Unit 2C.3: Objective Data | Vital Signs & Physical Assessment
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Vital Signs
Provide data that reflect status of several body systems including but not limited to cardiovascular, neurological, peripheralvascular, and respiratory systems
Temperature (TEMP)
Pulse/Heart Rate (PR)
Respiratory Rate (RR)
Blood Pressure (BP)
What is the typical sequence for vital signs?
RR
PR (using stethoscope)
TEMP
NO BP (unless in NICU or PICU)
What is the sequence for vital signs for pediatric clients?
36.5-37.5 degrees Celsius
Normal Range Adult Temperature
35-36.4 degrees Celsius
Normal Range Elderly Adult Temperature
Diurnal
Temperature has ___ variation, varying throughout the day.
4 AM - 6 AM
When is a persons temperature the lowest?
8 PM -12 AM
When is a persons temperature the highest?
Pulse Rate (PR)
Shock wave produces when heart pumps blood out of ventricles into aorta
Arterial/Peripheral Pulse
What is PR also called?
60-100 bpm
Normal Range for PR
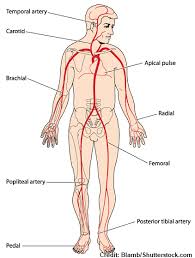
Temporal
Carotid
Apical
Radial
Brachial
Popliteal
Femoral
Dorsalis Pedis
What are the sites for PR?
Carotid
Apical
What sites is PR commonly taken for adults?
Radial
Brachial
What sites is PR commonly taken for pediatric clients?
False (Nurse MUST take RR without alerting the client since they may aleter their vital sign)
True or False: The nurse must alert the client prior to taking the RR.
12-20 cpm
Normal Value for RR
Dominant Arm
Where should BP be measured first?
Take on both arms
Subsequent readings taken in arm with highest measurement
What must be done regarding BP if it is the client's first time?
90-120 mmHg
Normal Value for Systolic BP
60-90 mmHg
Normal Value for Diastolic BP
Pulse Pressure
Is the difference between systolic and diastolic BP
30-60 mmHg
Normal Value for Pulse Pressure
decreases
When pulse pressure decreases, cardiac output ___
Heart is beating faster than normal
Heart attack
A decrease in pulse pressure are signs that…
Systolic: Less than 120 AND
Diastolic: Less than 80
According to the DOH, what is in the Normal Category (systolic and diastolic BP)?
Systolic: 120-129 AND
Diastolic: Less than 80
According to the DOH, what is in the Elevated Category (systolic and diastolic BP)?
Systolic: 130-139 OR
Diastolic: 80-89
According to the DOH, what is in the High BP Stage 1 Category (systolic and diastolic BP)?
Systolic: 140 or higher OR
Diastolic: 90 or higher
According to the DOH, what is in the High BP Stage 2 Category (systolic and diastolic BP)?
Systolic: Higher than 180 AND/OR
Diastolic: Higher than 120
According to the DOH, what is in the Hypertensive Crisis Category (systolic and diastolic BP)?
Head-to-Toe (Cephalocaudal)
Body Systems
Functional Health Patterns
Human Response Pattern
4 Components of Physical Assessment
Inspection, Palpation, Percussion, Auscultation (IPPA)
Physical Examination Techniques
Inspection
One of the Physical Examination Techniques
Involves using senses of vision, smell, and hearing to observe and detect any normal findings
May use special equipment (e.g., ophthalmoscope)
Room is at a comfortable temperature to ensure skin appearance is accurate
Room is has good lighting to ensure skin appearance is accurate
Look and observe prior to touching since appearance may be altered
Draping properly
Compare appearance of symmetric body parts
Guidelines for Inspection
SSS CLOMB PC
Acronym for 10 things that should be noted for in Inspection
Size
Symmetry
Sounds
Color
Location
Odor
Movement
Behavior
Patterns
Consistency
What 10 things should be noted for in Inspection?
Palpation
One of the Physical Examination Techniques
Involves using of hand to touch and feel
SSS MM TT DC
Acronym for 9 things that should be noted for in Palpation
Texture (Rough or Smooth)
Temperature (Hot or Cold)
Moisture (Dry or Wet)
Mobility (Fixed/Movable/Still/Vibrating)
Consistency (Soft/Hard/Fluid Filled)
Strength of Pulses (Strong/Weak/Thready)
Size (S/M/L)
Shape (Well-Defined/Irregular)
Degree of Tenderness (Pain upon palpation?)
What 9 things should be noted for in Palpation?
Fingerpads
Ulnar/Palmar Surface
Dorsal (Back) Surface
Parts of Hand to Use for Palpation
Fine discriminations (example: checking pulse, texture, size, consistency)
When should the Fingerpads of the hand be used in palpation?
Check vibrations, thrills, fremitus (vibration in chest wall)
When should the Ulnar/Palmar Surface of the hand be used in palpation?
Checking temperature
When should the Dorsal (back) Surface of the hand be used in palpation?
Light
Moderate
Deep
Bimanual
4 Types of Palpation
Light
One of the types of palpation
Little or no depression (<1cm); used to feel for pulses, tenderness, texture, temperature and moisture
pulses
tenderness
texture
temperature
moisture
When is Light Palpation used?
Moderate
One of the types of palpation
1 cm to 2 cm depression; used to feel for size, consistency and mobility of masses
Checking for thyroid/breast exam
Size, consistency and mobility of masses (including Thyroid and Breast exams)
When is Moderate Palpation used?
Deep
One of the types of palpation
2.5 cm to 5 cm depression; used to feel very deep organs covered by thick muscle
Deep organs covered by thick muscle
When is Deep palpation used?
Bimanual
One of the types of palpation
Using two hands (one hand applies pressure and other feels structure examined)
Percussion
One of the Physical Examination Techniques
Involves tapping of body parts to produce sound waves or vibrations to
Elicit pain
Determine location, size, and shape
Determine density (if organ is fluid or air filled)
Detect abnormal masses
Elicit reflexes
Elicit pain
Determine location, size, and shape
Determine density (if organ is fluid or air filled)
Detect abnormal masses
Elicit reflexes
5 Functions of Percussion
Direct
Blunt
Indirect/Mediate
3 Types of Percussion
Direct
One of the types of percussion
Tapping body part with one or two fingertips; may also use reflex hammer
Blunt
One of the types of percussion
Placing one hand flat on body surface and using fist of other hand to strike back of hand flat on body surface
Kidney Punch
Kidney Punch
Example of Blunt Percussion
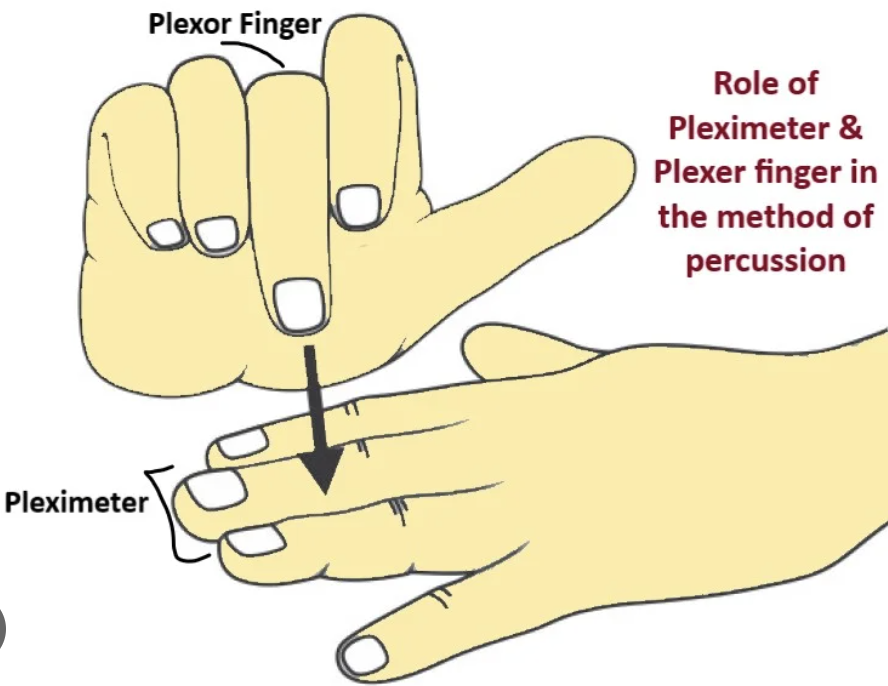
Indirect/Mediate
One of the types of percussion
Commonly used method, detects density of underlying structure
Putting pressure to listen
the pleximeter is the finger (usually the middle finger of the non-dominant hand) placed firmly on the body, acting as a stable surface to receive the percussion strike, while the plexor is the finger (typically the middle finger of the dominant hand) that delivers the controlled tap
Resonance (Hollow)
Hyperresonance
Tymphany (Drum-Like)
Dullness
Flatness
5 Types of Percussion Tones/Sounds
Resonance (Hollow)
One of the types of percussion tones/sounds
Normal lung
Hyperresonance
One of the types of percussion tones/sounds
Lung with emphysema
Usually if lung has too much air
Tymphany (Drum-Like)
One of the types of percussion tones/sounds
Puffed-out cheek,GI organs
Heard normally in stomach, not chest
Dullness
One of the types of percussion tones/sounds
Diaphragm, liver, pleural effusion
Heard over solid tissue
Flatness
One of the types of percussion tones/sounds
Muscle, bone
Auscultation
One of the Physical Examination Techniques
Requires the use of a stethoscope to listen for heart sounds, movement of blood through vessels, movement of the bowel, and movement of air through the respiratory tract
Eliminate distracting noises
Expose body part
Warm diaphragm/bell before placing on skin
Guidelines for Auscultation
Diaphragm
Bell
2 Parts of the Stethoscope
High-pitched sounds like
normal heart sounds
bowel sounds
breath sounds
When is the Diaphragm of the stethoscope used?
Low-pitched sounds like
murmurs
bruits
When is the Bell of the stethoscope used?