3: radiographic image characteristics
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Factors Controlling X Ray Beam
- Exposure Time (S)
- Tube Current (mA)
- Tube Voltage ( kVp)
mAs (quantity or quality?)
quantity of x rays produced
kVp (quantity or quality?)
quality of x rays produced
What are the imaging goals when taking x rays?
to produce an image with optimum diagnostic quality with minimal patient radiation exposure
Radiolucent
darkest area (black)
Radiopaque
brightest area (white)
A structure that appears radiolucent....
has less density
allows passage of more x ray beams through it
a structure that appears radiopaque...
has more density and absorbs more x rays
Factors influencing image quality
Radiation Characteristics
Visual Characteristics
Geometric Characteristics
Radiation Characteristics
X-ray beam quality, quantity, and intensity
Visual Characteristics
density and contrast
Geometric Characteristics
1. Sharpness
2. Magnification
3. Distortion
4. Resolution
Radiation Characteristics that Influence the Quality of the Image
Quality
Quantity
Intensity
Quality
Voltage
kVp
Quantity
Amperage, Milliamperage
Milliampere, Seconds
Intensity
Quality
Quantity
Distance
Inverse Square Law
Half Value Layer
Radiographic Density
the overall degree of blackness/darkness of an exposed film
Increased density results in
dark image
Decreased density results in
light image
Factors influencing density of image
exposure factors (mA, kVp, S)
subject thickness
increased kVp
increased density
Decreased kVp
decreased density
Increased mA
Increased density
Decreased mA
decreased density
increased time
increased density
decreased time
decreased density
relationship between kVp and density
non linear
increase in 15kVp causes...
two times increase in density
Factors in Radiographic Density
1) milliamperage
2) exposure time
3) distance
total exposure formula
mA x seconds = mAs
as long as mAs are equal, film density will be...
maintained
what should be adjusted according to a patient's size?
exposure factors : kVp or time
what happens to radiation when the subject is thicker?
less radiation is able to reach the image receptor
do children require less radiation than adults?
yes
contrast
a difference in the degree of blackness (densities) between adjacent areas of a dental radiograph.
an image that shows both dark and light areas has
high contrast
short grayscale
an image that shows only shades of gray has
low contrast
long grayscale
factors influencing contrast
Subject contrast
Radiation quality
Fog/scatter
subject contrast
the difference in the intensity of the beam caused by an object
most important contribution to subject contrast
attenuation of x ray beam by photoelectric effect
photoelectric effect is increased in...
substances with high atomic number
what attenuates more x rays? Bone or muscle?
bone
low kVp produces
high subject contrast
what happens if the kVp is too low?
almost all x rays are attenuated in patient and never reach film
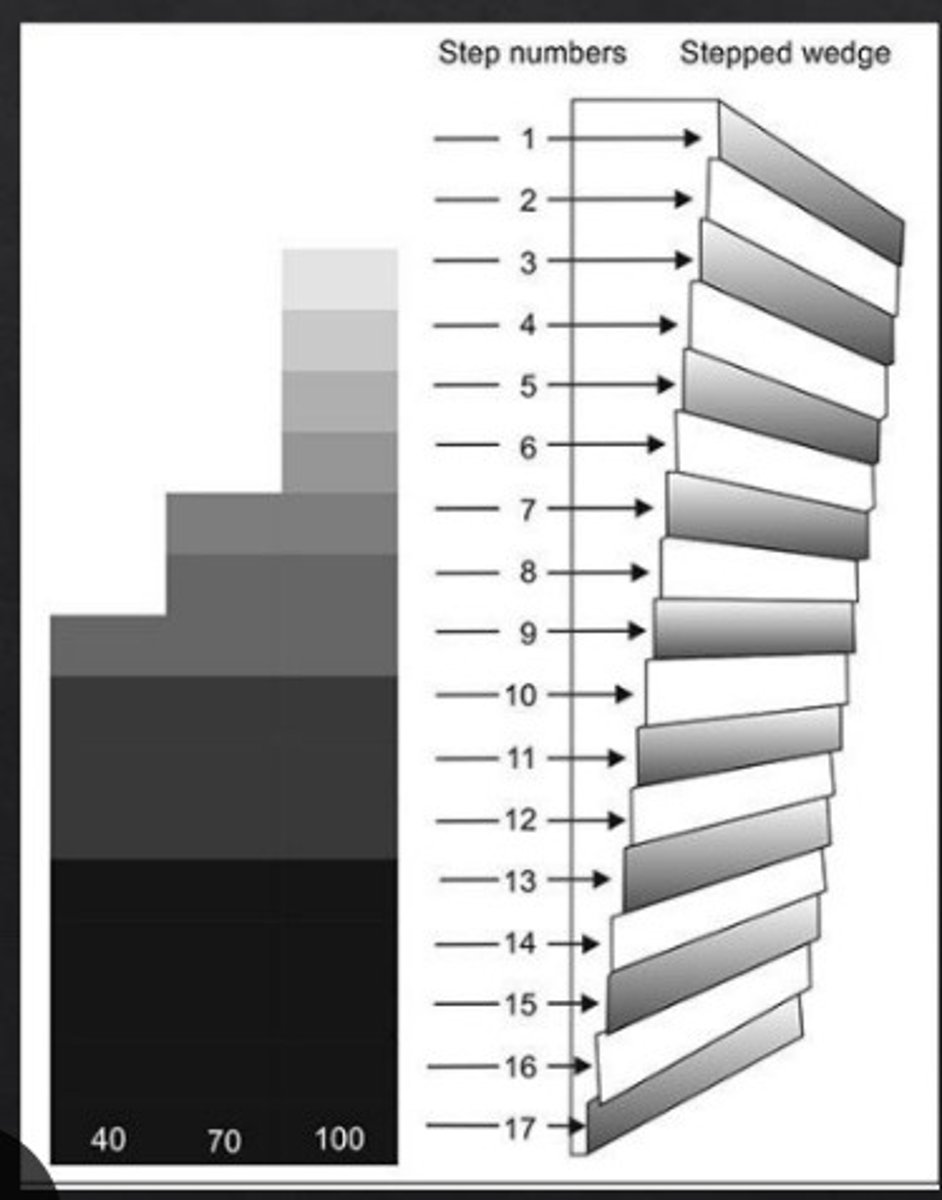
step wedge
- demonstrates short and long scale of contrast
- made of aluminum
- 2mm increments
- placed on top of image receptor and exposed
magnification
when an object is placed in the path of a beam it will cast a shadow on receptor that will show some degree of enlargement
magification is due to...
divergence of x ray beam
factors influencing magnification
source to image receptor distance
object to image receptor distance
source of image receptor distance is determined by...
length of PID
increasing source object distance results in images with...
increased sharpness and less magnification
relationship between length of cone and divergence
long cone = less divergence
decreasing object and image receptor distance...
increases sharpness and less magnification
distortion
variation in true size and shape of object
distortion results from...
unequal magnification of different parts of the same object
factors influencing distortion
object receptor alignment (x ray beam must be parallel)
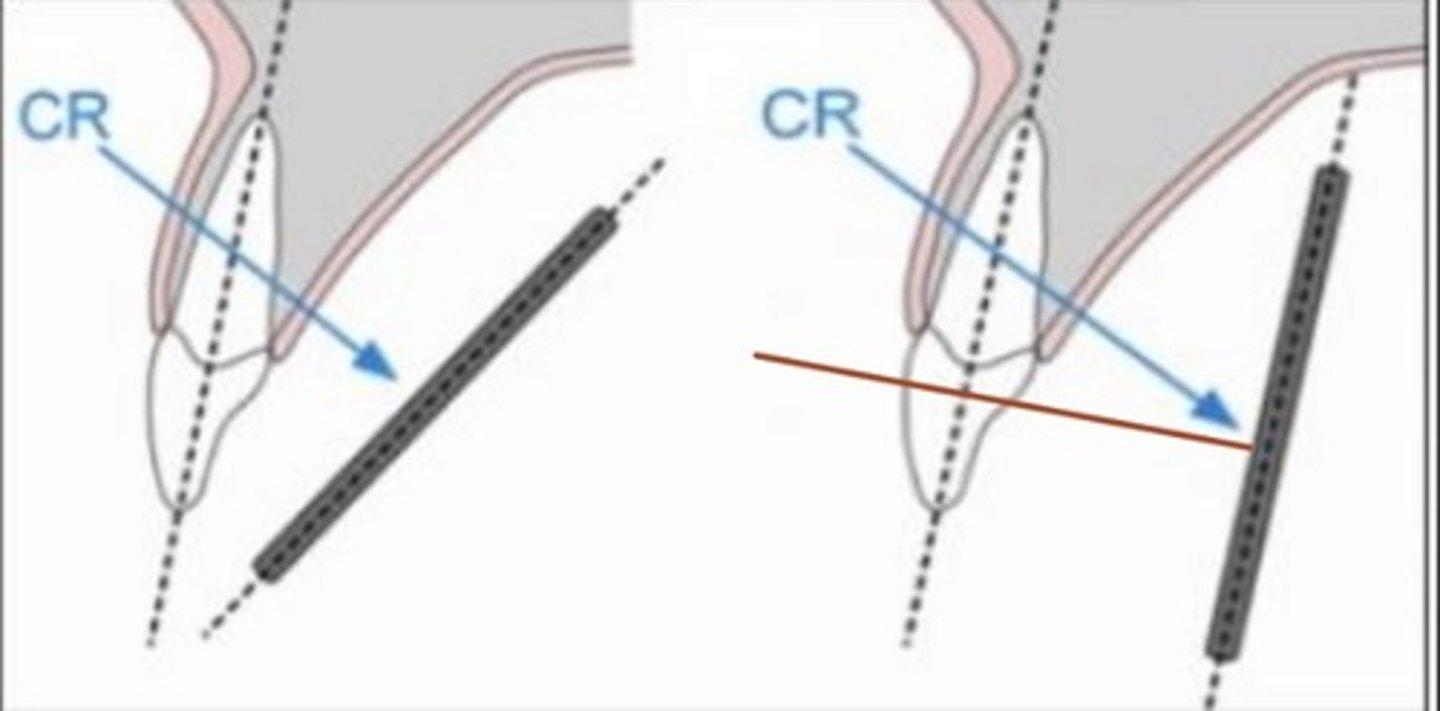
elongation occurs with
decreased vertical angulation
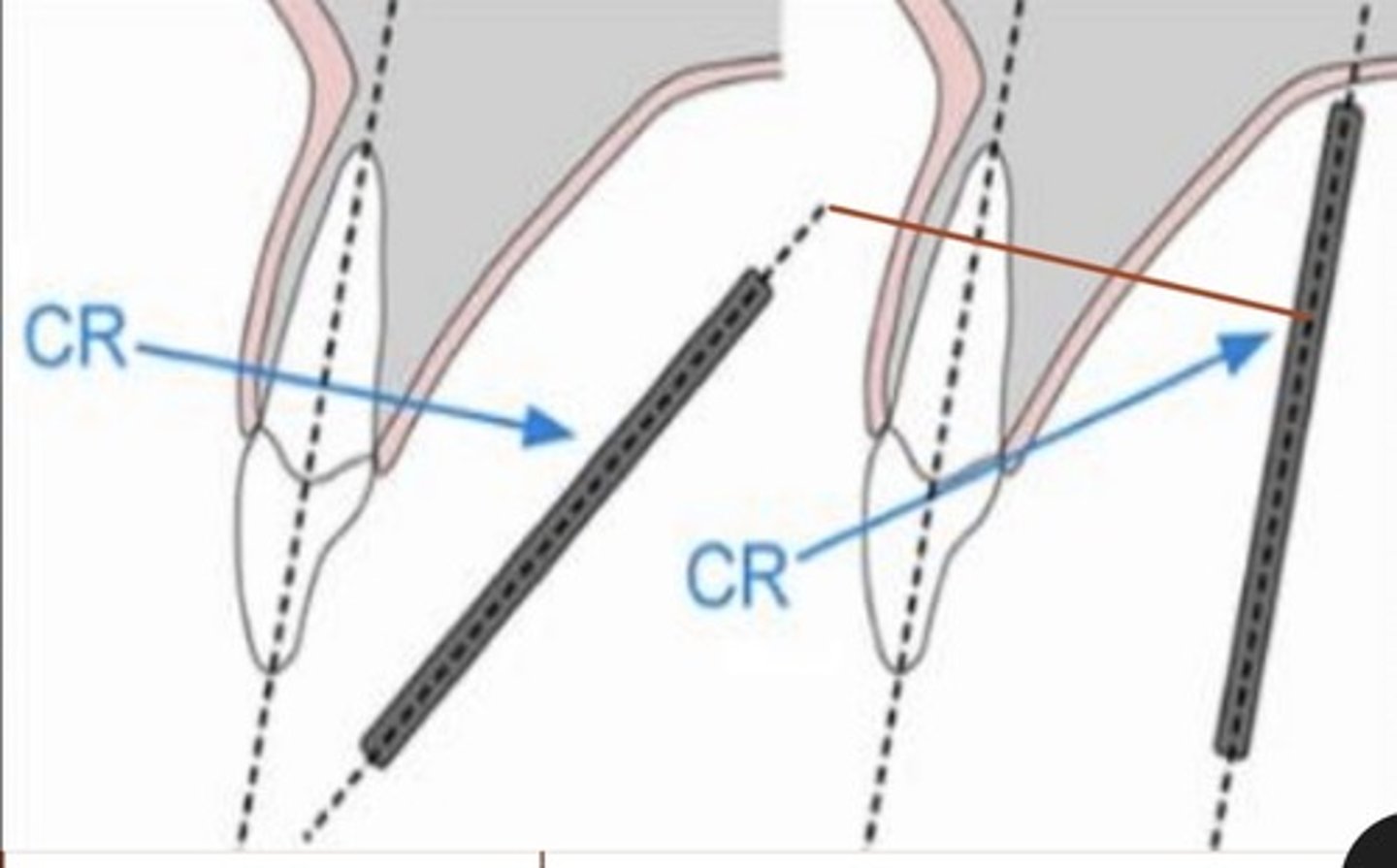
foreshortening occurs with
increased vertical angulation
radiographic sharpness
ability of the radiograph to define an edge precisely
penumbra
fuzzy/unclear area that surrounds the radiographic image
blurring of edges
small focal spot leads to
increased image sharpness and resolution
large focal spot leads to
loss of image clarity
radiographic resolution
the ability of the radiograph to record separate structures that are close together
high resolution
radiographs which resolve two adjacent high contrast objects as discrete entities
the smaller the structures visible the __________ the resolution of the image/system
higher