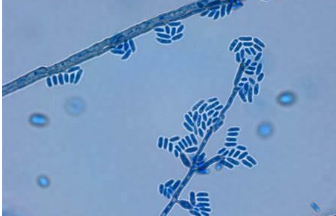
Exophiala (Wangiella) dermatitidis basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity — causes phaeohyphomycosis and seems to have a predilection for the CNS
rate of growth is slow (yeast-like within 10 days, filamentous within 25 days)
colony morphology — surface is at first black, moist, and yeast-like, then turns olive-gray with the development of aerial hyphae; dark reverse
Exophiala (Wangiella) dermatitidis microscopic morphology
young cultures contain oval or round budding yeast-like cells
septate hyphae are eventually produced which bear flask-shaped or cylindrical phialides that lacka flared tipe
round or oval conidia are produced which accumulate at the apex of the phialides and dow to the hyphae
‘black yeast’ differentiation
Exophiala jeanselmei spp. complex
casein decomposition negative
tyrosine decompositioin positive (78%)
NG in 15% NaCl
KNO assimilaiton positive
max growth </=37 C
Exophiala dermatitidis
casein decomposition negative
tyrosine decomposition positive (83%)
NG in 15% NaCl
KNO assimilation negative
max growth at 42 C
Hortaea werneckii
casein decomposition positive (78%)
tyrosine decomposition negative (only 22% pos)
Growth in 15% NaCl
KNO assimilation positive
max growth <37 C
Lomentospora prolificans: Scedosproium prolificans (inflatum) — basic info and pathogenicity
causes localized and disseminated infections in a variety of sites; isolates are often resistant to antifungal agents and disseminated infections are commonly fatal
rapid grower <5 days
colony morphology — begins cottony or moist (yeast-like) becoming gray to black w/ age; the reverse is dark
Lomentospora prolificans: Scedosproium prolificans (inflatum) — microscopic morphology
septate hyphae
similar to Scedosporium apiospermum
conidiogenous cells (annellides) have swollen base and elongated ‘neck’; conidia are dark, single-celled and ovoid w/ slightly narrowed, truncated (cut off) base
there is no known sexual state
no pigment, growth at 40C and variable growth at 45 C
NG in cyclohexamide, unlike Scedosporium spp.
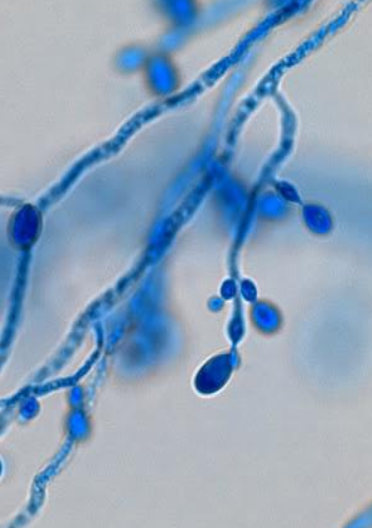
Hortae (phaeoannellomyces (exophiala)) werneckii — basic info and pathogenicity
pathogenicity — causes tinea nigra (brown or black ringworm)
slow grower <21 days
colony morphology — surface at first is lightly colored and yeast-like, turns dark w/ age; reverse is black
Hortae (phaeoannellomyces (exophiala)) werneckii — microscopic morphology
young cultures have yeast-like cells, some of which have a central septum — usually annelids, round at one end, while tapered and elongated w/ striations at the other end where conidia are formed
closely septate hyphae eventually produced
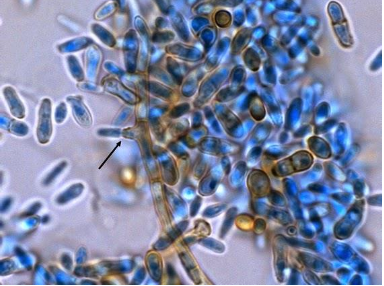
Piadraia hortae — basic info and pathogenicity
causes black piedra
slow grower <21 days
colony morphology — small, dark, compact colonies which may form a reddish-brown diffusible pigment; black reverse
Piadraia hortae — microscopic morphology
closely septated hyphae w/ thick walls and variations in diameter
intercalary chlamydoconidia
asci may be produced which release single-celled, curved, tapering ascospores w/ whip like extensions
overview of dermatophytes
among the most common infectious organisms of humans and are found worldwide
filamentous fungi that are able to digest and obtain nutrients from keratin; require keratin for growth (hair, skin, and rarely nails)
no invasion of living tissue, just colonization of the keratinized outermost layer of skin
only fungi that have developed a dependency on human/animal infection for survival; therefore, these fungi are the most common infectious agents of humans
dermatophyte infecitons
tinea or ringworm
capitis — scalp/hair
barbae — bearded areas, face, and neck
corporis — body/trunk
pedis — athelet’s foot
cruis - groin
manum — hand
unguium — nail
onychomycosis — any infeciton of the nail, not necessarily by dermatophytes
infection known as ______ is transmitted by direct contact w/ objects or materials contaminated w/ organism; the result of the host reaction to the enzymes released by the fungus during its digestive process
tinea/ringworm
most infectious element of dermatophytes
arthroconidia
media for dermatophytes =
dermatophyte testing media (DTM): contains chlortetracycline, gentamicin, and cycloheximide along w/ phenol red as a pH indicator; turns yellow to red in the presence of dermatophyte due to alkaline metabolites produced by the fungus
hair perforation test
arthroconidia can be seen outside of the hairshaft (ectothrix) or inside the shaft (endothrix)
test is performed by suspending hair and test organism in a solution of distilled water w/ dilute yeast extract — hair should NOT be bleached, sprayed, or permed
the hair is incubated for up to four weeks and regularly examined microscopically
a positive reaction is indicated by wedge-shaped perforations caused by hyphae that penetrate the hairs perpendicularly
flourescence w/ wood’s UV light
wood’s UV light at 365 nm can be helpful in detecting hairs infected w/ any of the fluorescent (bright greenish yellow) species of microsporum
M. audouinii
M. canis
M. ferrugineum
dermatophyte — basic differentiation by conidial formation:
Microsporum spp. — macroconidia are numerous, thick-walled, and rough; microconidia are usually present
Trichophyton spp. — macroconidia are rare, thin-walled, and smooth; microconidia are numerous
Epidermophyton floccusum — macroconidia are numerous, thin- and thick- walled, and smooth; microconidia are absent
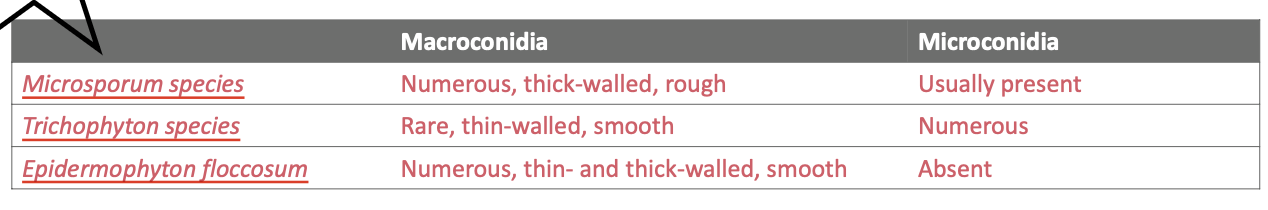
Microsporum audouinii
formerly caused widespread epidemics of ringworm of the scalp in children
hyphae are separated w/ terminal chlamydoconidia pointed on the end
pectinate (comb like) hyphae are regularly seen
can be diagnosed by apple-green fluorescence of infected hair
seldomly produces conidia
Microsporum canis
children tend to acquire infections of the scalp and skin from dogs/cats
macroconidia are spindle-shaped, rough, and thick-walled, taper to beak-like ends
microconidia are club-shaped and smooth-walled; form along the hyphae
colony is orange/yellow in color
contains >/= 6 septations
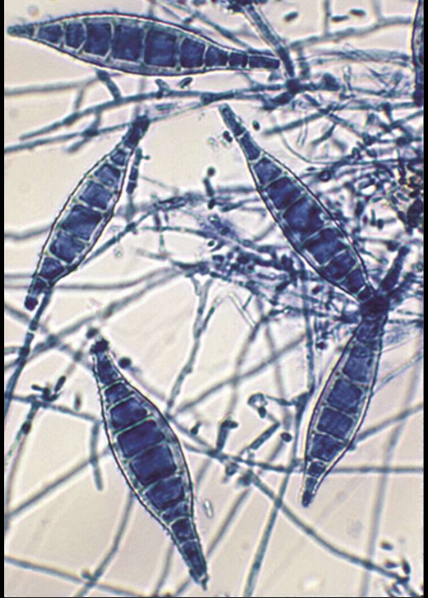
Microsporum gypseum
colony is cinnamon in color
</= 6 septations
Microsporum ferruguineum
primarily causes ringworm of the scalp (tinea capitis) in children
‘bamboo’ hyphae
Trichophyton overview
rare macroconidia, a thin wall, smooth surface, and multiseptate
elongated and pencil shaped
macrocondiia are NOT present in T. violaceum or T. schoeleinii
mciroconidia are usually very numerous except in T. violaceum or T. schoeleinii
testing for produciton of red pigment on cornmeal dextrose agar is useful to differentiate T. rubrum from T. mentagrophytes
hair, skin, nails — T. rubrum (most common dermatophyte) and T. mentagrophytes are quite common; hairs infected w/ T. schoenleinii also fluoresce (dull silvery to blue-green color)
T. rubrum
presently most frequently isolated dermatophyte infecting humans worldwide
feet and nails are most common sites
macroconidia are pencil-like ; microconidia form directly on hyphae; arthroconidia form on both hyphae and macroconidia
urea is negative
hair preformation is negative (ectothrix)
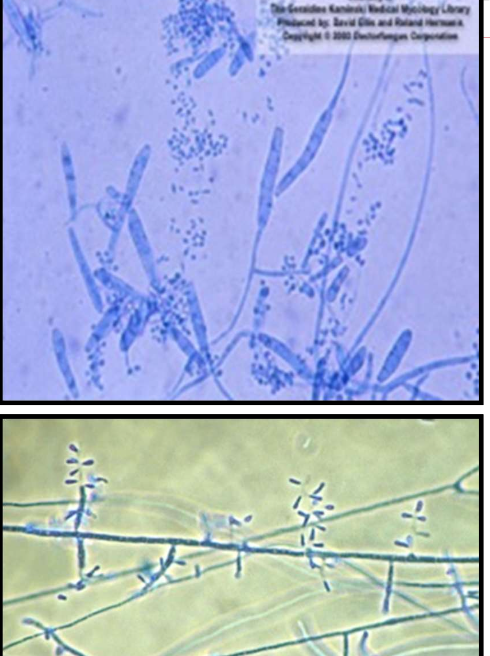
T. verrucosum
grows best at 37 C
forms hyphae w/ many intercalary chlamydoconidia (typically in chains) and some w/ antler-like branches; string-bean or rat tail macroconidia
requires thiamine and usually inositol for formation of macro/micro conidia; otherwise forms chlamydoconidia chains on SDA
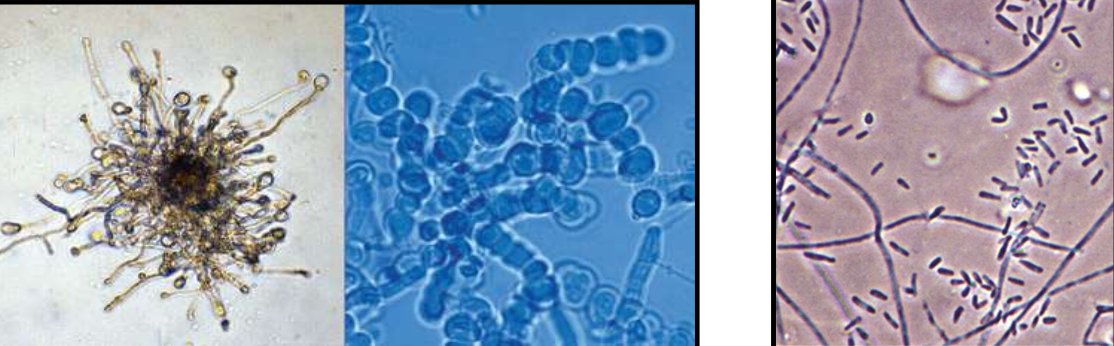
T. mentagrophytes
macroconidia are sometimes present but not always; they are cigar-shaped and thin-walled
invades all parts of the body surface, including hair and nails
common cause of athlete’s foot
urea is positive
hair perforation is positive (endothrix)
T. schoenleinii
causes favus — severe chronic, scarring scalp infection
can lead to permanent hair loss
dull silver fluorescence
hyphae appear as antler-like branching structures (favic chandeliers) with swollen tips that resemble nail heads
T. tonsurans
principal etiologic agent of scalp ringworm in the USA
also infects skin and nails
most common cause of outbreaks of tinea captis in children and is the main cause of endothrix (inside) hair infections
microconidia = teardrop or club-shaped but may elongate or enlarge to round balloon forms
intercalary and terminal chlamydoconida are common in older cultures
rare macroconidia — irregular form and bit thick-walled
Epidermophyton floccosum overview
macroconidia are presnt, thick and thin walled, with smooth surface; 2-6 cells
with age, macroconidia are often transformed into chlamydoconidia
microconidia are absent
infects skin and nails, NEVER hair
dermatophytes w/ round, tear-like or variously shaped microconidia, macroconidia w/ smooth thin walls may be present:

dermatophytes forming only hyphal elements — no conidia usually seen on SDA:

dermatophytes having macroconidia with thin or thick walls; usually no microconidia
