assisting with reproductive and urinary specialties
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
gynecology
care of the female reproductive system
obstetrics
the study of pregnancy, labor, delivery, and the period following labor (postpartum)
urology
focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the male and female urinary-tract system and the male reproductive organs
menstruation
the process of discharging blood from the lining of the uterus
starts in puberty until menopause except during pregnancy
periods are monthly and last for 3-7 days
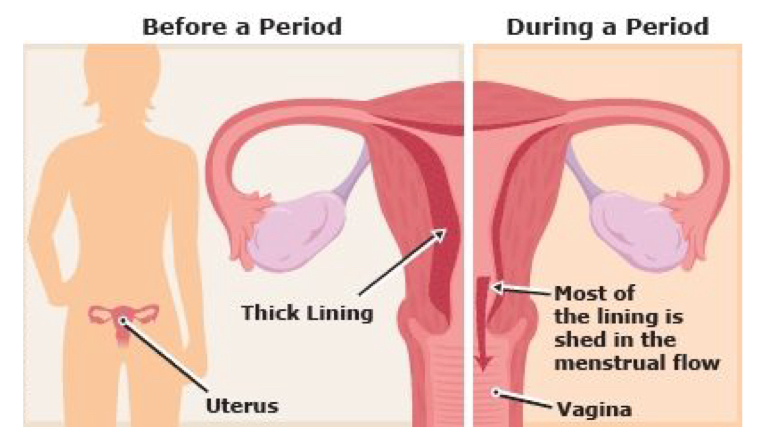
menarche
the first occurrence of menstruation
onset age approximately 10-15 years old
menopause
cessation of the menstrual cycle
naturally occurs between ages 45 and 55
surgically occurs through a hysterectomy
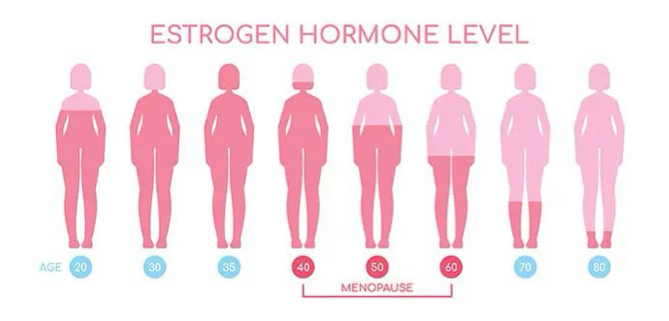
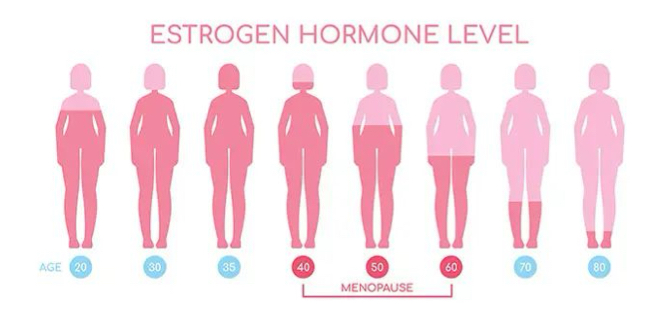
perimenopause
transitional period before menopause
levels of estrogen start to decrease
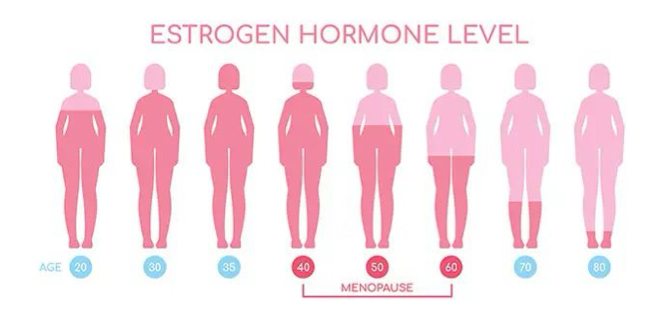
postmenopause
patient has been without a period for 12 months
what is the purpose of the gynecologic exam?
overview of a woman’s health and cancer-screening exams and tests
why does a female assistant need to be present during the gynecologic exam?
to assist the doctor
as a legal chaperone
what is the medical assistant’s role in the gynecologic exam?
have patient empty bladder and obtain urine specimen if needed
provide a gown and interview patient
discuss gynecologic and general health
review of factors that may indicate cancer or STIs
ask questions about the patient’s menstrual cycle
abnormal discharge
discomfort during sexual intercourse
check vital signs
determine the 1st day of her last menstrual period (LMP)
gather supplies and assist physician
what are the supplies needed for a pap smear?
vaginal speculum
gauze pads
cervical specimen collection kit (cervical broom, cervical scrape, endocervical brush, and cotton-tipped applicator)
exam light
glass slide and fixative or liquid collection medium for specimen preservation
water-based lubrication or warm water
breast exam
physician examines breasts and underarm areas to check for abnormal lumps
what is the MA’s role in breast cancer detection?
ask patient about any concerns or changes in her breasts
check and document when patient had last mammogram (patients over the age of 40)
mammograms should be ordered yearly
educate patient in self-breast exams
pelvic exam
inspection
external genitalia
vagina and cervic using a speculum
palpation
vagina
rectum
abdomen (to assess position of the uterus)
what are the medical assistant’s duties for an obstetrical patient?
prenatal care - educate on nutrition, exercise, medical monitoring
during pregnancy - set up childbirth classes, educate on healthy choices
monitor BP
urine testing
pregnancy tests
pregnancy tests
detect presence of hormone HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
STI tests
may require bacterial and tissue cultures, examining lesions, blood tests, and patient history
ultrasound
assess organs and structures (uterus, cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes, and ovaries) and produce pictures of a baby
hysterosalpingography
x-ray procedure used to view the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes
biopsy
tissue from the lining of the uterus is removed and examined under a microscope for cancer and other cell irregularities
coposcopy
when pap test shows abnormal cells
doctor can see the surface of the cervix up close
amniocentesis
needle inserted through the lower abdominal wall
fetal skin cells obtained and examined for chromosomal abnormalities
D & C
dilation of the cervix and scraping the uterine lining
to diagnose and treat uterine conditions and heavy bleeding
clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage or abortion
hysterectomy
removal of the uterus
hysterosalpingectomy
removal of the uterus and fallopian tubes
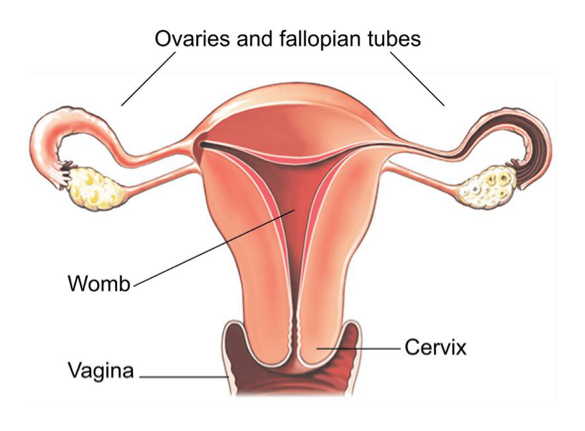
hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy
removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries (total hysterectomy)
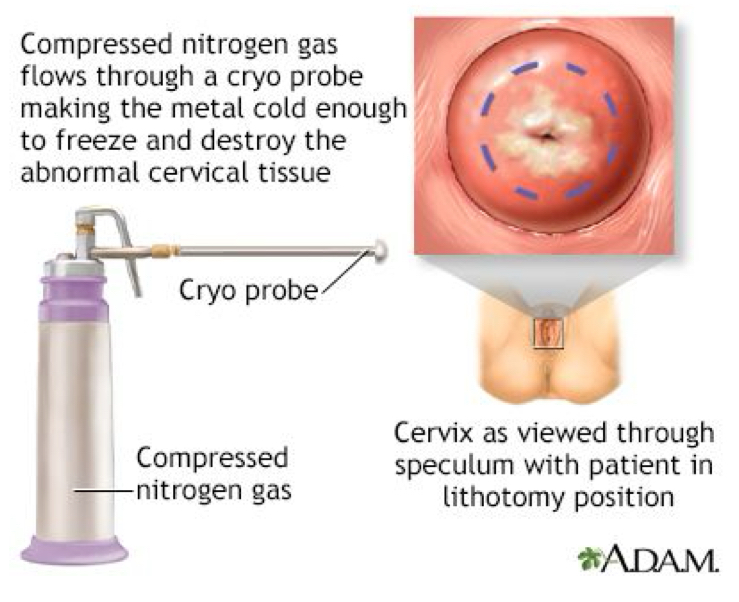
cryosurgery
of the cervix
uses extremely cold chemicals (liquid nitrogen) to destroy suspicious cells or tissue in a woman’s cervix
urologist
diagnoses and treats urological disorders and diseases
male and female urinary system
male reproductive system
assisting in urology
assists with general exams
collects and processes urine and blood
conducts patient education
patient chief complaint and history: check for any changes in urination
dysuria - discomfort or burning with urination
incontinence - lack of bladder control
the physical exam
palpation of the kidneys and bladder and visual inspection of the external genitalia
inspection and palpation of the penis and scrotum
the groin is examined for a hernia
in men over 40, the prostate gland is examined by digital insertion into the rectum
MA is responsible for teaching the patient to perform a regular testicular self-exam (TSE)
pyelography
x-ray of the kidney area with an iodine-based contrast agent
used to diagnose renal disorders
urinalysis
most commonly ordered test
blood testing
to monitor for dysfunctions of the prostate gland and certain STIs
semen analysis
determine fertility and evaluate success of vasectomy
smears
to diagnose infections
cystometry
measures bladder capacity and pressure
catheter is inserted through the urethra into the bladder
measurements taken of how much, if any, urine remains in the bladder and bladder pressure
cystoscopy
to examine the lining of the bladder and urethra
testicular biopsy
tissue sampling
alpha-blockers
work by relaxing muscles at the bladder neck to improve urinary flow
5-alpha inhibitors
treat enlarged prostate by blocking the production of the male hormones that are associated with prostate enlargement
anticholinergics
minimize bladder contractions and increase bladder capacity for people with an overactive bladder
ectopic pregnancy
fertilized egg unable to move out of fallopian tube into uterus for implantation
fibrocystic breast disease
benign, fluid-filled cysts or nodules in breast
ovarian cysts
sacs of fluid or semisolid material
usually benign
menstrual disturbances
amenorrhea - absence of menstruation
dysmenorrhea - painful menstrual periods
menorrhagia - heavy or prolong menstrual bleeding
metrorrhagia - abnormal bleeding
impotence
inability to achieve or to maintain an erection
cause may be physical, a side effect of medication, or psychological/emotional
sexual dysfunction disorders
interruption or lack of sexual response cycle
unhealthy view of one’s feelings about oneself and feelings toward sex
kidney stones
chemical substances in the urine form crystals in the kidney, ureter, or bladder
renal calculi, nephrolithiasis, or urolithiasis
what type of organism is chlamydia?
bacteria
what type of organism is gonorrhea?
bacteria
what type of organism is syphilis?
bacteria
what type of organism is trichomoniasis?
protozoa
what type of organism is HSV (herpes simplex virus)?
virus
what type of organism is HPV (human papilloma virus)?
virus
can chlamydia be cured?
yes
can gonorrhea be cured?
yes
can syphilis be cured?
yes
can trichomoniasis be cured?
yes
can HSV (herpes simplex virus) be cured?
no, but can be managed
can HPV (human papilloma virus) be cured?
no, but can be managed
how is chlamydia transmitted?
fluids
how is gonorrhea transmitted?
fluids
how is syphilis transmitted?
skin to skin
how is trichomoniasis transmitted?
fluids
how is HSV (herpes simplex virus) transmitted?
skin to skin
how is HPV (human papilloma virus) transmitted?
skin to skin
what is the average age range for the beginning of menstruation?
6 to 10 years old
8 to 12 years old
10 to 15 years old
12 to 18 years old
10 to 15 years old
what does the gynecology speciality focus on?
pregnancy
postpartum
female reproductive system
male reproductive system
female reproductive system
in addition to assisting in an gynecological exam, what other role might a female medical assistant have during the exam?
she may prescribe hormonal treatments if needed
she may perform the actual exam if the physician is male
her presence provides legal protection for a male physician
she may operate the microscope to check the specimens obtained
her presence provides legal protection for a male physician
the acronym LMP refers to the:
first day of a woman’s last menstrual period
date of a woman’s first menstrual cycle
last day of a woman’s last menstrual period
estimated date of a woman’s next menstrual period
first day of a woman’s last menstrual period
pregnancy tests detect the presence of which hormone?
THC
TSH
HBV
HCG
HCG
which procedure is the removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries?
hysterectomy
hysterosalpingectomy
hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy
partial hysterectomy
hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy
what is the most commonly ordered test in a urology practice?
semen analysis
cystometry
urinalysis
cystoscopy
urinalysis
what exam method does the physician use on the kidneys and bladder?
palpation and auscultation
palpation and inspection
inspection
palpation
palpation