APES Unit 7
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Pollutant
Any substance that contaminates the environment and causes harm to living organisms.
VOCs
hydrocarbons: methane, octane, benzene, formaldehyde (anything organic that can diffuse into the env)
primary air pollutant
put directly into the troposphere from natural events or human activities in a harmful form
-CO2 and NO2 gases from car exhaust
-ash produced from coal burning
-SO2 gas from volcanoes and coal
carbon monoxide
odorless gas air pollutant
NOx (nitrogen oxide)
examples: NO, NO2, N2O
sulfur dioxide
from the combustion of coal (SO2, SO3)
particulate matter
solids (dust, soot, lead, nitrate and sulfate salts)
liquids (sulfuric acid, PCB, pesticides, dioxins)
air pollution
presence of one of more chemicals in the atmosphere that:
-cause harm
-alter the climate
-solid, gaseous, or liquid form
-majority of pollutants are from natural sources (dust, forest fires, geological processes)
-added through burning fossil fuels, erosion of land, factory emissions
hazardous air pollutants
benzene, formaldehyde, chloroform, lead, radioactive
why do developing countries have worse air pollution?
laws are weak or not applied, vehicle emission standards are less stringent and coal power stations more prevalent
secondary pollutants
when primary pollutants react with one another to form new pollutants
-SO2(burning coal) + water vapor = acid rain
-grey smog
photochemical smog
formed when nitrogen oxide + VOCs react with heat and sunlight (associated w vehicle emissions)
-orange smog
-fertilizers responsible for 51% of NOx emissions in Cali
Industrial smog
sulfur dioxide emmissions + water = sulfuric acid (rain)
due to burning large amounts of coal and oil
-not a problem in developed countries(Londons Pea Soup Fog)
-prominent in urban areas: china, india, ukraine, eastern european countries
-gray smog
factors that influence smog
-local climate (temp/rain)
-population density
-amount of industry
-fuels used in the area
-urban buildings
-hills and mountains
-grasshopper effect (pollutants evaporate with warm air and return to earth with rain and snow in the colder areas of the globe)
Natural factors that reduce air pollution
-rain and snow (cleanse air, cities w drier climates have more photochemical smog)
-salty spray from ocean (washes out particulates and pollutant winds)'
-winds (sweeps pollutants away w clean air)
Thermal inversion
-when warm air layer in atmosphere is over a cool air layer
-pollutants are stuck below a warm “blanket”
ex: LA, Denver, Mexico City
health effects of air pollution
-irritation of respiratory system
-worsening asthma or bronchitis
-emphysema
-shortened life span
noise pollution
sounds at high enough levels to cause physiological stress and hearing loss
impacts on human hearing
-hearing loss caused by 85 dB or higher
-stereo-cilia (hear cells in inner ear) to break off and they never grow back
-damage to bones in middle ear or eardrum
Tinnitus
ringing/buzzing in ears or head
-can be temporary or permanent
formaldehyde
colorless, highly toxic, and flammable gas at room temperature
places effected by acid rain
Ohio Valley, mountain tops in LA, Asia (worst)
-in places with thin acidic soil, low buffering abilities
acid rain effects on the human/economy
-contributes to asthma and bronchitis
-leach toxic metals from water pipes to drinking water
-damages statues and buildings
acid rain effect on ecosystem
-decreased pH of soil and water
-foliage damage
-weakened plant immune systems
-inc solubility of heavy metals
-dec biodiversity (areas downwind of coal power plants)
acid rain prevention
-reduce energy use and burning coal
-switch to cleaner burning fuel
-burn low sulfur coal
install highly effective scrubbers that remove SO2, NOx, and particulates
-share cars
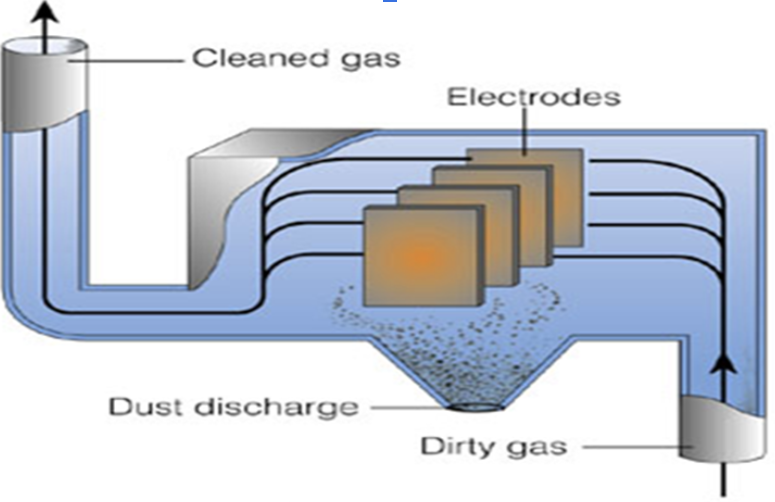
electrostatic precipitator
Use charges to separate the particulate matter from the gas
Suck up the “dirty gas” (filled with particulates) and the precipitator will impart a charge on the particulates.
charged particulates will stick to the oppositely charged electrodes…cause opposites attract!
Only clean air will leave!
shut the power off to the electrodes and the dust falls, collects at the bottom & is taken to a hazardous landfill.
Negative: Electrostatic Precipitators only remove large, medium and small particles…NOT the dangerous ULTRAFINE!
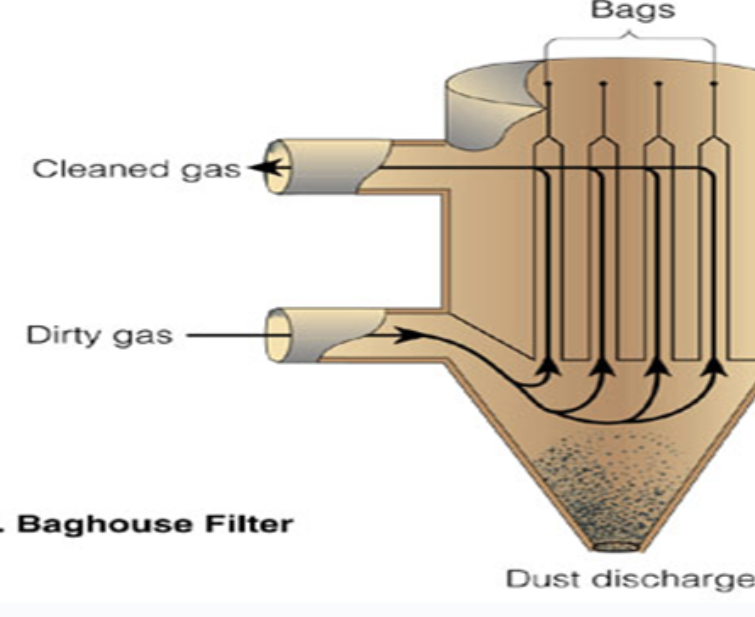
baghouse filters
gas filled with particulate matter will be sucked in and massed through several filters, with each filter becoming smaller and smaller.
Particulate matter stays behind, leaving clean gas.
These even remove ULTRAFINE!
These have a 99%
Collect dust & bury at haz landfill
Negatives: Expensive, not required
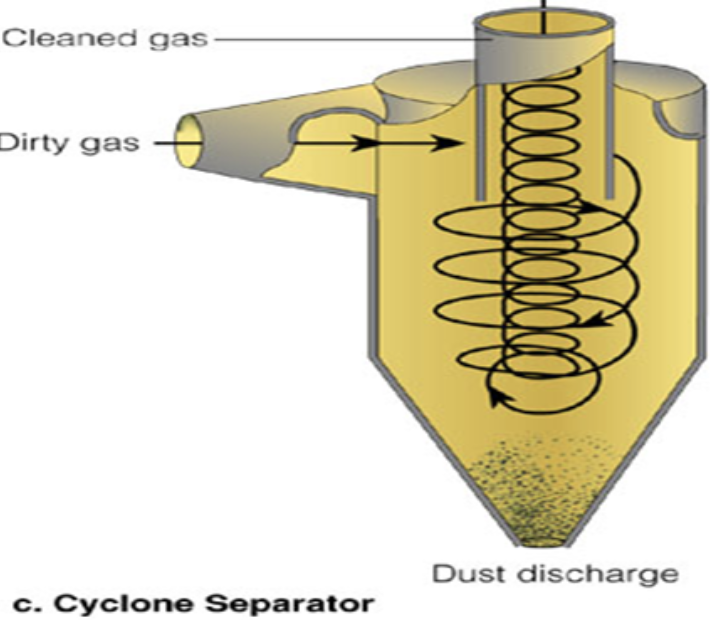
Cyclone Separators
cheap!
Suck in the dirty gas filled with particulates
The air is swirled like a vortex with heavy particulates falling out of the vortex to the bottom
Collect the ash & bury at haz landfill.
Negative: Really only removes large particulates
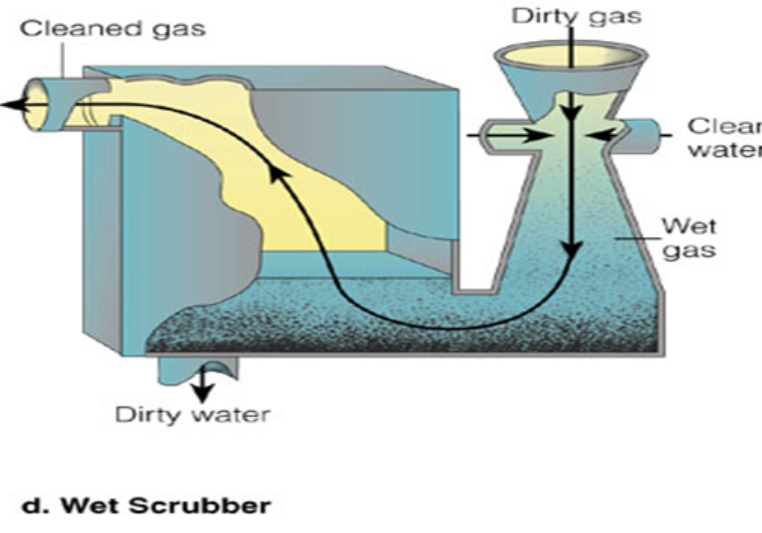
Wet Scrubbers
Dirty gas goes in and is passed through a water spray. The water captures particles AND…SO2 (because SO2 + water = H2SO4, sulfuric acid)
filters photochemical smog
The ash is disposed of in haz landfill, the acid neutralized sent to water treatment plant
Clean air leaves!
Adv—this is the ONLY one that will “scrub out” SO2 and particulates
Negatives: Does not remove the ultrafine particulates
vapor recovery nozzle
Stage I- When tanker replenish fuel supplies, vapors displaced in the storage tank and pumped through a recovery nozzle into the tanker
Stage II- Gasoline vapors in motor vehicles are sucked in through holes in the nozzle and pumped back into the gasoline storage tank underground.
Catalytic Converters
Found at the base of a car’s tailpipe
Converts harmful pollutants (CO, NOx, and hydrocarbons) into less harmful molecules (CO2, N2, O2, and H2O)
clean air act
1970- established NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards)
set 6 criterion air pollutants (CO, NO2, SO2, Particulates, Ozone, Lead)
1990- set up SO2 cap and trade
Enables the 110 most polluting power plants in 21 states to buy and sell SO2 pollution rights
Which type of pollutant is found in some types of carpet, furniture, and plywood and is dangerous to human health?
formaldehyde
Photochemical smog levels are usually highest in…
summer(hot)
Acid rain affects trees by…
I. damaging the protective coating on leaves
II. leaching nutrients from the soil and away from trees
III. stunting growth
Which of the following is used to reduce ultrafine particulate emissions from coal-burning power plants?
baghouse filters
Which of the following is not true of the Clean Air Act?
It was passed by Congress during the early 1970s
It regulates the amount of CO emitted by power plants.
It has remained largely unmodified since it was originally signed into law.
It established a cap-and-trade program for SO2 in 1990.
Which of the following is a primary pollutant?
carbon monoxide
sulfuric acid
nitric acid
ozone
Which of the following is NOT identified by the EPA as one of its six criteria air pollutants?
particulate matter
PANS
lead
ozone
Ozone in the troposphere can result in all of the following EXCEPT
eye irritation
lung cancer
bronchitis
headache
Which of the following is NOT true about noise pollution?
it can cause a decline in biodiversity
noise pollution does not affect humans
it can cause permanent hearing damage
all of these are true
major sources of outdoor air pollution
-57% transportation
-21% fuel combustion(except vehicles)
-12% industrial process
-10% other
5 most dangerous indoor pollutants
Cigarette smoke
Formaldehyde (from particle board, carpet, paneling, furniture)
Radon-222 gas (natural decay of uranium releases gas in ground)
Very small fine and ultrafine particles
Asbestos
cigarrette chemicals
Nicotine
Hydrogen cyanide
Formaldehyde
Lead
Arsenic
Ammonia
Benzene
Carbon monoxide
Over 70 different chemical found in cigarette smoke are KNOWN CARCINOGENS.
cigarrettes on health
Cigarette smoking causes more than 480K deaths EACH YEAR
90% of all lung cancer deaths
80% of COPD deaths
Formaldehyde
Colorless, extremely irritating gas for manufacturing common household materials
20-40 million Americans suffer from breathing problems, dizziness, headaches, rashes, sinus & eye irritation and nausea from daily exposure to low levels
Sources: building materials, plastics, furniture, wrinkle free coating on clothing
Formaldehyde
1 ounce dose at 37% formaldehyde = lethal
allows no more than 16 ppb formaldehyde in the air in new buildings constructed for that agency.
Homes will often measure 0.076 ppm (76 ppb) when brand new and 0.045 ppm after 30 days.
Radon-222
Colorless, odorless, tasteless, radioactive
Comes from the decay of uranium-238
common in granite, phosphate, uranium, shale soils & rocks
when rocks break down, gas is released, normally filters through soil & diluted in atmosphere
Radon problems
if seeps into buildings; can potentially increase the risk cancer
Radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer after smoking! More than 21,000 deaths per year.
ultrafine particles
Smaller than 100 nanometers, carbon based or metallic
Outdoor sources: volcanic lava, ocean spray, and smoke
Indoor sources: laser printers, fax machines, photocopiers, the peeling of citrus fruits, cooking, tobacco smoke, penetration of contaminated outdoor air, chimney cracks and vacuum cleaners
Not effectively captured by most air pollution control equipment
ultrafine particle problems
Small enough to penetrate body defenses
Bring other cancer/toxic substances into body
Can cause chronic irritation that can trigger asthma attacks, aggravate lung disease and cause lung cancer
interfere with bloods uptake of oxygen and release of CO2, which strains the heart and increases the risk of death from heart disease
asbestos
used extensively due to extreme resistance to heat
firefighters uniforms, building walls, ceilings, SCHOOLS etc
asbestos problems
Microscopic fibers decay-cannot be broken down by body when inhaled
lodges in lung and “saws” lung tissue over time= lung cancer
Over 172,000 Americans have died prematurely due to asbestos exposure
Mesothelioma kills 2,000 - 3,000 Americans each year
asbestos health concerns
Among miners and workers in developing countries
Remodeling, Tear-out, Demolition workers
90% of these deaths can be prevented by:
Wearing a mask
Wetting asbestos
Changing clothes before and after handling
how our body protects us from air pollution
Hairs in nose
Sticky mucus in lining of upper respiratory tract
Sneezing and coughing
Cilia in upper respiratory tract
BUT prolonged exposure can overload our defenses.
air pollution health concerns
Air pollution can lead to:
lung cancer
asthma
chronic bronchitis (often in children of smokers)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorders
emphysema- loss of lung elasticity (can’t pull in air)
Smoking makes all exposure worse- concentrated radiation of lungs breaks down natural defenses
limestone
limestone has basic pH —> neutralizes acid decomposition
-acid decomposition leeches(strips) soil of nutrients(aluminum)
if theres less limestone THAN there would be less aluminum because MORE acid decomposition would occur
annual change formula
change of y
change of x
percent change formula
new-old / old *100
source of acid decomposition
car exhaust emits nitrogen oxides
sulfur based acid rain from coal burning power plants equation
2SO2 + O2+ 2H2O —> 2H2SO4
nitrogen based acid rain from vehicle emissions
3NO2 + H2O —> 2HNO3 + NO