the oceans 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
__ bonds (pairs of shared electrons) bind atoms together
covalent
__ bonds are formed between oppositely charged sides of water molecules
hydrogen
due to its polarity, water forms __ bonds
hydrogen
the quantity of heat needed to increase the temperature of a specified quantity of a substance
heat capacity
heat aded to a substance that does not raise its temperature but instead changes its state
latent heat
the latent heat and heat capacity of water are very __ because the hydrogen bond is stronger than van der Waals forces
high
in water, the __ attraction between water molecules and ions is __ than either the attraction between H-bonds or between ions
collective
greater
__ is determined by input (sources) and removal (sinks) of constituents
salinity
salinity:
the equal rate of __ and __ of constituents result in the steady-state of the oceans’ salinity
salinity can be measured by density, __, and __
salinity ‘used to’ be expressed per thousand (ppt) but currently __ is most appropriate. It is a unitless ratio.
salinity of seawater varies __ (ex. habitat) and __ (seasons)
input, removal
refraction, conductivity
PSU
spatially, temporally
Ocean salinity:
elements __ in seawater include every element on the periodic table. This are often divided in __ constituents, __ constituents, and __ constituents based on their __
constituents that adhere to the principle of __ proportions do not vary in relative __ (ex. chlorine)
dissolved
major, minor, trace
abundance
constant, concentration
one of the parts of which something is made up of
constituents
ocean gases:
__ gases dissolve in seawater until __ is reached. This equilibrium varies by the __ of the gas, __, and __. Concentrations of seawater gases are __ from atmospheric concentrations
atmospheric, equilibrium
Solubility, temperature, salinity
different
when does out-gassing and in-gasses to the atmosphere occur?
when there is a gas that is supersaturated or undersaturated relative to the equilibrium
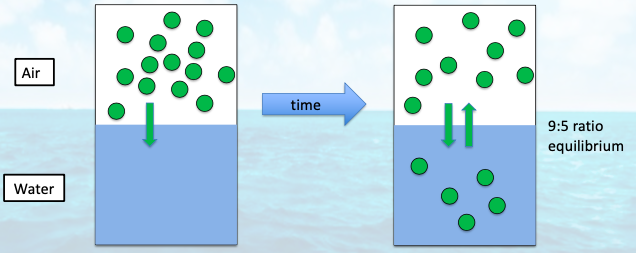
in-gassing occurs from __ to equilibrium
undersaturation
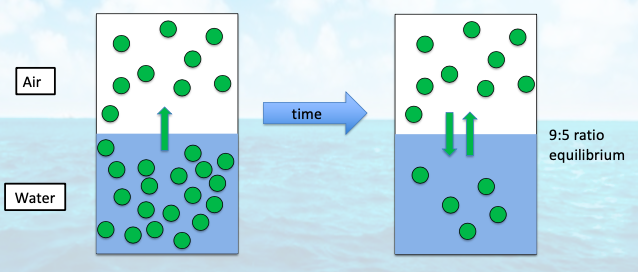
out-gassing occurs from __ to equilibrium
supersaturation
seawater pH:
the pH of seawater is __, where small changing in H+- concentration do not result in changes in __
substantial changes in __ concentrations does __ in changes in pH
as CO2 dissolves in water, it reacts with water, __ pH
buffered, pH
CO2, result
lowering
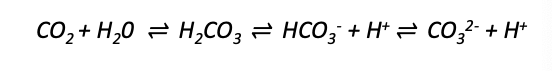
CO2 dissolving in water:
carbon dioxide → __ acid → __ → carbonate
carbonic
bicarbonate
intermolecular forces (ex. van der Waals forces and H- bonds) require or release __ (ex. heat) with __ changes between solids, liquids, and gases
energy
phase
thermal properties of water:
the high specific heat capacity and high latent heat of water lets water __ and release large amounts of __ (compared to other substances) with little __ change
absorb
energy
temperature
what are the thermal properties of water?
high latent heat, high specific heat capacity
density of water:
in the lattice structure of ice, water molecules are __ spaced, and the density is relatively __
from 0C to 4C, the lattice structure __ and the density __
above 4C, the lattice structure is __ and the density __ increasing with __
the density-optimum of 4C in water decreases with __ salinity
widely, low
collapses, increases
absent, decreases, temperature
increasing
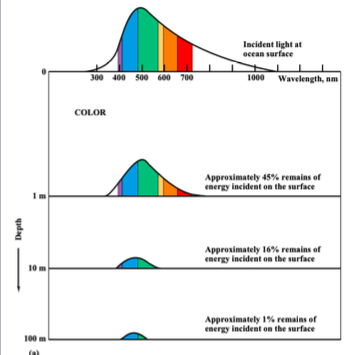
light and sound in water:
electromagnetic radiation is __ absorbed by water (does not travel through water)
long frequency __ waves travel __ of meters in water
__ light travels 10-__s meters, depending on frequency, __, and __
quickly
radio, 10s
visibly, 100s, intensity, turbidity
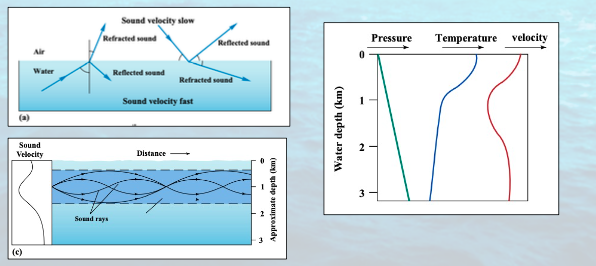
sound in water:
sound travels very __ through the water (10-1000s of meters and kilometers), depending on __ and __.
Changes in __ and __ refract sound and often dissipate it.
Sound travels best __ (no dissipation by refraction) or __ (smaller changes in velocity)
effectively, frequency, intensity
temperature, pressure
vertically, horizontally
1 PSU = 1 gram of salt per __ grams of water = 1 PPT
freshwater salinity has PSU of 0.0-__
estuarine water has a PSU of __-__
oceanic water has a PSU of __-__
seawater saturate with oxygen has ~_mg/l
typical seawater pH is __
freshwater is most dense at __C
0.5
0.5-30
30-38
7
8.1
4
keeps high-latitude water and atmosphere near freezing point all year
latent heat of fusion
the outermost layer of the earth, including sediments, the continental/oceanic crust, and the upper mantle of the earth
lithosphere
includes all the free water of the earth (marine and freshwater)
hydrosphere
includes the gasses surrounding the lithosphere and hydrosphere on earth
atmosphere
most the earth’s surface is __, and most of which is __-sea environment (dark and cold, detrital based)
water
deep
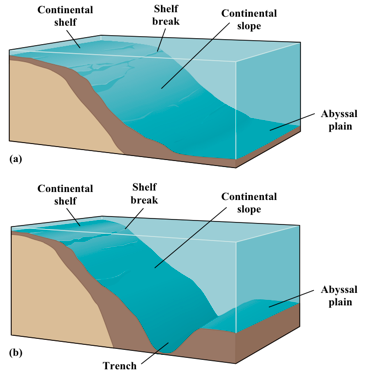
the continental slope transitions between the __ continental shelves of the continental crust and the __ oceanic crust.
Typically this is a smooth transition but can result in deep __ where the crust is pushed __ the continental crust (__)
shallow, deep
trenches, under, subduction
Present-day oceans:
the Pacific ocean is the __ and __ and has the oldest deep water. On the western side, the oceanic crust dips __ the continental crust. Deep __ and numerous islands are located here and where lots of __ activity occurs
The Atlantic ocean is an area of active seafloor __, the Mid-Atlantic ridge runs down the __ of the Atlantic from the __ to the Antarctic. Generally __ continental shelves
The Indian ocean is __. In the north, large rivers __ large amounts of sediments in the deep ocean around India and __. In the east, active __ of the oceanic crust results in deep __ an active __ activity. The Indian ocean includes __ connected ridges of seafloor spreading.
largest, deepest, under, volcanic
spreading, center, arctic, wide
smaller, deposited, China, subduction, trenches, volcanic, three
Lithogenous sediment is a category of sediments that are produced by the __ of rock. Most lithogenous sediments are produced on __ (terrigenous sediment) and typically transported to sea by __, __, and wind. __ and landslides can also contribute to this transport.
weathering
land, river, waves
Glaciers
Lithogenous Sediments: Rivers:
The sediment amount and particle size transported by rivers depend on the __ and __ of the river water. __ and faster rivers transport __ sediment.
When rivers meet sea, their velocity typically __. As velocity declines, __ sediment particles are deposited on the __, and smaller sediment particles stay __ longer.
volume, velocity, bigger
declines, larger, bottom, suspended
Lithogenous Sediments: Waves:
Waves produce __ currents - currents that move along the __. With this current, waves transport __ along the coast. The sediment amount and particle size that waves transport depends on the wave __ -- larger/__ waves transport/__ more sediment and of __ sizes
longshore, coast, sediment
energy, stronger, remove, larger
currents that move along the coasts
longshore current
Lithogenous Sediments: Wind:
Wind generally only transports __-size sediment (slit and clay), but is can do this across __distances. Sediments swept up by wind to __ altitudes and settles over time. Deserts and __ are typical sources of wind-deposited sediment
dust, large, high
volcanos
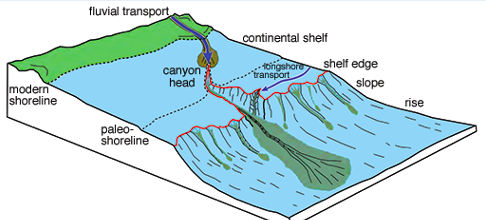
Turbidity currents:
The buildup of sediment on the continental slope can suddenly break __ and __ down the continental slope. The force of these turbidity currents break loose additional __ and transports __ amounts of sediment to the deep-sea. These sediments settle over large distances according to their __ size
loose, avalanche
sediment, large, particle
Biogenous sediments:
biogenous sediments are formed from __ that are produced through __ processes. Most biogenous sediments are produced from __ carbonate or __. Both are produced as __ by single-celled organisms.
particles, organic
calcium, silica, skeletons
Biogenous sediments: skeletons:
Coccolithophores and forminiferans produce skeletons made from __ carbonate.
Diatoms and radiolarians produce skeletons made from __.
As these organisms die or are consumed, their skeletons do not __ or are not __, sink to the __
calcium
silica
decompose, digested, seafloor
Biogenous sediments: CCD:
As biogenous particles sink, they __ at varying rates. Surface seawater is __ in dissolved silica and __ in dissolved calcium carbonate, which dictates the rate of __.
Below the __ Compensation Depth (CCD) the dissolution of calcium carbonate is so __ that __ carbonate can not persist in water. The CCD is determined by __ temperature, __ pressure, and __ pH
dissolve, undersaturated, supersaturated, dissolution
Carbonate, fast, solid
low, high, low
Distribution of surface seafloor sediments:
Deep sea __ is deposited everywhere (although not in equal quantities).
__ sediments are deposited over areas where biological production is __ (ex. on the equator, near the poles.)
If the seafloor is shallower than the __ (and biological production is sufficient), __ sediments are present.
clay
siliceous, high
CCD, calcareous
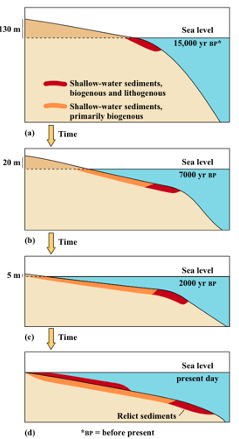
Sediments on continental shelves:
Sediment on continental shelves are generally __, with larger sediments __ to the shore and small grain sizes __ away from the shore.
Occasionally, sediments that are indicative of __ environments can be found __ away from the coast
lithogenous, closer, farther
costal, far
Typical ocean depth is __-__m
Depth on the continental shelves ranges typically from 0-__m
‘Deep sea’ is typically considered deeper than __m
CCD depth: Pacific __ than 4000m; Atlantic: __ than 4000m
Over the last 20,000 years, sea levels rose ~__m
Typical accumulation rate of sediment on the seafloor of the oceanic crust is from 1cm-_cm per __ years
3000-4000
200
200
less, greater
120
5, 1000
what is the average depth of the ocean
3,800m
what is the typical deepest depth of the continental shelves
200m