anatomy - cardiac/digestive/respiratory
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what are three characteristics of epithelial tissue?
next to a free surface, packed close together (leak-proof), and simple or stratified
what does simple squamous tissue look like and what does it do?
thin/flattened and rapid diffusion
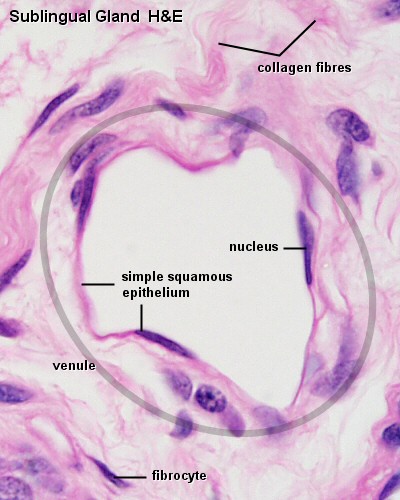
where is simple squamous tissue found?
in lungs and blood vessels as well as in the lining of body cavities.
what does simple columnar tissue look like and what does it do?
it is simple and columnar, and is used for secretion and absorption
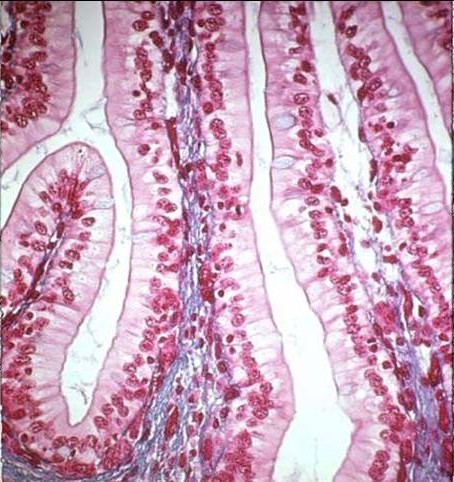
where is simple columnar tissue found?
in the small intestine
what does pseudostratified columnar tissue look like and what does it do?
it is single layered with multiple nuclei and has cilia to filter debris
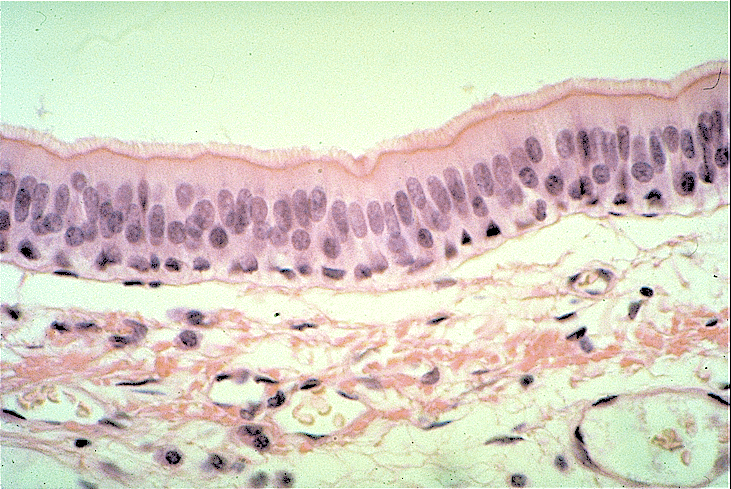
where is pseudostratified columnar tissue found?
in the respiratory pathways and in the trachea
what does glandular tissue look like and what does it do?
is it in a cuboidal shape and is used for secretion
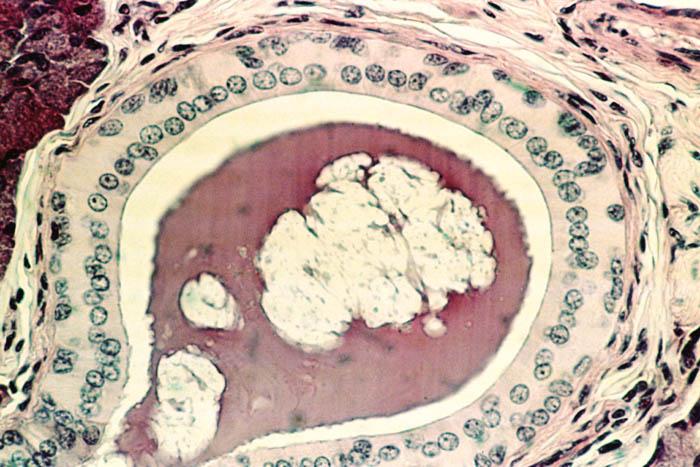
what is the digestive tract?
a tube from the mouth to the anus that is lined with epithelium
what are accessory organs?
organs that secrete substances into the digestive tract, made of cuboidal epithelium
what are the five general functions of the digestive system?
mechanical processing, secretion of enzymes, digestion, absorption, and elimination
what is mechanical processing?
segmentation into small pieces (chewing)
what is digestion?
chemical break-down to simple nutrients
what is absorption?
nutrients to blood
what is elimination?
unabsorbed waste
where is the mouth and what does it do?
a part of the digestive tract, used for chewing
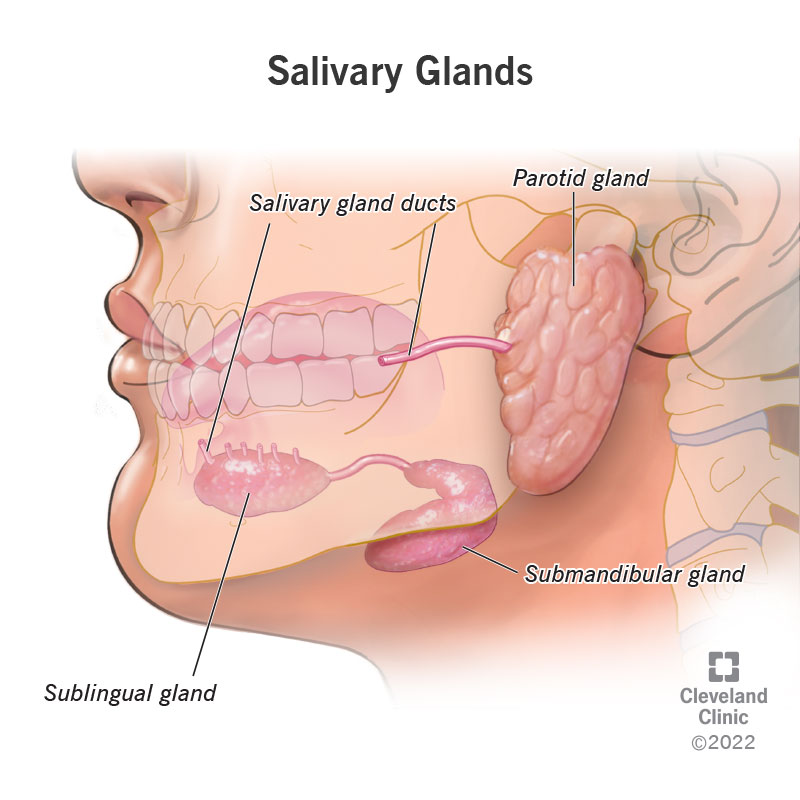
where are the salivary glands and what do they do?
accessory organs that release saliva to moisten and digest carbohydrates
where is the pharynx and what does it do?
a part of the digestive tract, it pulls food into the body
where is the esophagus and what does it do?
part of the digestive tract, it moves and moistens food

where is the stomach and what does it do?
part of the digestive tract, it stores and breaks up food and absorbs water and minerals
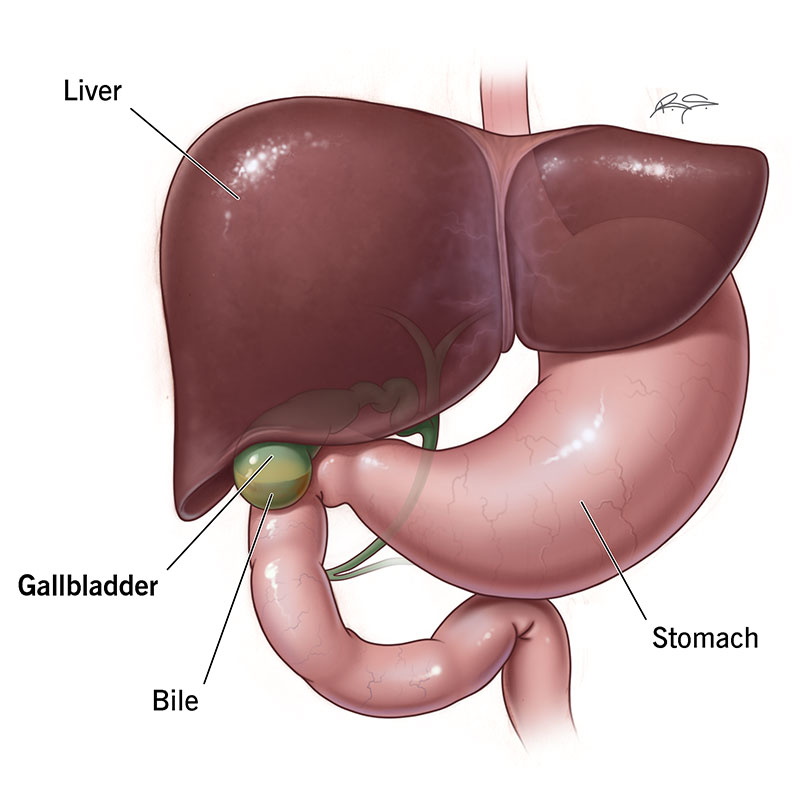
where are the liver and gallbladder and what do they do?
accessory organs, they make and send bile down bile duct
where is the pancreas and what does it do?
accessory organ, sends many enzymes down the pancreatic duct
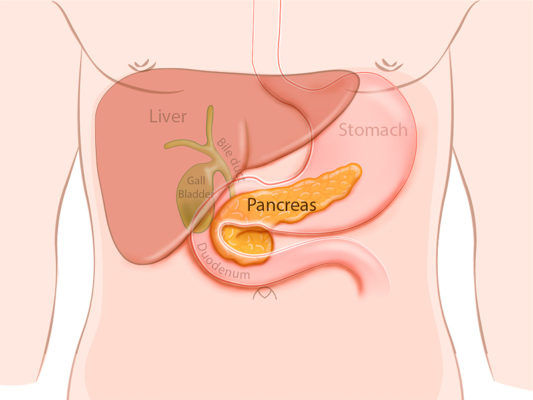
where is the small intestine
the interior intestine that is enclosed by the large intestine
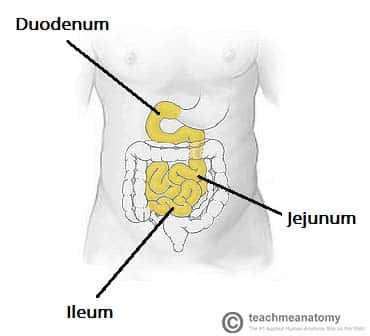
where is the duodenum and what does it do?
the top part of the small intestine that that follows the stomach, it mixes fluids from stomach, pancreas, and gallbladder
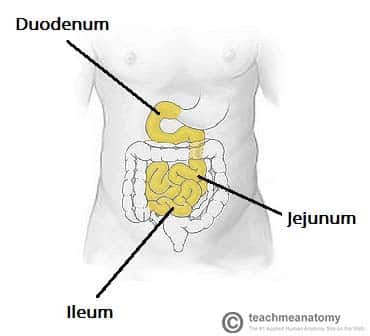
where is the jejunum and what does it do?
the middle part of the small intestine, it digests carbs, proteins, and fats. It also absorbs all nutrients.
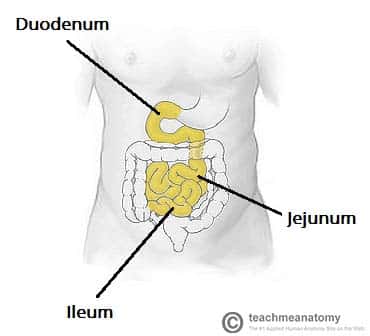
where is the ileum and what does it do?
the bottommost part of the small intestine, it helps with absorption
how are carbs digested?
amylase
how are proteins digested?
peptidase
how are fats digested?
bile
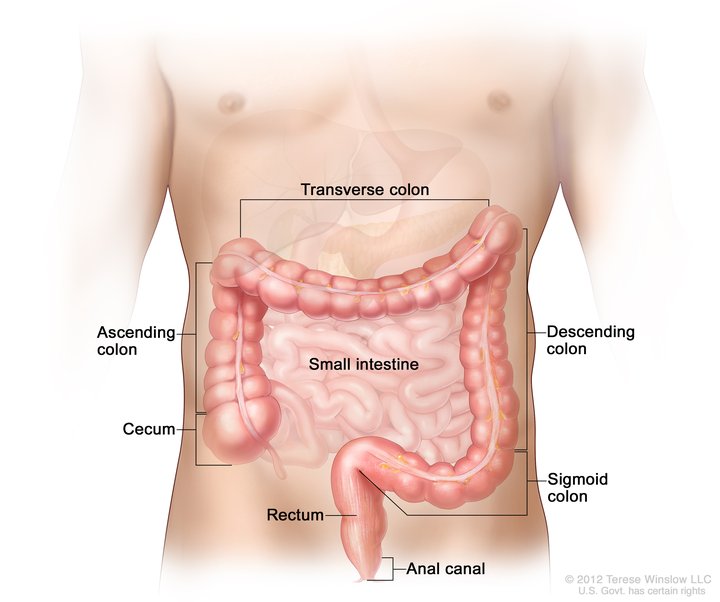
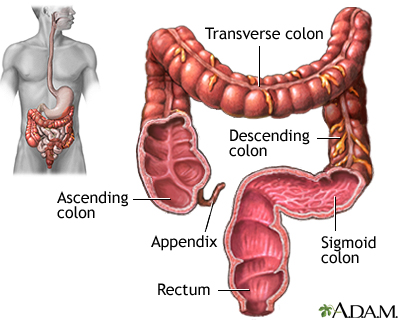
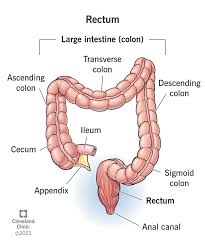
where is the large intestine/colon (all four parts) and what does it do?
part of the digestive track, the ascending is on the right side, transverse is along the top, descending is on the left side, and sigmoid is near the bottom. It’s function is to absorb water and minerals and concentrate undigested matter (fiber).
where is the rectum and what does it do?
part of the digestive track, it builds pressure and contracts to expel feces
where is the anus and what does it do?
part of the digestive track, it is the end of the system
what is respiration?
exchange of CO2 and O2 at alveoli —> the alveoli has concentrates O2 that it moves to blood, and the blood vessels have concentrated CO2 that it pushes out to the lungs
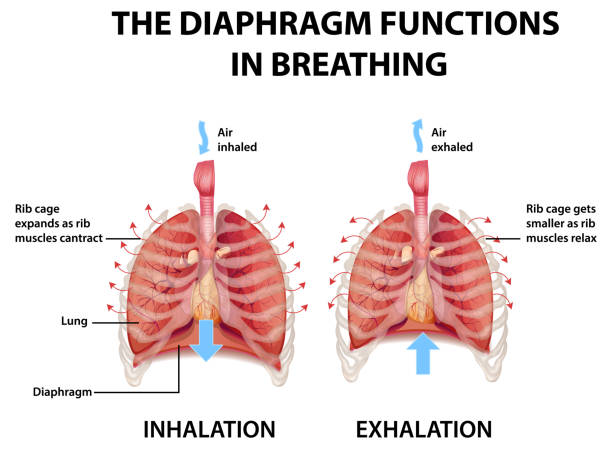
what is inhalation?
diaphragm contracts, flattens and the lungs expand
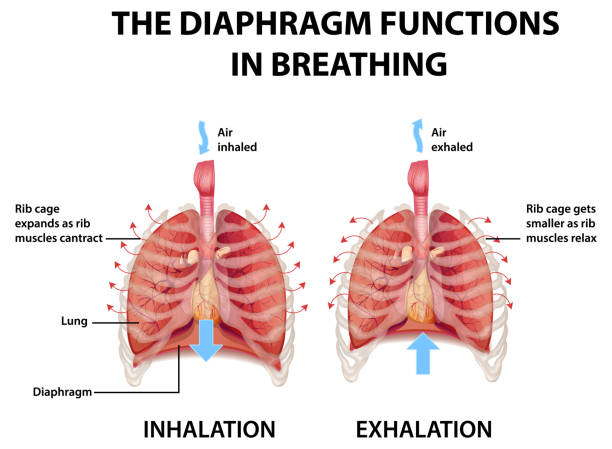
what is exhalation?
diaphragm relaxes, curves up and lungs shrink
what does ventilation do?
it speeds up diffusion by getting O2 closer to epithelium, and CO2 further away from blood vessels
what is the respiratory organ pathway?
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, primary bronchus, respiratory bronchioles to alveoli
where is the nasal cavity and what does it do?
it warms and moistens the air
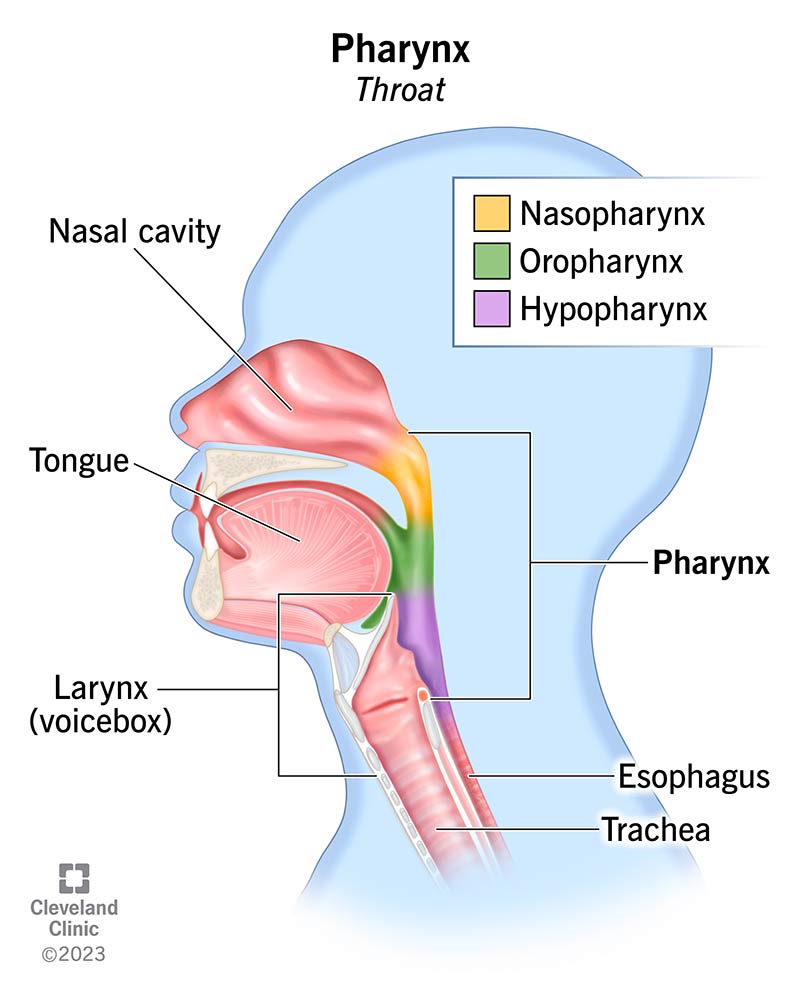
where is the pharynx and what does it do?
at the back of the mouth and throat, it filters air and is a passageway for air from the nasal cavity to larynx
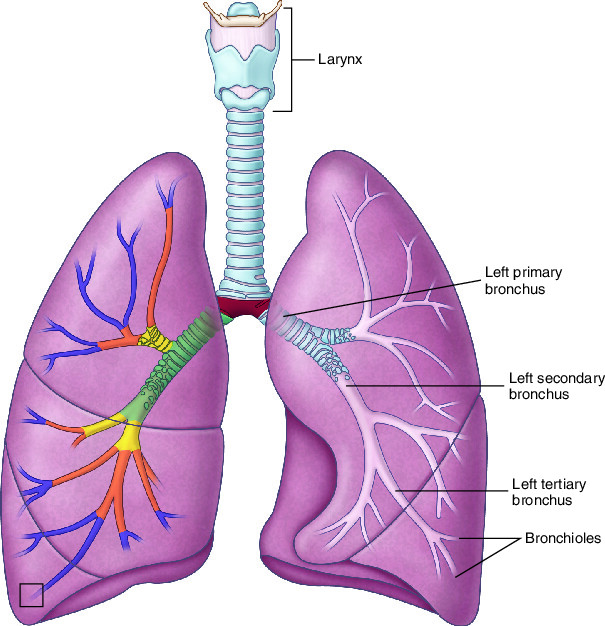
where is the larynx and what does it do?
it uses the voice box and vocal chords to produce sounds
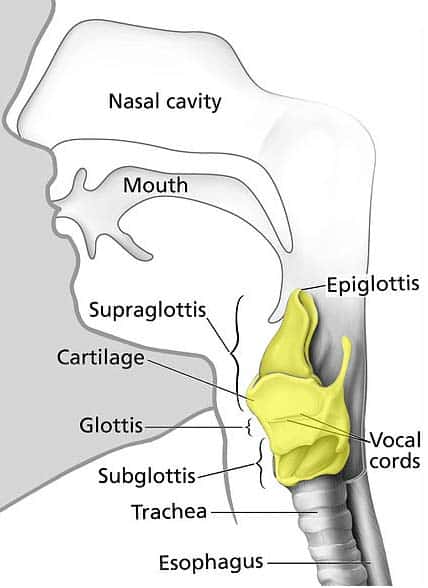
where is the trachea and what does it do?
helps to carry air into and out of the lungs
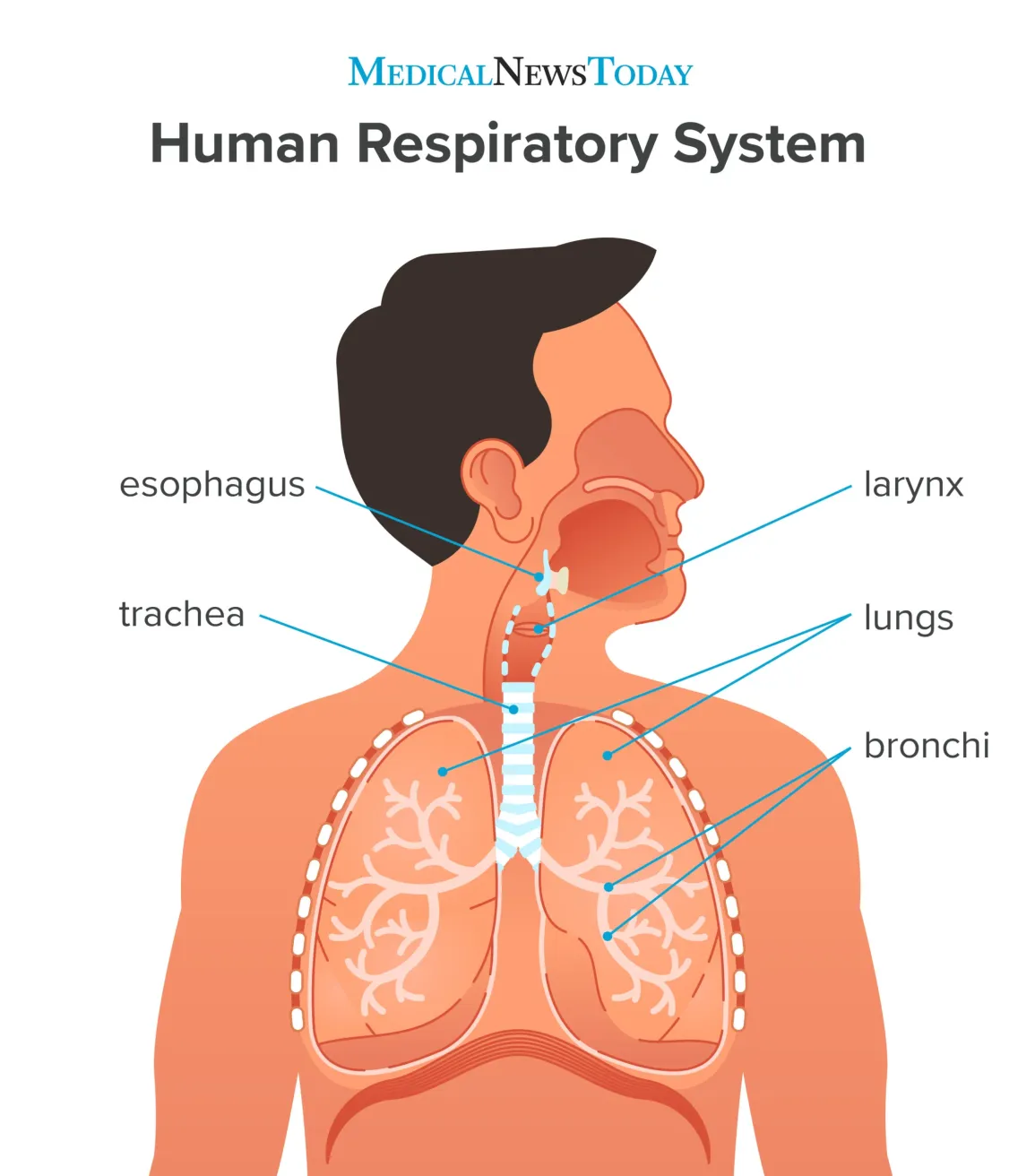
where are the primary bronchus and what do they do?
distributes air from the trachea to the lungs
what are red blood cells and what do they do?
hemoglobin that binds and carries O2 and CO2
what are white blood cells and what do they do?
housekeeping and defense (disease fighting)
what is the main function of platelets?
blood clotting
what is the main function of plasma?
carrying water and antibodies
what is circulation?
internal transport by blood
where does circulation exchange and what organs does it include?
at the capillary beds, organs: lungs, small intestine, kidneys, etc.
what are the two pathways of circulation and what do they go with?
pulmonary is with the lungs, and systemic is with the body
what is pulmonary flow (circulation)
right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins
what is systemic flow (circulation)?
left atrium → bicuspid valve → left ventricle → aorta → body → vena cava
what controls heartbeat and where is it located?
it is controlled by the SA node in the right atrium
what do arteries do?
carries blood AWAY from the body
what do veins do?
carries blood toward the heart