Neuropsychology; Brain, Neurons, Radiology, and the Nervous system
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
Motor (efferent) neurons
Neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs.
The brain and spinal cord
Where are interneurons located?
Soma (cell body)
Contains the nucleus; the cell’s life-support center
Dendrites
Bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrates messages, conducting impulses towards the cell body.
Axon
Segmented neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
Myelin sheath
Fatty tissue that encases the axons of some neurons; it enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hope from one node to the next.
Terminal buttons
Transmits signals from one neuron to another by releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft/gap/synapse.
Dendrites
A
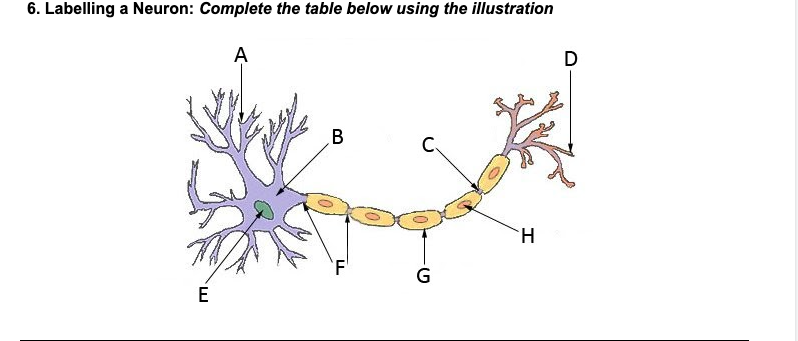
Nucleus
E
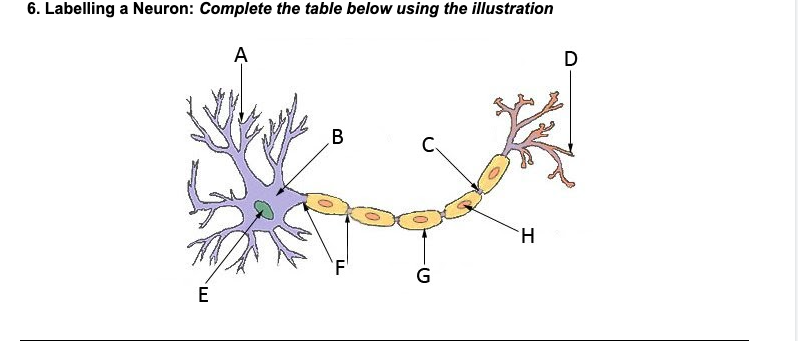
Soma (cell body)
B
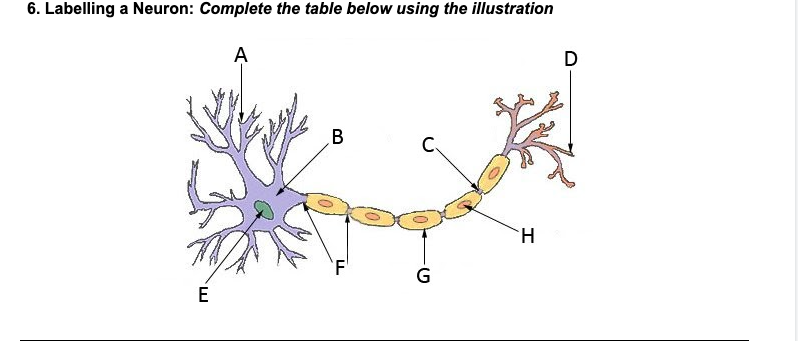
Axon
F
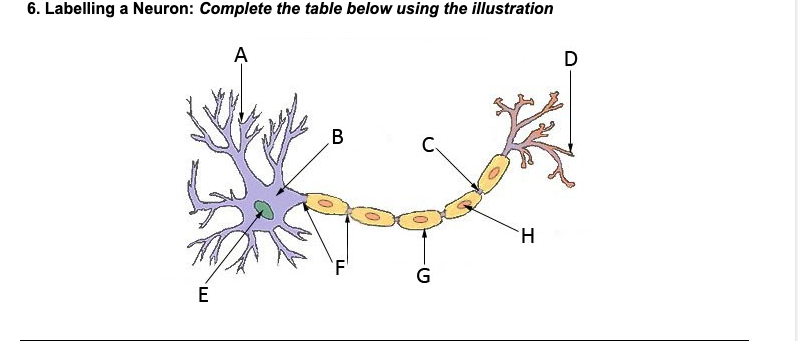
Myelin sheath
G
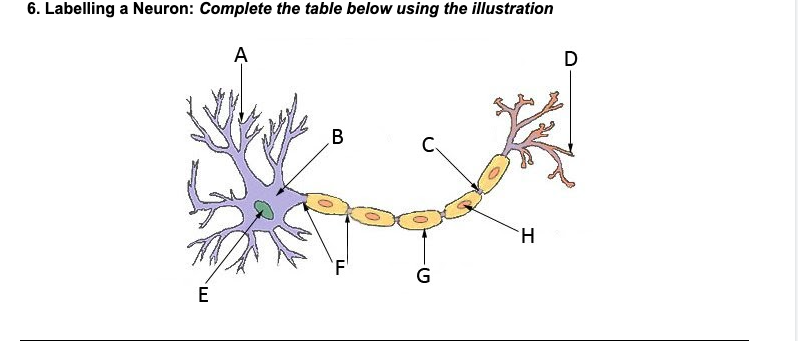
Terminal branches
D
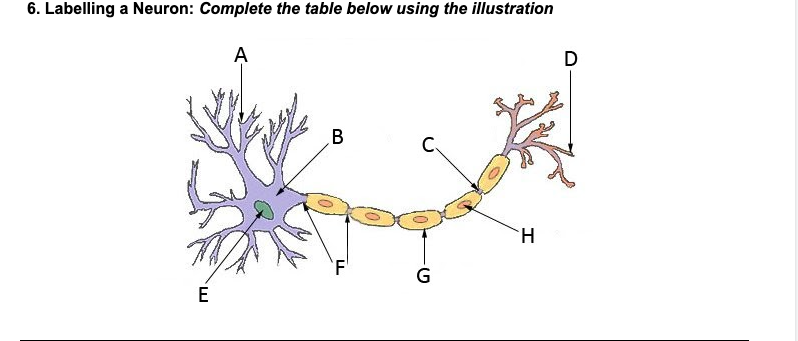
Terminal buttons
H
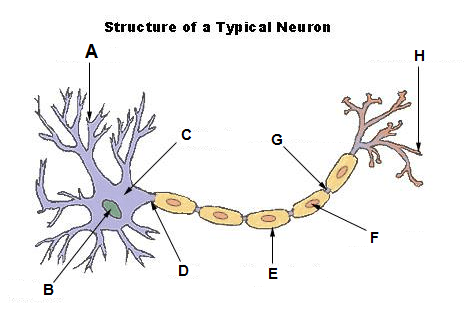
Synapse
4

Stimulus triggers electrical signal. Once the neuron reaches its threshold, an action potential is fired.
What is the first step in neuron communication?
The action potential travels down the neuron’s axon, until it reaches the synapse.
What is the second step in neuron communication?
One the axon potential reaches the synapse, the release of neurotransmitter molecules is triggered. These neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the receiving neurons dendrites.
What is the third step in neuron communication?
The neurotransmitter either excite or inhibit the receiving neuron, making it more likely to fire an action potential or less likely to fire an action potential.
What is the fourth step in neuron communication?
The minimum level of stimulation needed to trigger a neuron to fire an action potential.
What is a neurons threshold?
Resting potential
What state must the neuron be in before it can fire an action potential?
Negative charge inside and positive charge outside
What is resting potential defined as
Acetylcholine
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory.
Alzheimer’s
Undersupply of Acetylcholine leads to?
Dopamine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion.
Schizophrenia
Oversupply of dopamine leads to?
Tremors, Parkinson’s disease
Undersupply of dopamine leads to?
Endorphins
Neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure
Suppression of natural endorphin production
Overuse of opioids can lead to?
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal.
Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
A major inhibitory transmitter
Depression
Undersupply of serotonin leads to?
Seizures, tremor, insomnia.
Undersupply of GABA leads to?
Glutamate
Major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
Migraines or seizures
Oversupply of glutamate leads to?
Oxytocin
“Love” hormone. Plays role in childbirth, lactation, mother-infant bonds, and romantic relationships. Also regulates emotions.
Agonist
A molecule that increases a neurotransmitters function
Antagonist
A molecule that inhibits/blocks a neurotransmitters function
Central nervous system (CNS)
Receives sensory information, processes it, and sends out commands. Coordinates all bodily functions.
Brain
Processes sensory input, and directs thoughts, feelings, movement, and other bodily functions.
Spinal cord and brain
What makes up the central nervous system?
Spinal cord
Sends messages from the brain to the body’s organs and muscles, relays sensory information from the body back to the brain.
Somatic and Autonomic
What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Somatic division
Division of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement by transmitting motor commands from the central nervous system (CNS) to the skeletal muscles.
Motor and sensory neurons
Somatic division is made up of?
Autonomic division
Division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs.
Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
Autonomic division of the peripheral nervous system is made up of?
Sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
Arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
Parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
Calms the body, conserving its energy
Hindbrain
Consists of structures in the top part of the spinal cord. It is our life support system; it controls the basic biological functions that keep us alive.
Medulla
Automatically controls the beating of the heart, the breathing of our lungs, all without our conscious awareness.
Pons
Connects the hindbrain with the midbrain and forebrain. Involved in the control of facial expressions.
Cerebellum
Means “little brain” in Latin. Important structure for non-verbal learning and memory, controls voluntary movement and balance.
Brain stem
The oldest part of the brain in evolutionary terms, the core of the brain, where the spinal cord enters the skull.
Midbrain
Area between the hindbrain and the forebrain that integrates some types of sensory information and muscle movements. Includes the uppermost portion of the brainstem.
Reticular formation
Network inside the brain stem that is essential for arousal (ex: sleeping, alertness)
Forebrain
Controls what we think of as thought and reason. Most psychological researchers concentrate their efforts in this area of the brain.
Limbic system
Emotion subsystem
Amygdala, hypothalamus, and the hippocampus.
What is the limbic system made up of?
Hippocampus
Central to learning and consolidation of new memories.
To learn and remember
Why is there a hippo on campus?
Amygdala
Almond shapes neural clusters that are responsible for the experience of fear and the aggression response.
Thalamus
Receives and relays information relating to every sensory system except smell.
Hypothalamus
Tiny structure that regulates the body and its circadian rhythms. Controls the pleasure and reward system of the body, contains reward pathway, also controls arousal.
Fighting, fleeing, fortification, and feeding.
What are the four Fs of the hypothalamus?
Cerebral cortex (cerebrum)
The gray wrinkled surface (wrinkles are called fissures) you see when you think of the brain. The cortex is divided into two hemispheres and into four lobes.
Frontal lobe
Responsible for speaking, planning, judging, abstract thinking, and aspects of personality.
Motor cortex, prefrontal cortex, and Broca’s area.
What are the important areas of the frontal lobe?
Pons, medulla, cerebellum
What is the hindbrain made up of?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebrum
What is the forebrain made up of?
Broca’s area
Helps control language expression by directing the muscle movements involved in speech.
Motor cortex
Controls voluntary movements.
Parietal lobe
Responsible for processing information relating to our sense of touch and body position.
Somatosensory cortex
Registers and processes our sense of touch and body position.
Occipital lobe
Processes the information related to sight, houses the visual cortex.
Temporal lobe
Responsible for sound processing, speech, comprehension. Houses the auditory cortex,
Wernike’’s area
A brain area involved in language comprehension and expression.
Association Cortex
Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor sensory functions, rather, they are involved in higher mental functions, such as remembering, thinking and speaking. Connects sensory and motor output.
Cerebral hemispheres?
Control our bodies contralaterally
Corpus callosum
Connects the two cerebral hemispheres, allowing them to communicate. A band of axonal fibers.
Important concepts
To what extent can the damaged brain reorganize itself and what is neurogenesis?
Explain the Left and Right brain specializations.
Explain what is meant by split brain and briefly explain the classic split-brain studies.
EEG
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface. Electrodes placed on the scalp measure electrical activity in neurons.
Lesioning
Medical procedure that involves destructing tissues experimentally through using electrodes. Can treat chronic pain and allow for study of brain function.
MEG
A brain-imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity.
CT
A series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure.
PET
A technique for detecting brain activity that displays where a radioactive form of glucose foes while the brain preforms a given task.
MRI
A technique that uses magnetic field and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. Show brain anatomy.
fMRI
A technique for revealing the blood flow, and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRI scans show brain function as well as structure.
Staining
Using dyes and other chemicals to visualize and study the microscopic structures of neurons and other brain tissue.
BOLD (blood oxygen level dependent contrast)
A mechanism in functional MRI (fMRI) that uses magnetic properties of oxygenated vs deoxygenated blood to create images.
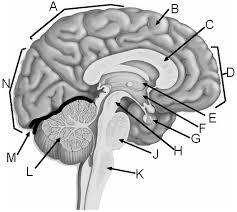
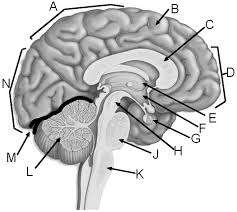
Parietal lobe
A
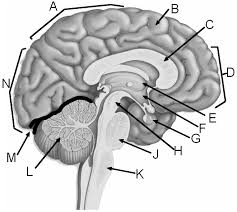
Corpus callosum
C
The bloodstream
What do hormones travel through?
Frontal lobe
D
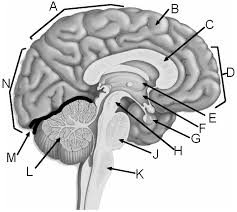
Thalamus
E
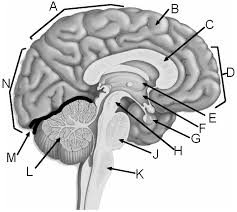
Hypothalamus
F
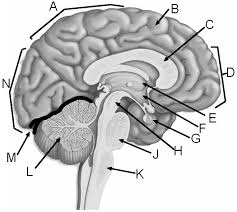
Pituitary gland
G
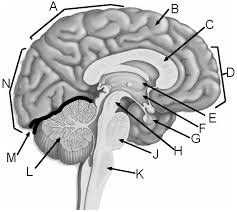
Midbrain
H