Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
depolarization
transmission of the electrical impulse that achieves a contraction of the heart
repolarization
heart relaxes + prepares to receive the next electrical impulse
P Wave
atrial depolarization
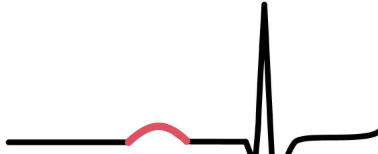
PR interval
related to the rate of cardiac impulse transmitted from the AV node
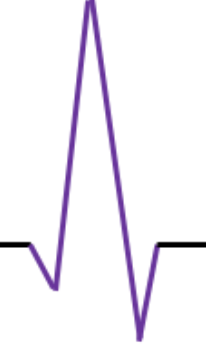
QRS Complex
ventricular depolarization
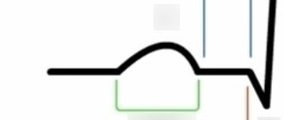
ST segment
follows ventricular depolarization + occurs prior to the start of ventricular repolarization
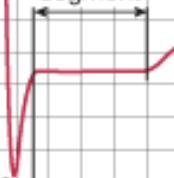
T wave
ventricular repolarization is occuring
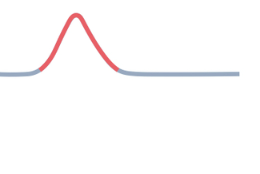
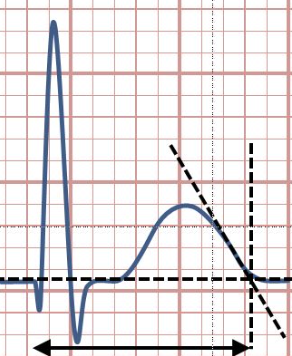
QT Interval
time for ventricular repolarization is complete
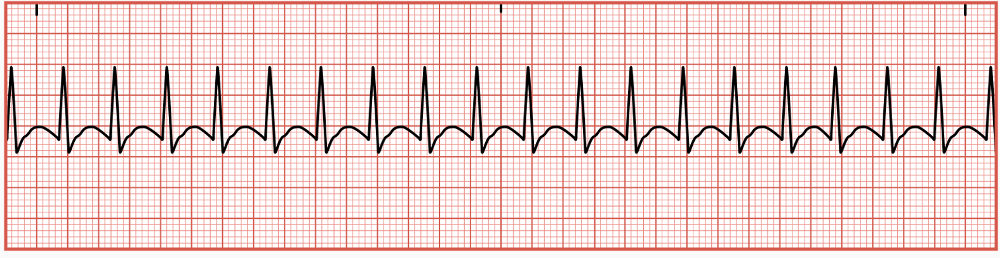
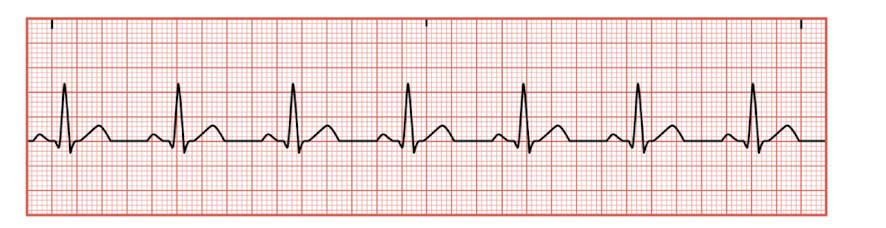
Normal Sinus Rhythm
normal conduction of the cardiac electrical
SA node
AV node
Bundle of HIS
R+L bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Sinus Bradycardia
Occurs when SA node sends an electrical impulse slower than 60bom
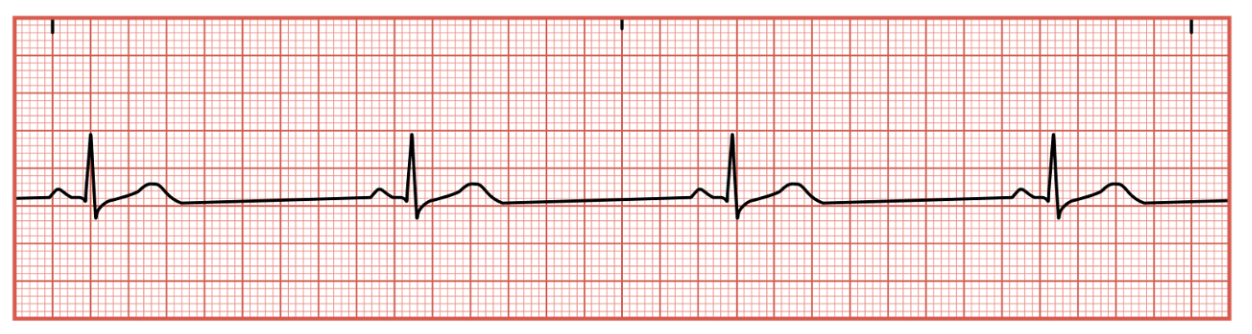
Sinus Tachycardia
Occurs when SA node sends a faster electrical impulse greater than 100 bpm
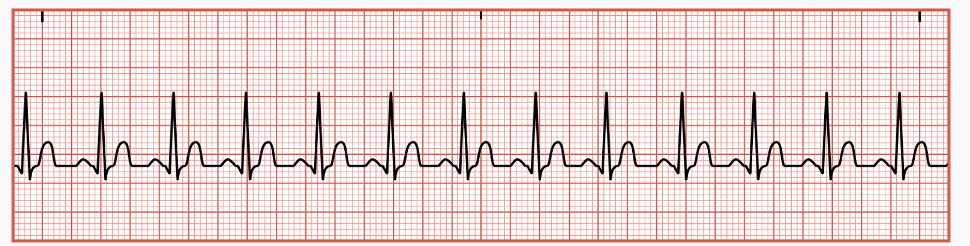
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
occur when early electrical impulses, originating from irritated ventricular cells are transmitted before the next normal impulse is expected from the SA node
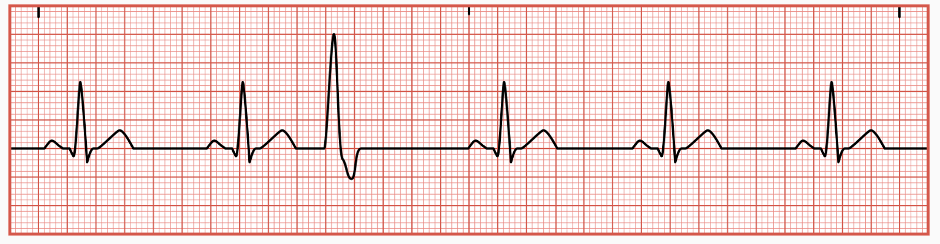
Premature Atrial Contractions
occur when irritated atrial tissue fires an early electrical impulse before the next normal impulse is expected from the SA node
causing the heart’s electrical conduction system to activate an early heartbeat or impulse from one of the two atrial chambers
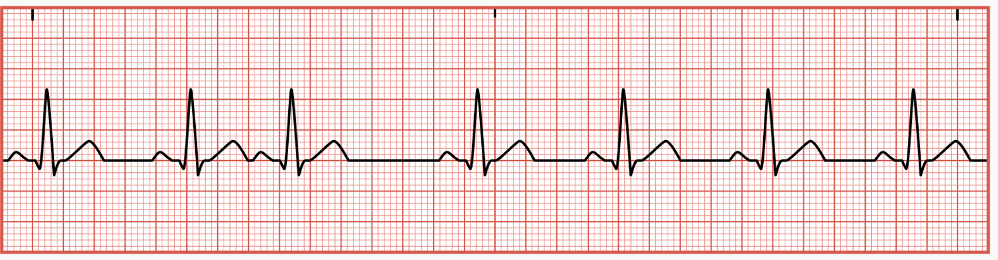
First Degree Heart Block
occurs when cardiac conduction system is delayed in transmitting an electrical signal through the right atrium to the AV node, resulting in a PR interval greater than 0.20 seconds
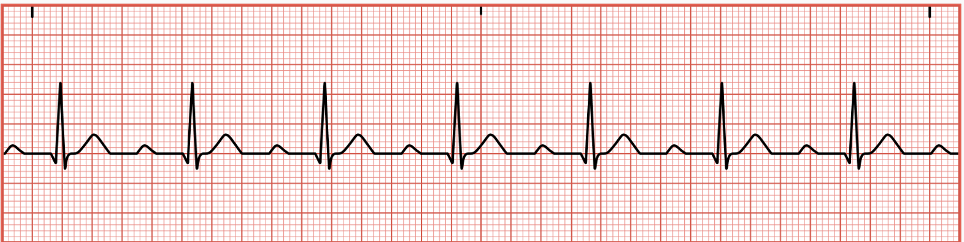
Atrial Fibrillation
occurs when the SA node is not firing appropriately
electrical impulses are rapid, chaotic, and irregular
blood clots can form
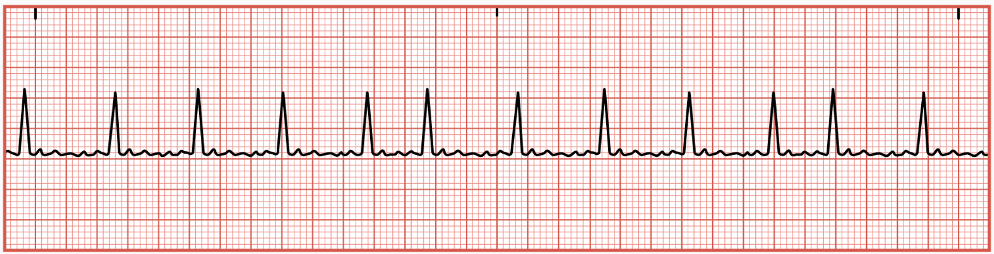
Atrial Flutter
occurs when the atria are beating in a regular rhythm + increased rate
caused by multiple rapid electrical impulses being sent from the atrial too quickly for the AV node to process before the transmission to the ventricles
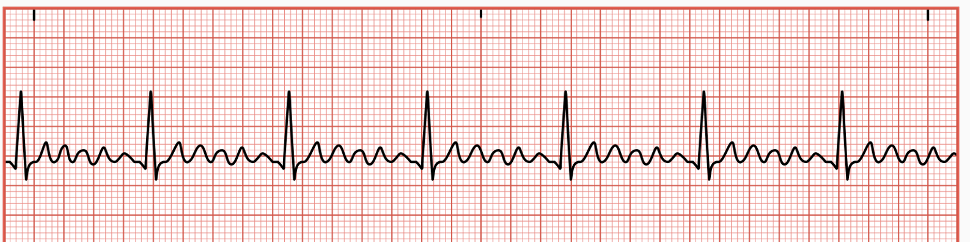
Supraventricular Tachycardia
originates in AV node and can cause excessive excitability of the atrial tissue resulting in an increased HR
occurs abruptly and suddenly ends without warning