RCT- Dr.Z
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based off her study guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
FYI on what to focus on for each section for Dr. Z:
green section- characteristics of RCTs
2 Exam Q
FYI on what to focus on for each section for Dr. Z:
blue section- internal v external validity
2 Exam Q
FYI on what to focus on for each section for Dr. Z:
purple section- randomization, blinding, and sample size
2 Exam Q
FYI on what to focus on for each section for Dr. Z:
orange section- different equations dealing w/ risk
2 Exam Q
FYI on what to focus on for each section for Dr. Z:
pink section- 3 strengths and weaknesses of RCTs
1 Exam Q

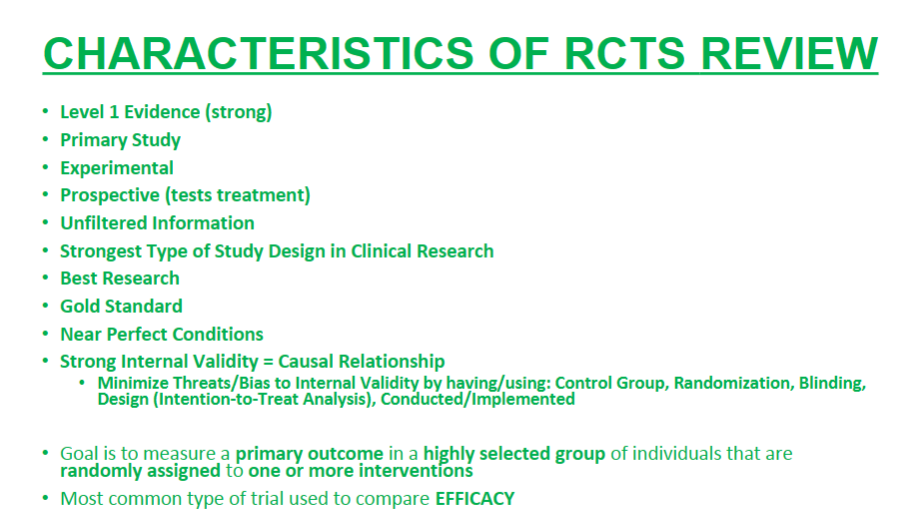
What are the 10 characteristics of RCTs?
2 EXAM Q from this LIST!!!!
Primary study
Near Perfect Conditions
Level 1 Evidence
Experimental
Strongest type of study design
strong internal validity
Prospective
Unfiltered
Best Research
GOLD STANDARD
A characteristic of RCT is strong internal validity. If a RCT has strong internal validity, it indicates what? Additionally, to minimize threats to Internal validity, what can we do?
Strong Internal Validity= Causal Relationship
To minimize threats: control group, randomization, blinding, etc.
What is bias and how is it minimized?
bias- systematic error in study design or implementation that can lead to incorrect findings
to minimize- use the right study design and implement it
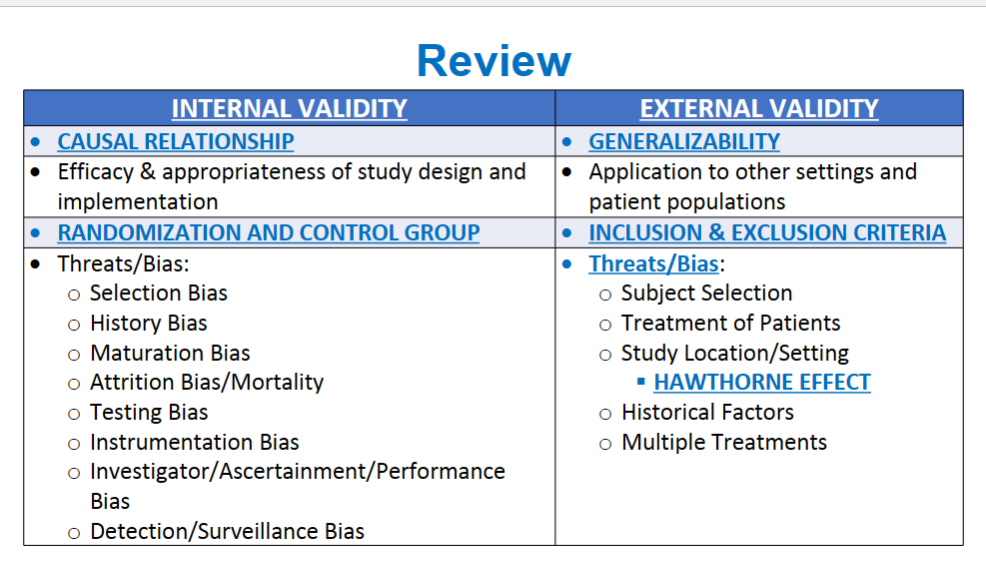
What’s validity and the 4 subtypes of validity?
Validity- degree to which findings represent TRUTH (I think we know what the word valid means)
face (are they testing what they say they are going to test)
content- (is it correct to experts?)
criterion- (Does it match up w/ a gold standard)
construct- (Does it relate to theoretical concepts)
What is internal validity? How is internal validity strengthened?
Internal Validity- Degree to which the study outcome (efficacy or safety) can be explained by the differences in the intervention (treatment)
Strengthened: by having a control group and randomization
List and briefly describe the 8 key biases that threaten internal validity?
selection Bias- putting pts. in specific groups
history Bias- study outcome may be bc of External events
maturation Bias- normal change in pts. over time
Attribution Bias/ Mortality- “Drop-Out” (pt. leaves)
Testing Bias- pts. taking tests repeatedly
Instrumentation Bias- sensitivity of instrument, improved technology, changes in measurement
Investigator Bias- error by investigator
Detection/Surveillance Bias- difference btwn groups in how outcomes are determined
Which of the 8 key biases can be minimized by randomization?
selection bias
maturation bias
Which of the 8 key biases can be minimized by control group?
history bias
maturation bias
testing bias
Which of the 8 key biases can minimized by blinding?
investigator
detection/surveillance bias
What is external validity and what criteria does it relate to?
indicates that the findings of a given study can be generalized to other settings
inclusion and exclusion criteria
What 5 key factors that threaten external validity?
subject selection
treatment of patients
study location/setting
HAWTHORNE EFFECT
historical factors
multiple treatments
What is the Hawthorne Effect?
study subjects modify their behaviors due to longitudinal learning over the course of a study or because they know they are being observed
basically: subjects act different because they know ppl are watching them
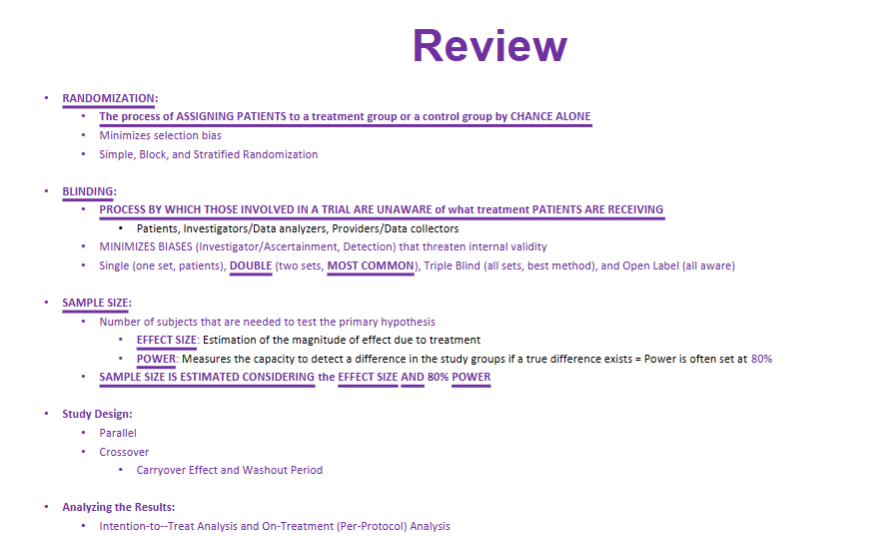
What is randomization and what are the 3 methods of randomization?
process of assigning pts. to a treatment or control group based on chance alone
simple- random # generator
stratified- by characteristics
block- divided into blocks before, then blocks randomized
List and describe the 4 types of blinding:
single blind- pt/investigator unaware
double blind- both pt/investigator unaware
triple blind- everyone unaware (pts, investigator, data collectors)
open label- everyone IS AWARE
Sample size is the number of subjects that are needed to test the primary hypothesis… WHAT 2 KEY FACTORS does it take into consideration.
PLEASE KNOW THIS
EFFECT SIZE
POWER
What are the 3 most common types of control groups and when are they used?
placebo control- when no known effective therapy
active control- when KNOWN effective therapy
historical (external) control- pts. compared to an old control group
Describe each of the following RCT designs:
parallel
crossover
superiority
noninferiority
parallel- each subject either tx or control group
ex: drug A or placebo
crossover- each subject receives all txs
ex: drug A and drug B
superiority- one better than the other
noninferiority- sees whether two interventions are equivalent
2 disadvantages of crossover RCT design:
carryover effect
washout period
What is intention-to-treat analysis?
analyzes patients AS IF THEY COMPLETED the study in their originally assigned group
preferred in superiority trials
Describe on-treatment (per-protocol) analysis:
we can see the true effect of study drug
preferred in noninferiority trials
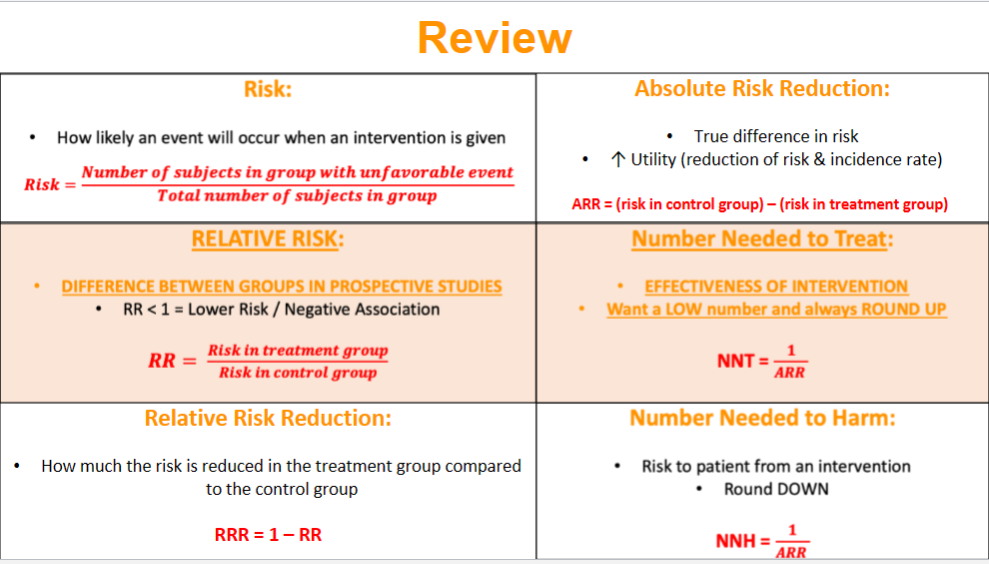
What is risk and how do we calculate it?
probability of an event when an intervention is given
What is relative risk and how do we calculate it?
difference between groups in PROSPECTIVE STUDIES
RR < 1 means lower risk/negative association
RR= risk in tx group/ risk in control group
What is relative risk reduction and how do we calculate it?
how much the risk is reduced in the treatment group compared to the control group
RRR- 1- RR
What is absolute risk reduction and how do we calculate it?
true difference in risk
increase utility
ARR= (risk in control group) - (risk in treatment group)
What is the “number needed to treat” and how do we calculate it?
effectiveness of intervention
want a LOW number
always ROUND UP
NNT= 1/ ARR
What is the “number needed to harm” and how do we calculate it?
risk to pt. from an intervention
ROUND DOWN
NNH= 1/ ARR
What are the 3 strengths of RCTs?
can determine UNBIASED EFFICACY of an intervention
PROSPECTIVE DESIGN allows for control
Methods and protocols allow ability to IDENTIFY CAUSAL RELATIONSHIPS
What are the 3 weaknesses of RCTs?
limitations on generalizability
potential HAWTHORNE EFFECT
takes lots of time/expensive