Development (I hate mr jasir)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Brain diagram
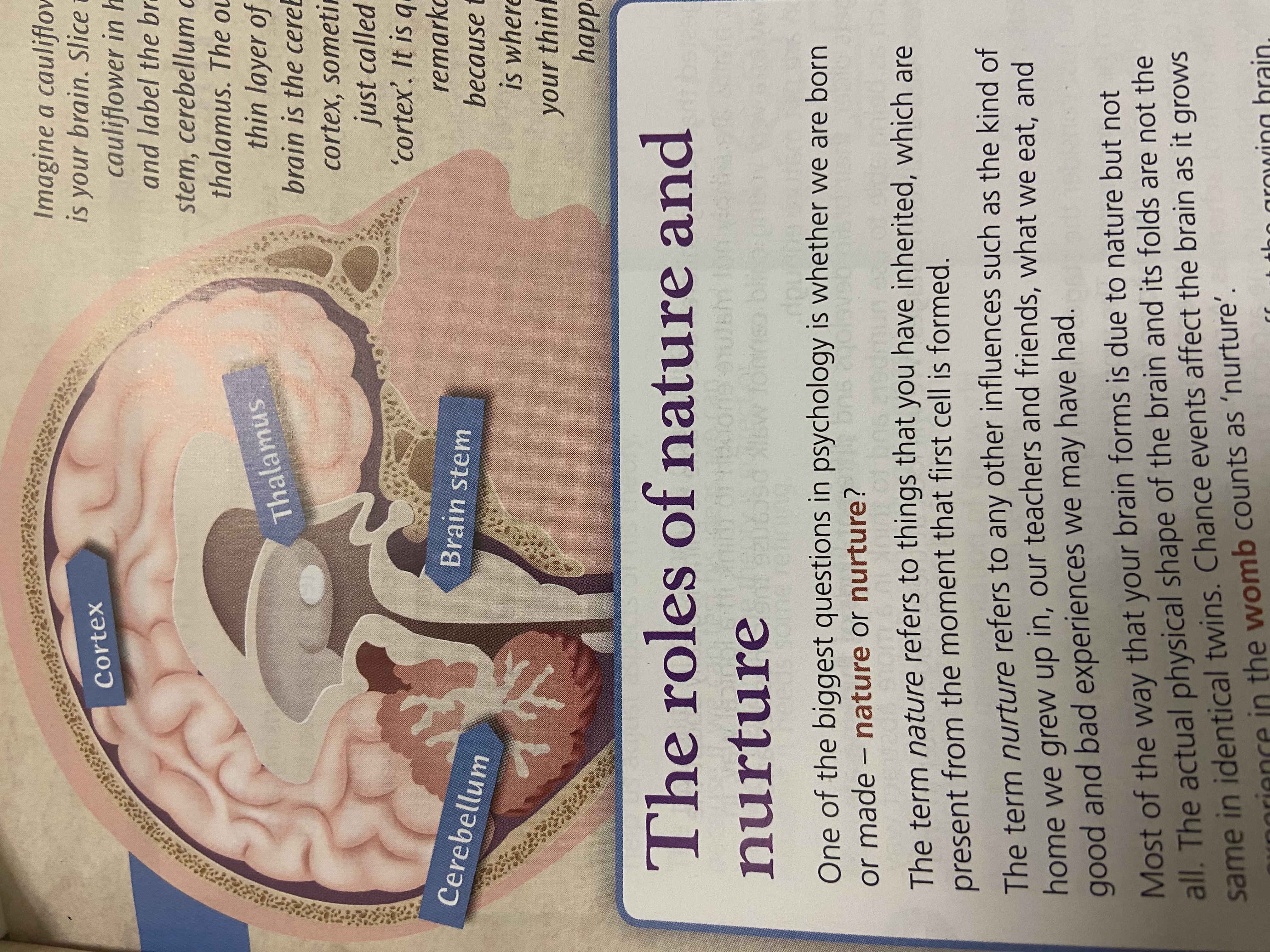
Role of Brain stem
Connects to spinal cord
Carries motor/sensory nerves to brain from body
Autonomic functions: Basic life functions, heartbeat, breathing, (automatic) not conscious.
Developed at birth
Role of Cerebellum
Near top of spinal cord
Coordination of movement and balance
Coordinates sensory info with motor activity
Language/Emotions
Last to develop
Thalamus
Deep inside brain (Two, left and right)
Receives/sends signals
Receives sensory signals from retina and sends onto visual area where visual info is processed
Coordinates motor signals
Cortex
Divided into two halfs, outer covering of brain, 3mm thick
Thinking/processing
Cognition, frontal cortex
sensory processing, auditory, visual
Motor area directs movement
Smoking/ Infection/Voices
Effects size of brain/body, slowed growth
Rubella: Brain damage, hearing loss (20 weeks)
Babies regocnise their mothers voice, brain responds to external stimuli before birth
Idk books or smth
Piagets theory of cognitive development
Before him, people thought children knew less than adults, but Piaget proposed this to be false, stating that children don’t simply know less, but think in different ways. Some ways are: Stages. Children cannot think logically due to a lack of maturity, as they get older, their brain changes. Schemas: As they grow, they develop more complex mental representations, mental structures. These grow through the process of Assimilation: When we learn something new but only an advanced understanding and not a radical different, causing us to adjust our schemas. Accommodation: When we learn new info to the extent we need to form a new schema to deal with new understanding.
Piagets theory of cognitive development- Evaluation
S: Influcned how children learn in classrooms. In the 1960’s many schools began to replace their old fashioned classroom with copying info to more activity orientated classrooms, engaging in tasks to further develop their understanding and schemas.
W: Only involved middle class European children. Developed his theory from expereince in Switzerland, with european academic families that valued education. In other cultures, education is overshadowed by other factors and “intelligence” varies from child to child. So it cant be generalised and is less valid.
Piagets theory of conservation
Piaget proposed that young children find it difficult to understand that quantities do not change with appearance, like if water is poured into a tall or wide glass, young children may struggle to understand that just because the taller glass looks like it has more water, the volume is the same (Conservation) He demonstrated this with numbers too, he spread two identical rows of 6 counters equally spaced, but when Piaget moved them closer together, they struggled to conserve that the quantity was the same,
Donaldons et all Naughty Teddy
Donaldson et all aimed to see if a children would still struggle to conserve if the change seemed to be accidental and not deliberate in the row of counters. They gathered 80 children from scottland (4-5 years) and presented them with a naughty teddy that would jump out his box, and two rows of counters, 4 red/white. The teddy jumped out from the box and messed up the counters in one row. Before and after the change, the child was asked about the rows of counters and whether they were the same or not. 41% of children gave the correct answer if the display was changed deliberately, while 68% answered correctly when the change was accidental. This study shows that the traditional method of testing conservation underestimates children ability.
Donaldons et all Naughty Teddy Evaluation
One strength of this study is that its a lab. This means it could be carefully controlled and Donaldson et all could manipulate the IV, and eliminate extraneous variables. One way they did this is by having two conditions: One with Primary school children and one with Nursery, this allowed them to measure the individual effect of the experiment on both sets of the children, this increases the reliability of the results as we can measure the effect separately.
W: Weakness is the primary aged children all came from one school. They could have done better due to differences in educational background, they may have had a more developed sense of language and coped better with tasks; Decreases validity.
Egocentrism:
Young children only see the world from their view with mountain displays and a doll. When the doll is placed behind a mountain and they are asked to choose what the doll would see, they are unable to. From 7 onwards they can develop more.
Hughes Policeman Study
Aimed to see if a egocentrism task would have less difficulty if the task made sense. He tested 30 children (3 and a half to 5) in Edinburgh. Each child was introduced carefully, shown a model with intersecting walls. A policeman doll was placed on one side. He then put a doll in each section and asked if the policeman could see the doll (at first it couldnt) Then the policeman was moved to point X and the child was asked to hide the doll. The test was repeated if children got confused. Then the test started offically, with different points. 90% of them were able to position the doll where the policeman could not see them. 3 years old had 60% correct while 4yr olds had 90%. Piaget underestimated them, what can he do right dawg. but ig it changed the way they age.
Hughes Policeman Study evalutation
S:Task was more sensical and effiecent. Was more similar to the kind of problem children encounter irl rather than mountains. Its easier with a person view. He made sure they understood. Increases validity.
W: Researcher could have unconsciously hinted at answers; like gazing in directions. Bad validity.
Stages of cognitive development
Brain changes as you grow, not you know more, just the maturity and quality. 4 stages: Sensorimotor (0-2) Physical/motor. Develop object permanence.
Pre operational (2-7) Lack of conservation and egocentrism, cant think logically
Concrete operational (7-11) Logical thinking, conserve, not egocentric. Only applied to physical, still strugle with abstract ideas.
Formal operational (11+) Develop logical+ abstract/scientific ideas
Stages of cognitive development-Evaluation
Underestimates childrens abilites-bro was wrong about everything else, other researchers found childlren performed better than Piaget thought. Might develop earlier.
Piaget: Application in education
Piaget belivied cognitive development came with time and physical maturity, it would be a waste of time to teach a child in the pre operational stage to think logically because they are not biologically developed. For true understadning to develop, children should discover things themselves through activities they engage in. Teachers should plan activities to accommodate and assimilate. All children should also be indivudlaised and all children learn different, group tasks or collective activites may not be effective. Apply to stages so sensorimotor: sensory toys
pre op: role play
conc op: cooking, math-logic
formal op: science
Piaget: Application in education-Eval
S: Influential: Plowden report 1967, that relied on piagets theory and recommended indivuliased learning and what not. High value
W: Possible to improve with practice. Bryant et all found that pre op kids could do some logical thinking if given practice, they argued it was a memory issue and not biological. so he wrong!
Dweck mindset theory
Carol Dweck argued that most people fell under two mindsets (or mix) when it came to tasks and challenges. A growth mindset: ability develops through practice and anything can be achieved no matter its difficulty, failure is a challange and not a sign to stop. Effort is important. Fixed: Often believe ability is innate, and dont have to work hard to be good at something, no amount of effort will change skill. Failure= gives up
Dweck mindset theory- Eval
S: Supporting evidence. Dweck got 48 (12-13) low acheving students. One group was taught that intelligence can grow like a muscle if practiced (growth mind) the other was taught a session on memory. Students in growth class has improved grades and motivation compared to others.
W: Any praise is damaging. Both minds are dependent on praise, praise for effort or ability. Even effort praise leads to learner working for someone elses praise than personal satisfaction. Better to be motivated by yourself.
Praise and Self Efficacy
Positive effect of praise: A reward. Makes someone feel good so positive behaviour is repeated. Praise effort not performance: Enables control, demotivating. Self efficacy: Understanding own abilities, increases or decreases future sucess
Self EFF on motivation: High self EF: high motivation
Praise and Self Efficacy -Eval
S:Low self Ef lowers performance. Research by Steele et al found that african american students did lower on IQ tests when asked to indicate their ethnicity before. Being reminded of their ethnicity and the racist ideas, lowered theoir self efficacy and yeah
W: Praise destroys motivation. Research shows that when children were rewarded for doing tasks they were less intersted in doing them with no reward, not sense of personal achievement.
Learning styles
People differ in how they learn with different principles. Matching teaching to learning style should improve learning. Verbaliser: Focus on words, process hearing/reading info. Visualiser: Diagrams, spatial, mind maps
Kinasthetic: Touch, acitivyt
Learning styles Eval
S: Traditional teaching focuses too much on verbal methods. Its better to adopt a mixed approach, draw attention and encourage learners. Beneficial.
W: No evidence. Pashler et all saw that a large no. of articles on styles has no experimental evidence and reports based on research found no evidence to support idea that performance is imporved when matched to a style. No validity.
Willingham
Educational evidences should be evidence based. Cognitive pysch and neurosceince can be used to improve learning. Praise: Praising effort should be unexpected, praise before a task leads to less motivation. Memory: Forgetting occurs due to a lack of cues, practice retrieving info. Self regulation: Delay gratification. Neuroscience: Brain waves in dyslexics are diff, knowlege could benefit for support
Willingham-Eval
S: Based on sound scientific research. hes a cognitive pyschologist, aware of research results. Trustful conclusions.
W: wrong to assume all ppl may have dyslexia or smth